文章目录
-
-
- [Combination Patterns](#Combination Patterns)
-
- [Basic Rules of Combinations组合的基本规律](#Basic Rules of Combinations组合的基本规律)
- [Specific Combination Patterns](#Specific Combination Patterns)
-
- [1. First 8 Combinations (1 to 8)](#1. First 8 Combinations (1 to 8))
- [2. Middle 8 Combinations (9 to 16)](#2. Middle 8 Combinations (9 to 16))
- [3. Last 8 Combinations (17 to 24)](#3. Last 8 Combinations (17 to 24))
- [Summary of Combinations](#Summary of Combinations)
- [Key Variables and Parameters with Their Relevant Clauses](#Key Variables and Parameters with Their Relevant Clauses)
- [Process and Decision Points](#Process and Decision Points)
-
Combination Patterns
To remember these wind load combinations, you can observe the pattern in which they are generated. Here are some key points and patterns to help with memorization:要记住这些风荷载组合的规律,可以通过观察它们的生成模式。以下是一些帮助记忆的要点和规律:
Basic Rules of Combinations组合的基本规律
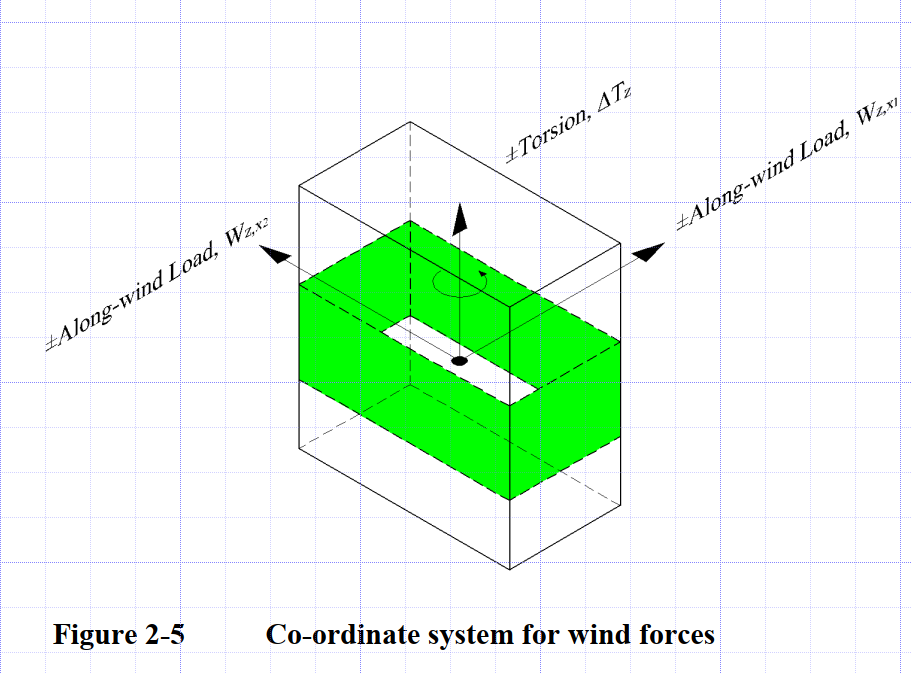
-
Presence of Variables :变量的存在:
- Each combination consists of three variables:
Fx,Fy, andMz - The coefficient in front of each variable can be
positive,negative
- Each combination consists of three variables:
-
Combination Form:
- Each combination form is a linear combination of three variables with coefficients of
1.0or0.55.
- Each combination form is a linear combination of three variables with coefficients of
Specific Combination Patterns
1. First 8 Combinations (1 to 8)
- Form : ± 1.0 F x ± 0.55 F y ± 0.55 M z \pm1.0Fx \pm 0.55Fy \pm 0.55Mz ±1.0Fx±0.55Fy±0.55Mz
- Pattern :
- The coefficient of F x Fx Fx is fixed at ± 1.0 \pm1.0 ±1.0.
- The coefficients of F y Fy Fy and M z Mz Mz are fixed at ± 0.55 \pm0.55 ±0.55.
- Memory Tip : Keep the coefficient of F x Fx Fx at ± 1.0 \pm1.0 ±1.0, then take all combinations of ± 0.55 \pm0.55 ±0.55 coefficients for F y Fy Fy and M z Mz Mz.
2. Middle 8 Combinations (9 to 16)
- Form : ± 0.55 F x ± 1.0 F y ± 0.55 M z \pm0.55Fx \pm 1.0Fy \pm 0.55Mz ±0.55Fx±1.0Fy±0.55Mz
- Pattern :
- The coefficient of F y Fy Fy is fixed at ± 1.0 \pm1.0 ±1.0.
- The coefficients of F x Fx Fx and M z Mz Mz are fixed at ± 0.55 \pm0.55 ±0.55.
- Memory Tip : Keep the coefficient of F y Fy Fy at ± 1.0 \pm1.0 ±1.0, then take all combinations of ± 0.55 \pm0.55 ±0.55 coefficients for F x Fx Fx and M z Mz Mz.
3. Last 8 Combinations (17 to 24)
- Form : ± 0.55 F x ± 0.55 F y ± 1.0 M z \pm0.55Fx \pm 0.55Fy \pm 1.0Mz ±0.55Fx±0.55Fy±1.0Mz
- Pattern :
- The coefficient of M z Mz Mz is fixed at ± 1.0 \pm1.0 ±1.0.
- The coefficients of F x Fx Fx and F y Fy Fy are fixed at ± 0.55 \pm0.55 ±0.55.
- Memory Tip : Keep the coefficient of M z Mz Mz at ± 1.0 \pm1.0 ±1.0, then take all combinations of ± 0.55 \pm0.55 ±0.55 coefficients for F x Fx Fx and F y Fy Fy.
Summary of Combinations
Following these patterns, you can summarize the combinations as:
- Each group of 8 combinations corresponds to one variable's coefficient fixed at 1.0 or -1.0, with the other two variables' coefficients at ± 0.55 \pm0.55 ±0.55.
- Each group of combinations includes all possible arrangements of positive and negative signs.
Here are the specific forms of the combinations, arranged according to these patterns:
markdown
Fx 固定为 ±1.0,
1. 1.0Fx + 0.55Fy + 0.55Mz
2. 1.0Fx + 0.55Fy - 0.55Mz
3. 1.0Fx - 0.55Fy + 0.55Mz
4. 1.0Fx - 0.55Fy - 0.55Mz
5. -1.0Fx + 0.55Fy + 0.55Mz
6. -1.0Fx + 0.55Fy - 0.55Mz
7. -1.0Fx - 0.55Fy + 0.55Mz
8. -1.0Fx - 0.55Fy - 0.55Mz
Fy 固定为 ±1.0
9. 0.55Fx + 1.0Fy + 0.55Mz
10. 0.55Fx + 1.0Fy - 0.55Mz
11. 0.55Fx - 1.0Fy + 0.55Mz
12. 0.55Fx - 1.0Fy - 0.55Mz
13. -0.55Fx + 1.0Fy + 0.55Mz
14. -0.55Fx + 1.0Fy - 0.55Mz
15. -0.55Fx - 1.0Fy + 0.55Mz
16. -0.55Fx - 1.0Fy - 0.55Mz
Mz 固定为 ±1.0
17. 0.55Fx + 0.55Fy + 1.0Mz
18. 0.55Fx + 0.55Fy - 1.0Mz
19. 0.55Fx - 0.55Fy + 1.0Mz
20. 0.55Fx - 0.55Fy - 1.0Mz
21. -0.55Fx + 0.55Fy + 1.0Mz
22. -0.55Fx + 0.55Fy - 1.0Mz
23. -0.55Fx - 0.55Fy + 1.0Mz
24. -0.55Fx - 0.55Fy - 1.0Mz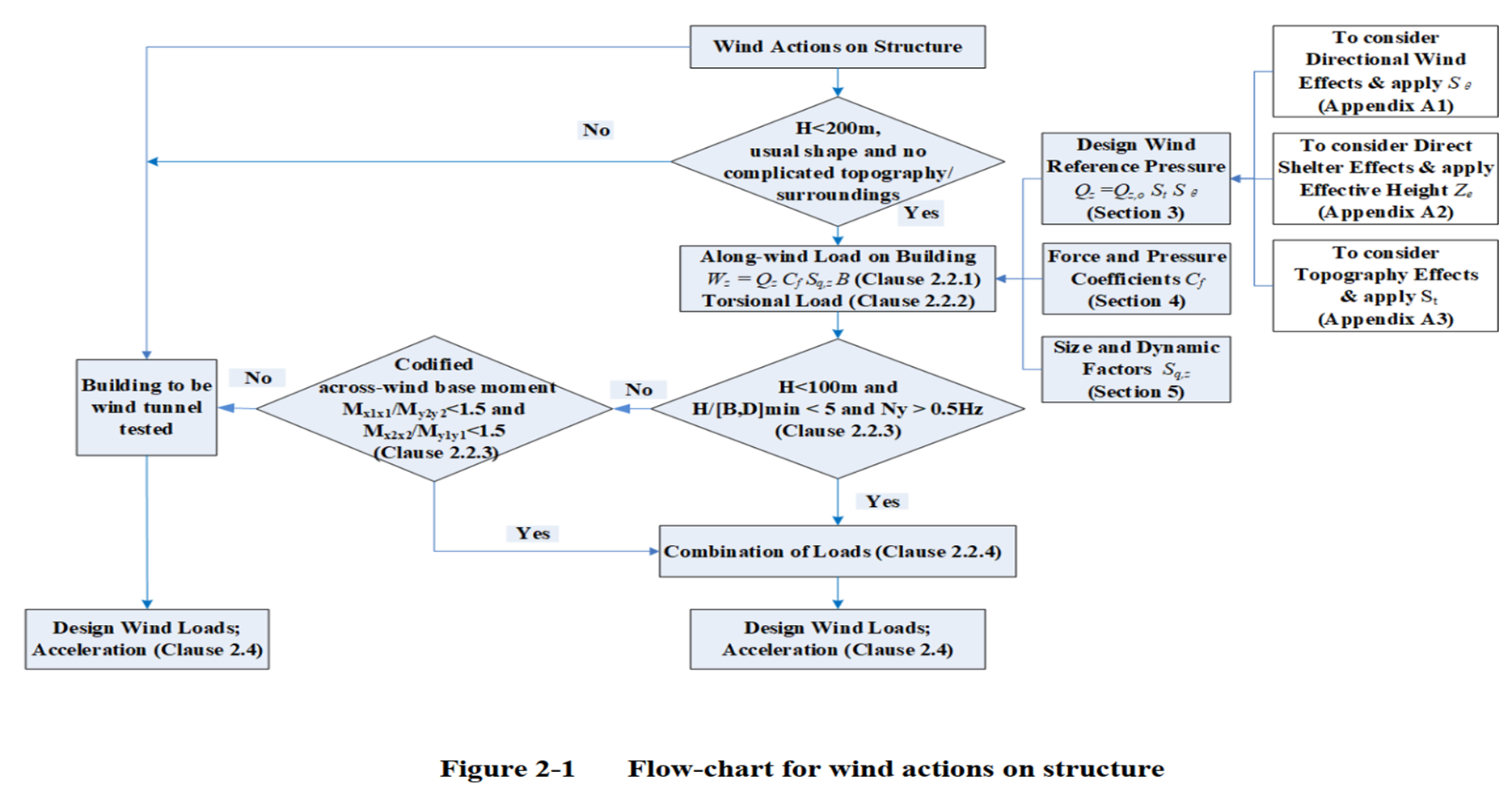
Key Variables and Parameters with Their Relevant Clauses
- H H H (Height)建筑高度
- Crucial Value :
- 200m/100m
- Relevant Clauses :
- H < ' 200 ' m H < `200 `\text{m} H<'200'm, typical shape, and no complex terrain/surroundings (Clause 2.2.1, 2.2.2)
- H < 100 m H < 100 \text{m} H<100m and H / [ B , D ] min < 5 H/[B,D]_{\min} < 5 H/[B,D]min<5 and N y > 0.5 Hz N_y > 0.5 \text{Hz} Ny>0.5Hz (Clause 2.2.3)
- Crucial Value :
- B B B (Width) and D D D (Depth)建筑宽度和深度
- Relevant Clauses :
- H / [ B , D ] min < 5 H/[B,D]_{\min} < 5 H/[B,D]min<5 and N y > 0.5 Hz N_y > 0.5 \text{Hz} Ny>0.5Hz (Clause 2.2.3)
- Relevant Clauses :
- N y N_y Ny (Natural Frequency)自振频率
- Crucial Value :
- 0.5Hz
- Relevant Clauses :
- N y > 0.5 Hz N_y > 0.5 \text{Hz} Ny>0.5Hz (Clause 2.2.3)
- Crucial Value :
- M X 1 X 1 / M Y 2 Y 2 M_{X1X1} / M_{Y2Y2} MX1X1/MY2Y2 (Base Moment due to Wind Load)风荷载基地弯矩
- Relevant Clauses :
- M X 1 X 1 M Y 2 Y 2 < 1.5 \frac{M_{X1X1}}{M_{Y2Y2}} < 1.5 MY2Y2MX1X1<1.5 (Clause 2.2.3)
- M X 2 X 2 M Y 1 Y 1 < 1.5 \frac{M_{X2X2}}{M_{Y1Y1}} < 1.5 MY1Y1MX2X2<1.5 (Clause 2.2.3)
- Relevant Clauses :
- Q Q Q (Design Wind Pressure)设计风压
- Relevant Clauses :
- Q = Q o S 1 S e Q = Q_o S_1 S_e Q=QoS1Se (Section 3)
- Relevant Clauses :
- C f C_f Cf (Force and Pressure Coefficient)力和压力系数
- Relevant Clauses :
- C f C_f Cf (Section 4)
- Along-wind load W e = Q ⋅ C f ⋅ S g , z ⋅ B W_e = Q \cdot C_f \cdot S_{g,z} \cdot B We=Q⋅Cf⋅Sg,z⋅B (Clause 2.2.1)
- Torsional load (Clause 2.2.2)
- Relevant Clauses :
- S g , z S_{g,z} Sg,z (Size and Dynamic Coefficient)尺寸和动态系数
- Relevant Clauses :
- S g , z S_{g,z} Sg,z (Section 5)
- Relevant Clauses :
- S e S_e Se (Directional Wind Effect Coefficient)方向风效应系数
- Relevant Clauses :
- S e S_e Se (Appendix A1)
- Relevant Clauses :
- Z e Z_e Ze (Effective Height)有效高度
- Relevant Clauses :
- Z e Z_e Ze (Appendix A2)
- Relevant Clauses :
- S t S_t St (
TerrainEffect Coefficient)地形效应系数- Relevant Clauses :
- S t S_t St (Appendix A3)
- Relevant Clauses :
Process and Decision Points
-
Determining if the Building Needs
Wind Tunnel Testing:- Relevant Clauses :
- Based on the building's height, shape, and surrounding terrain complexity to decide if wind tunnel testing is necessary.
- Relevant Clauses :
-
Comparing
Base Moments:- Relevant Clauses :
- Comparing the ratio of base moments to see if it is less than 1.5 to decide which design clauses to use (Clause 2.2.3)
- Relevant Clauses :
-
Combining LoadsUnder Different Conditions:- Relevant Clauses :
- Based on the building's height, size, and natural frequency, determine if different load conditions need to be combined (Clause 2.2.4)
- Relevant Clauses :
These variables and parameters play a crucial role in wind load design, ensuring the safety and stability of the building under wind forces. The flowchart helps systematically evaluate and calculate the impact of wind loads on the structure.