目录
前言
组合是一种结构型设计模式,你可以使用它将对象组合成树状结构,并且能像使用独立对象一样使用它们。
问题
如果应用的核心模型能用树状结构表示, 在应用中使用组合模式才有价值。
例如, 你有两类对象:产品 和 盒子。 一个盒子中可以包含多个产品或者几个较小的盒子 。 这些小盒子 中同样可以包含一些产品 或更小的 盒子 , 以此类推。
假设你希望在这些类的基础上开发一个定购系统。 订单中可以包含无包装的简单产品, 也可以包含装满产品的盒子......以及其他盒子。 此时你会如何计算每张订单的总价格呢?
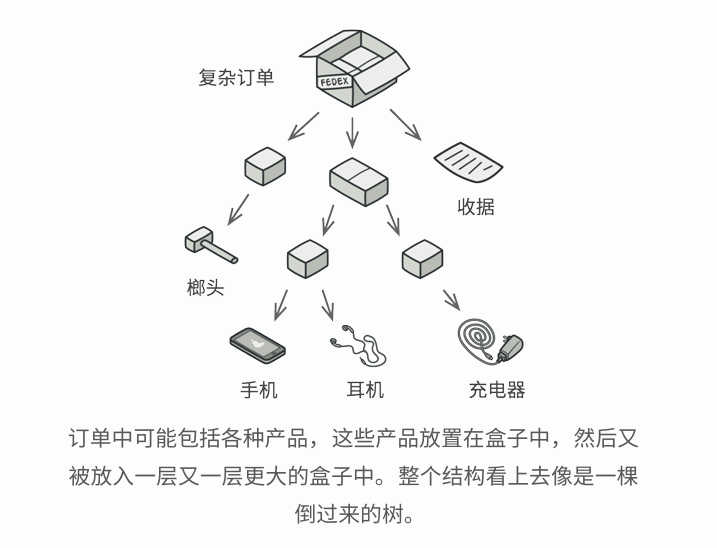
你可以尝试直接计算: 打开所有盒子, 找到每件产品, 然后计算总价。 这在真实世界中或许可行, 但在程序中, 你并不能简单地使用循环语句来完成该工作。 你必须事先知道所有 产品 和盒子的类别, 所有盒子的嵌套层数以及其他繁杂的细节信息。 因此, 直接计算极不方便, 甚至完全不可行。
解决方案
组合模式建议使用一个通用接口来与 产品 和盒子进行交互, 并且在该接口中声明一个计算总价的方法。
那么方法该如何设计呢? 对于一个产品, 该方法直接返回其价格; 对于一个盒子, 该方法遍历盒子中的所有项目, 询问每个项目的价格, 然后返回该盒子的总价格。 如果其中某个项目是小一号的盒子, 那么当前盒子也会遍历其中的所有项目, 以此类推, 直到计算出所有内部组成部分的价格。 你甚至可以在盒子的最终价格中增加额外费用, 作为该盒子的包装费用。
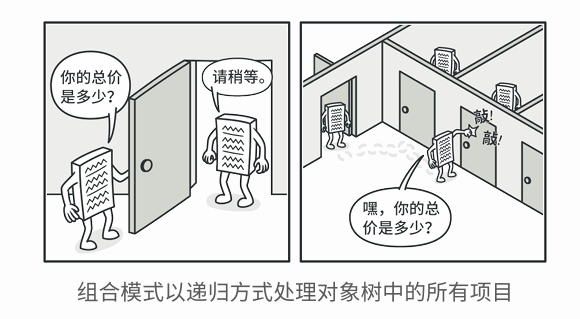
该方式的最大优点在于你无需了解构成树状结构的对象的具体类。 你也无需了解对象是简单的产品还是复杂的盒子。 你只需调用通用接口以相同的方式对其进行处理即可。 当你调用该方法后, 对象会将请求沿着树结构传递下去。
结构
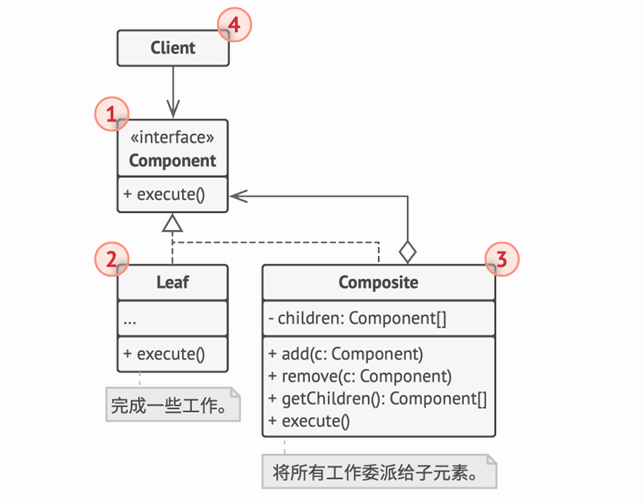
代码
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <list>
#include <cstdlib> // 包含 rand() 和 srand()
#include <ctime> // 包含 time() 用于获取系统时间作为种子
using namespace std;
class Component{
public:
virtual int execute()=0;
virtual ~Component(){}
};
class Leaf:public Component{
public:
int execute() override{
int r=rand()%10;
cout<<"返回叶子节点随机数: "<<r<<endl;
return r;
}
};
class Composite:public Component{
public:
int execute() override{
int sum=0;
for(auto child:m_children){
sum+=child->execute();
}
return sum;
}
void add(shared_ptr<Component> c){
m_children.push_back(c);
}
void remove(shared_ptr<Component> c){
for(auto it=m_children.begin();it!=m_children.end();it++){
if(*it==c){
it = m_children.erase(it); // erase返回下一个有效迭代器
break; // 找到并删除后可以退出循环
}
}
}
list<shared_ptr<Component>> getChildren(){
return m_children;
}
private:
list<shared_ptr<Component>> m_children;
};
int main(){
srand(time(nullptr));
auto root=make_shared<Composite>();
auto leaf01=make_shared<Leaf>();
auto leaf02=make_shared<Leaf>();
auto node01=make_shared<Composite>();
auto leaf03=make_shared<Leaf>();
auto leaf04=make_shared<Leaf>();
root->add(leaf01);
root->add(leaf02);
node01->add(leaf03);
node01->add(leaf04);
root->add(node01);
int sum=root->execute();
cout<<"----------------"<<endl;
cout<<"总和为: "<<sum<<endl;
root->remove(leaf02);
sum=root->execute();
cout<<"----------------"<<endl;
cout<<"删除一叶子后,总和为: "<<sum<<endl;
return 0;
}