手写Promise
javascript
class MyPromise {
constructor(executor) { // executor执行器
this.status = 'pending' // 等待状态
this.value = null // 成功或失败的参数
this.fulfilledCallbacks = [] // 成功的函数队列
this.rejectedCallbacks = [] // 失败的函数队列
const that = this
function resolve(value) { // 成功的方法
if (that.status === 'pending') {
that.status = 'resolved'
that.value = value
that.fulfilledCallbacks.forEach(myFn => myFn(that.value)) //执行回调方法
}
}
function reject(value) { //失败的方法
if (that.status === 'pending') {
that.status = 'rejected'
that.value = value
that.rejectedCallbacks.forEach(myFn => myFn(that.value)) //执行回调方法
}
}
try {
executor(resolve, reject)
} catch (err) {
reject(err)
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
if (this.status === 'pending') {
// 等待状态,添加回调函数到成功的函数队列
this.fulfilledCallbacks.push(() => {
onFulfilled(this.value)
})
// 等待状态,添加回调函数到失败的函数队列
this.rejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
onRejected(this.value)
})
}
if (this.status === 'resolved') { // 支持同步调用
console.log('this', this)
onFulfilled(this.value)
}
if (this.status === 'rejected') { // 支持同步调用
onRejected(this.value)
}
}
}
// 测试
function fn() {
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
if(Math.random() > 0.6) {
resolve(1)
} else {
reject(2)
}
}, 1000)
})
}
fn().then(
res => {
console.log('res', res) // res 1
},
err => {
console.log('err', err) // err 2
})解析:
首先是初始化了一个Promise实例,并定义了状态、值、成功回调和失败回调,并使用that来指向调用者。
resolve函数用于执行成功回调
reject函数用于执行失败函数
try尝试执行executor函数,并传入resolve和reject,当发生err的时候捕捉err
再用then方法注册Promise成功和失败的回调函数
这边可以看下运行的顺序来更好的理解代码
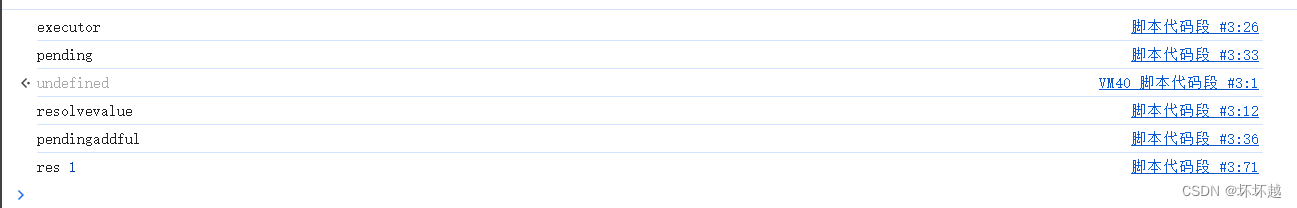
首先executor(resolve,reject)会try,然后最开始肯定是pending状态,会将回调函数调到列队中。
随后settimeout启动生成random,开始执行resolve or reject
这边是调用了resolve,他会更换状态并且执行列队中的函数
res => {
console.log('res', res) // res 1
},
手写AJAX
拿下Promise后就可以趁热打铁来了解AJAX了
javascript
// url:"url路径" type:请求方式 data:请求参数类型 dataType:返回的字符串类型
function ajax({url,type,data,dataType}){
return new Promise(function(resolve,reject){
//1. 创建异步请求对象
var xhr=getXhr();
// 备注:无需通过上面的方式,简单的创建异步请求对象的简化代码如下:
// var xhr = window.XMLHttpRequest ? new XMLHttprequest() : new ActiveXObject('Microsoft.XMLHttp');
//2.绑定监听事件
xhr.onreadystatechange=function(){
// 当异步请求状态变为4时,并且返回的状态码为200,接收响应成功
if(xhr.readyState==4&&xhr.status==200){
// 当返回接收的字符串类型为json串时,自动转换json串
if(dataType!==undefined
&&dataType.toLowerCase()==="json")
var res=JSON.parse(xhr.responseText)
else
// 否则直接获取返回的响应文本中的内容
var res=xhr.responseText
// 通过Promise,将返回的数据向后传递,相当于获取到请求数据将数据return出来
resolve(res);
}
}
// 如果请求方式为get请求,则将请求参数拼接在url后
if(type.toLowerCase()==="get"&&data!==undefined){
url+="?"+data;
}
//3.打开连接
xhr.open(type,url,true);
// 如果请求方式为post请求,则修改请求消息头
if(type.toLowerCase()==="post")
//增加:设置请求消息头
xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-Type","application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
//4.发送请求
if(type.toLowerCase()==="post"&&data!==undefined)
xhr.send(data);
else
xhr.send(null);})首先定义了一个函数ajax,并有四个传值,这边可以看下实例,来了解参数定义
javascript
// 定义一个函数,使用 ajax 发送请求
function fetchData() {
// 请求配置对象,包括 url、type、data、dataType
const config = {
url: 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1', // 示例 API
type: 'GET', // 请求方式,GET 或 POST
data: null, // 请求参数,对于 GET 请求,参数直接拼接在 URL 后面
dataType: 'json' // 返回的数据类型,这里指定为 JSON
};
// 调用 ajax 函数,并返回 Promise 对象
return ajax(config)
.then(response => {
console.log('请求成功:', response);
// 这里可以对获取到的数据进行进一步处理或返回
return response;
})
.catch(error => {
console.error('请求失败:', error);
throw error; // 可以选择抛出异常或者进行其他处理
});
}然后rentun了一个Promise
这里面有很多可能不认识的东西,要逐一了解下
比如toLowerCase,他不会改变原字符串,可以将来的字母都转化为小写字母
JSON.parse可以将字符串转化为javascript对象,但key必须是用双引号包裹的
javascript
let str = "Hello World";
let lowerCaseStr = str.toLowerCase();
console.log(lowerCaseStr); // 输出: "hello world"
console.log(str); // 输出: "Hello World",原始字符串未被改变
javascript
// JSON 字符串
const jsonStr = '{"name": "John", "age": 30, "city": "New York"}';
// 使用 JSON.parse 解析 JSON 字符串
const jsonObj = JSON.parse(jsonStr);
console.log(jsonObj); // 输出: { name: 'John', age: 30, city: 'New York' }
console.log(jsonObj.name); // 输出: "John"
console.log(jsonObj.age); // 输出: 30这样xhr.onreadystatechange里面的内容就很好理解了,就是当请求成功后将相应内容提取出来作为resolve。