目录
[7、deny 和 allow](#7、deny 和 allow)
一、概述
虚拟主机,就是把一台物理服务器划分成多个 "虚拟" 的服务器,这样我们的一台物理服务器就可以当做多个服务器来使用,从而可以配置多个网站。Nginx 提供虚拟主机的功能,就是为了让我们不需要安装多个 Nginx,就可以运行多个域名不同的网站。或者虚拟主机技术是将一台服务器的某项或者全部服务内容逻辑划分为多个服务单位,对外表现为多个服务器,从而充分利用服务器硬件资源。
Nginx 下,一个 server 标签就是一个虚拟主机。nginx 的虚拟主机就是通过 nginx.conf 中 server 节点指定的,想要设置多个虚拟主机,配置多个server节点即可。
此server块是位于http块下的。
二、虚拟主机设置的三种形式
为了方便测试,我们现在html目录下,新建两个html文件
html
[root@localhost html]# vim test1.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=utf-8">
<style>
html { color-scheme: light dark; }
body { width: 39em; margin: 0 auto;
font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
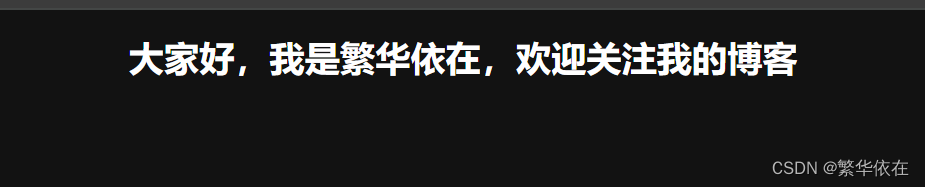
<h1>大家好,我是繁华依在,欢迎关注我的博客</h1>
</body>
</html>
[root@localhost html]# vim test2.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=utf-8">
<style>
html { color-scheme: light dark; }
body { width: 39em; margin: 0 auto;
font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>>Hello everyone, I am Fanhua Yizai. Welcome to follow my blog!</h1>
</body>
</html>1、基于端口号配置
基于端口的虚拟主机配置,使用端口来区分;浏览器使用同一个域名 + 端口 或 同一个ip地址 + 端口访问;
配置如下:
html
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html;
index test1.html;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
server {
listen 81;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html;
index test2.html;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}此时,浏览器中访问

2、基于域名配置
基于域名的虚拟主机是最常见的一种虚拟主机.
在 :C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc中在添加一个映射,如果文件修改不了,需要给文件权限,再此不做讲解。
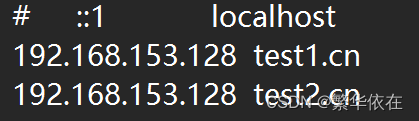
然后修改配置文件
html
server {
listen 80;
server_name test1.cn;
location / {
root html;
index test1.html;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
server {
listen 81;
server_name test2.cn;
location / {
root html;
index test2.html;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
保存,重启下nginx浏览器访问: http://test1.cn/

浏览器访问:http://test2.cn/

3、基于ip配置
基于IP的再此不做详解,因为很少用。
三、常用参数
1、listen
html
server {
#用于指定虚拟主机的服务端口
listen 80;
示例:
listen 127.0.0.1:8000; # listen localhost:8000 监听指定的IP和端口
listen 127.0.0.1; #监听指定IP的所有端口
listen 8000; #监听指定端口
listen *:8000; #监听指定端口上的连接
2、server_name
html
server {
#用于指定虚拟主机的服务端口
listen 80;
#用来指定IP地址或者域名,多个域名之间用空格分 开
server_name localhost;
关于server_name的配置方式有三种,分别是:
1、精确匹配
如:server_name test1.cn;
2、通配符匹配
server_name中支持通配符"*",但需要注意的是通配符不能出现在域名的中间,只能出现在首段或尾段。
如:server_name *1.cn tes1.*;
3、正则表达式匹配
server_name中可以使用正则表达式,并且使用~作为正则表达式字符串的开始标记。
正则表达式的相关文档后续会单独出一篇。再此不做讲解
如:server_name ~^www\.(\w)+\.cn$;3、location
html
location
#:用来设置请求的URI 匹配访问路径的,默认匹配斜杠/开头的请求,当访问路径中有斜杠/,会被该location匹配到并进行处理
#http://192.168.153.128:80/
# uri变量是待匹配的请求字符串,可以不包含正则表达式,也可以包含正则表达式,那么nginx服务器在搜索匹配location的时候,是先使用不包含正则表达式进行匹配,找到一个匹配度最高的一个,然后在通过包含正则表达式的进行匹配,如果能匹配到直接访问,匹配不到,就使用刚才匹配度最高的那个location来处理请求。
server{
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
}
location /abc{
}
...
}
# 属性介绍
#1、不带符号,要求必须以指定模式开始。
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.test1.cn;
location /abc{
default_type text/plain;
return 200 "access success";
}
}
# 以下访问都是正确的,只要以abc开头的请求都是正确的。
http://192.168.153.128/abc
http://192.168.153.128/abc?p1=TOM
http://192.168.153.128/abc/
http://192.168.153.128/abcdef
# 2、= 用于不包含正则表达式 uri前,必须与指定的模式精确匹配。
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.test1.cn;
location =/abc{
default_type text/plain;
return 200 "access success";
}
}
可以匹配到
http://192.168.200.133/abc
http://192.168.200.133/abc?p1=TOM
匹配不到
http://192.168.200.133/abc/
http://192.168.200.133/abcdef
#3、~:表示当前uri中包含了正则表达式,并且区分大小写。
#4、~*:表示当前uri中包含了正则表达式,并且不区分大小写。
换句话说,如果uri包含了正则表达式,需要用上述两个符号来标识。
server {
listen 80;
server_name 127.0.0.1;
location ~^/abc/\w${
default_type text/plain;
return 200 "access_success";
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name 127.0.0.1;
location ~*^/abc/\w${
default_type text/plain;
return 200 "access_success";
}
}
# ^/abc/\w$: 这是正则表达式的内容。
# ^: 表示字符串的开始。
# /abc/: 匹配字面字符串 "/abc/"。
# \w: 匹配任何单字字符,等同于 [a-zA-Z0-9_]。
# $: 表示字符串的结束。因此,这个正则表达式将匹配 URI 路径以 "/abc/" 开始,后面紧接着一个单字字符,并且字符串在这里结束的请求。例如,它将匹配 "/abc/a" 但不会匹配 "/abc/abc" 或 "/abc/"。
#5、^~ 用于不包含正则表达式的uri前,功能和不加符号的一致,唯一不同的是,如果模式匹配,那么就停止搜索其他模式了。
3.1、常见的Nginx正则表达式
html
^ :匹配输入字符串的起始位置
$ :匹配输入字符串的结束位置
* :匹配前面的字符零次或多次。如"ol*"能匹配"o"及"ol"、"oll"
+ :匹配前面的字符一次或多次。如"ol+"能匹配"ol"及"oll"、"olll",但不能匹配"o"
? :匹配前面的字符零次或一次,例如"do(es)?"能匹配"do"或者"does","?"等效于"{0,1}"
. :匹配除"\n"之外的任何单个字符,若要匹配包括"\n"在内的任意字符,请使用诸如"[.\n]"之类的模式
\ :将后面接着的字符标记为一个特殊字符或一个原义字符或一个向后引用。如"\n"匹配一个换行符,而"\$"则匹配"$"
\d :匹配纯数字
{n} :重复 n 次
{n,} :重复 n 次或更多次
{n,m} :重复 n 到 m 次
[] :定义匹配的字符范围
[c] :匹配单个字符 c
[a-z] :匹配 a-z 小写字母的任意一个
[a-zA-Z0-9] :匹配所有大小写字母或数字
() :表达式的开始和结束位置
| :或运算符 //例(js|img|css)3.2、location正则:
html
//location大致可以分为三类
精准匹配:location = /{}
一般匹配:location /{}
正则匹配:location ~/{}
//location常用的匹配规则:
= :进行普通字符精确匹配,也就是完全匹配。
^~ :表示前缀字符串匹配(不是正则匹配,需要使用字符串),如果匹配成功,则不再匹配其它 location。
~ :区分大小写的匹配(需要使用正则表达式)。
~* :不区分大小写的匹配(需要使用正则表达式)。
!~ :区分大小写的匹配取非(需要使用正则表达式)。
!~* :不区分大小写的匹配取非(需要使用正则表达式)。
//优先级
首先精确匹配 =
其次前缀匹配 ^~
其次是按文件中顺序的正则匹配 ~或~*
然后匹配不带任何修饰的前缀匹配
最后是交给 / 通用匹配
注意:
精确匹配: = , 后面的表达式中写的是纯字符串
字符串匹配: ^~ 和 无符号匹配 , 后面的表达式中写的是纯字符串
正则匹配: ~ 和 ~* 和 !~ 和 !~* , 后面的表达式中写的是正则表达式3.3示例
html
(1)location = / {}
=为精确匹配 / ,主机名后面不能带任何字符串,比如访问 / 和 /data,则 / 匹配,/data 不匹配
再比如 location = /abc,则只匹配/abc ,/abc/或 /abcd不匹配。若 location /abc,则即匹配/abc 、/abcd/ 同时也匹配 /abc/。
(2)location / {}
因为所有的地址都以 / 开头,所以这条规则将匹配到所有请求 比如访问 / 和 /data, 则 / 匹配, /data 也匹配,
但若后面是正则表达式会和最长字符串优先匹配(最长匹配)
(3)location /documents/ {}
匹配任何以 /documents/ 开头的地址,匹配符合以后,还要继续往下搜索其它 location
只有其它 location后面的正则表达式没有匹配到时,才会采用这一条
(4)location /documents/abc {}
匹配任何以 /documents/abc 开头的地址,匹配符合以后,还要继续往下搜索其它 location
只有其它 location后面的正则表达式没有匹配到时,才会采用这一条
(5)location ^~ /images/ {}
匹配任何以 /images/ 开头的地址,匹配符合以后,停止往下搜索正则,采用这一条
(6)location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {}
匹配所有以 gif、jpg或jpeg 结尾的请求
然而,所有请求 /images/ 下的图片会被 location ^~ /images/ 处理,因为 ^~ 的优先级更高,所以到达不了这一条正则
(7)location /images/abc {}
最长字符匹配到 /images/abc,优先级最低,继续往下搜索其它 location,会发现 ^~ 和 ~ 存在
(8)location ~ /images/abc {}
匹配以/images/abc 开头的,优先级次之,只有去掉 location ^~ /images/ 才会采用这一条
(9)location /images/abc/1.html {}
匹配/images/abc/1.html 文件,如果和正则 ~ /images/abc/1.html 相比,正则优先级更高
优先级总结:
(location =) > (location 完整路径) > (location ^~ 路径) > (location ~,~* 正则顺序) > (location 部分起始路径) > (location /)4、root
用于配置服务器的默认网站根目录位置,默认为nginx安装主目录下的html目录。此项位于location块中。
html
#语法:
location / {
root path;
}
#默认值:root html;
#位置:http、server、location
path: 为Nginx服务器接收到请求以后查找资源的根目录路径。
alias :用来更改location的URI
注意:如果location路径是以/结尾,则alias也必须是以/结尾
这俩的区别不在解释。可以自己查下5、index
:用于设置网站的默认首页,此项位于location块中。
html
#语法:
index file ...;
#默认值:index index.html;
#位置:http、server、location
location / {
root html;
index test2.html test1.html;
}
index后面可以跟多个设置,如果访问的时候没有指定具体访问的资源,则会依次进行查找,找到第一个为止。
访问该location的时候,可以通过 http://ip:port/,地址后面如果不添加任何内容,则默认依次访问index.html和index.htm,找到第一个来进行返回6、error_page
设置网站的错误页面
html
#语法:
error_page code ... [=[response]] uri;
#位置:http、server、location...
#在默认情况下,Nginx会在主目录的html目录中查找指定的返回页面,特别需要注意的是,这些错误信息的返回页面大小一定要超过512K,否者会被ie浏览器替换为ie默认的错误页面。
1、可以指定具体跳转的地址
server {
listen 80;
server_name location;
location /abc{
default_type text/plain;
return 200 "access success";
}
error_page 403 404 https://www.baidu.com/;
}
当访问的资源不存在时,例如:192.168.153.128/qwe,就回跳转到404,然后在跳转到百度界面
2、可以指定重定向地址
server {
listen 80;
server_name location;
location /abc{
default_type text/plain;
return 200 "access success";
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; #配置50x错误页面
#精确匹配
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
3、使用location的@符号完成错误信息展示
server {
listen 80;
server_name location;
location /abc{
default_type text/plain;
return 200 "access success";
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; #配置50x错误页面
error_page 404 @error;
location @error{
default_type text/plain;
return 404 "error";
}
#精确匹配
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}7、deny 和 allow
此项位于location块中
html
#拒绝的ip
deny 127.0.0.1;
#允许的ip
allow 172.18.5.54;