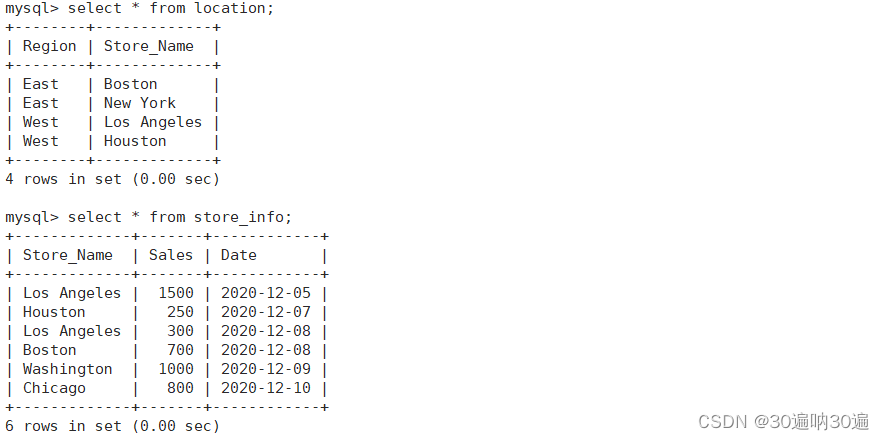
MySQL版的葵花宝典,欲练此功,挥刀自。。。呃,,,说错了,是先创建两个表,分别是location表和store_info表
示例表为location表和store_info表,如下图所示:
操作一:
---- DISTINCT ----不显示重复的数据记录
语法:SELECT DISTINCT "字段" FROM "表名";
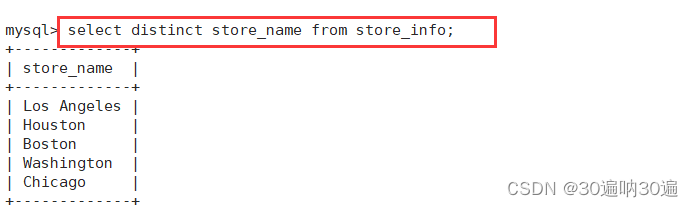
示例:select distinct store_name from store_info;
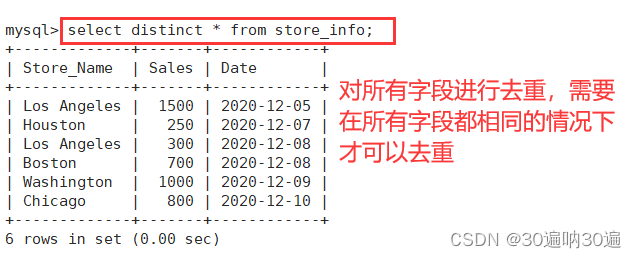
注:如果需要使用select *对所有字段进行去重,只能对所有字段都相同的记录进行去重。
操作二:
---- WHERE ----有条件查询
语法:SELECT "字段" FROM "表名" WHERE "条件";
示例:select * from store_info where store_name = 'Los Angeles';
select * from store_info where store_name != 'Los Angeles';

where 语句搭配AND OR
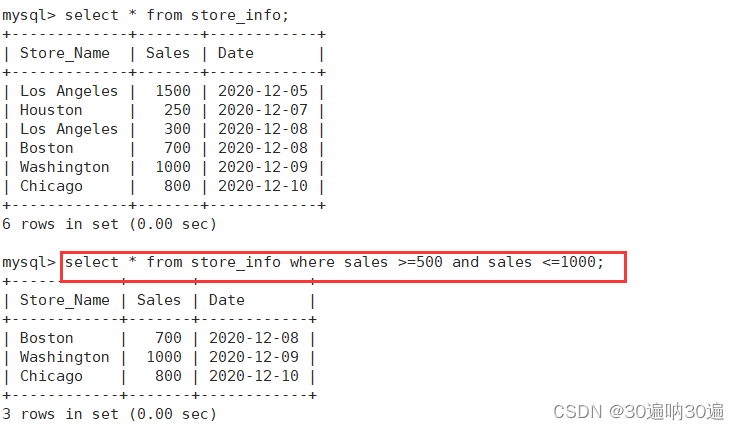
示例:select * from store_info where sales >=500 and sales <=1000;
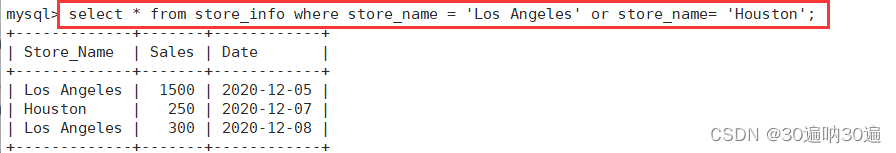
select * from store_info where store_name = 'Los Angeles' or store_name= 'Houston';
---- IN ----显示已知的值的数据记录
语法:SELECT "字段" FROM "表名" WHERE "字段" IN ('值1', '值2', ...);
示例:select * from store_info where store_name in ('Los Angeles','Houston');
select * from store_info where store_name not in ('Los Angeles','Houston');

---- BETWEEN ----显示两个值范围内的数据记录
示例:select * from store_info where sales between 500 and 1000;
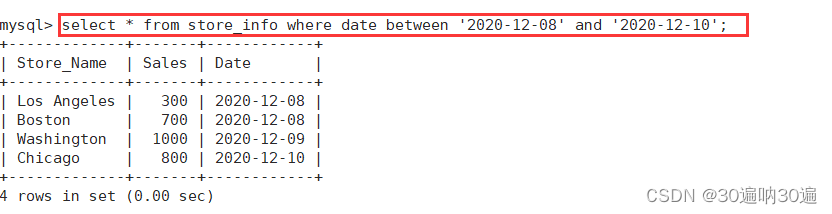
select * from store_info where date between '2020-12-08' and '2020-12-10';

---- 通配符 ----通常通配符都是跟 LIKE 一起使用
% :百分号表示零个、一个或多个字符
_ :下划线表示单个字符
详细说明:
'A_Z':所有以 'A' 起头,另一个任何值的字符,且以 'Z' 为结尾的字符串。例如,'ABZ' 和 'A2Z' 都符合这一个模式,而 'AKKZ' 并不符合 (因为在 A 和 Z 之间有两个字符,而不是一个字符)。
'ABC%': 所有以 'ABC' 起头的字符串。例如,'ABCD' 和 'ABCABC' 都符合这个模式。
'%XYZ': 所有以 'XYZ' 结尾的字符串。例如,'WXYZ' 和 'ZZXYZ' 都符合这个模式。
'%AN%': 所有含有 'AN'这个模式的字符串。例如,'LOS ANGELES' 和 'SAN FRANCISCO' 都符合这个模式。
'_AN%':所有第二个字母为 'A' 和第三个字母为 'N' 的字符串。例如,'SAN FRANCISCO' 符合这个模式,而 'LOS ANGELES' 则不符合这个模式。
---- LIKE ----匹配一个模式来找出我们要的数据记录
语法:SELECT "字段" FROM "表名" WHERE "字段" LIKE {模式};
所用表如下:
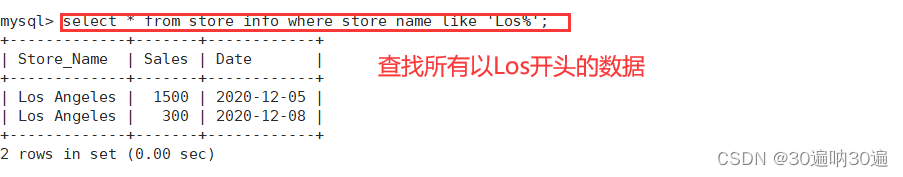
例: select * from store_info where store_name like 'Los%';
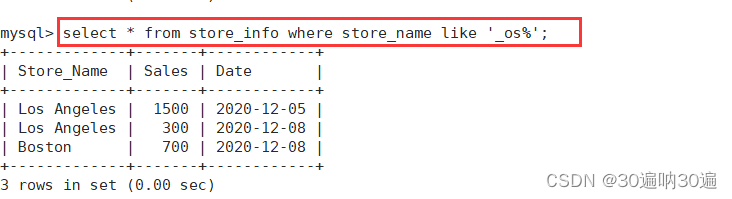
select * from store_info where store_name like '_os%';
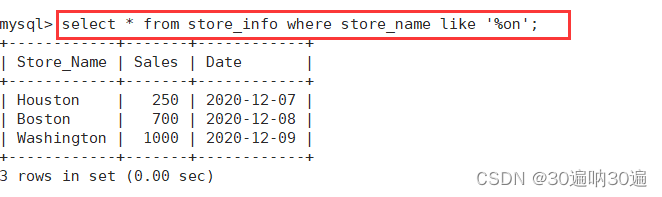
select * from store_info where store_name like '%on';
注:like查询中,将%放在开头会导致索引失效,要注意!
---- ORDER BY ----按关键字排序
语法:SELECT "字段" FROM "表名" [WHERE "条件"] ORDER BY "字段" [ASC, DESC];
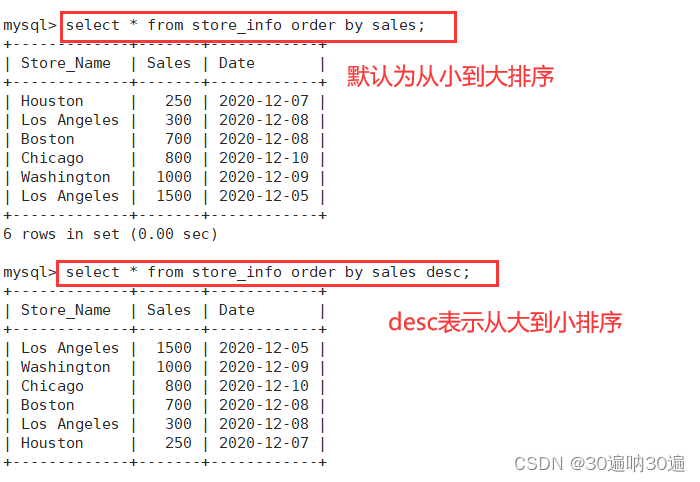
#ASC 是按照升序进行排序的,是默认的排序方式。
#DESC 是按降序方式进行排序。
例:select * from store_info order by sales;
select * from store_info order by sales desc;
---- 函数 ----
数学函数:
- abs(x) 返回 x 的绝对值
- rand() 返回 0 到 1 的随机数
- mod(x,y) 返回 x 除以 y 以后的余数
- power(x,y) 返回 x 的 y 次方
- sqrt(x) 返回 x 的平方根
- round(x) 返回离 x 最近的整数
- round(x,y) 保留 x 的 y 位小数四舍五入后的值
- truncate(x,y) 返回数字 x 截断为 y 位小数的值
- ceil(x) 返回大于或等于 x 的最小整数
- floor(x) 返回小于或等于 x 的最大整数
- greatest(x1,x2...) 返回集合中最大的值,也可以返回多个字段的最大的值
- least(x1,x2...) 返回集合中最小的值,也可以返回多个字段的最小的值
例:

聚合函数:
- avg() 返回指定列的平均值
- count() 返回指定列中非 NULL 值的个数
- min() 返回指定列的最小值
- max() 返回指定列的最大值
- sum(x) 返回指定列的所有值之和
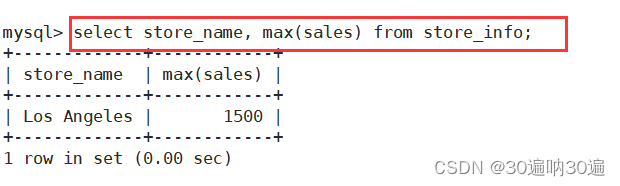
例: select store_name, max(sales) from store_info;
select store_name,sales from store_info where sales = (select min(sales) from store_info);
select avg(sales) from store_info;
select sum(sales) from store_info;



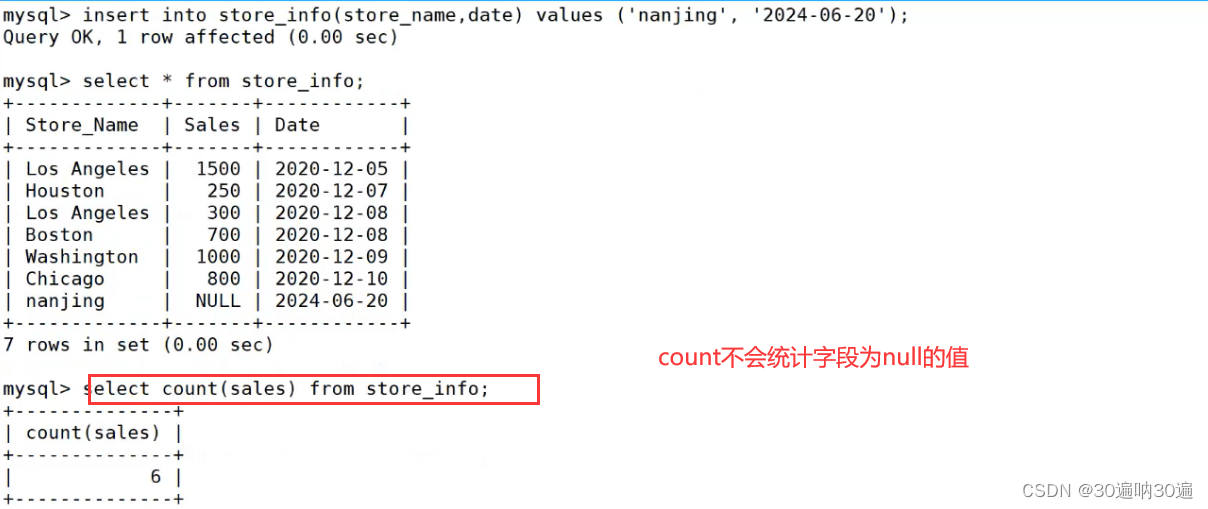
注:
#count(*) 包括了所有的列的行数,在统计结果的时候,不会忽略列值为 NULL
#count(列名) 只包括列名那一列的行数,在统计结果的时候,会忽略列值为 NULL 的行
字符串函数:
- concat(x,y) 将提供的参数 x 和 y 拼接成一个字符串
- substr(x,y) 获取从字符串 x 中的第 y 个位置开始的字符串,跟substring()函数作用相同
- substr(x,y,z) 获取从字符串 x 中的第 y 个位置开始长度为 z 的字符串
- length(x) 返回字符串 x 的长度
- replace(x,y,z) 将字符串 z 替代字符串 x 中的字符串 y
- trim() 返回去除指定格式的值
- upper(x) 将字符串 x 的所有字母变成大写字母
- lower(x) 将字符串 x 的所有字母变成小写字母
- left(x,y) 返回字符串 x 的前 y 个字符
- right(x,y) 返回字符串 x 的后 y 个字符
- repeat(x,y) 将字符串 x 重复 y 次
- space(x) 返回 x 个空格
- strcmp(x,y) 比较 x 和 y,返回的值可以为-1,0,1
- reverse(x) 将字符串 x 反转


字符串拼接
例:select concat('nan',' ','jing');
select concat('nan','jing');
select region || store_name from location;
select region || ' ' || store_name from location;


例:select substring(store_name, 5, 6) from location where store_name='Los Angeles';

例:select store_name,length(store_name) from location; 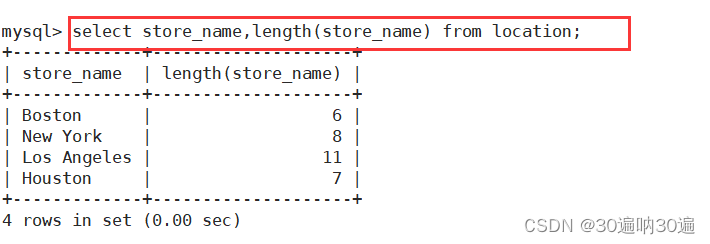
移除字符串
SELECT TRIM ([ [位置] [要移除的字符串] FROM ] 字符串);
#[位置]:的值可以为 LEADING (起头), TRAILING (结尾), BOTH (起头及结尾)。
#[要移除的字符串]:从字串的起头、结尾,或起头及结尾移除的字符串。缺省时为空格。
例: select trim(leading 'New' from 'New York');
select trim(trailing 'York' from 'New York');

例:select trim(both 'York' from (select store_name from location where store_name='New York'));

例:select left(store_name,3) from location where store_name='New York';
select right(store_name,4) from location where store_name='New York';

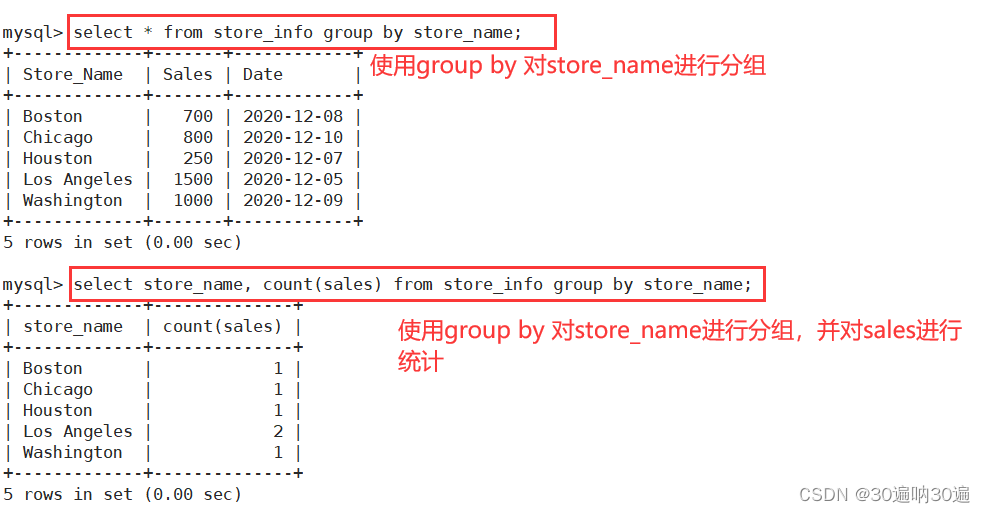
GROUP BY 用于对GROUP BY后面的字段的查询结果进行汇总分组,通常是结合聚合函数一起使用的
GROUP BY 有一个原则,凡是在 GROUP BY 后面出现的字段,必须在 SELECT 后面出现;
凡是在 SELECT 后面出现的、且未在聚合函数中出现的字段,必须出现在 GROUP BY 后面
语法:SELECT "字段1", SUM("字段2") FROM "表名" GROUP BY "字段1";
例:select * from store_info group by store_name;
select store_name, count(sales) from store_info group by store_name;
例: select region, count(store_name) from location group by region;

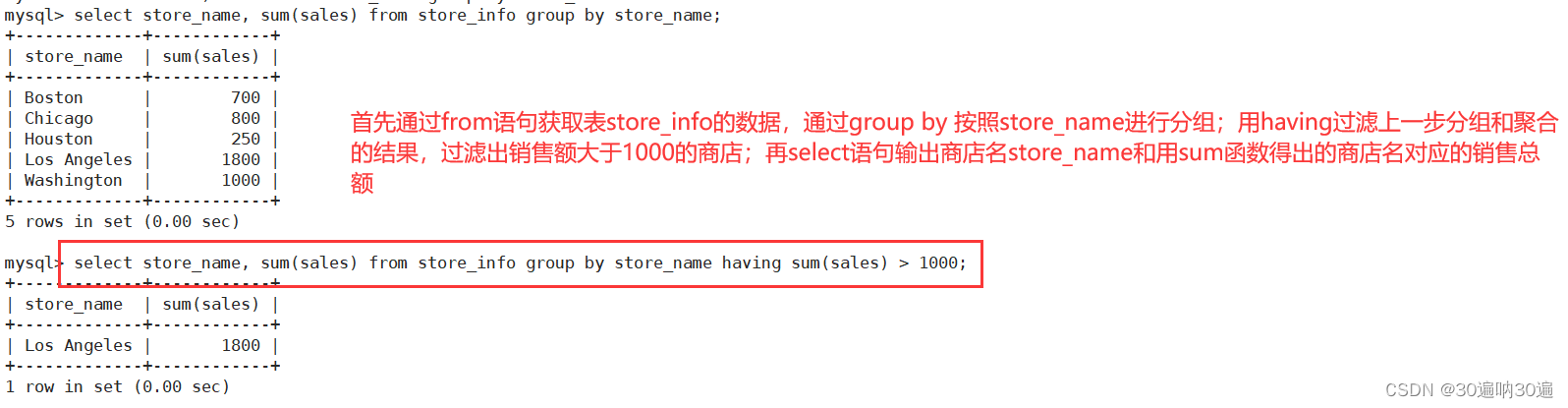
---- HAVING ----用来过滤由 GROUP BY 语句返回的记录集,通常与 GROUP BY 语句联合使用
HAVING 语句的存在弥补了 WHERE 关键字不能与聚合函数联合使用的不足。
语法:SELECT "字段1", SUM("字段2") FROM "表格名" GROUP BY "字段1" HAVING (函数条件);
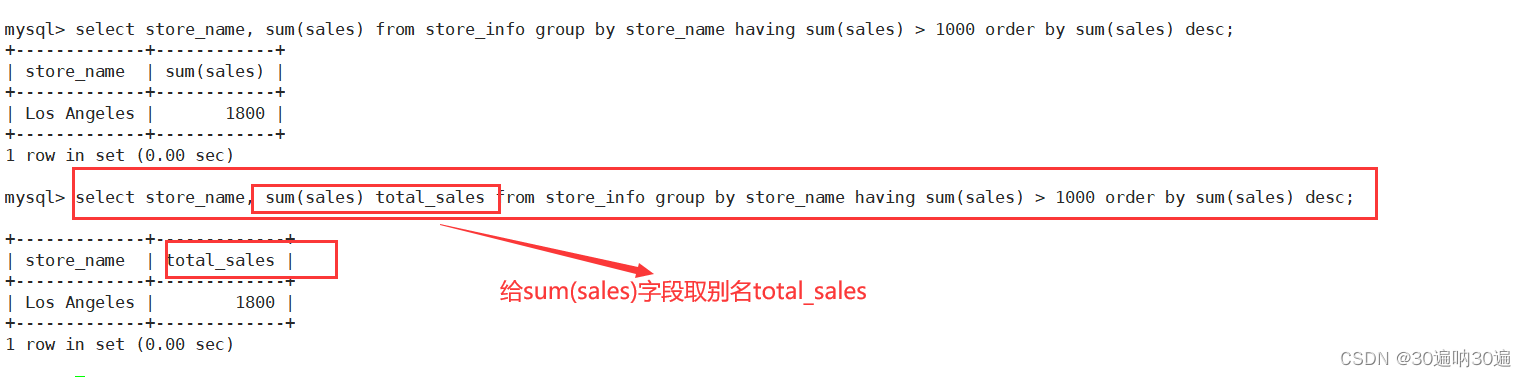
例:select store_name, sum(sales) from store_info group by store_name having sum(sales) > 1000;
select store_name, sum(sales) from store_info group by store_name having sum(sales) > 1000 order by sum(sales) desc;

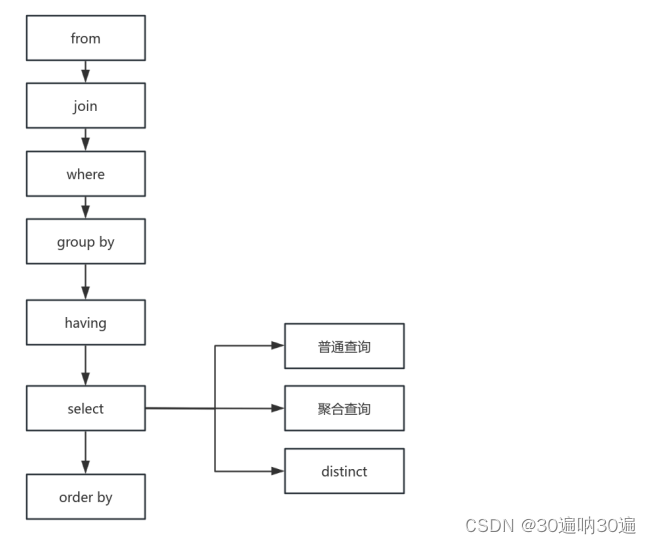
SQL执行顺序:
- 先执行from,join来确定表之间的连接关系,得到初步的数据
- where对数据进行普通的初步的筛选
- group by 分组
- 各组分别执行having中的普通筛选或者聚合函数筛选
- 然 后 把 再 根 据 我 们 要的数 据 进行select,可以是普通字段查询也可以是获取聚合函数的查询结果,如果是集合函数,select的查询结果会新增一条字段
- 将查询结果去重distinct
- 最后合并各组的查询结果,按照order by的条件进行排序
---- 别名 ----字段別名 表格別名
语法:SELECT "表格別名"."字段1" [AS] "字段別名" FROM "表格名" [AS] "表格別名";
例:mysql> select store_name, sum(sales) total_sales from store_info group by store_name having sum(sales) > 1000 order by sum(sales) desc;
---- 子查询 ----连接表格,在WHERE 子句或 HAVING 子句中插入另一个 SQL 语句
语法:SELECT "字段1" FROM "表格1" WHERE "字段2" [比较运算符] #外查询
(SELECT "字段1" FROM "表格2" WHERE "条件"); #内查询
例:select store_name, sales from store_info where sales = (select min(sales) from store_info);

---- EXISTS ----用来根据条件过滤查询结果,并只返回满足条件的行
语法:SELECT "字段1" FROM "表格1" WHERE EXISTS (SELECT * FROM "表格2" WHERE "条件");
#这里的子查询作为条件进行判断。如果子查询返回至少一行结果,则外部查询的结果将包含该行

连接查询
内连接
select A.字段 from 左表 A inner join 右表 B on A.字段=B.字段;
select A.字段 from 左表 A inner join 右表 B using(字段);
inner join(内连接):只返回两个表中联结字段相等的行
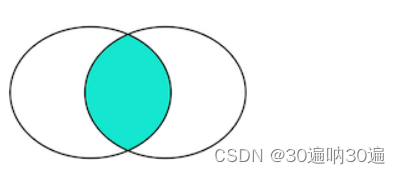

例:select * from location A inner join store_info B on A.store_name = B.store_name;

左连接
select B.字段 from 左表 A left join 右表 B on A.字段 = B.字段 where B.字段 is not null;
left join(左连接):返回包括左表中的所有记录和右表中联结字段相等的记录
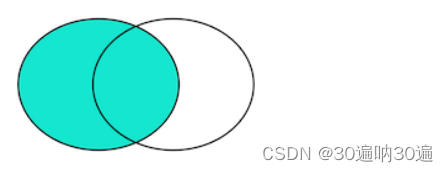
例:select * from location A left join store_info B on A.store_name = B.store_name;
select distinct B.store_name from location A left join store_info B on A.store_name = B.store_name where B.store_name is not null;
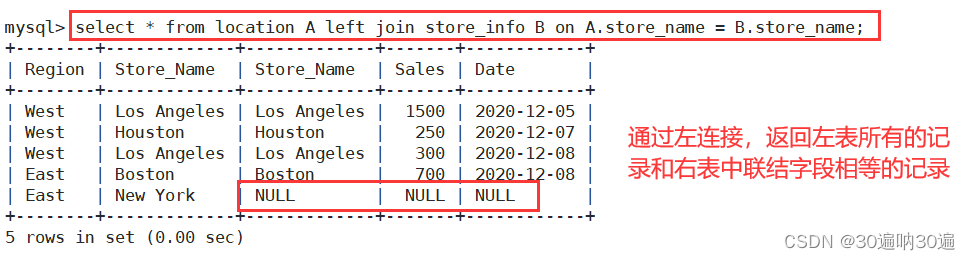

右连接
select A.字段 from 左表 A left join 右表 B on A.字段 = B.字段 where A.字段 is not null;
right join(右连接):返回包括右表中的所有记录和左表中联结字段相等的记录
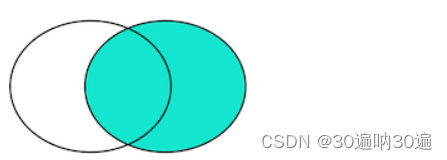
例: select * from location A right join store_info B on A.store_name = B.store_name;
select distinct A.store_name from location A right join store_info B on A.store_name = B.store_name where A.store_name is not null;

子查询求交集
格式:select A.字段 from 左表 A where A.字段 in (select B.字段 from 右表 B);
select A.字段 from 左表 A where exists (select B.字段 from 右表 B where A.字段 = B.字段);
select A.store_name from store_info A where A.store_name in (select B.store_name from location B);

select A.store_name from store_info A where exists (select B.store_name from location B where A.store_name = B.store_name);

多表查询求交集
多表查询:select A.字段 from 左表 A, 右表 B where A.字段 = B.字段;
select A.store_name from store_info A, location B where A.store_name = B.store_name;
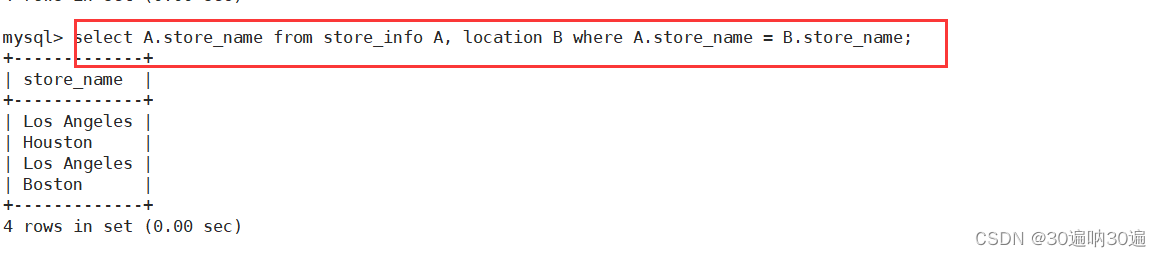
UNION 联集
将两个SQL语句的结果合并起来,两个SQL语句所产生的字段需要是同样的数据记录种类
UNION :生成结果的数据记录值将没有重复,且按照字段的顺序进行排序
语法:[SELECT 语句 1] UNION [SELECT 语句 2];
UNION ALL :将生成结果的数据记录值都列出来,无论有无重复
语法:[SELECT 语句 1] UNION ALL [SELECT 语句 2];
select store_name from store_info union select store_name from location;
select store_name from store_info union all select store_name from location;

分组实现查询交集
方法:联集+分组
select A.store_name from (select distinct store_name from store_info union all select distinct store_name from location) A group by A.store_name having count(A.store_name) > 1;

求左表无交集
select A.字段 from 左表 A left join 右表 B on A.字段 = B.字段 where B.字段 is null;
select 字段 from 左表 where 字段 not in (select 字段 from 右表);
select A.字段 from 左表 A where not exists (select B.字段 from 右表 B where A.字段 = B.字段);
例:select A.store_name from location A left join store_info B on A.store_name = B.store_name where B.store_name is null;

求右表无交集
select B.字段 from 左表 A right join 右表 B on A.字段 = B.字段 where A.字段 is null;
select 字段 from 右表 where 字段 not in (select 字段 from 左表);
select A.字段 from 右表 A where not exists (select B.字段 from 左表 B where A.字段 = B.字段);
例: select B.store_name from location A right join store_info B on A.store_name = B.store_name where A.store_name is null;
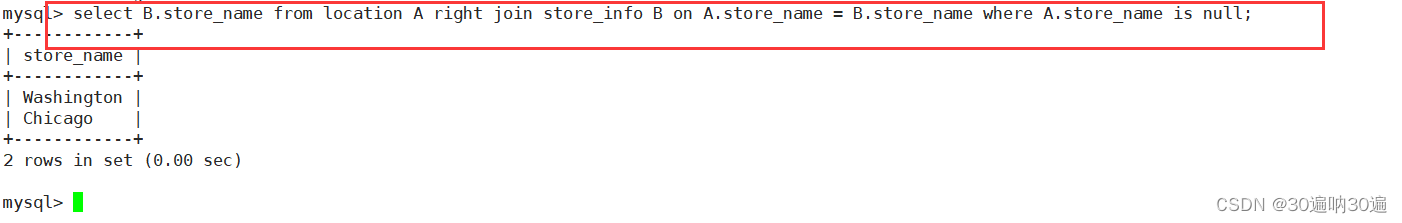
求两个表无交集
select A.字段 from 左表 A left join 右表 B on A.字段 = B.字段 where B.字段 is null
union all
select B.字段 from 左表 A right join 右表 B on A.字段 = B.字段 where A.字段 is null;select A.字段 from (select distinct 字段 from 左表 union all select distinct 字段 from 右表) A group by A.字段 having count(A.字段) = 1;
---- CREATE VIEW ----视图,可以被当作是虚拟表或存储查询
语法:CREATE VIEW "视图表名" AS "SELECT 语句";
例:create view v_sales as select sum(sales) from store_info;
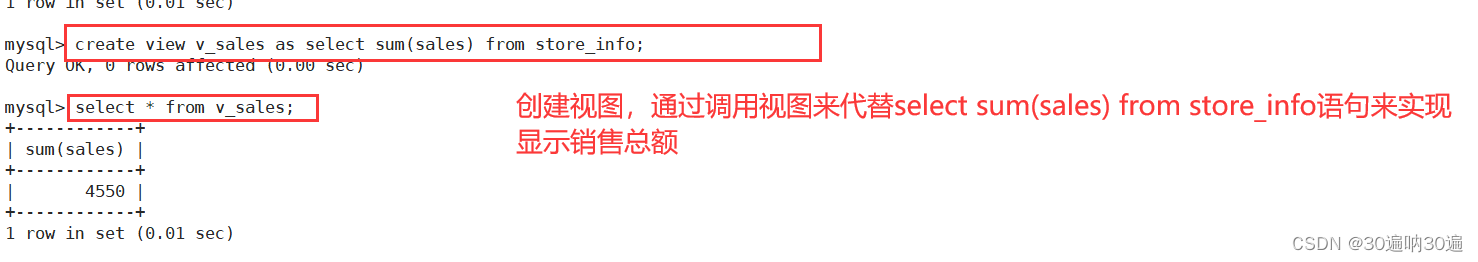
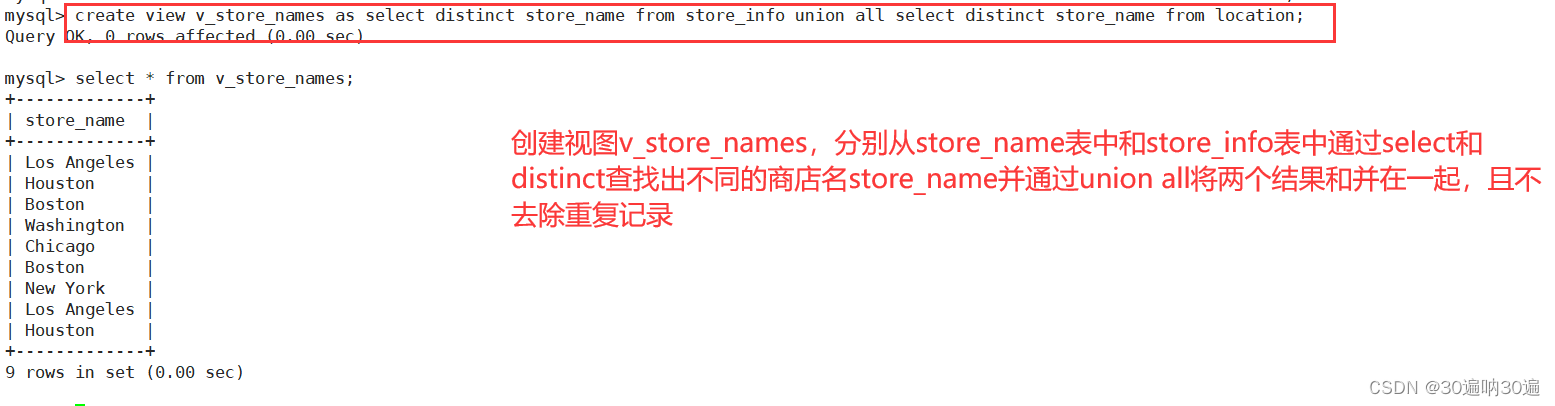
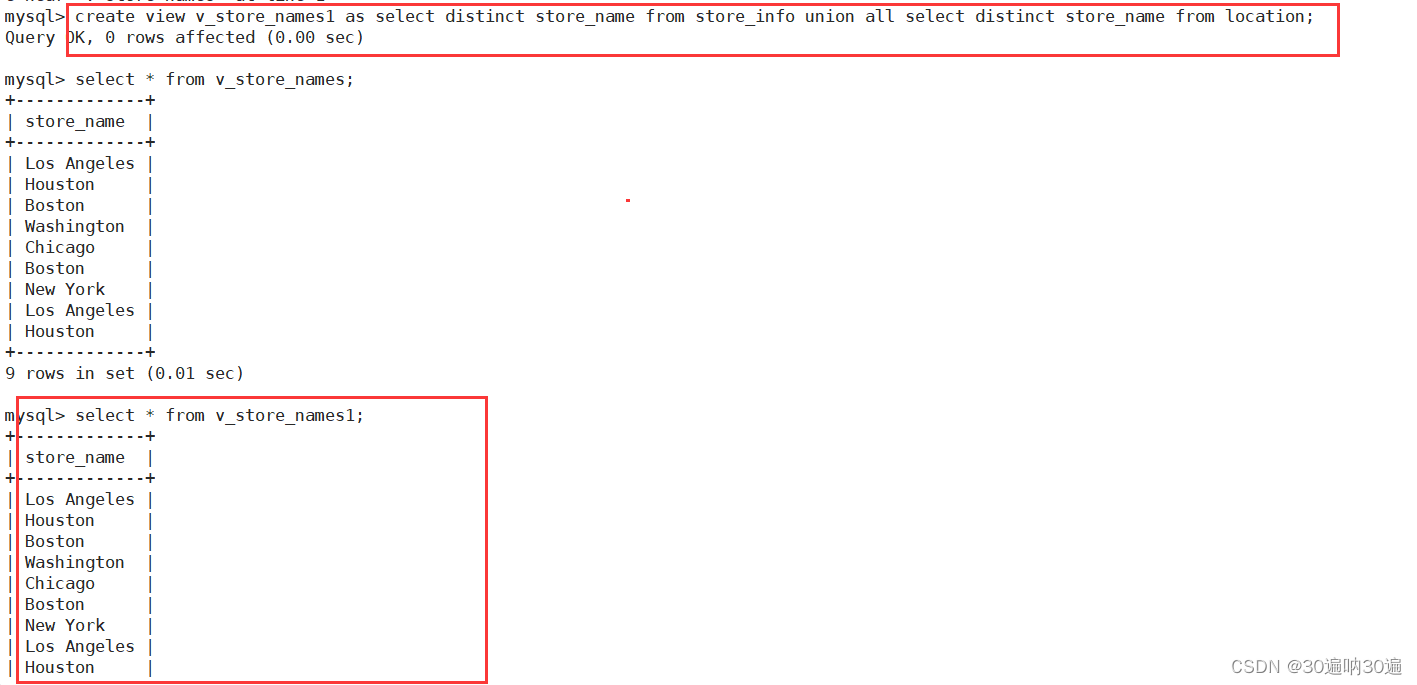
例1: create view v_store_names as select distinct store_name from store_info union all select distinct store_name from location;
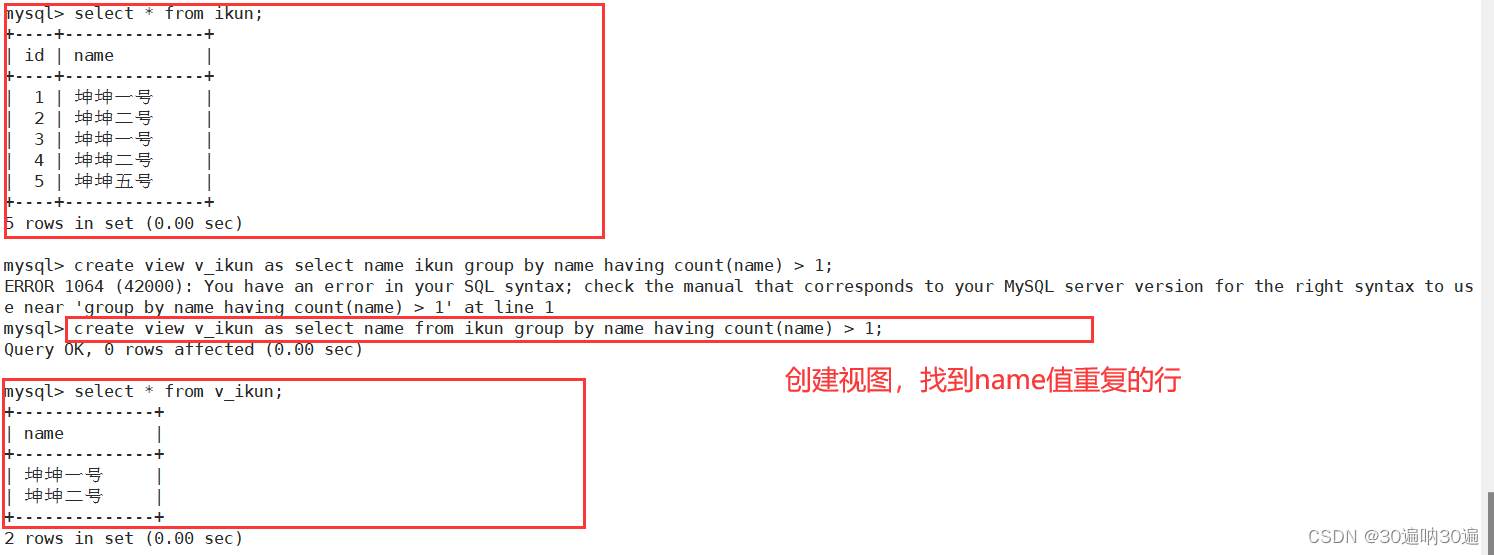
例2:通过创建视图删除表内具有重复内容的行

视图表View里面的数据是否能修改?
视图表保存的是select查询语句的定义
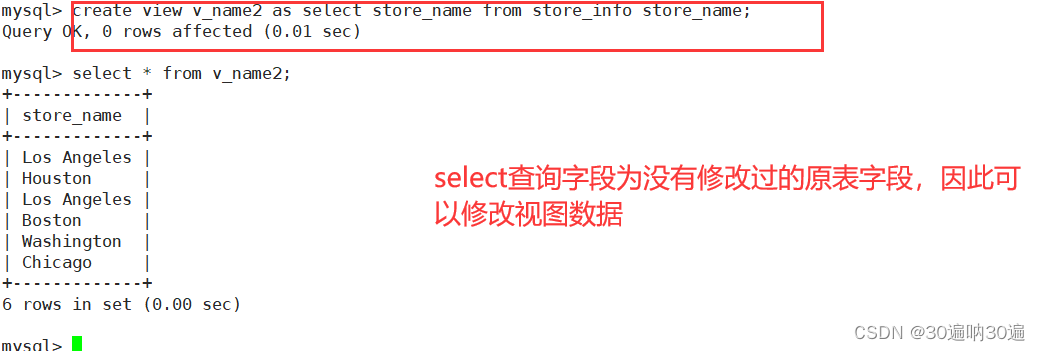
如果select语句查询的字段是没有被处理过的原表字段,则可以通过视图表修改原表里面的数据。
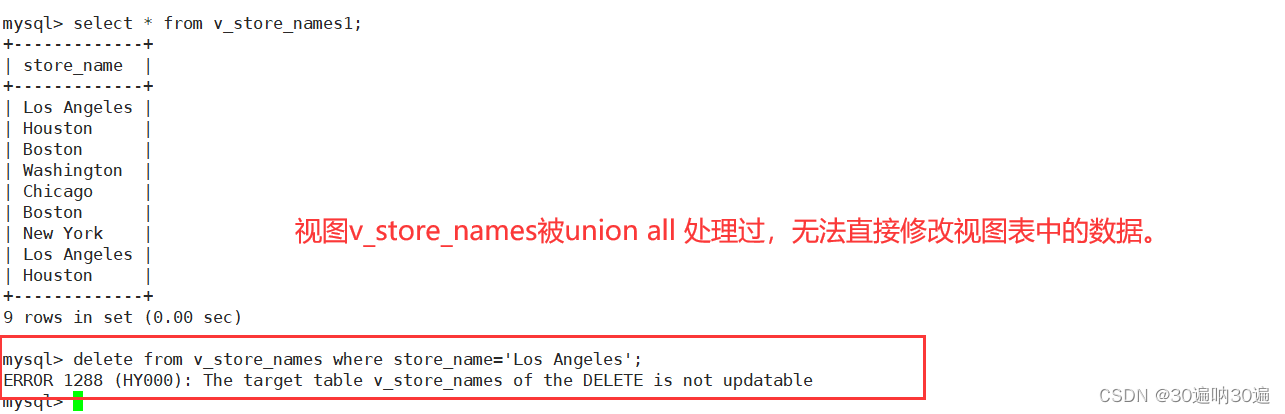
如果select语句查询的字段被函数或group by 等处理过,则不能直接修改视图表的数据。
例:create view v_name as select store_name from store_info group by store_name;
delete from v_name where store_name='Boston ';

例:create view v_name2 as select store_name from store_info store_name;

例:create view v_store_names1 as select distinct store_name from store_info union all select distinct store_name from location;
delete from v_store_names where store_name='Los Angeles';
CASE语句
SQL 用来做为 IF-THEN-ELSE 之类逻辑的关键字
**语法一:
SELECT CASE "字段名"
WHEN "数值1" THEN "结果1"
WHEN "数值2" THEN "结果2"
...
ELSE "default"
END
FROM "表名";**
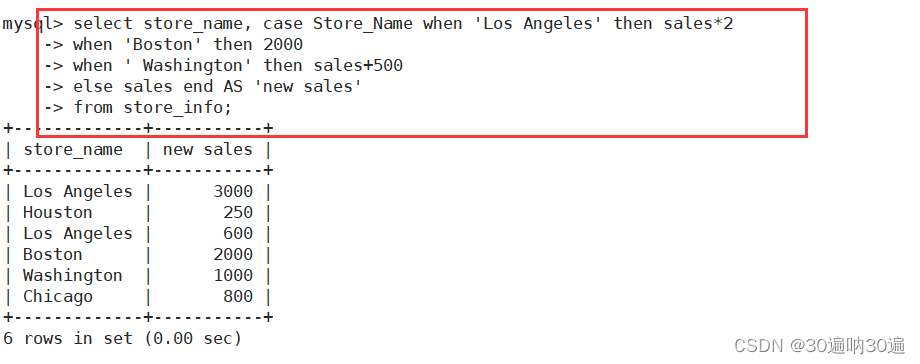
例:mysql> select store_name, case Store_Name when 'Los Angeles' then sales*2
-> when 'Boston' then 2000
-> when ' Washington' then sales+500
-> else sales end AS 'new sales'
-> from store_info;
**语法二:
SELECT CASE
WHEN "公式1" THEN "结果1"
WHEN "公式2" THEN "结果1"
...
ELSE "default"\] END** **例:mysql\> select store_name, case when store_name='Los Angeles' then sales\*2 -\> when store_name!='Los Angeles' then sales/2 -\> end 'new sales' -\> from store_info;** 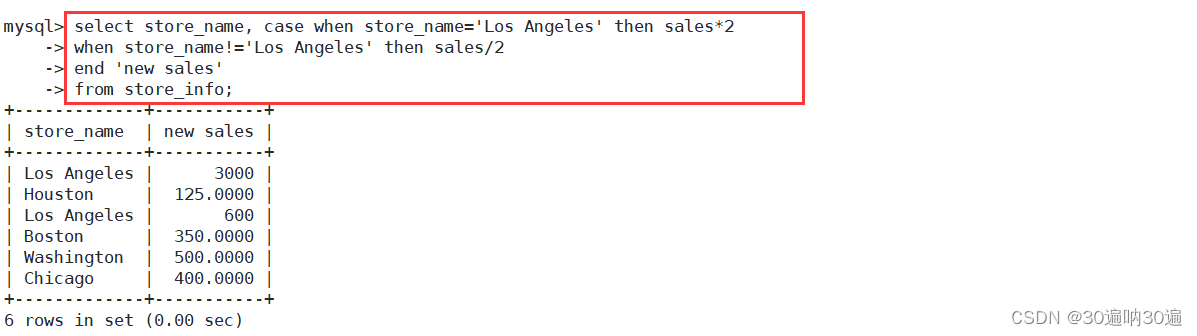 **空值(NULL) 和 无值('') 的区别** 1.无值的长度为 0,不占用空间的;而 NULL 值的长度是 NULL,是占用空间的。 2.IS NULL 或者 IS NOT NULL,是用来判断字段是不是为 NULL 或者不是 NULL,不能查出是不是无值的。 3.无值的判断使用=''或者\<\>''来处理。\<\> != 代表不等于。 4.在通过 count()指定字段统计有多少行数时,如果遇到 NULL 值会自动忽略掉,遇到无值会加入到记录中进行计算。 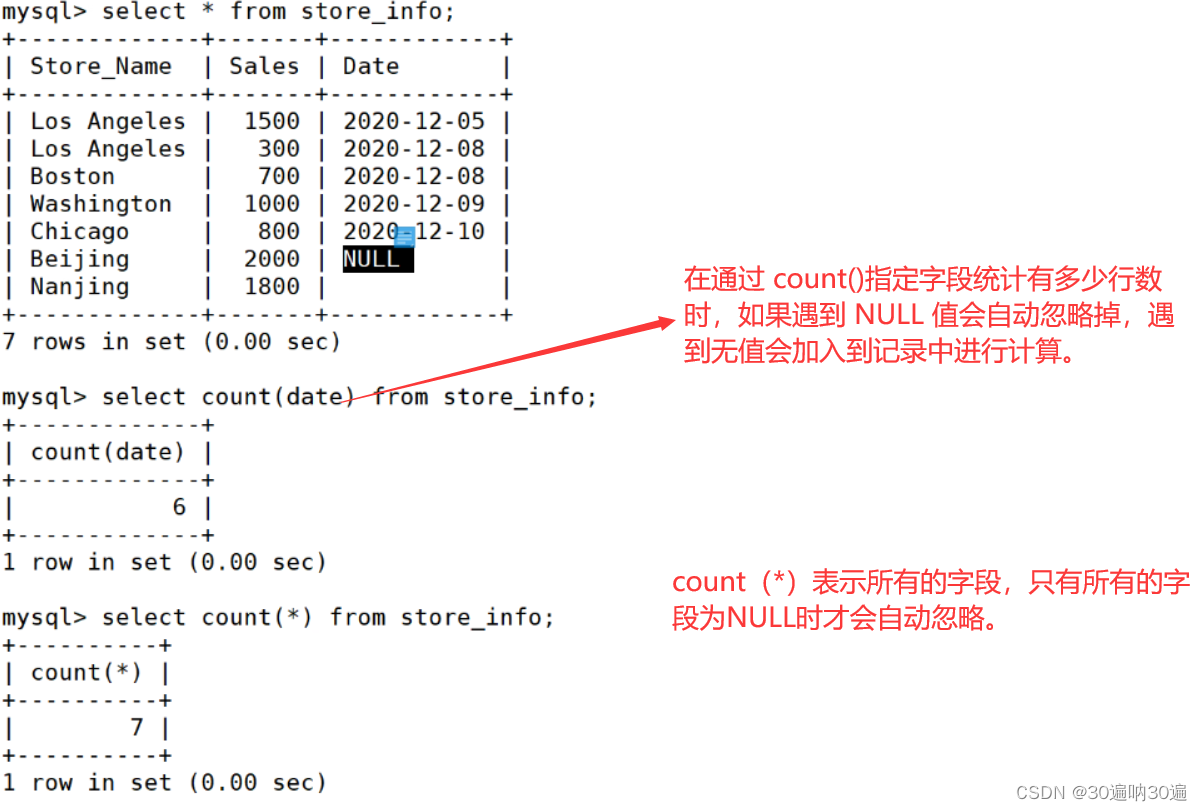 总结: 无值'' 的长度为 0,不占用空间;可以通过 字段名 = '' 或 字段名 != '' 来过滤字段的值是否为无值的行;指定字段使用函数 count(字段) 不会忽略 无值 的行 空值NULL 的长度为 NULL,占用空间;可以通过 "字段名 is null" 或 "字段名 is not null" 来过滤字段的值是否为NULL的行;指定字段使用函数 count(字段) 会忽略 NULL 的行 **---- 正则表达式 ----** |-----------|----------------------|-------------------------------| | 匹配模式 | 描述 | 实例 | | \^ | 匹配文本的开始字符 | '\^bd' 匹配以 bd 开头的字符串 | | $ | 匹配文本的结束字符 | 'qn$' 匹配以 qn 结尾的字符串 | | . | 匹配任何单个字符 | 's.t' 匹配任何 s 和 t 之间有一个字符的字符串 | | \* | 匹配零个或多个在它前面的字符 | 'fo\*t' 匹配 t 前面有任意个 o | | + | 匹配前面的字符 1 次或多次 | 'hom+' 匹配以 ho 开头,后面至少一个m 的字符串 | | 字符串 | 匹配包含指定的字符串 | 'clo' 匹配含有 clo 的字符串 | | p1\|p2 | 匹配 p1 或 p2 | 'bg\|fg' 匹配 bg 或者 fg | | \[...\] | 匹配字符集合中的任意一个字符 | '\[abc\]' 匹配 a 或者 b 或者 c | | \[\^...\] | 匹配不在括号中的任何字符 | '\[\^ab\]' 匹配不包含 a 或者 b 的字符串 | | {n} | 匹配前面的字符串 n 次 | 'g{2}' 匹配含有 2 个 g 的字符串 | | {n,m} | 匹配前面的字符串至少 n 次,至多m 次 | 'f{1,3}' 匹配 f 最少 1 次,最多 3 次 | **例:select \* from store_info where store_name regexp '(go\|on)$';** 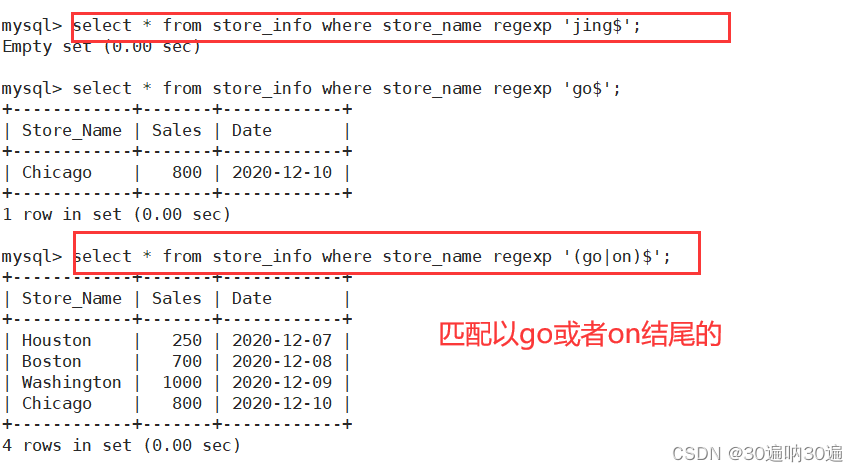 **例:mysql\> select \* from store_info where store_name regexp '\^\[ABC\].\*go$';** 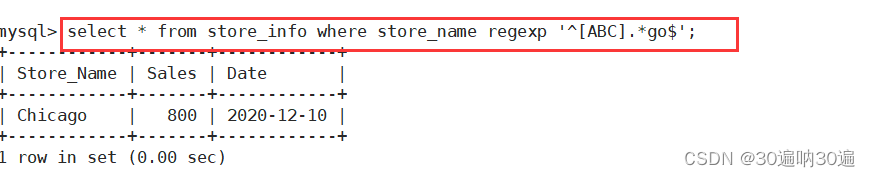 **存储过程** **存储过程是一组为了完成特定功能的SQL语句集合。** 存储过程在使用过程中是将常用或者复杂的工作预先使用SQL语句写好并用一个指定的名称存储起来,这个过程经编译和优化后存储在数据库服务器中。当需要使用该存储过程时,只需要调用它即可。存储过程在执行上比传统SQL速度更快、执行效率更高。 **存储过程的优点:** 1、执行一次后,会将生成的二进制代码驻留缓冲区,提高执行效率 2、SQL语句加上控制语句的集合,灵活性高 3、在服务器端存储,客户端调用时,降低网络负载 4、可多次重复被调用,可随时修改,不影响客户端调用 5、可完成所有的数据库操作,也可控制数据库的信息访问权限 **##创建存储过程##** DELIMITER $$ #将语句的结束符号从分号;临时改为两个$$(可以是自定义) CREATE PROCEDURE Proc() #创建存储过程,过程名为Proc,不带参数 -\> BEGIN #过程体以关键字 BEGIN 开始 -\> select \* from store_info; #过程体语句 -\> END $$ #过程体以关键字 END 结束 DELIMITER ; #将语句的结束符号恢复为分号 **##调用存储过程##** CALL Proc; **##查看存储过程##** SHOW CREATE PROCEDURE \[数据库.\]存储过程名; #查看某个存储过程的具体信息 SHOW CREATE PROCEDURE Proc; SHOW PROCEDURE STATUS \[LIKE '%Proc%'\] \\G **如何导出数据库文件?** **第一步:** **vim /etc/my.cnf 进入修改配置文件**  **重启数据库,systemctl restart mysqld** **第二步:** 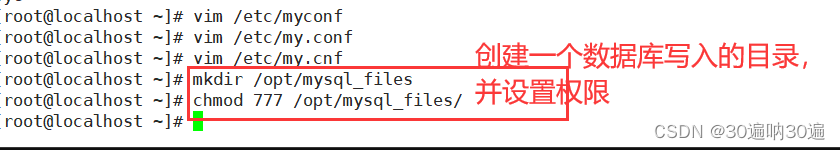  **第三步:**    **如何导入数据库文件?** **步骤一:导入表数据时,表要存在,若不存在则应先创建表** 此时将store_info删除,模拟数据导入  **先创建表结构** **create table store_info (Store_Name char(20),Sales int(10),Date char(10));** **步骤二:指定所需导入数据的所在位置** 