store对象的创建
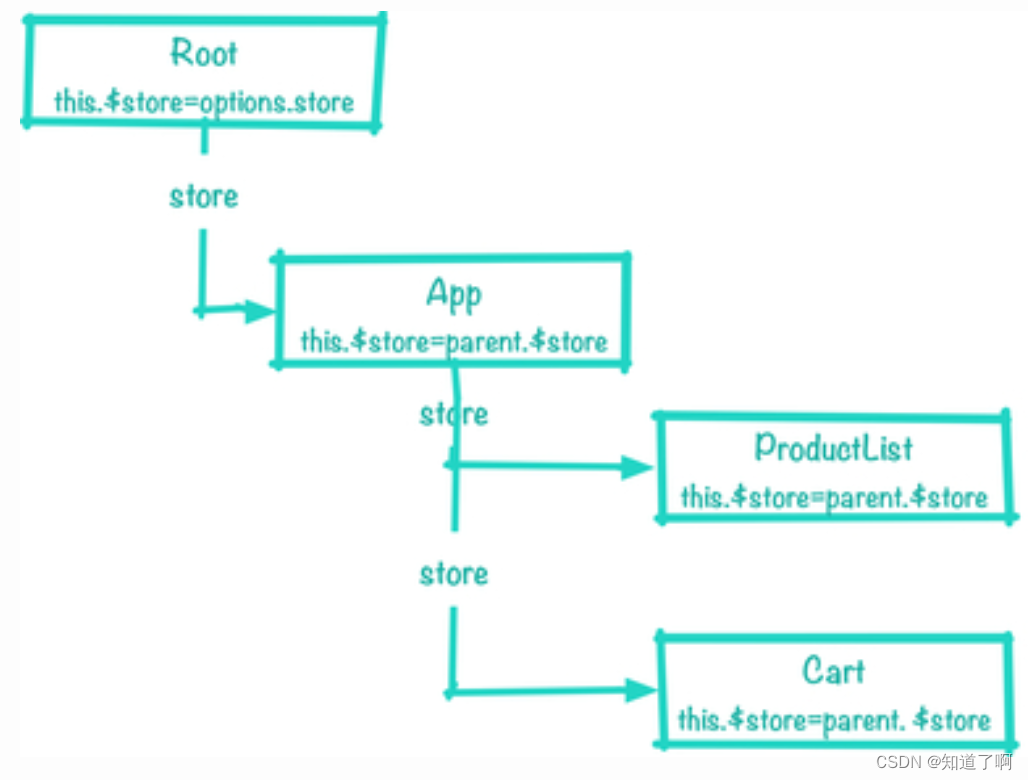
store的传递图

创建语句索引
- 创建vuex的语句为new Vuex.Store({...})
- Vuex的入口文件是index.js,store是index.js导出的store类
- store类是store.js文件中定义的。
Store的构造函数constructor
- 判断vuex是否被注入,就是将vue挂载在window对象上,自动检测window.Vue,如果有挂载,而且没有被注册过,则调用注册方法
javascript
if (!Vue && typeof window !== 'undefined' && window.Vue) {
install(window.Vue)
}- 断言
断言是否被注册,是否支持promise,断言类有没有被正确的实例化,这些断言语句,在vue build出来以后,报错信息会被忽略
javascript
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
assert(Vue, `must call Vue.use(Vuex) before creating a store instance.`)
assert(typeof Promise !== 'undefined', `vuex requires a Promise polyfill in this browser.`)
assert(this instanceof Store, `store must be called with the new operator.`)
}- 支持promise语法
- 已经执行安装函数进行装载
- 在webpack配置的时候,npm build会将process.env.NODE_ENV 设置为true
javascript
function assert(condition, msg) {
if(!condition) throw new Error(`[vuex] ${msg}`)
}- 部分重要的容器
javascript
this._committing = false // 表示状态标识,在严格模式下,防止非commit操作下,state被修改
this._actions = Object.create(null) // action函数的数组的对象,保存所有action回调函数。从null中创建对象,object.create(null)没有继承任何原型方法,也就是说他的原型链没有上一层,从而定义纯粹的对象
this._actionSubscribers = [] // 订阅action操作的函数数组,里面的每个函数,将在action函数被调用之间被调用,该功能类似于插件,和主功能无关。
this._mutations = Object.create(null) // mutation函数的数组的对象,保存所有的mutations回调函数
this._wrappedGetters = Object.create(null) //保存getter函数的函数数组对象容器
this._modules = new ModuleCollection(options) // 解析并生成模块树,通过树结构,保存配置文件内容
this._modulesNamespaceMap = Object.create(null) // 保存命名空间的模块对象,以便在辅助函数createNamespacedHelpers中快速定位到待命名空间的模块。
this._subscribers = [] // 订阅mutation操作的函数数组,里面的每个函数,将在commit执行后被调用,类似于插件,和主功能无关。
this._watcherVM = new Vue() // 定义一个vue对象,vue类将在调用vuex安装函数,install 的时候,被传递进来。简洁版
javascript
this._committing = false // 是否在进行提交状态标识
this._actions = Object.create(null) // acitons操作对象
this._mutations = Object.create(null) // mutations操作对象
this._wrappedGetters = Object.create(null) // 封装后的getters集合对象
this._modules = new ModuleCollection(options) // Vuex支持store分模块传入,存储分析后的modules
this._modulesNamespaceMap = Object.create(null) // 模块命名空间map
this._subscribers = [] // 订阅函数集合,Vuex提供了subscribe功能
this._watcherVM = new Vue() // Vue组件用于watch监视变化ModuleCollection
javascript
this._modules = new ModuleCollection(options)ModuleCollection函数主要是讲传入的options对象构造为一个module对象,并循环调用(this.register[key], rawModul, false)为其中的modules属性进行模块注册,使得其称为module对象后,最后options对象被构成一个完整的组件树,ModuleCollection类还提供了modules的更替功能。
constructor
javascript
export default class ModuleCollection {
constructor(rawRootModule) {
this.register([], rawRootModule, false)
}
}- 形参: rawRootModule,在store中new ModuleCollection(options)传入,而options是store的构造函数参数,就是new Vuex.Store({...})传入的参数
javascript
{
state,
getters,
actions,
mutations
}register
javascript
register (path, rawModule, runtime = true) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
assertRawModule(path, rawModule)
}
const newModule = new Module(rawModule, runtime)
if (path.length === 0) {
this.root = newModule
} else {
const parent = this.get(path.slice(0, -1))
parent.addChild(path[path.length - 1], newModule)
}
if (rawModule.modules) {
forEachValue(rawModule.modules, (rawChildModule, key) => {
this.register(path.concat(key), rawChildModule, runtime)
})
}
}参数解析
- path是注册模块的层级关系数组,保存当前模块及各个祖先模块的名字。[a, b, c, 当前模块] =>
{modules: {a, modules: {b, module:{当前模块} }}} - rawModule是模块的配置参数,在定义模块的时候,开发者定义的模块配置内容,比如state, getter, actions等等
- runtime标识是否是运行状态,在运行状态下,不能进行某些特定的操作。
assertRawModule
javascript
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
assertRawModule(path, rawModule)
}- 对模块的配置信息进行断言
- 判断了getters,mtations, actions等配置的数据类型是否正确。
const newModule = new Module(rawModule, runtime),找到module.js文件找到其构造函数
javascript
constructor (rawModule, runtime) {
this.runtime = runtime
this._children = Object.create(null) // 定义子模块对象容器
this._rawModule = rawModule // 保存配置参数本身
const rawState = rawModule.state // 从配置参数中获得了state这个参数
this.state = (typeof rawState === 'function' ? rawState() : rawState) || {} // 解析state,如果是函数,则运用工厂模式产生配置对象
}根据path模块判断当前是否为根模块
-
如果是根模块,则通过this.root进行保存
-
如果不是根模块
- get方法传入的是路径数组,slice(0,-1)是为了去除本模块名,保留所有祖先模块的路径,从而获取夫模块。
- get函数内部,使用了数组的reduce方法
javascriptget (path) { return path.reduce((module, key) => { return module.getChild(key) }, this.root) }javascriptgetChild (key) { return this._children[key] } addChild (key, module) { this._children[key] = module }
if(rawModule.modules)判断模块配置信息中,有没有子模块的配置
如果有,则递归调用注册函数register本身,传入的参数加上了子模块名的path模块层级数组,rawchildmodule是子模块配置文件,runtime是继承而来的运行标识符
获取dispatch和commit函数,并复写该函数
javascript
const store = this
const { dispatch, commit } = this
this.dispatch = function boundDispatch (type, payload) {
return dispatch.call(store, type, payload)
}
this.commit = function boundCommit (type, payload, options) {
return commit.call(store, type, payload, options)
}复写的作用是将两个函数的this值绑定到vuex实例本身上,防止因为this的指向修改而被修改
这两个函数可以通过mapMutations和mapActions辅助函数转换为Vue中的普通函数,这时this指向Vue组件,而不是Vuex实例
后续代码
javascript
this.strict = strict
const state = this._modules.root.state //根据根模块的state变量索引
installModule(this, state, [], this._modules.root)//安装根模块,设置commit,dispatch函数的重载,根据是否设置命名空间,设置参数前缀,将getter,commit,action放到相对应的容器中保存起来。
resetStoreVM(this, state)// 借助vue的watch功能和computed功能,实现数据的响应式
plugins.forEach(plugin => plugin(this)) // 插件的注册,和主功能无关
const useDevtools = options.devtools !== undefined ? options.devtools : Vue.config.devtools
if (useDevtools) { // vue调试工具的处理
devtoolPlugin(this)
}installModule(模块安装函数)
参数介绍
- store: store对象实例,new Vuex.store({...})生成的对象
- rootState: 根模块的state对象
- path: 当前模块所处的层级数组
- module: 模块对象
- hot
实例代码
javascript
function installModule (store, rootState, path, module, hot) {
const isRoot = !path.length // 判断当前模块是否为根模块
const namespace = store._modules.getNamespace(path) // 获取模块的命名空间
if (module.namespaced) {
store._modulesNamespaceMap[namespace] = module
}
if (!isRoot && !hot) {
const parentState = getNestedState(rootState, path.slice(0, -1))
const moduleName = path[path.length - 1]
store._withCommit(() => {
Vue.set(parentState, moduleName, module.state)
})
}
}补充
getNamespace
javascript
//从跟模块中出发,根据给出的路径数组,递归每一个层级的模块
getNamespace(path) {
let module = this.root
return path.reduce((namespace, key) => {
module = module.getChild(key)
return namespace + (module.namespaced ? key + "/" : '')
}, '')
}
json
{
moduleA:{
namespaced:true,
modules:{
moduleB:{
namespaced:false,
modules:{
moduleC:{
namespaced:true,
}
}
}
}
}
}