一. 数据解析和绑定
1.1 Json数据解析和绑定
html文件:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/loginForm" method="post"enctype="application/x-www-form-urlencoded">
用户名<input type="text" name="username"><br>
密码<input type="password" name="password">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>代码:
- gin.Context中的ShouldBind方法将请求中的正文中的数据,自动按照json格式解析到结构体。
Go
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
// 定义接收数据的结构体
type Login struct {
//binding:"required"修饰字段,若接收为空值,则报错
Account string `form:"username" json:"user" uri:"user" xml:"user" binding:"required"`
Passwd string `form:"password" json:"password" uri:"password" xml:"password" binding:"required"`
}
func main() {
//创建路由
r := gin.Default()
//设置HTML文件所在目录
r.LoadHTMLGlob("./*.html")
r.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
//发送html文件内容
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", nil)
})
r.POST("/loginForm", func(c *gin.Context) {
//声明接收变量
var json Login
//将request的body中的数据,自动按照json格式解析到结构体
if err := c.ShouldBindJson(&json); err != nil {
//gin.H封装了生成json数据工具
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{
"error": err.Error(),
})
return
}
//判断用户名密码是否正确
if json.Account != "root" || json.Passwd != "admin" {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{
"status": ".304",
})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"status": "ok",
})
})
r.Run()
}演示:

1.2. 表单数据解析和绑定
html文件:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/loginForm" method="post"enctype="application/x-www-form-urlencoded">
用户名<input type="text" name="username"><br>
密码<input type="password" name="password">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>代码:
- gin.Context的Bind方法默认解析并绑定form格式,根据请求头中的content-type自动推断。
Go
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
// 定义接收数据的结构体
type Login struct {
//binding:"required"修饰字段,若接收为空值,则报错
Account string `form:"username" binding:"required"`
Passwd string `form:"password" binding:"required"`
}
func main() {
//创建路由
r := gin.Default()
//设置HTML文件所在目录
r.LoadHTMLGlob("./*.html")
r.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
//发送html文件内容
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", nil)
})
r.POST("/loginForm", func(c *gin.Context) {
//声明接收变量
var form Login
//Bind()默认解析并绑定form格式
//根据请求头中的content-type自动推断
if err := c.Bind(&form); err != nil {
//gin.H封装了生成json数据工具
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{
"error": err.Error(),
})
return
}
//判断用户名密码是否正确
if form.Account != "root" || form.Passwd != "admin" {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{
"status": ".304",
})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"status": "ok",
})
})
r.Run()
}1.3. URI数据解析和绑定
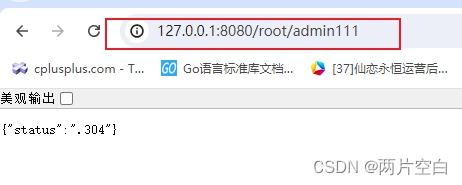
- gin.Context中的ShouldBindUri方法将uri中的数据,自动按照uri格式解析到结构体。
Go
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
// 定义接收数据的结构体
type Login struct {
//binding:"required"修饰字段,若接收为空值,则报错
Account string `uri:"user" binding:"required"`
Passwd string `uri:"password" binding:"required"`
}
func main() {
//创建路由
r := gin.Default()
r.GET("/:user/:password", func(c *gin.Context) {
//声明接收变量
var uri Login
if err := c.ShouldBindUri(&uri); err != nil {
//gin.H封装了生成json数据工具
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{
"error": err.Error(),
})
return
}
//判断用户名密码是否正确
if uri.Account != "root" || uri.Passwd != "admin" {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{
"status": ".304",
})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"status": "ok",
})
})
r.Run()
}演示:

二. gin渲染
2.1 各种数据的响应
多种响应方式:
Go
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin/testdata/protoexample"
)
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
//1. json
r.GET("/someJson", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"message": "someJson",
"status": "ok",
})
})
//2. 结构体响应
r.GET("/someStruct", func(c *gin.Context) {
var msg struct {
Name string
Message string
Number int
}
msg.Name = "root"
msg.Message = "someStruct"
msg.Number = 1
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, msg)
})
//3. xml
r.GET("/someXml", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.XML(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"message": "abc"})
})
//4. YAML响应
r.GET("/someYaml", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.YAML(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"message": "123",
})
})
//5. protobuf格式
//构建一个自己的传输格式
r.GET("/someProtobuf", func(c *gin.Context) {
resp := []int64{int64(1), int64(2)}
lable := "lable"
data := &protoexample.Test{
Label: &lable,
Reps: resp,
}
c.ProtoBuf(http.StatusOK, data)
})
r.Run()
}2.2 HTML模板渲染
- gin支持加载HTML模板,然后根据模板进行配置并返回相应的数据,本质就是字符串替换。
- LoadHTMLGlob()方法可以加载模板文件
目录结构:
html文件:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>{{.title}}</title>
</head>
<body>
fgkjdskjdsh{{.ce}}
</body>
</html>代码:
Go
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
r.LoadHTMLGlob("./tem/*") //从运行文件位置开始 需要加载的html文件路径
r.GET("/someHtml", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", nil)
})
r.Run()
}- 当html的目录结构如下时

html:
Go
{{ define "user/index.html" }}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>{{.title}}</title>
</head>
<body>
fgkjdskjdsh{{.message}}
</body>
</html>
{{ end }}代码:
Go
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
r.LoadHTMLGlob("tem/*/*") //从运行文件位置开始 需要加载的html文件路径
r.GET("/someHtml", func(c *gin.Context) {
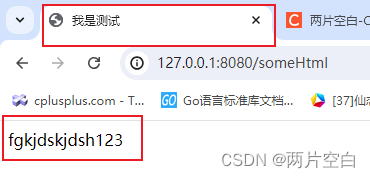
//user/index.html为html中的define
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "user/index.html", gin.H{"title": "我是测试", "message": "123"})
})
r.Run()
}演示:
- html头尾分离
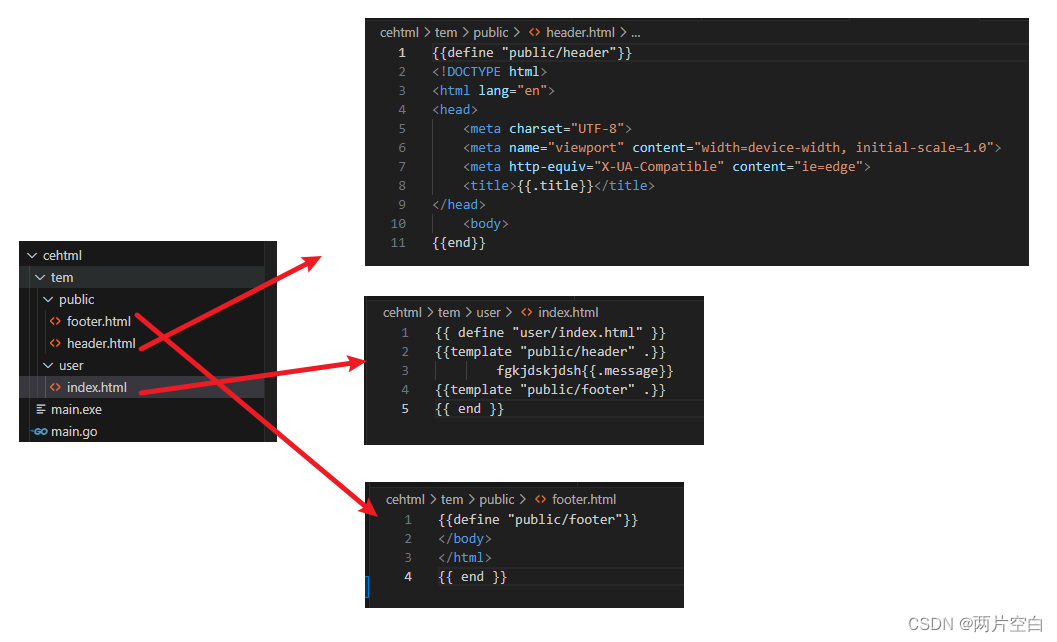
代码:
Go
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
r.LoadHTMLGlob("tem/*/*") //从运行文件位置开始 需要加载的html文件路径
r.GET("/someHtml", func(c *gin.Context) {
//user/index.html为html中的define
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "user/index.html", gin.H{"title": "我是测试", "message": "123"})
})
r.Run()
}演示:
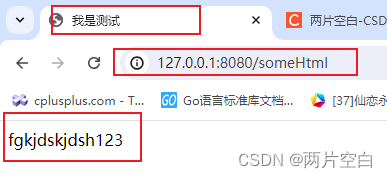
- 如果你需要引入静态文件需要定义一个静态文件目录
Go
r.Static("./assets", "./assets")2.3 重定向
- 使用gin.Context的Redirect方法
Go
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
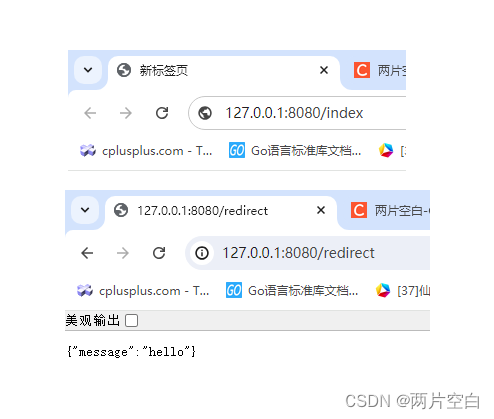
r.GET("/index", func(c *gin.Context) {
//重定向
c.Redirect(http.StatusMovedPermanently, "redirect")
})
r.GET("/redirect", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"message": "hello",
})
})
r.Run()
}
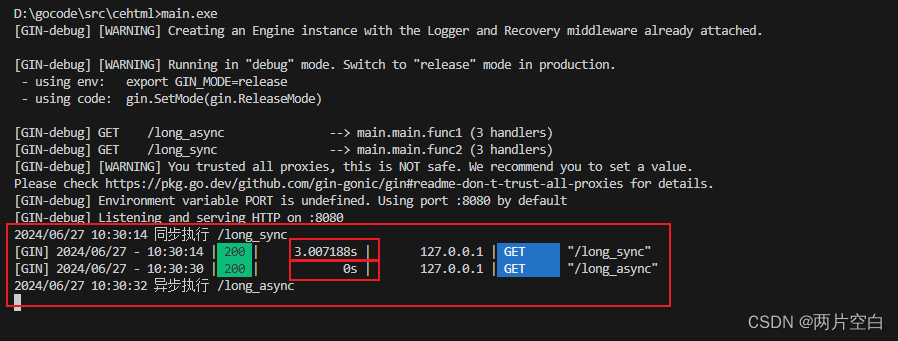
2.4 同步异步
- goroutine机制可以方便地实现异步处理
- 另外,在启动新的goroutine时,不应该使用原始上下文context,必须使用它的只读副本
Go
package main
import (
"log"
"time"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
r.GET("/long_async", func(c *gin.Context) {
//上下文副本
c_tmp := c.Copy()
//异步处理
go func() {
time.Sleep(2 * time.Second)
log.Println("异步执行 " + c_tmp.Request.URL.Path)
}()
})
r.GET("/long_sync", func(c *gin.Context) {
time.Sleep(3 * time.Second)
log.Println("同步执行 " + c.Request.URL.Path)
})
r.Run()
}异步是启动一个协程去执行请求。