栈:
- 线性的集合。
- 后进先出(LIFO,last in first out)。
- 两个指针:指向栈顶和栈底。栈顶指向最后进入且第一个出去的元素。栈底指向第一个进入且最后一个出去的元素。
- 两个操作:入栈(往栈尾添加元素),出栈(从栈尾取出元素)。
- 可以使用链表实现,也可以使用数组实现。本文使用双链表举例。
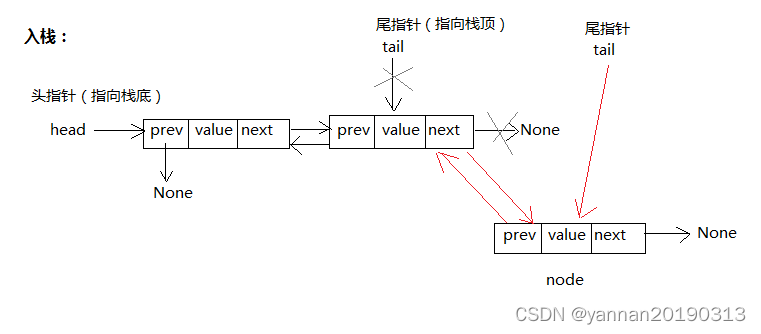
入栈:往栈顶(栈尾部)添加元素。
(头指针:指向第一个元素。尾指针:指向最后的元素。)
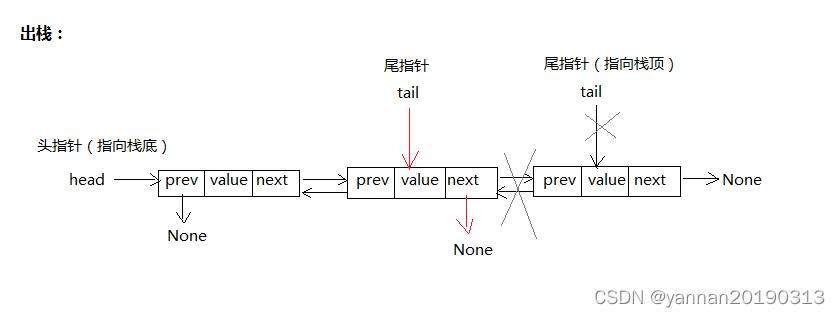
出栈:从栈顶(栈尾部)删除元素。
(头指针:指向第一个元素。尾指针:指向最后的元素。)
C语言实现(双链表):
创建节点(结构体数据类型),并创建具体节点实例的函数:
cpp
// 节点(结构体数据类型)
typedef struct Node
{
int value; // 存储数据为整数
struct Node *next; // 指向下一个数据的指针
struct Node *prev; // 指向上一个数据的指针
} LinkNode; // 别名LinkNode
cpp
// 创建具体节点实例的函数
LinkNode * createNode(int data)
{
LinkNode *node = (LinkNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode)); // 分配内存空间
if(node == NULL)
{
perror("Memory allocation failed");
exit(-1);
}
node->value = data;
node->prev = NULL;
node->next = NULL;
return node;
}本文将头指针、尾指针和栈长度作为全局变量:
cpp
LinkNode *header = NULL; // 头指针,指向第一个节点,初始化为NULL
LinkNode *tail = NULL; // 尾指针,指向最后节点,初始化为NULL
int length = 0; // 统计栈有多少元素,初始化为0入栈:
cpp
// 入栈(往栈顶即尾部添加数据)
void push(int data)
{
LinkNode *node = createNode(data);
if(length == 0) // 空栈,头指针和尾指针都指向新节点
{
header = node;
tail = node;
length++;
return ;
}
tail->next = node; // 原最后节点的下一个为新节点
node->prev = tail; // 新节点的上一个为原最后节点
tail = node; // 尾指针指向新节点,即新节点为最后节点
length++; // 每添加一个元素,length+1
}获取栈顶元素:
cpp
int gettop(void)
{
// 栈不为空,则栈顶元素为尾指针指向的最后节点的值
if(length != 0) return tail->value;
}出栈:
cpp
int pop(void)
{
if(length != 0)
{
// 获取最后节点的值
int top = tail->value;
// 通过最后节点的prev找到倒数第二个节点,其next指向NULL,则原倒数第二个节点为新的最后节点
tail->prev->next = NULL;
// 每删除一个节点,length-1
length--;
// 返回原最后节点的值
return top;
}
}遍历栈:
cpp
void travel(void)
{
if(length == 0) return ;
LinkNode *cur = header; // 从链表头部开始遍历,直到最后
printf("stack elements:");
while(cur != NULL)
{
printf("%d \t", cur->value);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}完整代码:(stack**.**c)
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
/* structrue */
typedef struct Node // node structure
{
int value;
struct Node *next;
struct Node *prev;
} LinkNode;
/* global variables */
LinkNode *header = NULL; // the header pointer
LinkNode *tail = NULL; // the tailer pointer
int length = 0; // the number of the stack elements
/* function prototype */
void push(int data); // add element to the end of the stack
int pop(void); // delete element from the end of the stack
int gettop(void); // show element at the end of the stack
void travel(void); // show element one by one
/* main function */
int main(void)
{
// cycle input a number until 'q' or non-numeric, add the number to the stack
while(1) // 循环输入数字,并入栈,输入q退出输入循环
{
int data = 0, c;
printf("if quit,input 'q'. Input a number: ");
c = getchar(); // 获取输入的一个字符
if(tolower(c) == 'q') break; // 若输入q,则退出输入循环
if(c < '0' || c > '9') break; // 输入的不是数字,则退出输入循环
while(c != '\n') // 若整数为多位数,通过一位一位计算最终获得多位整数
{
data *= 10;
data += c - 48; // ASCII码表中,0对应码值48
c = getchar();
}
push(data); // 入栈
printf("length is %d \n", length); // 输出栈元素个数
travel(); // 遍历栈
}
// when stack not empty,cycle look and delete the top element until input 'n'
if(length == 0) exit(-1);
char k;
printf("if you want to look and delete the top element? (y/n) ");
scanf(" %c", &k); // 获取输入的内容
while(tolower(k) == 'y' && length != 0) // 循环输入是否查看并删除栈顶元素
{
printf("top element is %d \n", gettop()); // 输出栈顶元素
pop(); // 出栈
printf("length is %d \n", length); // 输出栈元素个数
travel(); // 遍历栈
printf("if you want to look and delete the top element? (y/n) ");
scanf(" %c", &k); // 获取下一个输入的内容
}
}
/* subfunction */
LinkNode * createNode(int data) // create a node
{
LinkNode *node = (LinkNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
if(node == NULL)
{
perror("Memory allocation failed");
exit(-1);
}
node->value = data;
node->prev = NULL;
node->next = NULL;
return node;
}
void push(int data) // add element to the end of the stack
{
LinkNode *node = createNode(data);
if(length == 0)
{
header = node;
tail = node;
length++;
return ;
}
tail->next = node;
node->prev = tail;
tail = node;
length++;
}
int pop(void) // delete element from the end of the stack
{
if(length != 0)
{
int top = tail->value;
tail->prev->next = NULL;
length--;
return top;
}
}
int gettop(void) // show element at the end of the stack
{
if(length != 0) return tail->value;
}
void travel(void) // show element one by one
{
if(length == 0) return ;
LinkNode *cur = header;
printf("stack elements:");
while(cur != NULL)
{
printf("%d \t", cur->value);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}编译链接: gcc -o stack stack**.**c
执行可执行文件: ./stack
