WebSocket
因为一般的请求都是HTTP请求(单向通信),HTTP是一个短连接(非持久化),且通信只能由客户端发起,HTTP协议做不到服务器主动向客户端推送消息。WebSocket确能很好的解决这个问题,服务端可以主动向客户端推送消息,客户端也可以主动向服务端发送消息,实现了服务端和客户端真正的平等
特点
1.全双工通信:允许服务器和客户端在同一连接上同时进行双向通信
2.持久连接:连接一旦建立,会一直保持打开状态,减少了每次连接建立和关闭的开销,使通信更加高效
3.低延迟:由于连接保持打开状态,WebSocket 通信具有较低的延迟,适用于实时性要求较高的应用
4.兼容性:代浏览器和大多数服务器支持 WebSocket
5.安全性:与其他网络通信协议一样,WebSocket 通信也需要一些安全性的考虑。可以使用加密协议(如 TLS)来保护数据在网络传输中的安全性
实战
1.添加依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-websocket</artifactId> </dependency>
2.创建配置类
创建配置类,并将其注入到Bean容器中
@Configuration public class WebSocketConfig { /** * 注入ServerEndpointExporter, * 这个bean会自动注册使用了@ServerEndpoint注解声明的Websocket endpoint */ @Bean public ServerEndpointExporter serverEndpointExporter() { return new ServerEndpointExporter(); } }
3.创建WebSocketServer类
创建WebSocketHandler类,并将其注入到Bean容器中
@ServerEndpoint("/websocket/{equipmentId}"),该注解用于配置建立WebSocket连接的路径,可以按需修改
@Component @Slf4j @ServerEndpoint("/websocket/{equipmentId}") public class WebSocketHandler { private Session session; //concurrent包的线程安全Set,用来存放每个客户端对应的WebSocket对象。 private static CopyOnWriteArraySet<WebSocketHandler> webSocketUtils = new CopyOnWriteArraySet<>(); // 用来存在线连接数 private static Map<String, Session> sessionPool = new HashMap<>(); private static EquipmentService equipmentService = SpringContextHolder.getBean(EquipmentService.class); /** * 链接成功调用的方法 */ @OnOpen public void onOpen(Session session, @PathParam(value = "equipmentId") String equipmentId) { try { this.session = session; webSocketUtils.add(this); sessionPool.put(equipmentId, session); sendOneMessage(equipmentId, ""); equipmentService.onlineRecord(equipmentId,0); log.info("【websocket消息】有新的连接,总数为:" + webSocketUtils.size()); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 链接关闭调用的方法 */ @OnClose public void onClose(@PathParam(value = "equipmentId") String equipmentId) { try { webSocketUtils.remove(this); equipmentService.onlineRecord(equipmentId,1); log.info("【websocket消息】连接断开,总数为:" + webSocketUtils.size()); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 收到客户端消息后调用的方法 * * @param message * @param */ @OnMessage public void onMessage(@PathParam(value = "equipmentId") String equipmentId, String message) { log.info("【websocket消息】收到客户端消息:" + message); sendOneMessage(equipmentId, message); } /** * 发送错误时的处理 * * @param session * @param error */ @OnError public void onError(Session session, Throwable error) { log.error("用户错误,原因:" + error.getMessage()); error.printStackTrace(); } /** * 推消息给前端 * * @param equipmentId * @param message * @return */ public static Runnable sendOneMessage(String equipmentId, Object message) { Session session = sessionPool.get(equipmentId); if (session != null && session.isOpen()) { try { log.info("【推给前端消息】 :" + message); //高并发下,防止session占用期间,被其他线程调用 synchronized (session) { session.getBasicRemote().sendText(Objects.toString(message)); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } return null; }}
功能点:
1.处理异常: 与任何网络通信一样,WebSocket 连接可能会面临各种异常情况,如断开连接、网络问题等。WebSocket 服务器需要能够处理这些异常情况,进行适当的清理和处理。
2.消息处理: 一旦客户端连接成功,WebSocket 服务器需要处理客户端发送过来的消息。这可以在 WebSocket 端点中的方法上定义处理逻辑。服务器可以根据不同的业务需求处理不同类型的消息
3.WebSocket 服务器负责监听客户端的连接请求,一旦有客户端连接,服务器会创建一个 WebSocket 会话(Session)来管理这个连接。服务器需要能够维护这些连接,包括打开、关闭、保持心跳等操作。
4.WebSocket 服务器需要注册一个或多个 WebSocket 端点。每个端点对应一种处理逻辑,可以处理客户端发送过来的消息,以及向客户端发送消息。这些端点通过注解或配置来定义
因业务需求,常需要对获取的消息进行处理,websocket 不能注入( @Autowired ) service,解决办法:
private static EquipmentService equipmentService = SpringContextHolder.getBean(EquipmentService.class);
@Component public class SpringContextHolder implements ApplicationContextAware, DisposableBean { private static ApplicationContext applicationContext = null; /** * 取得存储在静态变量中的ApplicationContext. */ public static ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() { assertContextInjected(); return applicationContext; } /** * 从静态变量applicationContext中取得Bean, 自动转型为所赋值对象的类型. */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public static <T> T getBean(String name) { assertContextInjected(); return (T) applicationContext.getBean(name); } /** * 从静态变量applicationContext中取得Bean, 自动转型为所赋值对象的类型. */ public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) { assertContextInjected(); return applicationContext.getBean(requiredType); } /** * 清除SpringContextHolder中的ApplicationContext为Null. */ public static void clearHolder() { applicationContext = null; } /** * 实现ApplicationContextAware接口, 注入Context到静态变量中. */ @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext appContext) { applicationContext = appContext; } /** * 实现DisposableBean接口, 在Context关闭时清理静态变量. */ @Override public void destroy() throws Exception { SpringContextHolder.clearHolder(); } /** * 检查ApplicationContext不为空. */ private static void assertContextInjected() { Validate.validState(applicationContext != null, "applicaitonContext属性未注入, 请在applicationContext.xml中定义SpringContextHolder."); } }
4.测试
Redis 发布/订阅
特点
发布/订阅是一种消息通信模式,其中发送者(发布者)发布消息,多个接收者(订阅者)订阅并接收这些消息。发布者和订阅者之间没有直接联系,消息由消息中间件(如 Redis)传递。
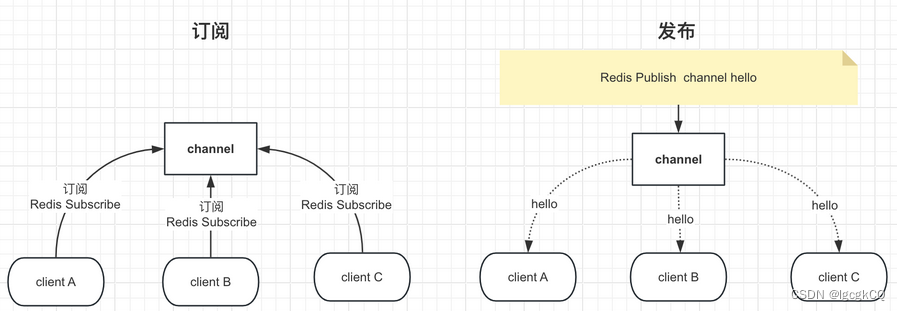
优点
高性能:Redis 作为内存存储,具备极高的读写性能,能够快速处理发布和订阅消息
简单易用:Redis 的发布/订阅接口简单,易于集成和使用
实时性强:发布的消息会立即传递给所有订阅者,具备高实时性
缺点
消息丢失:由于 Redis 是内存存储,如果 Redis 实例宕机,未处理的消息可能会丢失
无法持久化:Redis 的发布/订阅模式不支持消息持久化,无法存储和检索历史消息
订阅者不可控:发布者无法控制订阅者的数量和状态,无法保证所有订阅者都能接收到消息
无确认机制:发布者无法确认消息是否被订阅者接收和处理
Redis 的发布订阅功能并不可靠,如果我们需要保证消息的可靠性、包括确认、重试等要求,我们还是要选择MQ实现发布订阅
运用场景
对于消息处理可靠性要求不强
消息无需持久化
消费能力无需通过增加消费方进行增强
架构简单 中小型系统不希望应用过多中间件
发布订阅命令
SpringBoot整合
1.添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.配置redis
application.yml
spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
3.创建redis配置类
public void sendMsg(String key,Object msg){ redisTemplate.convertAndSend(key,msg); }
注意:
当发布消息时,订阅着输出消息,可能会出现乱码情况:
设置实例化对象
@Bean public RedisTemplate redisTemplateInit() { //设置序列化Key的实例化对象 redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()); //设置序列化Value的实例化对象 redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()); return redisTemplate; }
4.创建消息监听器
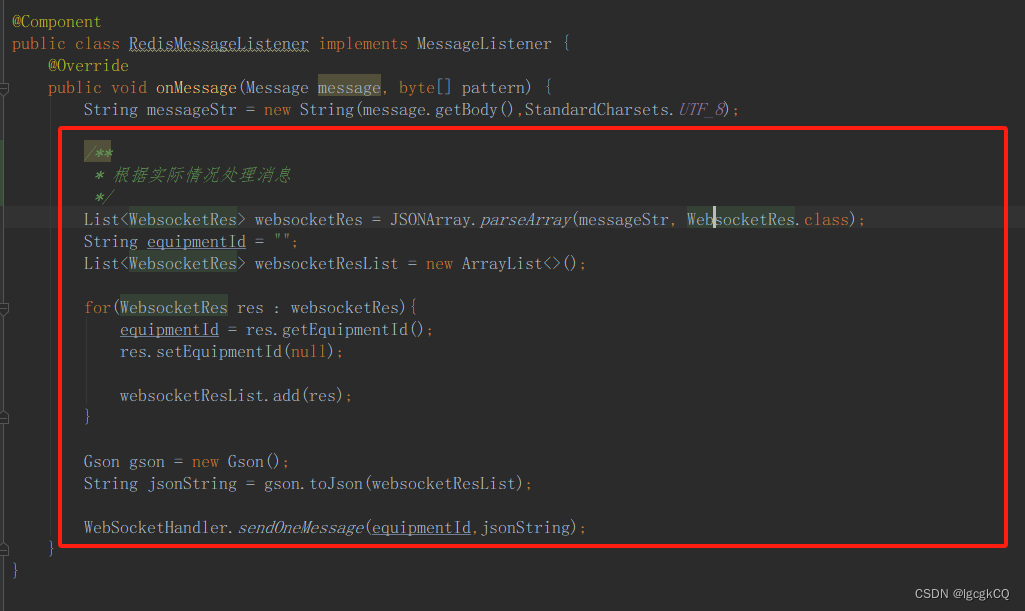
@Component public class RedisMessageListener implements MessageListener { @Override public void onMessage(Message message, byte[] pattern) { String messageStr = new String(message.getBody(),StandardCharsets.UTF_8); /** * 根据实际情况处理消息 */ List<WebsocketRes> websocketRes = JSONArray.parseArray(messageStr, WebsocketRes.class); String equipmentId = ""; List<WebsocketRes> websocketResList = new ArrayList<>(); for(WebsocketRes res : websocketRes){ equipmentId = res.getEquipmentId(); res.setEquipmentId(null); websocketResList.add(res); } Gson gson = new Gson(); String jsonString = gson.toJson(websocketResList); WebSocketHandler.sendOneMessage(equipmentId,jsonString); } }
5.配置消息监听容器
@Configuration public class RedisConfig { @Autowired private RedisMessageListener redisMessageListener; @Bean RedisMessageListenerContainer container(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory, MessageListenerAdapter listenerAdapter) { RedisMessageListenerContainer container = new RedisMessageListenerContainer(); container.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory); // 订阅一个或多个频道 container.addMessageListener(listenerAdapter, new PatternTopic("my-topic")); return container; } @Bean MessageListenerAdapter listenerAdapter(RedisMessageListener redisMessageListener) { return new MessageListenerAdapter(redisMessageListener); } }
6.发布消息
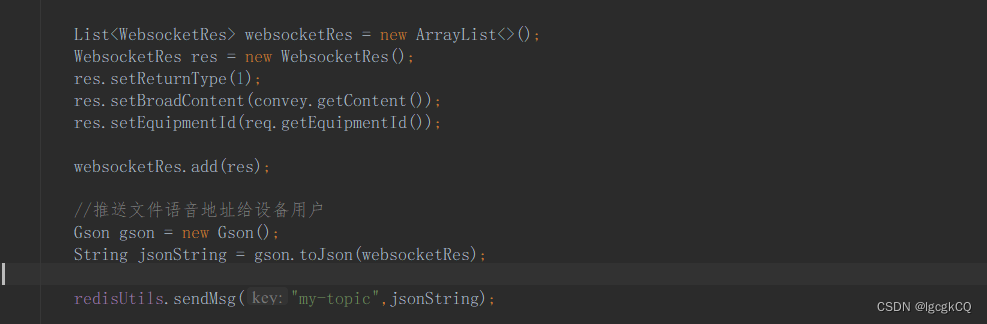
redisUtils.sendMsg("my-topic",jsonString);
websocket与发布/订阅结合
并发过高时,websocket连接需单独部署,减缓压力;websocket将业务信息实时推送给前端,就用到了redis 发布订阅功能。
使用
socket消息推送时,把信息发布到redis中。socket服务订阅redis的消息,订阅成功后进行推送
1.在websocket服务中创建消息监听器(处理消息)
2.在websocket服务中创建消息监听容器
3.在业务服务中发布消息