HTTP服务
本小节主要讲解HTTP服务如何创建服务,查看HTTP请求&响应报文,还有注意事项说明,另外讲解本地环境&Node环境&浏览器之间的链路图示,如何提取HTTP报文字符串,及报错信息查询。
创建HTTP服务端
const http = require('http');
const server = http.createServer((request, response) => {
response.end('Hello Http Server');
});
server.listen(9000, () => {
console.log('服务已启动');
});浏览器输入http://127.0.0.1:9000/,可以看到node服务终端窗口打印日志:服务已启动。
查看报文
打开Fiddler,可以看到浏览器发送的请求报文和响应报文。
请求报文:
GET http://127.0.0.1:9000/favicon.ico HTTP/1.1
Host: 127.0.0.1:9000
Connection: keep-alive
sec-ch-ua: "Not/A)Brand";v="8", "Chromium";v="126", "Google Chrome";v="126"
sec-ch-ua-mobile: ?0
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/126.0.0.0 Safari/537.36
sec-ch-ua-platform: "Windows"
Accept: image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,image/svg+xml,image/*,*/*;q=0.8
Sec-Fetch-Site: same-origin
Sec-Fetch-Mode: no-cors
Sec-Fetch-Dest: image
Referer: http://127.0.0.1:9000/
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br, zstd
Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.9
(空格)响应报文:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Fri, 28 Jun 2024 06:07:06 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
Keep-Alive: timeout=5
Content-Length: 17
Hello Http Server链路
本地环境 Node服务器 浏览器 const http = require('http') createServer((req, res) => res.end('Hello Http Server')) listen(9000, () => console.log('服务已启动')) GET / HTTP/1.1 HTTP/1.1 200 OK Hello Http Server 本地环境 Node服务器 浏览器
- 引入http模块:
const http = require('http');这行代码引入了Node.js的内置http模块,该模块提供了创建HTTP服务器的功能。 - 创建服务器:
http.createServer()方法用于创建一个HTTP服务器。它接受一个回调函数作为参数,该回调函数会在每次有请求到达服务器时被调用。回调函数有两个参数:request和response,分别代表请求对象和响应对象。 - 处理请求和响应:在这个例子中,当服务器接收到任何请求时,都会执行回调函数
(request, response) => { response.end('Hello Http Server'); }。这意味着无论你向服务器发送什么请求,它都会简单地结束响应,并向客户端发送字符串'Hello Http Server'作为响应体。 - 监听端口:
server.listen(9000, () => { console.log('服务已启动'); });这段代码让服务器开始监听9000端口。一旦服务器成功启动并开始监听指定端口,就会在控制台打印出 '服务已启动' 。这意味着你的HTTP服务器现在正在监听本机的9000端口,等待接收HTTP请求。 - 浏览器访问:通过在浏览器中输入
http://localhost:9000来访问这个本地运行的Node.js服务器。浏览器会发送一个HTTP请求到这个地址,你的服务器会接收到这个请求,并返回'Hello Http Server'的消息,这将在浏览器窗口中显示出来。
停止HTTP服务
当前命令行(终端)ctrl+C
更新HTTP服务
停止服务后,重新执行node脚本。(暂时)
注意事项
乱码
response不能返回中文,否则出现乱码,后续通过字符集处理。
const server = http.createServer((request, response) => {
response.set('content-type', 'text/html;charset-utf-8');
response.end('你好');
});端口占用
Error: listen EADDRINUSE: address already in use :::9000结束端口
- cmd
netstat -aon|findstr "8080" - 复制返回当前端口的
pid进程号,比如是16712 - taskkill /pid 是16712 /f
- 终端打印
成功:已终止PID为16712的进程
更改端口
server.listen(9001, () => {
console.log('服务已启动');
});默认端口
HTTP协议80是默认的端口,HTTP服务常用端口有3000,8080,9000。80端口的好处是简化访问过程,用户在浏览器中输入网址时无需指定端口号,因为浏览器默认使用80端口进行HTTP请求。还可以减少配置需求,无需额外配置端口映射或转发等。
请求行 & 请求头
const http = require('http');
const server = http.createServer((request, response) => {
// 获取请求方法
console.log(request.method);
// 获取请求的url
console.log(request.url);
// 获取请求的版本号
console.log(request.httpVersion);
// 获取Http的请求头
console.log(request.headers);
response.end('Hello Http Server');
});
server.listen(9000, () => {
console.log('服务已启动');
});响应行
const http = require('http');
const server = http.createServer((request, response) => {
// 1. 申明
let body = '';
// 2. 绑定事件
// 2.1 request本身就是可读流对象
// 2.2 当请求体的数据到来时,会触发'data'事件。这里通过监听这个事件,将接收到的数据块chunk(Buffer类型)拼接到body字符串上。这是因为HTTP请求体可能分多个数据包到达,'data'事件可能触发多次,每次传递一部分数据。
request.on('data', chunk => {
body += chunk;
});
// 3. 绑定end
request.on('end', () => {
console.log('body', body);
})
response.end('Hello Http Server');
});
// 使用listen方法指定服务器监听的端口号(本例中为9000)
server.listen(9000, () => {
console.log('服务已启动');
});由于get请求body中是不带信息的,所以新建html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="http://127.0.0.1:9000" method="post">
<input type="text" name="username">
<input type="text" name="password">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
点击提交,控制台输出:
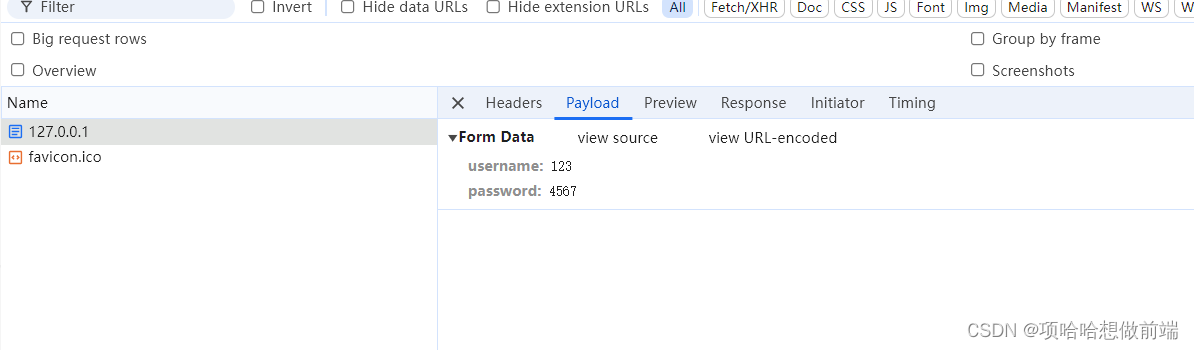
终端打印:

提取 http 报文字符串
url.parse 提取
const http = require('http');
const url = require('url');
const server = http.createServer((request, response) => {
// 解析request.url
// console.log('request', request.url);
let res = url.parse(request.url, true);
console.log('res', res);
// 路径
let pathName = res.pathName;
// 查询字符串
let keyword = res.query.keyword;
response.end('Hello Http Server');
});
server.listen(9000, () => {
console.log('服务已启动');
});new URL 构造函数提取
const http = require('http');
const server = http.createServer((request, response) => {
let url = new URL(request.url, 'https://www.baidu.com');
console.log('url', url);
// 输出路径
console.log('pathName', url.pathname);
// 取出传参 这里以keyword为例
console.log(url.searchParams.get('keyword'))
response.end('Hello Http Server');
});
server.listen(9000, () => {
console.log('服务已启动');
});new URL(input[, base])
new URL(input[, base]) 是一个 JavaScript 构造函数,用于从给定的输入字符串(input)创建一个新的 URL 对象。这个函数允许你以一种标准化的方式解析和操作网址。
- input:这个参数是一个字符串,代表想要解析成URL对象的地址信息,它可以是绝对地址(如https://www.baidu.com/serach?keyword=1),也可以是相对网址(如`path/to/page?keyword=1`),如果提供的是相对地址,那么解析时就需要用到`base`参数。
- base(可选参数):基准URL,当
input是一个相对网址时,例如,如果base是https://www.example.com/,并且input是path/to/page,那么最终解析得到的完整URL就会是https://www.example.com/path/to/page。如果input是一个绝对网址,那么base参数将被忽略,即使提供了也不会影响结果。
建议使用new URL,因为url.parse在Node.js v22.3.0版本被弃用了。
常见报错信息:
| 错误代码 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ERR_INVALID_PROTOCOL | 表示提供的URL协议部分无效或不受支持。 |
| ERR_UNKNOWN_URL_SCHEME | 遇到了未知的URL方案(协议),即URL的开头部分没有被识别 |
| ERR_INVALID_CHAR | URL中包含了无效的字符 |
| ERR_FILE_NOT_FOUND | 尝试访问的文件不存在(在涉及文件系统操作时) |
| ERR_HTTP2_PROTOCOL_ERROR | HTTP/2协议层面的错误 |
| ERR_TLS_CERT_ALTNAME_INVALID | TLS证书的备用名称不匹配或无效 |
| ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR | SSL/TLS握手过程中发生协议错误。 |
| ERR_SOCKET_CLOSED | 套接字意外关闭,可能是因为网络问题或远程端点主动关闭连接 |
| ERR_CONNECTION_REFUSED | 连接被目标主机拒绝,通常是由于目标端口无服务监听 |
| ERR_CONNECTION_TIMED_OUT | 连接尝试超时,没有在预定时间内收到响应 |
| ERR_ABORTED | 请求被用户或程序主动中断 |