模拟准备
避免和库冲突,自己定义一个命名空间
cpp
namespace yx
{
template<class T>
struct ListNode
{
ListNode<T>* _next;
ListNode<T>* _prev;
T _data;
};
template<class T>
class list
{
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
public:
private:
Node* _head;
};
}这里的ListNode类为什么用struct呢?
知识点:
class:如果类里有公有,有私有,建议用
struct:如果一个类,全部成员不做访问限定,全公有,建议用
因为下面的list类是要经常访问ListNode的,所以建议用struct
模拟实现
模板ListNode的构造
封装节点的数据
cpp
template<class T>
struct ListNode
{
ListNode<T>* _next;
ListNode<T>* _prev;
T _data;
ListNode(const T& data)
:_next(nullptr)
, _prev(nullptr)
,_data(data)
{
}
};list的构造
cpp
void list()
{
//哨兵位
_head = new Node;
_head->next = _head;
_head->prev = _head;
}定义一个哨兵位,自己指向自己。
push_back( )
尾插

cpp
void push_back(const T& x)
{
Node* newnode = new Node(x);
Node* tail == _head->prev;
tail->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev - tail;
newnode->_next = _head;
}最后一个节点就是头节点的前一个
如果是一个空链表呢?满足条件么?
是可以的,这时候_head 和 tail都是哨兵位(head)
迭代器
说起迭代器,我们先考虑如何遍历链表吧。
我们是否可以像vector那样呢?
cpp
typedef Node* iterator;当然是不可以的。
vector的空间是连续的,而list的空间不连续,那我们如何获取Node*呢?
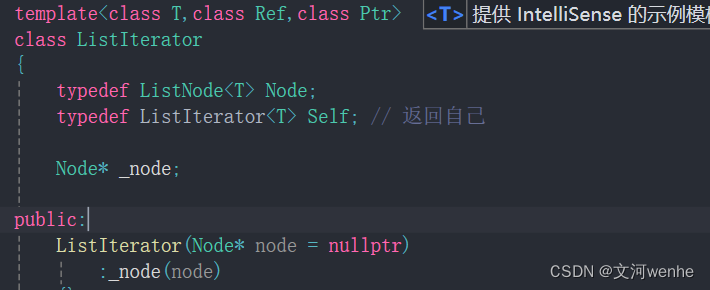
定义迭代器类
我们可以定义一个类,把节点_node封装起来,来弥补空间不连续的缺陷,能像vector那样一样来进行访问。
cpp
template<class T>
class ListIterator
{
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
Node* _node;
};template定义的模板参数只能供当前类或当前函数用
而且我们可以在这个类里重载想要的东西
使用时,我们就可以给每个类规范这个迭代器使用的名字,方便我们使用
cpp
typedef ListIterator<T> iterator;
cpp
template<class T>
class ListIterator
{
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef ListIterator<T> self; // 返回自己
Node* _node;
self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;//返回节点自己
}
T& operator*()
{
return _node->_data;//返回数据,数据类型为T
}
bool operator!=(const self& it)
{
return _node != it._node;
}
};iterator begin( ) 、 iterator end( )
我们实现了迭代器,我们来实现一下链表的头指针和尾指针吧
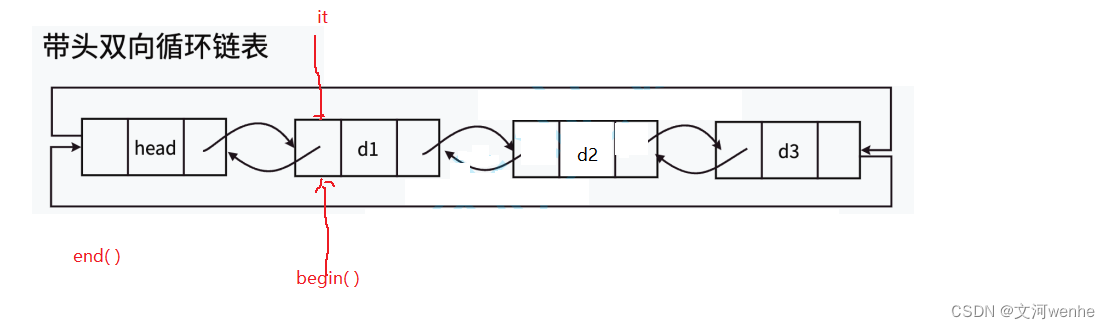
在list类里
cpp
iterator begin()
{
//iterator it(_head->_next);
//return it;
//我们采用匿名对象
return iterator(_head->_next);
}
cpp
iterator end()
{
return iterator(_head;
}测试通过
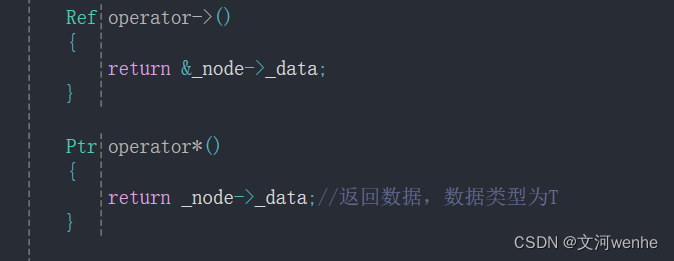
operator->( )
cpp
T* operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}我们来测试一下下面的代码
cpp
struct pos
{
int _row;
int _col;
pos(int row = 0, int col = 0)
:_row(row)
, _col(col)
{
}
};
void test2()
{
list<pos> lt1;
lt1.push_back(pos(100, 100));
lt1.push_back(pos(200, 100));
lt1.push_back(pos(300, 100));
list<pos>::iterator it = lt1.begin();
while (it != lt1.end())
{
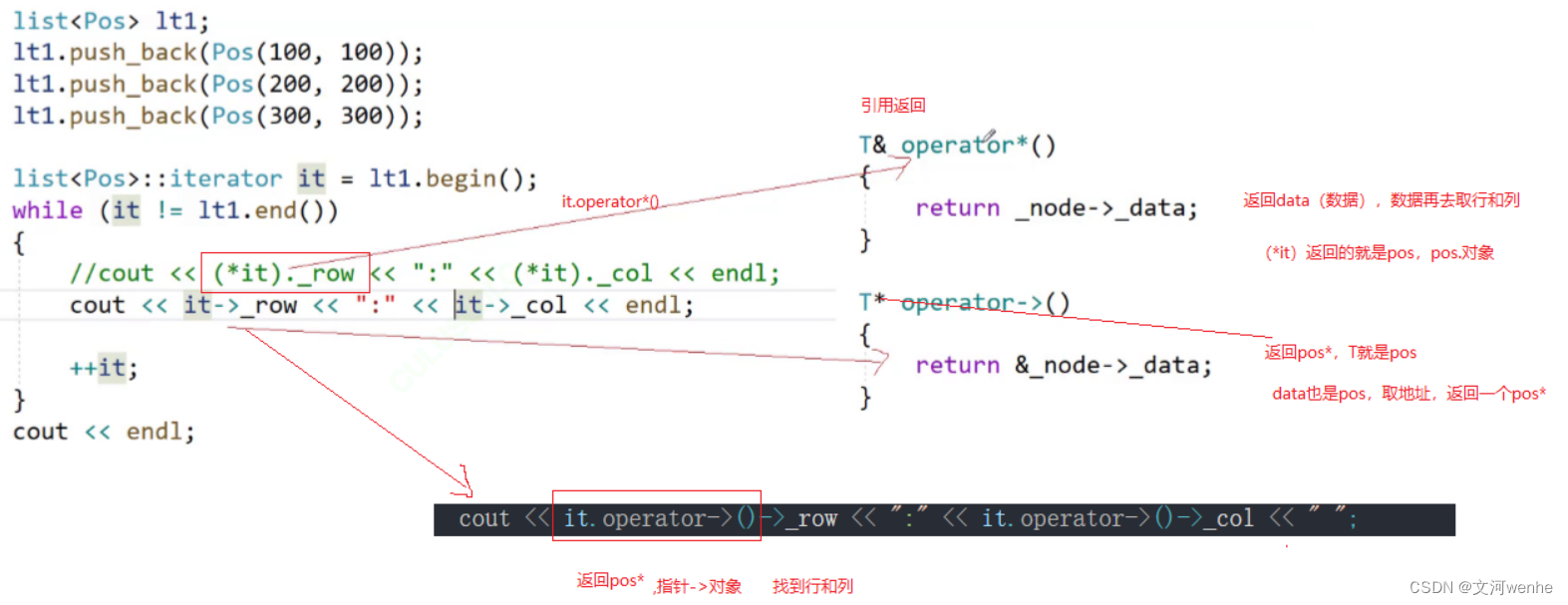
cout << (*it)._row << ":" << (*it)._col << " ";
cout << it->_row << ":" << it->_col << " ";
++it;
}cout << endl;
}第一种用的是对象.成员
第二种指针->成员
第一种比较好理解,it调用operator*(),返回data数据,也就是pos,然后pos._row,pos._col来访问
第二种比较绕,这里为了可读性,省略可一个->,但如果写两个的话不符合语法,于是
cpp
cout << it.operator->()->_row << ":" << it.operator->()->_col << " ";第一个->是operator重载的,而第二个是原生指针的解引用
const迭代器
不能是普通迭代器前面+const修饰。
如:const iterator const
const迭代器目标本身可以修改,指向的内容不能修改 ,
类似:const T* p
p可以修改,*p不能修改
因为T* 和 T&,这里我们可以写一个和迭代器一样的const迭代器类,但我们也可以类模板,传不同的参数,形成不同的类,让编译器帮我们实现。避免了写连个差不多重复的类,减少代码量
insert( )
cpp
//在pos前插入val
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val)
{
Node* pNewNode = new Node(val);
Node* pCur = pos._node;
pNewNode->_prev = pCur->_prev;
pNewNode->_next = pCur;
pNewNode->_prev->_next = pNewNode;
pCur->_prev = pNewNode;
return iterator(pNewNode);
}erase( )
cpp
//删除pos节点
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
Node* pDel = pos._node;
Node* pRet = pDel->_next;
pDel->_prev->_next = pDel->_next;
pDel->_next->_prev = pDel->_prev;
delete pDel;
return iterator(pRet);
}clear()
cpp
void clear()
{
Node* cur = _head->_next;
while (cur != _head)
{
//从头开始删(从左向右)
_head->_next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = _head->_next;
}
_head->_next = _head->_prev = _head;
}~list()
cpp
~list()
{
clear();
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}