1.list
-
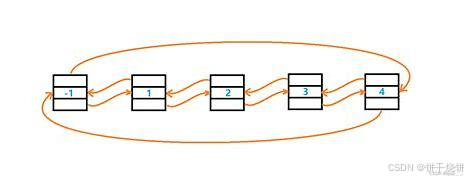
list是可以在常数范围 内在任意位置进行插入和删除 的序列式容器 ,并且该容器可以前后双向迭代 。
-
list的底层是双向链表结构 ,双向链表中每个元素存储在互不相关的独立节点中,在节点中通过指针指向其前一个元素和后一个元素。
-
list与forward_list非常相似:最主要的不同在于forward_list是单链表 ,只能朝前迭代,已让其更简单高效。
-
与其他的序列式容器相比(array,vector,deque),list通常在任意位置进行插入、移除元素的执行效率更好 。
-
与其他序列式容器相比,list和forward_list最大的缺陷是不支持任意位置的随机访问,比如:要访问list的第6个元素,必须从已知的位置(比如头部或者尾部)迭代到该位置,在这段位置上迭代需要线性的时间开销;list还需要一些额外的空间,以保存每个节点的相关联信息(对于存储类型较小元素的大list来说这可能是一个重要的因素)
2.list的使用
2.1 构造函数
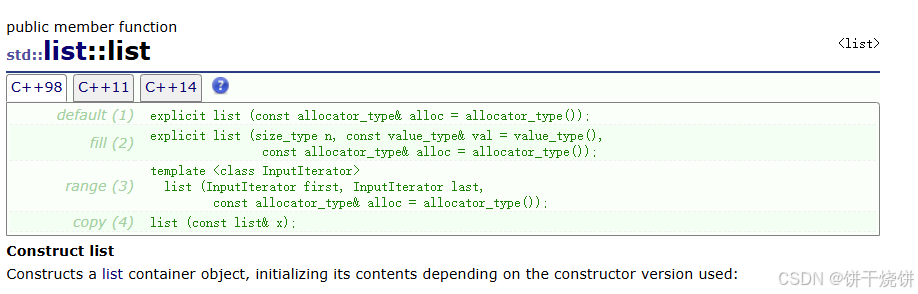
cpp
void test1()
{
//无参构造
list<int> l1;
//有参构造
list<int> l2(10, 1);//10个1
list<int> l3(10);
//使用迭代器范围构造
list<int> l4(l2.begin(), l2.end());//双向迭代器不支持加减法
vector<int> v = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
list<int> l5(v.begin() + 2, v.end());
//拷贝构造
list<int> l6(l5);
//使用initializer_list初始化
list<int> l7 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 };
}2.2operator=()
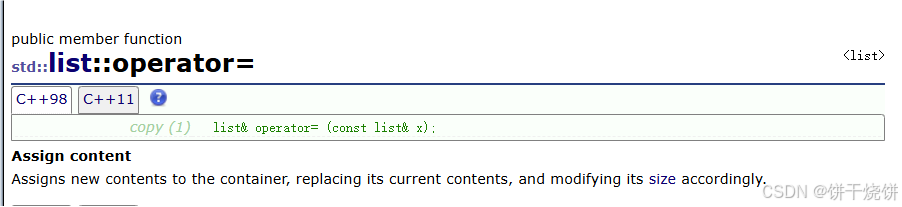
赋值运算符重载,进行深拷贝
cpp
//int类型
void PrintList(const list<int>& l)
{
for (auto e : l)
{
cout << e << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
void test2()
{
//operator=
list<int> l1 = { 1,2,3 };
list<int> l2;
//深拷贝
l2 = l1;
PrintList(l1);
PrintList(l2);
}2.3begin() 和 end()
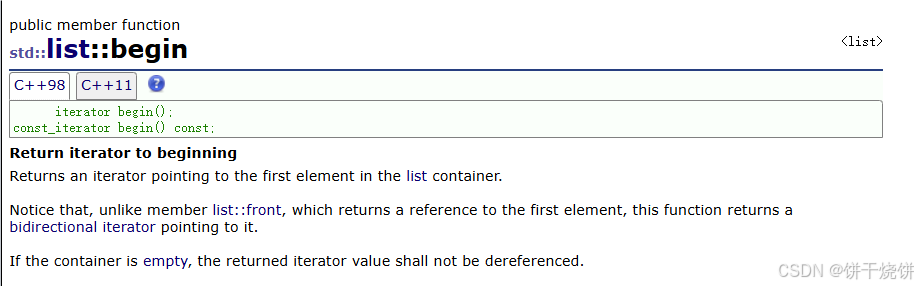
 begin():返回第一个元素的双向迭代器,如果容器为空,则返回的迭代器值不能被解引用。
begin():返回第一个元素的双向迭代器,如果容器为空,则返回的迭代器值不能被解引用。
end():返回最后一个元素的下一位双向迭代器,如果容器为空,返回的迭代器与begin()返回的迭代器相同。
双向迭代器不支持加减法,支持 ++ 、 -- 、 * 、 == 、 != 、= 等操作。
cpp
void test3()
{
//begin() and end()
list<int> l = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 };
list<int>::iterator it = l.begin();//返回双向迭代器
while (it != l.end())
{
cout << *(it++) << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}2.4 rbegin() 和 rend()
 rbegin():返回最后一个元素的反向双向迭代器
rbegin():返回最后一个元素的反向双向迭代器
rend():返回第一个元素前一位的反向双向迭代器
使用++是向前迭代,--是向后迭代
cpp
void test4()
{
list<int>l = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 };
list<int>::reverse_iterator it = l.rbegin();
while (it != l.rend())
{
cout << *(it++) << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}2.5 cbegin()、cend()、crbegin()、 crend()
 无论调用对象是否const修饰,这四个函数返回const迭代器,不能通过迭代器修改指向内容,但迭代器本身可以改变。
无论调用对象是否const修饰,这四个函数返回const迭代器,不能通过迭代器修改指向内容,但迭代器本身可以改变。
2.6 empty()
 判断容器是否为空,空返回true,非空返回false
判断容器是否为空,空返回true,非空返回false
cpp
void test5()
{
list<int>l = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 };
while (!l.empty())
{
cout << l.front() << ' ';
l.pop_front();
}
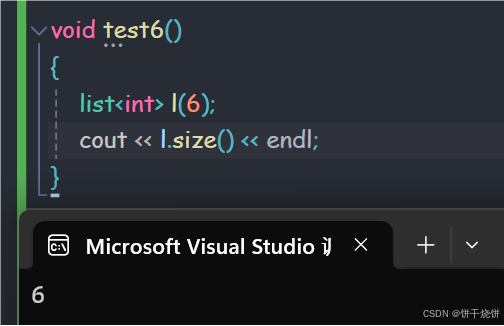
}2.7 size()
用于返回有效元素个数
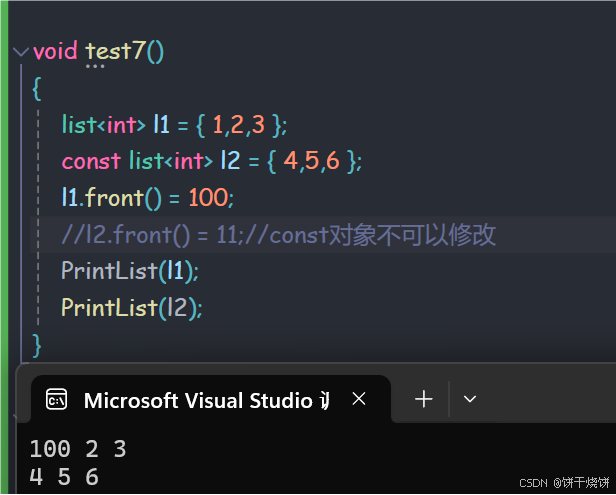
2.8 front()
返回容器第一个元素的引用,对空容器使用front是未定义行为
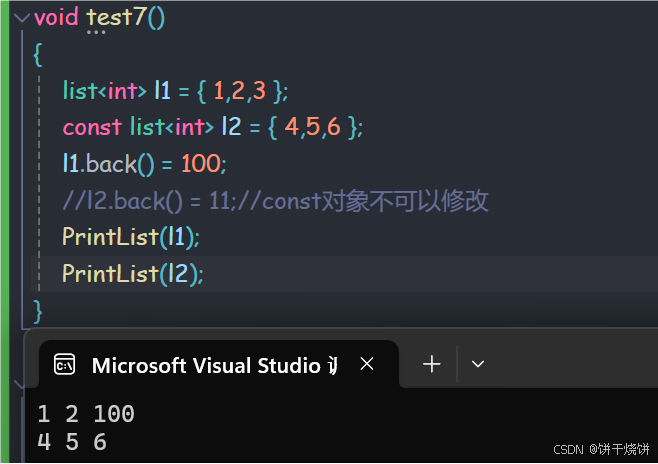
2.9 back()
返回容器最后一位元素的引用,对空容器使用back是未定义行为
2.10 assign()
将新内容替换原本的全部内容
cpp
void test8()
{
//assign
list<int> l1 = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
list<int> l2 = { 11,22 };
vector<int> v = { 121,23,43,54,54,5,454 };
//范围替换
l1.assign(v.begin(), v.begin() + 3);
l2.assign(l1.begin(), l1.end());
PrintList(l1);
PrintList(l2);
//n个val替换
l1.assign(10, 2);
l2.assign(2, 0);
PrintList(l1);
PrintList(l2);
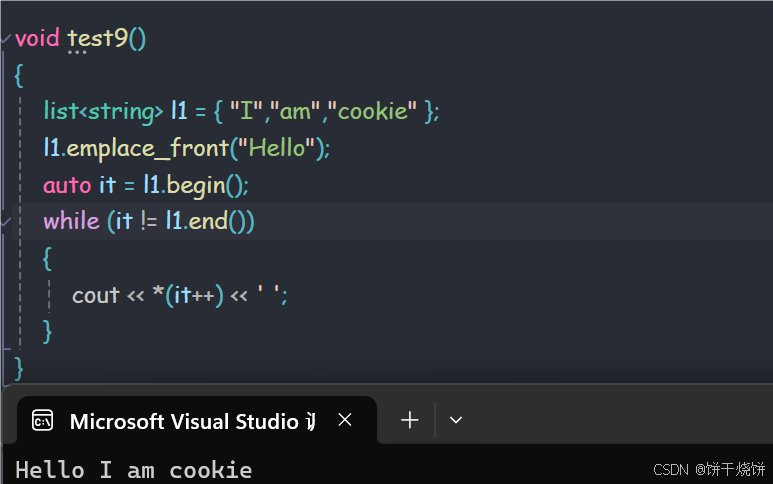
}2.11 emplace_front
在开头构造并插入元素
在列表的开头插入一个新元素,就在它当前的第一个元素之前。这个新元素是使用args作为其构造的参数来就地构造的 。
这有效地将容器大小增加了1。
该元素是通过调用allocator_traits::construct来就地构造 的,并将参数转发。
存在一个类似的成员函数push_front,它复制或移动一个现有对象到容器中。
cpp
class A
{
public:
A(int a, int b)
:_a(a), _b(b)
{
cout << "构造" << endl;
}
A(const A& a)
{
cout << "拷贝构造" << endl;
}
void Print()
{
cout << _a << ' ' << _b << endl;
}
private:
int _a;
int _b;
};
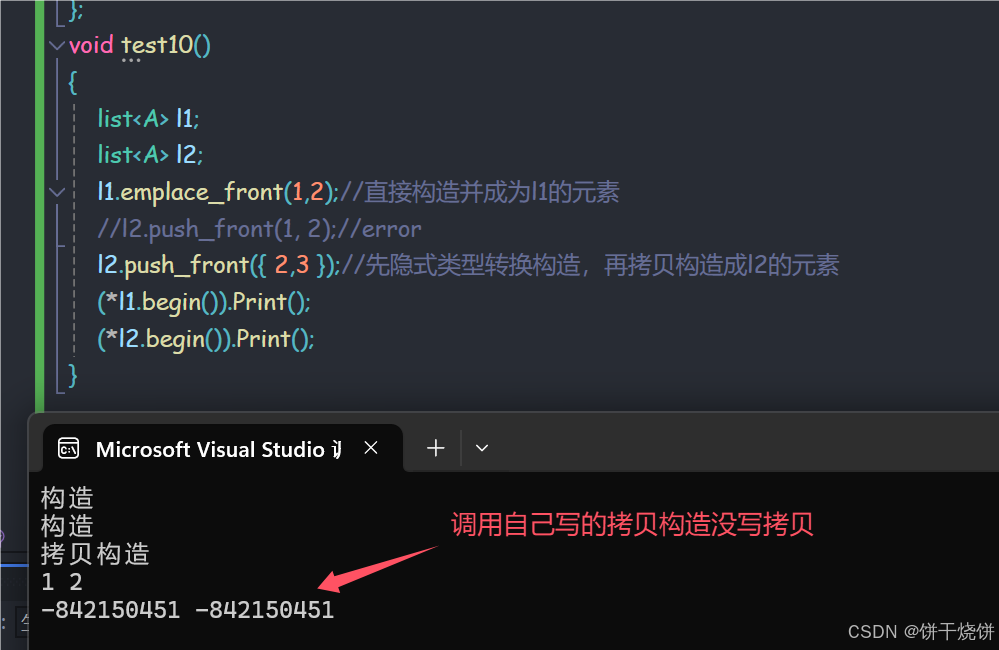
void test10()
{
list<A> l1;
list<A> l2;
l1.emplace_front(1,2);//直接构造并成为l1的元素
//l2.push_front(1, 2);//error
l2.push_front({ 2,3 });//先隐式类型转换构造,再拷贝构造成l2的元素
(*l1.begin()).Print();
(*l2.begin()).Print();
}
2.12 push_front()
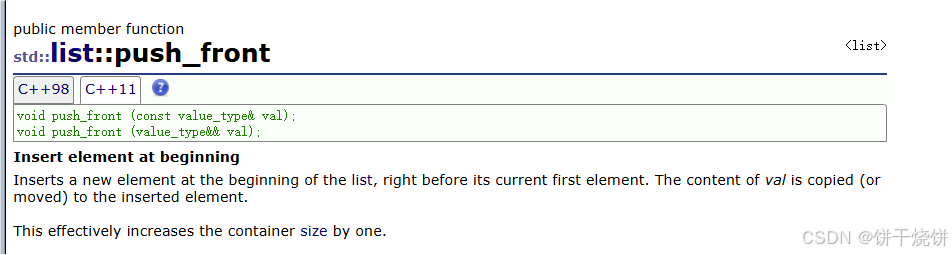
在容器第一个元素前插入一个元素, val的内容被拷贝(或移动)到插入的元素。
push_back()执行拷贝行为还是移动行为取决于传递给它的参数类型,传递左值触发拷贝构造函数 执行拷贝行为 ,传递右值触发移动构造函数 执行移动操作 。
(在 C++ 中,左值 (lvalue)和 右值 (rvalue)是用来区分表达式的值在内存中的存在方式和生命周期的术语。)
移动构造函数是 C++11 引入的一种特殊构造函数,旨在高效地转移资源的所有权,而不是进行昂贵的复制。它通过移动语义来减少不必要的拷贝,提高程序性能。
移动构造函数通常在以下情况下被调用:
- 对象临时生命周期结束后:当你通过一个临时对象(右值)初始化另一个对象时,移动构造函数会被调用。
- 使用
std::move:当你显式调用std::move函数将一个对象转换为右值引用时,会触发移动构造函数。

2.13 pop_front()
 用于删除第一个元素
用于删除第一个元素
2.14 emplace_back()

在末尾构造并插入元素
2.15 push_back()
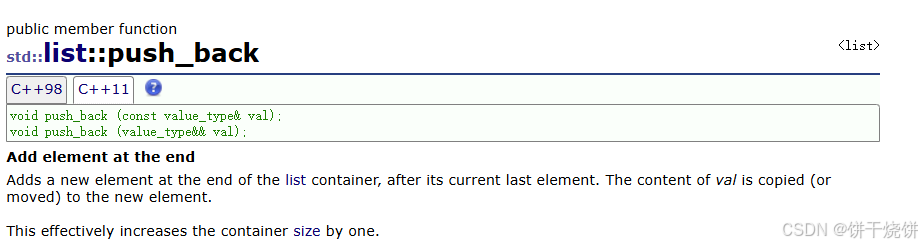
在最后一个元素之后插入一个元素,val的内容被拷贝(或移动)到新元素。
2.16 pop_back()

删除最后一个元素
2.17 emplace()
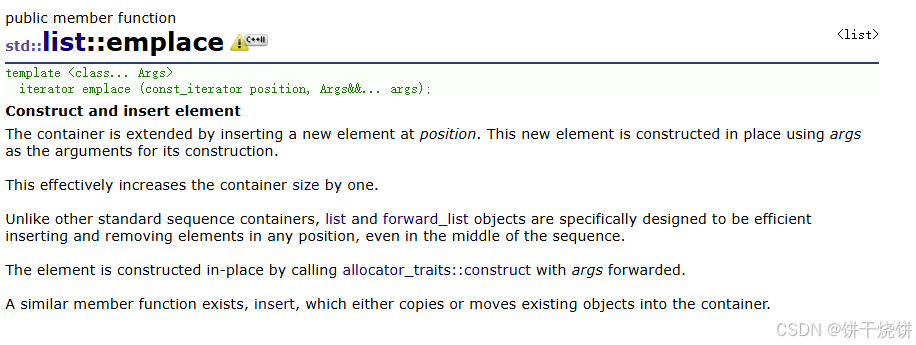
在pos位置的元素之前构造并插入一个元素
2.18 insert()
 在指定位置的元素之前插入新元素(一个或多个)
在指定位置的元素之前插入新元素(一个或多个)
cpp
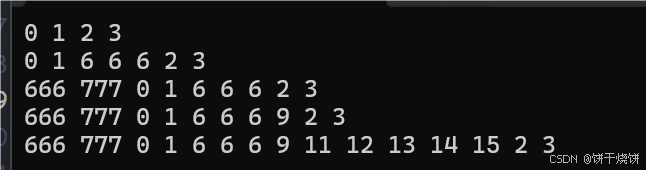
void test13()
{
list<int> l1 = {1,2,3};
vector<int> v = { 444,555,666,777 };
auto it = l1.begin();
//iterator insert (const_iterator position, const value_type& val);
l1.insert(it, 0);
PrintList(l1);
//iterator insert (const_iterator position, size_type n, const value_type& val);
it++;
l1.insert(it, 3, 6);
PrintList(l1);
//template <class InputIterator>
//iterator insert(const_iterator position, InputIterator first, InputIterator last);
l1.insert(l1.begin(), v.begin() + 2, v.end());
PrintList(l1);
//iterator insert (const_iterator position, value_type&& val);//右值引用
l1.insert(it, 9);
PrintList(l1);
//iterator insert(const_iterator position, initializer_list<value_type> il);
l1.insert(it, { 11,12,13,14,15 });
PrintList(l1);
}
2.19 erase()
 从容器中删除一个或者范围内的元素
从容器中删除一个或者范围内的元素
2.20 swap()
交换两个容器的内容
2.21 resize()
调整容器的有效元素的个数,使其包含n个元素
n小于当前个数,元素将减少到前n个,超出部分删除并销毁
n大于当前个数,元素将尾插至n个,如果指定了val,则新元素初始化为val的副本
cpp
class A
{
public:
A()
{
cout << "无参构造" << endl;
}
A(int a, int b)
:_a(a), _b(b)
{
cout << "有参构造" << endl;
}
A(const A& a)
{
cout << "拷贝构造" << endl;
}
void Print()
{
cout << _a << ' ' << _b << endl;
}
private:
int _a;
int _b;
};
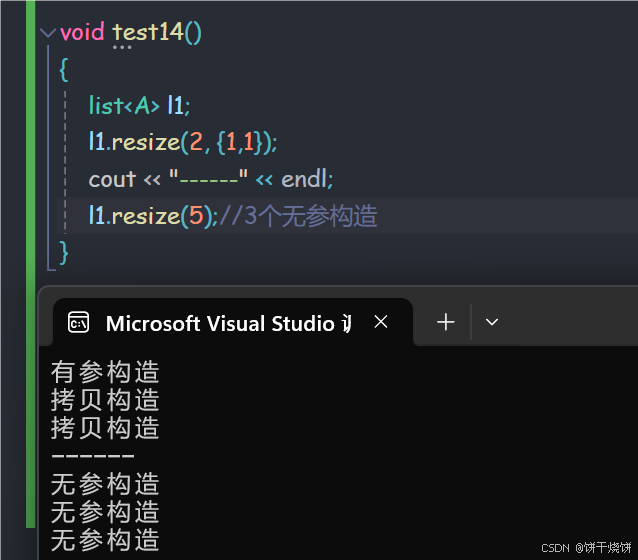
void test14()
{
list<A> l1;
l1.resize(2, {1,1});
cout << "------" << endl;
l1.resize(5);//3个无参构造
}
2.22 clear()
 删除容器的所有内容
删除容器的所有内容
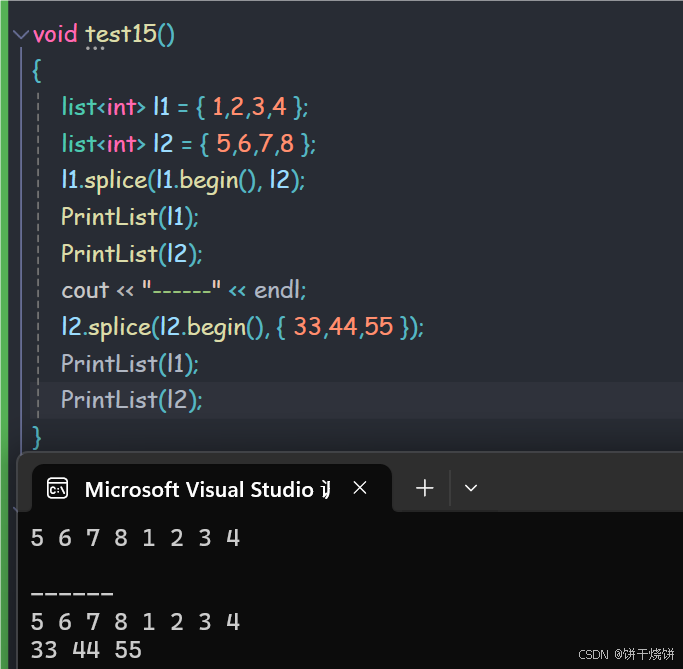
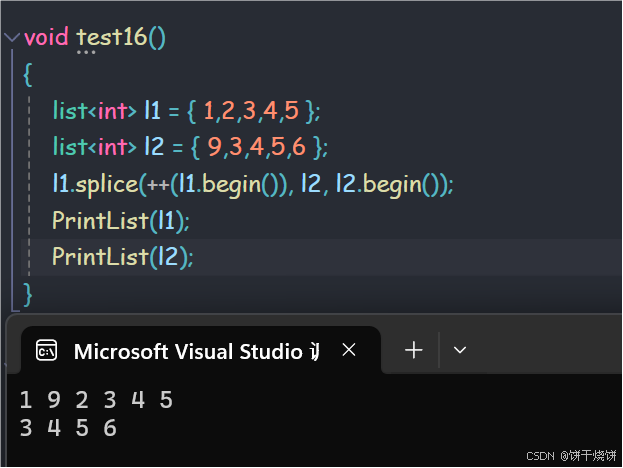
2.23 splice()
 用于将元素从一个list转移到另一个list(转移:将元素从原来的list移除,原封不动转移到另一个list)
用于将元素从一个list转移到另一个list(转移:将元素从原来的list移除,原封不动转移到另一个list)
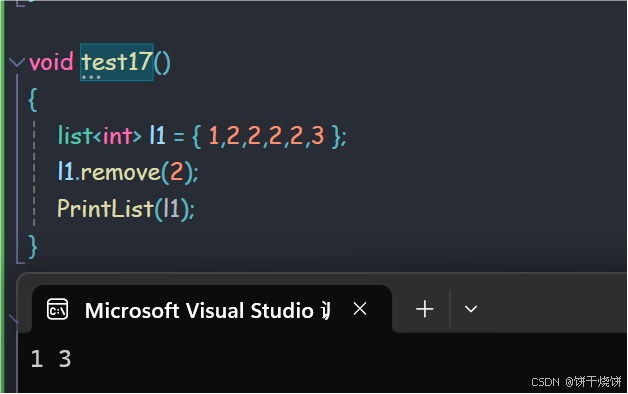
2.24 remove()
 从容器中删除所有与val相同的元素
从容器中删除所有与val相同的元素
2.25 remove_if()

用于从容器中移除满足特定条件 的元素
remove_if()传入一个谓语函数(返回bool值的函数)

2.26 unique()
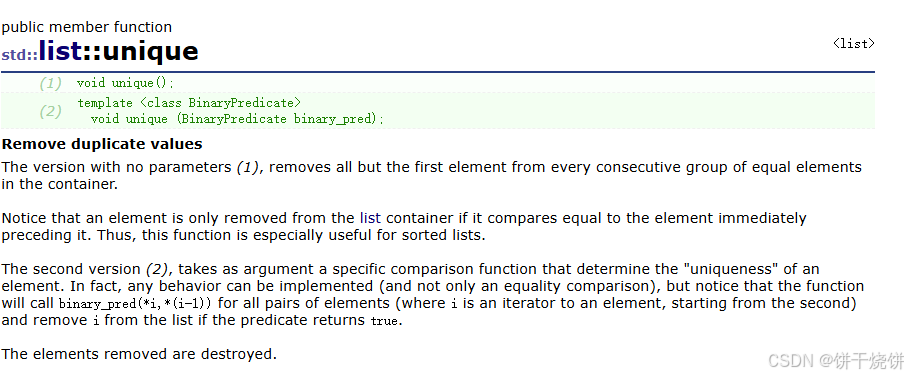
删除相邻val值重复的元素
需要给整个容器去重:先排序,再unique

2.27 merge()
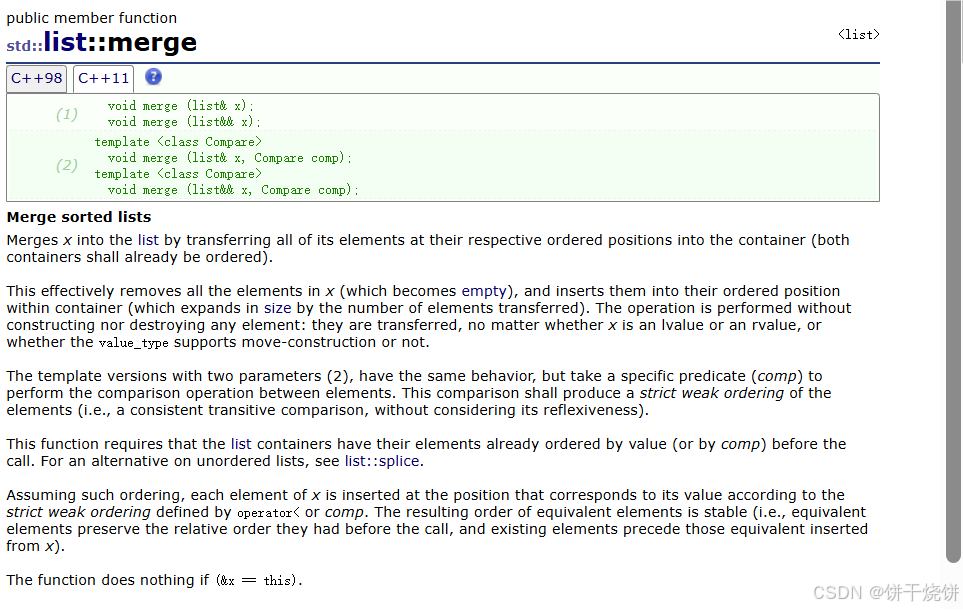
用于将两个已排序 的列表合并成一个排序后 的列表。需要注意的是,两个列表必须都是按顺序排列的。合并操作会通过移动节点来达成,而不需要额外分配内存。
两个列表的排序方式需要与合并成一个列表后的排序方式保持一致(即两个升序列表合并成一个升序列表,两个降序列表合并成一个降序列表)

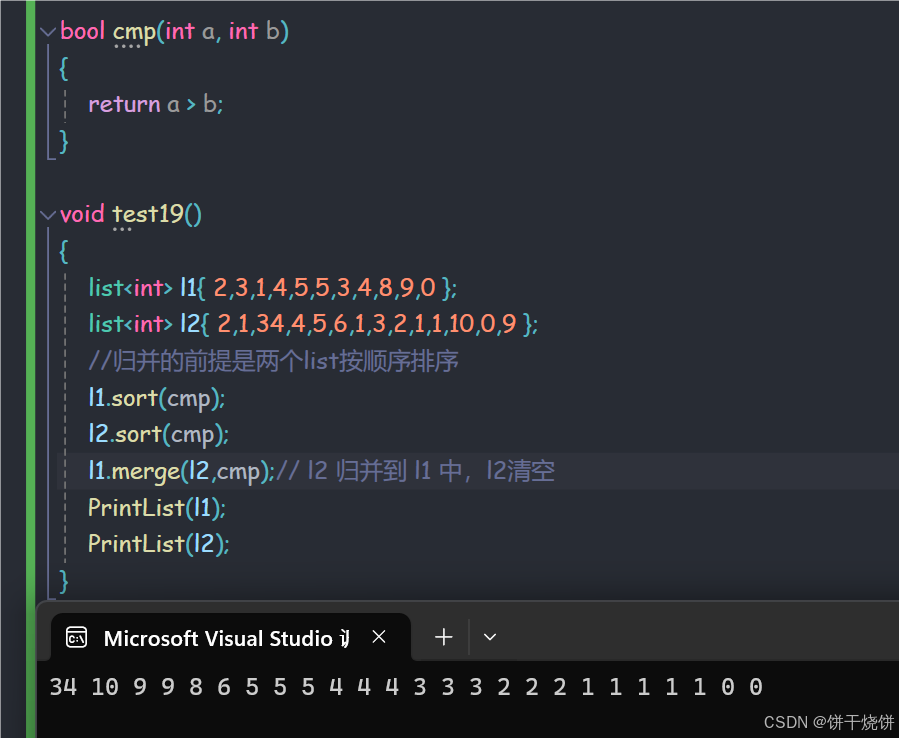
2.28 sort()

sort() 函数会对列表中的元素进行升序排序。默认情况下,它使用元素的 < 运算符进行比较, 也可以提供一个自定义的比较函数。
list的sort()底层是基于归并排序实现的,归并排序在处理链表时的性能非常优越,因为它可以高效地操作节点而不需要额外的空间消耗。归并排序通过分割链表和合并已排序的部分,能够快速地处理链表的节点。

2.29 reverse()
 用于反转list
用于反转list
2.30 关系运算符重载(非成员函数)
3.operator->()
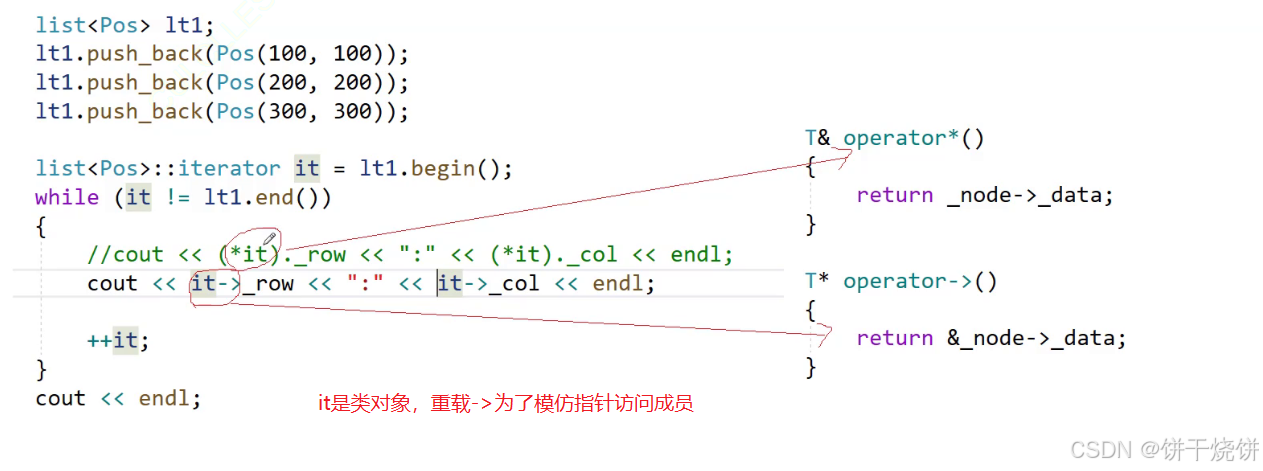
 为了可读性,强制剩下一个->
为了可读性,强制剩下一个->
4. 部分模拟实现
cpp
#pragma once
#include<assert.h>
namespace myList
{
template<class T>
struct ListNode
{
ListNode<T>* _next;
ListNode<T>* _prev;
T _data;
ListNode(const T& data = T())
:_next(nullptr)
,_prev(nullptr)
,_data(data)
{}
};
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct ListIterator
{
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
Node* _node;
ListIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
// ++it;
Self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
Self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)
{
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
Self& operator--(int)
{
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& it)
{
return _node != it._node;
}
bool operator==(const Self& it)
{
return _node == it._node;
}
};
//template<class T>
//class ListConstIterator
//{
// typedef ListNode<T> Node;
// typedef ListConstIterator<T> Self;
// Node* _node;
//public:
// ListConstIterator(Node* node)
// :_node(node)
// {}
// // ++it;
// Self& operator++()
// {
// _node = _node->_next;
// return *this;
// }
// Self& operator--()
// {
// _node = _node->_prev;
// return *this;
// }
// Self operator++(int)
// {
// Self tmp(*this);
// _node = _node->_next;
// return tmp;
// }
// Self& operator--(int)
// {
// Self tmp(*this);
// _node = _node->_prev;
// return tmp;
// }
// //*it
// const T& operator*()
// {
// return _node->_data;
// }
// const T* operator->()
// {
// return &_node->_data;
// }
// bool operator!=(const Self& it)
// {
// return _node != it._node;
// }
// bool operator==(const Self& it)
// {
// return _node == it._node;
// }
//};
template<class T>
class list
{
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
public:
// 不符合迭代器的行为,无法遍历
//typedef Node* iterator;
//typedef ListIterator<T> iterator;
//typedef ListConstIterator<T> const_iterator;
typedef ListIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef ListIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
//iterator it(_head->_next);
//return it;
return iterator(_head->_next);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return const_iterator(_head->_next);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(_head);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(_head);
}
void empty_init()
{
_head = new Node();
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
}
list()
{
empty_init();
}
list(initializer_list<T> il)
{
empty_init();
for (const auto& e : il)
{
push_back(e);
}
}
// lt2(lt1)
list(const list<T>& lt)
{
empty_init();
for (const auto& e : lt)
{
push_back(e);
}
}
// lt1 = lt3
list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt)
{
swap(_head, lt._head);
return *this;
}
~list()
{
clear();
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}
void clear()
{
auto it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
it = erase(it);
}
}
void push_back(const T& x)
{
/*Node* newnode = new Node(x);
Node* tail = _head->_prev;
tail->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = tail;
newnode->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = newnode;*/
insert(end(), x);
}
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());
}
void push_front(const T& x)
{
insert(begin(), x);
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
// 没有iterator失效
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* newnode = new Node(x);
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
// prev newnode cur
prev->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = prev;
newnode->_next = cur;
cur->_prev = newnode;
return iterator(newnode);
}
// erase 后 pos失效了,pos指向节点被释放了
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos != end());
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
Node* next = cur->_next;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
delete cur;
return iterator(next);
}
private:
Node* _head;
};
}
