Intended Learning Outcomes
- To understand abstract type.
- To enforce a design protocol by using abstract classes or interfaces.
- To know the similarities and differences between an abstract class and an
interface. - To become familiar with the process of program development.
- To discover classes using CRC cards.
- To understand the impacts of coupling to a system.
- To learn the relationship types: association, aggregation, composition,
realization and generalization.(UML class diagram) - To understand design principles and guidelines
Interface Syntax
- Similar to a class but contains only constants and abstract methods.
- Using abstract modifier.
java
public interface InterfaceName{
constant declarations;
method signatures;
}
public interface Stack{
public static final int MAX_SIZE=100;
public abstract int pop();
public abstract void push(int e);
}- Interface class is a special class:
- interfaces contain abstract methods which don't define method bodies, you can't create instances from an interface using the new as usual, but you can use an interface to declare a variable.
java
Stack s1;//no instance,only reference var
Stack[] s2=new Stack[10];-
Properties of Interface(these modifiers can be omitted)
- All Data fields: constant--public static final
- All methods:abstract--public abstract
-
Using Interface(relying another class to implement the abstract class)
java
public interface Colorable{
abstract public void color();
}
class Apple implements Colorable{
@override
public void color(){
System.out.println("red");
}
}
class Banana implements Colorable{
@override
public void color(){
System.out.println("Yellow");
}
}The abstract Modifier
- Abstract also can be used in class
- Having both ordinary class and interface.
- Having both abstract and non-abstract method
- Being extended and the subclass override the abstract method from parent class with a concrete method.
- Can't be instantiated.(can't use new operator)(can usr reference variable)
java
public abstract class shape{
protected char drawingchar='*';
public abstract void draw();//abstract method
public char getDrawingChar(){//non-abstract method
return drawingchar;
}
}-
Abstract Class(define)
- an abstract class can contains no abstract methods
- But a class that includes abstract methods must be an abstract class(but not all abstract)
-
Why Abstract Type?
Abstract types are useful that they can be used to define and enforce a
protocol ; a set of operations which all objects that implement the protocolmust support.
Interfaces VS. Abstract Classes
| Abstract Class | Interfaces |
|---|---|
| no restrictions of variables | All variables must be public static final |
| no restrictions of methods | All methods must be public abstract |
| Constructors are invoked by subclasses through constructor chaining. An abstract class cannot be instantiated using the new operator. | No constructors. An interface cannot be instantiated using the new operator. |
| single Inheritance,extend one class only | multiple inheritance more than one interface |
Object-oriented-Design Principles
-
software development process

- Requirement Specification:understand the problem
- System analysis: analyze the business process, capture the essential elements
- System design: decompose the problem, establish relationships
- Implementation: coding,testing,debugging
- Testing:ensure the code meet the requirement
- Deployment: available for use
- Maintainance: provide upgrades of the product to fix newly discovered bugs
-
CRC code
-


-
Coupling
- Association, aggregation, composition, realization and generalization all describe the coupling between two classes.
- The difference is the degree of coupling.
- In general, lower degree of coupling implies higher stability of the system.
- Low coupling is often a desirable system property.

-
Association
- Object of one class is connecte to object of another and there is a channel between them through which message can be sent.
- send message each other
- one change another change too
- the connection relationship is usually implemented using data fields (Strong connection between 2 classes)

-
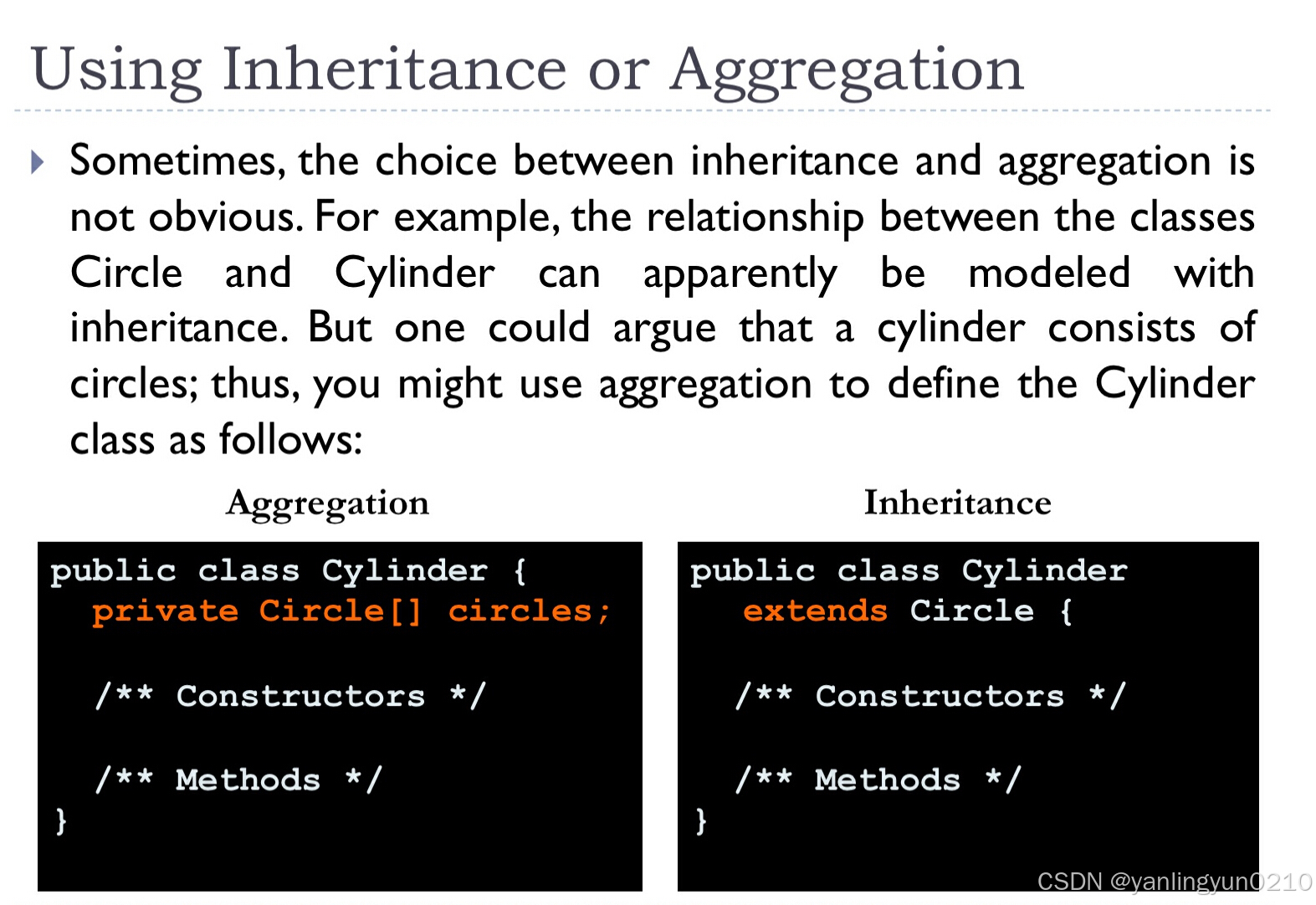
Composition and Aggregation
- they represent a whole-part relationship (between two classes.)
- whole contains part, but part can't contain whole
- Composition stronger than Aggregation(because:adds lifetime responsibility--the part must be created and destroyed with whole together.)
- Usually represented as a data field in the 'owner' class.

-
Inner class
- If Department is used in the University class only,it is usually declared as an inner class of University.(表示这个子类只属于它,其他类中没有该子类)
- There are three types of inner class:
- Member inner class - declared within another class
- Local inner class - declared within the body of a method
- Anonymous inner class - declared within the body of a method without name
example : member inner class.
java
public class University {
private Department[] depts;
...
private class Department {
...
}
}-
Generalization (Extend relationship)
- models the inheritance relationship(between 2 classes)
- Generalized class(superclass)
- Specialized class(subclass)

-
Realization
- Represents the is-a-kind-of relationship(Implementation of interface)

- Represents the is-a-kind-of relationship(Implementation of interface)
Class design in 4 steps
- Identify classes for the system.
Ordinary classes, abstract classes, interfaces - Describe attributes and methods in each class.
Using Modifiers public, protected, private and static - Establish relationships among classes.
Association, generalization,realization, ... etc. - Create classes.