接上篇React渲染机制和源码初探(一)_react19 19.0.0-rc.0-CSDN博客React的一些优秀架构思维,值得我们反复的去探讨,因为在其内部有很多很多的知识点。今天我们从react- reconciler这个包入手,开始分析React Fiber 架构原理,从这里开始了解关于 Fiber 树的一切。
先看一下Fiber的定义和类型:
Fiber定义
React Fiber 是 React 核心算法的重新实现。
它的主要特点是渐进式渲染: 能够将渲染工作分割成块,并将其分散到多个帧。
其他关键特性包括在新的更新到来时暂停、中止或重用工作的能力; 为不同类型的更新分配优先级的能力; 以及新的并发方式。
------ GitHub - acdlite/react-fiber-architecture: A description of React's new core algorithm, React Fiber
广义的 Fiber,是一种新架构。为了实现这套架构,React 也在 Virtual DOM 上重建了树和节点结构,叫做 fiber 树和 fiber 节点。
Fiber类型(摘自源码)
export type Fiber = {
tag: WorkTag,
key: null | string,
elementType: any,
type: any,
stateNode: any,
return: Fiber | null,
child: Fiber | null,
sibling: Fiber | null,
index: number,
ref:
| null
| (((handle: mixed) => void) & {_stringRef: ?string, ...})
| RefObject,
refCleanup: null | (() => void),
// Input is the data coming into process this fiber. Arguments. Props.
pendingProps: any, // This type will be more specific once we overload the tag.
memoizedProps: any, // The props used to create the output.
// A queue of state updates and callbacks.
updateQueue: mixed,
// The state used to create the output
memoizedState: any,
// Dependencies (contexts, events) for this fiber, if it has any
dependencies: Dependencies | null,
mode: TypeOfMode,
// Effect
flags: Flags,
subtreeFlags: Flags,
deletions: Array<Fiber> | null,
lanes: Lanes,
childLanes: Lanes,
alternate: Fiber | null,
actualDuration?: number,
actualStartTime?: number,
selfBaseDuration?: number,
treeBaseDuration?: number,
_debugInfo?: ReactDebugInfo | null,
_debugOwner?: ReactComponentInfo | Fiber | null,
_debugStack?: string | Error | null,
_debugTask?: ConsoleTask | null,
_debugIsCurrentlyTiming?: boolean,
_debugNeedsRemount?: boolean,
// Used to verify that the order of hooks does not change between renders.
_debugHookTypes?: Array<HookType> | null,
};workTag标识:(28种)
export type WorkTag =| 0| 1| 2| 3| 4| 5| 6| 7| 8| 9| 10| 11| 12| 13| 14| 15| 16| 17| 18| 19| 20| 21| 22| 23| 24| 25| 26| 27| 28;
export const FunctionComponent = 0;
export const ClassComponent = 1;
export const HostRoot = 3; // Root of a host tree. Could be nested inside another node.
export const HostPortal = 4; // A subtree. Could be an entry point to a different renderer.
export const HostComponent = 5;
export const HostText = 6;
export const Fragment = 7;
export const Mode = 8;
export const ContextConsumer = 9;
export const ContextProvider = 10;
export const ForwardRef = 11;
export const Profiler = 12;
export const SuspenseComponent = 13;
export const MemoComponent = 14;
export const SimpleMemoComponent = 15;
export const LazyComponent = 16;
export const IncompleteClassComponent = 17;
export const DehydratedFragment = 18;
export const SuspenseListComponent = 19;
export const ScopeComponent = 21;
export const OffscreenComponent = 22;
export const LegacyHiddenComponent = 23;
export const CacheComponent = 24;
export const TracingMarkerComponent = 25;
export const HostHoistable = 26;
export const HostSingleton = 27;
export const IncompleteFunctionComponent = 28;并发渲染模式下,首先入口主要函数:renderRootConcurrent,workLoopConcurrent,performUnitOfWork,beginWork,completeUnitOfWork
这里省略粘贴源码部分😄。。。
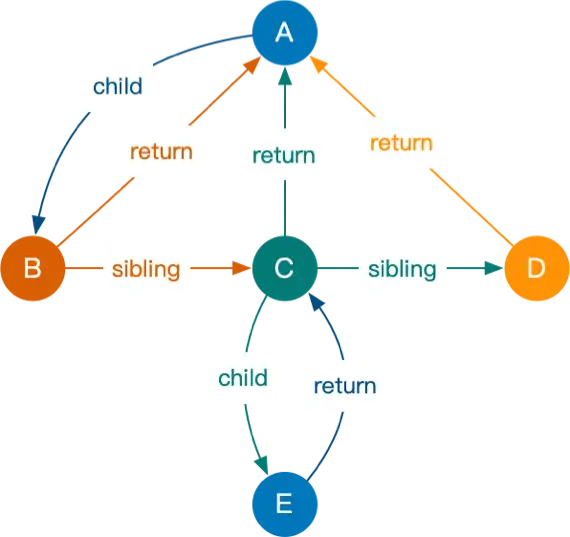
假设我们有如下这样一棵树

- 整个遍历由 performUnitOfWork 发起,为深度优先遍历
- 从根节点开始,循环调 beginWork 向下爬树(黄色箭头,每个箭头表示一次调用)
- 到达叶子节点(beginWork 爬不下去)后,调 completeUnitOfWork 向上爬到下一个未遍历过的节点,也就是第一个出现的祖先兄弟节点(绿色箭头,每个箭头表示一次调用)
- 所以 beginWork 可能连续调用多次,一次最多只爬一步,但 completeUnitOfWork 只可能在 beginWork 之间连续调用一次,一次可以向上爬若干步
- completeUnitOfWork 内部包下了若干步循环向上的爬树操作(绿色虚线箭头)
可以看到,Fiber 树是边创建边遍历的,每个节点都经历了「创建、Diffing、收集副作用(要改哪些节点)」的过程。其中,创建、Diffing要自上而下,因为有父才有子;收集副作用要自下而上最终收集到根节点。这里深度优先遍历内外两层循环,外层也就是beginWork(负责创建)自上而下保证每个节点只走一次,内层循环completeUnitOfWork自下而上负责收集副作用(需要修改哪些节点)。
两棵树的diff
在React中最多会同时存在两棵Fiber树:
- 当前屏幕上显示内容对应的Fiber树称为 current Fiber 树
- 正在构建的Fiber树称为 workInProgress Fiber 树,我们这里讨论的所有遍历都在这棵树上
当一次协调发起,首先会开一棵新 workInProgress Fiber 树,然后从根节点开始构建并遍历 workInProgress Fiber 树。这样下来,如果构建到一半被打断,current 树还在。如果构建并提交完成,直接把 current 树丢掉,让 workInProgress Fiber 树成为新的 current 树。
所谓 Diffing 也是在这两棵树之间,如果构建过程中确认新节点对旧节点的复用关系,新旧节点间也会通过 alternate 指针相连。

接下来,比较两棵树
Diffing 算法
Diffing 算法进行了3种情况的假定:
一:不同类型的节点元素会有不同的形态
当节点为不同类型的元素时,React 会拆卸原有节点并且建立起新的节点。举个例子,当一个元素从 a 变成 img,从 Article 变成 Comment,都会触发一个完整的重建流程。
该算法不会尝试匹配不同组件类型的子树。如果你发现你在两种不同类型的组件中切换,但输出非常相似的内容,建议把它们改成同一类型。
二:节点不会进行跨父节点移动
只会对比两个关联父节点的子节点,多了就加少了就减。没有提供任何方式追踪他们是否被移动到别的地方。
三:用户会给每个子节点提供一个 key,标记它们"是同一个"
当子元素拥有 key 时,React 使用 key 来匹配原有树上的子元素以及最新树上的子元素。在新增 key 之后,使得树的转换效率得以提高。比如两个兄弟节点调换了位置,有 key 的情况下能保证二者都复用仅做移动,但无 key 就会造成两个不必要的卸载重建。
深入diff过程,
function performUnitOfWork(unitOfWork: Fiber): void {
// The current, flushed, state of this fiber is the alternate. Ideally
// nothing should rely on this, but relying on it here means that we don't
// need an additional field on the work in progress.
const current = unitOfWork.alternate;
let next;
if (enableProfilerTimer && (unitOfWork.mode & ProfileMode) !== NoMode) {
startProfilerTimer(unitOfWork);
if (__DEV__) {
next = runWithFiberInDEV(
unitOfWork,
beginWork,
current,
unitOfWork,
entangledRenderLanes,
);
} else {
next = beginWork(current, unitOfWork, entangledRenderLanes);
}
stopProfilerTimerIfRunningAndRecordDelta(unitOfWork, true);
} else {
if (__DEV__) {
next = runWithFiberInDEV(
unitOfWork,
beginWork,
current,
unitOfWork,
entangledRenderLanes,
);
} else {
next = beginWork(current, unitOfWork, entangledRenderLanes);
}
}
if (!disableStringRefs) {
resetCurrentFiber();
}
unitOfWork.memoizedProps = unitOfWork.pendingProps;
if (next === null) {
// If this doesn't spawn new work, complete the current work.
completeUnitOfWork(unitOfWork);
} else {
workInProgress = next;
}
}对每个遍历到的新节点 unitOfWork,取出它关联复用的 current 树节点,称为「current」,然后新旧节点一并传给 beginWork。这个关联关系是在前面某轮循环执行 beginWork 构造 unitOfWork 时建立的,取决于当时的 Diffing 判断新旧节点是否复用。所以可能存在 current 为 null 的情况。
function beginWork(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
renderLanes: Lanes,
): Fiber | null {
if (__DEV__) {
if (workInProgress._debugNeedsRemount && current !== null) {
// This will restart the begin phase with a new fiber.
const copiedFiber = createFiberFromTypeAndProps(
workInProgress.type,
workInProgress.key,
workInProgress.pendingProps,
workInProgress._debugOwner || null,
workInProgress.mode,
workInProgress.lanes,
);
if (enableOwnerStacks) {
copiedFiber._debugStack = workInProgress._debugStack;
copiedFiber._debugTask = workInProgress._debugTask;
}
return remountFiber(current, workInProgress, copiedFiber);
}
}
if (current !== null) {
const oldProps = current.memoizedProps;
const newProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
if (
oldProps !== newProps ||
hasLegacyContextChanged() ||
// Force a re-render if the implementation changed due to hot reload:
(__DEV__ ? workInProgress.type !== current.type : false)
) {
// If props or context changed, mark the fiber as having performed work.
// This may be unset if the props are determined to be equal later (memo).
didReceiveUpdate = true;
} else {
// Neither props nor legacy context changes. Check if there's a pending
// update or context change.
const hasScheduledUpdateOrContext = checkScheduledUpdateOrContext(
current,
renderLanes,
);
if (
!hasScheduledUpdateOrContext &&
// If this is the second pass of an error or suspense boundary, there
// may not be work scheduled on `current`, so we check for this flag.
(workInProgress.flags & DidCapture) === NoFlags
) {
// No pending updates or context. Bail out now.
didReceiveUpdate = false;
return attemptEarlyBailoutIfNoScheduledUpdate(
current,
workInProgress,
renderLanes,
);
}
if ((current.flags & ForceUpdateForLegacySuspense) !== NoFlags) {
// This is a special case that only exists for legacy mode.
// See https://github.com/facebook/react/pull/19216.
didReceiveUpdate = true;
} else {
// An update was scheduled on this fiber, but there are no new props
// nor legacy context. Set this to false. If an update queue or context
// consumer produces a changed value, it will set this to true. Otherwise,
// the component will assume the children have not changed and bail out.
didReceiveUpdate = false;
}
}
} else {
didReceiveUpdate = false;
if (getIsHydrating() && isForkedChild(workInProgress)) {
// Check if this child belongs to a list of muliple children in
// its parent.
//
// In a true multi-threaded implementation, we would render children on
// parallel threads. This would represent the beginning of a new render
// thread for this subtree.
//
// We only use this for id generation during hydration, which is why the
// logic is located in this special branch.
const slotIndex = workInProgress.index;
const numberOfForks = getForksAtLevel(workInProgress);
pushTreeId(workInProgress, numberOfForks, slotIndex);
}
}
workInProgress.lanes = NoLanes;
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case LazyComponent: {
const elementType = workInProgress.elementType;
return mountLazyComponent(
current,
workInProgress,
elementType,
renderLanes,
);
}
case FunctionComponent: {
const Component = workInProgress.type;
const unresolvedProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
const resolvedProps =
disableDefaultPropsExceptForClasses ||
workInProgress.elementType === Component
? unresolvedProps
: resolveDefaultPropsOnNonClassComponent(Component, unresolvedProps);
return updateFunctionComponent(
current,
workInProgress,
Component,
resolvedProps,
renderLanes,
);
}
case ClassComponent: {
const Component = workInProgress.type;
const unresolvedProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
const resolvedProps = resolveClassComponentProps(
Component,
unresolvedProps,
workInProgress.elementType === Component,
);
return updateClassComponent(
current,
workInProgress,
Component,
resolvedProps,
renderLanes,
);
}
case HostRoot:
return updateHostRoot(current, workInProgress, renderLanes);
case HostHoistable:
if (supportsResources) {
return updateHostHoistable(current, workInProgress, renderLanes);
}
// Fall through
case HostSingleton:
if (supportsSingletons) {
return updateHostSingleton(current, workInProgress, renderLanes);
}
// Fall through
case HostComponent:
return updateHostComponent(current, workInProgress, renderLanes);
case HostText:
return updateHostText(current, workInProgress);
case SuspenseComponent:
return updateSuspenseComponent(current, workInProgress, renderLanes);
case HostPortal:
return updatePortalComponent(current, workInProgress, renderLanes);
case ForwardRef: {
const type = workInProgress.type;
const unresolvedProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
const resolvedProps =
disableDefaultPropsExceptForClasses ||
workInProgress.elementType === type
? unresolvedProps
: resolveDefaultPropsOnNonClassComponent(type, unresolvedProps);
return updateForwardRef(
current,
workInProgress,
type,
resolvedProps,
renderLanes,
);
}
case Fragment:
return updateFragment(current, workInProgress, renderLanes);
case Mode:
return updateMode(current, workInProgress, renderLanes);
case Profiler:
return updateProfiler(current, workInProgress, renderLanes);
case ContextProvider:
return updateContextProvider(current, workInProgress, renderLanes);
case ContextConsumer:
return updateContextConsumer(current, workInProgress, renderLanes);
case MemoComponent: {
const type = workInProgress.type;
const unresolvedProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
// Resolve outer props first, then resolve inner props.
let resolvedProps = disableDefaultPropsExceptForClasses
? unresolvedProps
: resolveDefaultPropsOnNonClassComponent(type, unresolvedProps);
resolvedProps = disableDefaultPropsExceptForClasses
? resolvedProps
: resolveDefaultPropsOnNonClassComponent(type.type, resolvedProps);
return updateMemoComponent(
current,
workInProgress,
type,
resolvedProps,
renderLanes,
);
}
case SimpleMemoComponent: {
return updateSimpleMemoComponent(
current,
workInProgress,
workInProgress.type,
workInProgress.pendingProps,
renderLanes,
);
}
case IncompleteClassComponent: {
if (disableLegacyMode) {
break;
}
const Component = workInProgress.type;
const unresolvedProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
const resolvedProps = resolveClassComponentProps(
Component,
unresolvedProps,
workInProgress.elementType === Component,
);
return mountIncompleteClassComponent(
current,
workInProgress,
Component,
resolvedProps,
renderLanes,
);
}
case IncompleteFunctionComponent: {
if (disableLegacyMode) {
break;
}
const Component = workInProgress.type;
const unresolvedProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
const resolvedProps = resolveClassComponentProps(
Component,
unresolvedProps,
workInProgress.elementType === Component,
);
return mountIncompleteFunctionComponent(
current,
workInProgress,
Component,
resolvedProps,
renderLanes,
);
}
case SuspenseListComponent: {
return updateSuspenseListComponent(current, workInProgress, renderLanes);
}
case ScopeComponent: {
if (enableScopeAPI) {
return updateScopeComponent(current, workInProgress, renderLanes);
}
break;
}
case OffscreenComponent: {
return updateOffscreenComponent(current, workInProgress, renderLanes);
}
case LegacyHiddenComponent: {
if (enableLegacyHidden) {
return updateLegacyHiddenComponent(
current,
workInProgress,
renderLanes,
);
}
break;
}
case CacheComponent: {
if (enableCache) {
return updateCacheComponent(current, workInProgress, renderLanes);
}
break;
}
case TracingMarkerComponent: {
if (enableTransitionTracing) {
return updateTracingMarkerComponent(
current,
workInProgress,
renderLanes,
);
}
break;
}
}
throw new Error(
`Unknown unit of work tag (${workInProgress.tag}). This error is likely caused by a bug in ` +
'React. Please file an issue.',
);
}beginWork 根据当前节点 tag 做分发,这里的 tag 比较丰富,都是从shared/ReactWorkTags.js导入的常量,常见的 HostComponent、FunctionComponent、ClassComponent、Fragment 等都在此列。以 updateHostComponent 为例。
updateHostComponent 从 workInProgress 属性中取出 children,这个 children 不是 fiber 节点,而是组件 render 方法根据 JSX 结构 createElement 创建的 element 数组,这点不要混淆。
然后在 reconcileChildren 中构造子节点。可以看到如果 current 节点为 null,也就是当前节点无复用,就直接放弃子节点 Diffing 了。所以父节点可复用,是子节点复用的必要不充分条件。
这里也遵循了 Diffing 算法的假设二------节点不会进行跨父节点移动,只对比关联节点的子节点的增减,不管它们有没有被移动到别处或从别处移动来。
再往下看触发 Diffing 的 reconcileChildFibers即createChildReconciler,😂这个方法上千行代码。额,我们做个减法,
function reconcileChildFibers(returnFiber: Fiber, currentFirstChild: Fiber | null, newChild: any): Fiber | null {
const isObject = typeof newChild === 'object' && newChild !== null;
if (isObject) {
switch (newChild.$$typeof) {
case REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE:
return placeSingleChild(reconcileSingleElement(returnFiber, currentFirstChild, newChild));
}
}
if (isArray(newChild)) {
return reconcileChildrenArray(returnFiber, currentFirstChild, newChild);
}
}children 可能是单个对象也可能是数组,这里优先走 reconcileSingleElement 处理单个子节点情况,其次走 reconcileChildrenArray 处理多个子节点。说明单多节点是不一样的逻辑。
无论内部逻辑有什么差异,单多节点的协调函数都要做几件事:
- 和 current 节点的子节点做 Diffing,创建或复用
- 为可复用的新旧子节点建立 alternate 关联
- 返回第一个子节点(会一直往外返回给到 next 指针,作为下一步遍历对象)
子节点 Diffing:当 workInProgress 子节点为单节点
先想一下,为什么说单节点的场景计算简单?因为我只需要一层循环,把 current 节点的所有子节点挨个拿出来对比,找到一个和单节点匹配的就算 Diffing 完了。看代码:
function reconcileSingleElement(returnFiber: Fiber, currentFirstChild: Fiber | null, element: ReactElement): Fiber {
const key = element.key;
let child = currentFirstChild;
while (child !== null) {
if (child.key === key) {
if (child.elementType === element.type) {
deleteRemainingChildren(returnFiber, child.sibling);
const existing = useFiber(child, element.props);
existing.return = returnFiber;
return existing;
} else {
deleteRemainingChildren(returnFiber, child);
break;
}
} else {
deleteChild(returnFiber, child);
}
child = child.sibling;
}
const created = createFiberFromElement(element, returnFiber.mode);
created.return = returnFiber;
return created;
}- 去 current 子节点里找一个和 workInProgress 唯一子节点 key 相同的节点,过程中遍历到的所有 key 不相同的都 deleteChild 删掉
- 找得到且 type 相同,就 useFiber 复用,并把复用节点挂到 workInProgress 下
- 找得到但 type 不同,就 deleteChild 删掉,创建一个新节点并挂在 workInProgress 下。无论2、3哪一种,剩余的 current 子节点都可以 deleteRemainingChildren 批量删掉,因为不会再有 key 相同的了
- 找不到,创建一个新节点并挂在 workInProgress 下
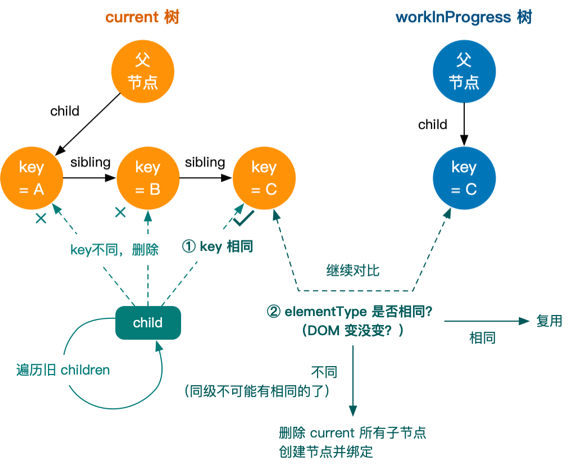
这里的2、3遵循了 Diffing 思想的假设一------不同类型的节点元素会有不同的形态,所以 type 不同就直接被删掉了。
useFiber 做了什么
基于可复用节点和新属性复制一个 workInProgress 节点出来,并将二者通过 alternate 关联。这就是 useFiber 做的事。
function useFiber(fiber: Fiber, pendingProps: mixed): Fiber {
// We currently set sibling to null and index to 0 here because it is easy
// to forget to do before returning it. E.g. for the single child case.
const clone = createWorkInProgress(fiber, pendingProps);
clone.index = 0;
clone.sibling = null;
return clone;
}
function createWorkInProgress(current: Fiber, pendingProps: any): Fiber {
let workInProgress = createFiber(current.tag, pendingProps, current.key, current.mode);
workInProgress.alternate = current;
current.alternate = workInProgress;
return workInProgress;
}其实 createWorkInProgress 还有很大篇幅的其他属性复制,这里没有列出来。
...后面还有,篇幅问题放到下个章节