Semantic Alignment for Multimodal Large Language Models
Semantic Alignment for Multimodal Large Language Models (mccartney01.github.io)
[2408.12867] Semantic Alignment for Multimodal Large Language Models (arxiv.org)

Research on M ulti-modal L arge L anguage M odels (MLLMs ) towards the multi-image cross-modal instruction has received increasing attention and made significant progress, particularly in scenarios involving closely resembling images (e.g. , change captioning). Existing MLLMs typically follow a two-step process in their pipelines: first, extracting visual tokens independently for each input image, and then aligning these visual tokens from different images with the Large Language Model (LLM) in its textual feature space. However, the independent extraction of visual tokens for each image may result in different semantics being prioritized for different images in the first step, leading to a lack of preservation of linking information among images for subsequent LLM analysis. This issue becomes more serious in scenarios where significant variations exist among the images (e.g. , visual storytelling). To address this challenge, we introduce S emantic A lignment for M ulti-modal large language models (SAM ). By involving the bidirectional semantic guidance between different images in the visual-token extraction process, SAM aims to enhance the preservation of linking information for coherent analysis and align the semantics of different images before feeding them into LLM. As the test bed, we propose a large-scale dataset named MmLINK consisting of 69K samples. Different from most existing datasets for MLLMs fine-tuning, our MmLINK dataset comprises multi-modal instructions with significantly diverse images. Extensive experiments on the group captioning task and the storytelling task prove the effectiveness of our SAM model, surpassing the state-of-the-art methods by a large margin (+37% for group captioning and +22% for storytelling on CIDEr score).
面向多图像跨模态指令的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)研究日益受到关注,并取得了显著进展,特别是在涉及紧密相似图像(如更改描述)的场景中。
现有的MLLMs通常在其处理流程中遵循两步过程:首先,为每个输入图像独立提取视觉标记,然后将这些来自不同图像的视觉标记在其文本特征空间内与大型语言模型(LLM)进行对齐。
然而,为每个图像独立提取视觉标记可能会导致在第一步中不同图像被赋予不同的语义优先级,从而在后续LLM分析中缺乏图像之间的链接信息的保留。在图像之间存在显著差异(如视觉故事讲述)的场景中,这一问题变得更加严重。
为了应对这一挑战,本文引入了多模态大型语言模型的语义对齐(SAM)。通过在视觉标记提取过程中引入不同图像之间的双向语义引导,SAM旨在增强链接信息的保留,以便进行连贯分析,并在将图像输入LLM之前对齐不同图像的语义。
作为测试平台,本文提出了一个名为MmLINK的大规模数据集,包含69K个样本。与大多数现有的用于MLLMs微调的数据集不同,我们的MmLINK数据集包含具有显著不同图像的多模态指令。
在群组描述任务和故事讲述任务上的广泛实验证明了本文的SAM模型的有效性,在CIDEr评分上大大超越了最先进的方法(群组描述任务提升+37%,故事讲述任务提升+22%)。

MLLMs能够通过对齐高度相似图像之间的相似性和明确指出差异来有效解决推理任务。
然而,当面临在内容、上下文或风格上存在显著差异的图像时,包括GPT-4V在内的MLLMs的有效性会降低。
当模型需要对齐角色身份或知识概念时,这一问题尤为明显。
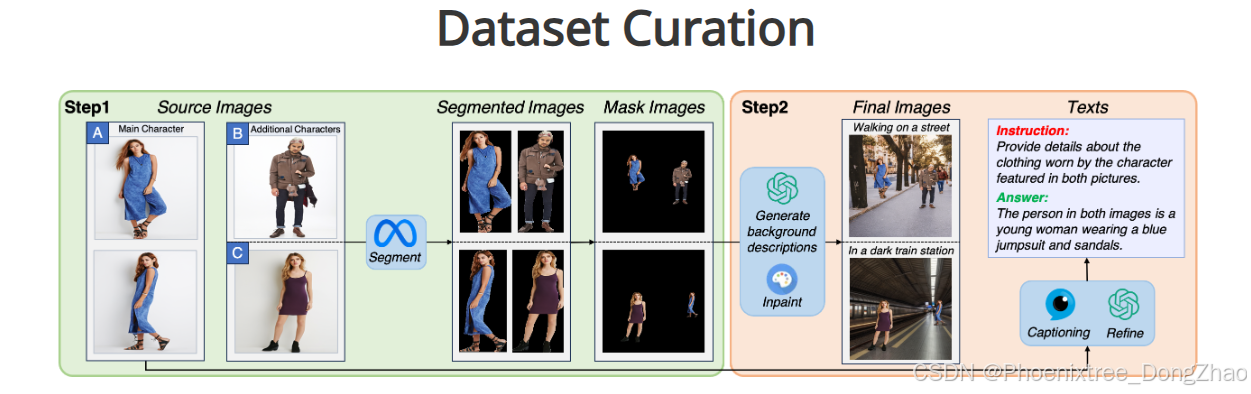
首先从选择展示不同姿势角色(A)的图像开始,同时选择另外两个不同的角色(B、C)。将所选图像进行分割以隔离每个角色,然后将它们合并成掩模图像。
接着,利用ChatGPT生成的描述,使用修复技术填充这些掩模图像的背景区域,以获得最终图像。文本注释由InstructBLIP生成,并通过ChatGPT进一步细化。

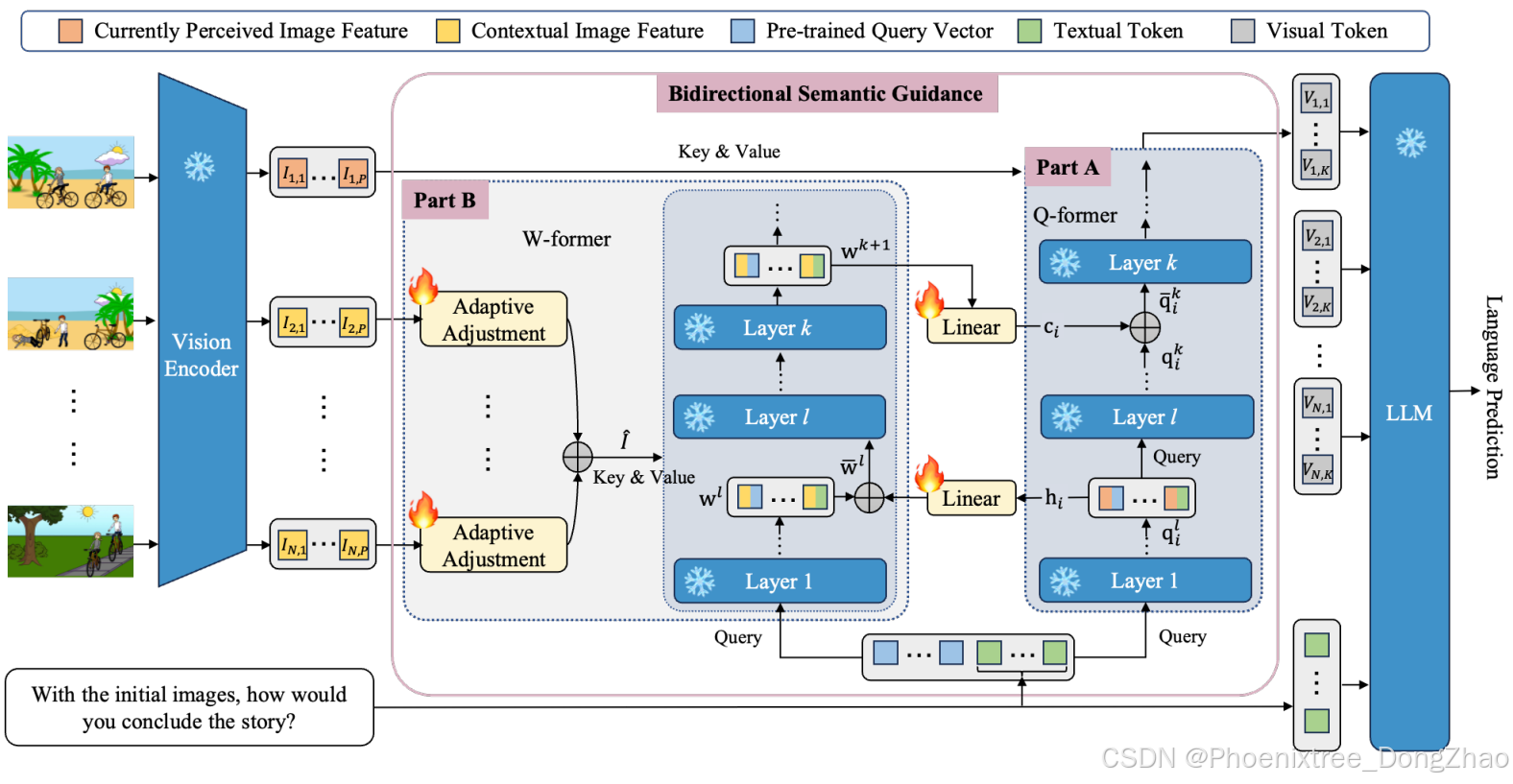
SAM模型的核心机制是双向语义引导机制,该机制包含两个交互过程:辅助视觉标记提取(部分A)和上下文语义生成(部分B)。
在部分A中,Q-former模块利用从部分B中的多模态指令的上下文图像(即当前感知图像以外的图像)生成的上下文语义ci,来指导从当前感知图像特征中提取视觉标记。
在部分B中,W-former模块用于从上下文图像的视觉上下文中选择上下文语义。这一选择过程在自适应调整中的注意力机制的辅助下进行,同时得到从部分A中当前感知图像中提取的初始视觉标记hi的帮助。

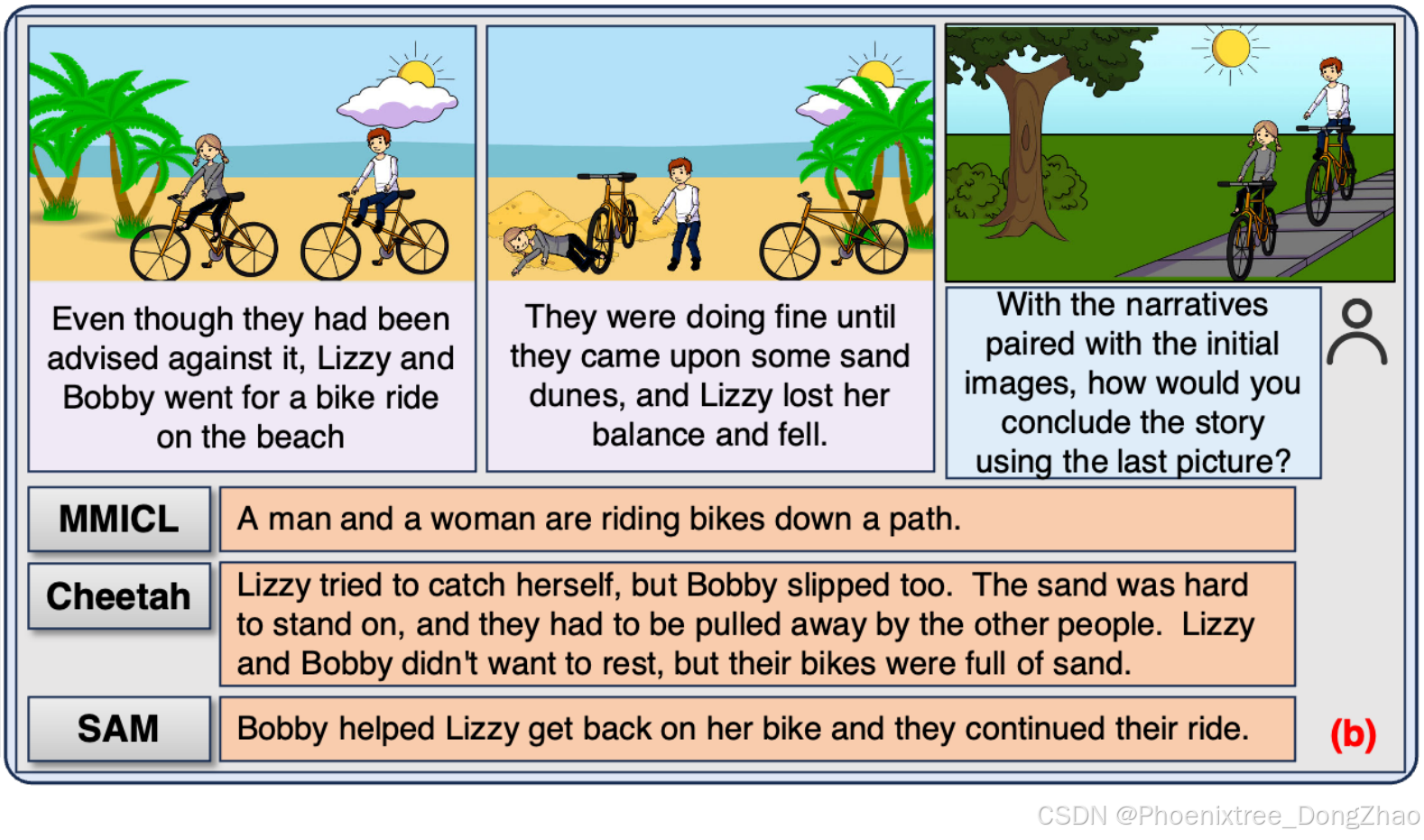
SAM与其他MLLMs生成的案例示例。其他MLLMs的回答要么表现出较弱的指令遵循能力,要么包含幻觉,而SAM则成功地进行了语义对齐并产生了准确的回应。
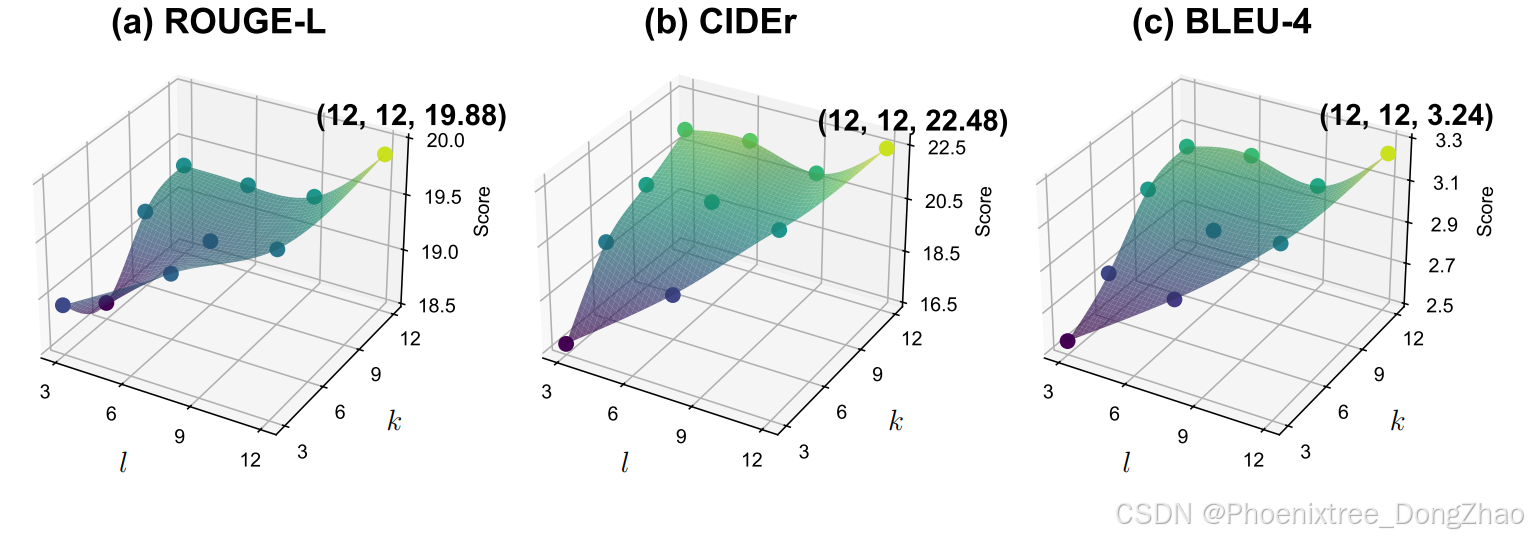
不同交互层级的6个数据集上的平均分数。l是传递初始视觉标记的层,k是传递上下文语义的层,k ≥ l(l和k在4.2节中定义)。标记了原始的10个点,并从这些点中插值得到表面图。