一、引言
在人工智能技术日益普及的今天,计算机视觉正以前所未有的方式改变着我们的日常生活。YOLO作为先进的目标检测算法,以其快速和精准的特性,成为了实现智能视觉应用的得力工具。今天我们将通过四个贴近生活的趣味场景------智能厨房助手、植物健康监测、智能衣橱管理和宠物行为分析,一起领略YOLO技术的魅力。
无论你是烹饪爱好者、园艺新手、时尚达人还是宠物主人,这些应用都能为你的生活带来便利与乐趣。通过简单的代码实现,就可以让计算机识别食材并推荐菜谱,监测植物的健康状况,管理衣橱并提供穿搭建议,甚至分析宠物的行为状态。这些示例不仅展示了YOLO技术的广泛应用,也为初学者提供了实践机会,让我们在动手实现中深入理解计算机视觉的原理。让我们一起探索如何用YOLO模型构建智能生活助手,开启人工智能的奇妙之旅。
二、智能厨房助手
1. 场景描述
基于YOLO模型的智能厨房助手,能够识别图像中的食材,并根据识别到的食材推荐菜谱和计算营养成分。整个示例包含了食材检测、菜谱推荐、营养计算和结果可视化四个主要部分;
2. 示例代码
python
import cv2
from ultralytics import YOLO
import requests
import json
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用黑体显示中文
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 正常显示负号
class SmartKitchenAssistant:
def __init__(self, model_size='n'):
# 加载YOLO模型
self.model = YOLO(f'yolov8{model_size}.pt')
# 食材与菜谱映射
self.ingredient_recipes = {
'banana': ['香蕉奶昔', '香蕉面包', '香蕉煎饼'],
'apple': ['苹果派', '苹果沙拉', '烤苹果'],
'orange': ['橙汁', '橙子蛋糕', '水果沙拉'],
'carrot': ['胡萝卜汤', '胡萝卜沙拉', '炒胡萝卜'],
'broccoli': ['西兰花炒肉', '烤西兰花', '西兰花汤'],
'tomato': ['番茄炒蛋', '番茄汤', '番茄沙拉'],
'egg': ['煎蛋', '炒蛋', '蛋花汤'],
'bread': ['吐司', '三明治', '法式吐司'],
'chicken': ['烤鸡', '炸鸡', '鸡汤'],
'fish': ['烤鱼', '炸鱼', '鱼汤']
}
# 食材营养成分(每100克)
self.nutrition_info = {
'banana': {'calories': 89, 'carbs': 23, 'protein': 1.1, 'fat': 0.3},
'apple': {'calories': 52, 'carbs': 14, 'protein': 0.3, 'fat': 0.2},
'orange': {'calories': 47, 'carbs': 12, 'protein': 0.9, 'fat': 0.1},
'carrot': {'calories': 41, 'carbs': 10, 'protein': 0.9, 'fat': 0.2},
'broccoli': {'calories': 34, 'carbs': 7, 'protein': 2.8, 'fat': 0.4},
'tomato': {'calories': 18, 'carbs': 3.9, 'protein': 0.9, 'fat': 0.2},
'egg': {'calories': 155, 'carbs': 1.1, 'protein': 13, 'fat': 11},
'bread': {'calories': 265, 'carbs': 49, 'protein': 9, 'fat': 3.2},
'chicken': {'calories': 165, 'carbs': 0, 'protein': 31, 'fat': 3.6},
'fish': {'calories': 206, 'carbs': 0, 'protein': 22, 'fat': 12}
}
def detect_ingredients(self, image_path):
"""检测图像中的食材"""
results = self.model.predict(source=image_path, conf=0.3)
result = results[0]
detected_ingredients = {}
if result.boxes is not None:
for box, cls in zip(result.boxes.xyxy, result.boxes.cls):
class_name = self.model.names[int(cls)]
# 只关注食材类别的检测
if class_name in self.ingredient_recipes:
if class_name not in detected_ingredients:
detected_ingredients[class_name] = 0
detected_ingredients[class_name] += 1
return detected_ingredients
def recommend_recipes(self, ingredients):
"""根据检测到的食材推荐菜谱"""
all_recipes = []
for ingredient in ingredients:
if ingredient in self.ingredient_recipes:
all_recipes.extend(self.ingredient_recipes[ingredient])
# 去除重复菜谱
unique_recipes = list(set(all_recipes))
# 根据食材匹配度排序(匹配食材越多的菜谱排前面)
recipe_scores = {}
for recipe in unique_recipes:
score = 0
for ingredient in ingredients:
if ingredient in self.ingredient_recipes and recipe in self.ingredient_recipes[ingredient]:
score += 1
recipe_scores[recipe] = score
sorted_recipes = sorted(recipe_scores.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
return [recipe for recipe, score in sorted_recipes[:5]] # 返回前5个推荐
def calculate_nutrition(self, ingredients):
"""计算检测食材的总营养成分"""
total_nutrition = {'calories': 0, 'carbs': 0, 'protein': 0, 'fat': 0}
for ingredient, count in ingredients.items():
if ingredient in self.nutrition_info:
# 假设每个检测到的食材约100克
nutrition = self.nutrition_info[ingredient]
for key in total_nutrition:
total_nutrition[key] += nutrition[key] * count
return total_nutrition
def analyze_kitchen_scene(self, image_path):
"""完整的厨房场景分析"""
# 检测食材
ingredients = self.detect_ingredients(image_path)
if not ingredients:
return {
'ingredients': {},
'recipes': [],
'nutrition': {},
'message': '未检测到食材,请确保食材在视野范围内'
}
# 推荐菜谱
recipes = self.recommend_recipes(ingredients.keys())
# 计算营养
nutrition = self.calculate_nutrition(ingredients)
# 可视化结果
self.visualize_results(image_path, ingredients, recipes, nutrition)
return {
'ingredients': ingredients,
'recipes': recipes,
'nutrition': nutrition,
'message': f'检测到 {len(ingredients)} 种食材,推荐 {len(recipes)} 个菜谱'
}
def visualize_results(self, image_path, ingredients, recipes, nutrition):
"""可视化分析结果"""
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
import numpy as np
# 读取图像并转换为RGB
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 使用YOLO绘制检测结果
results = self.model.predict(source=image_path, conf=0.3)
result_img = results[0].plot()
# 转换为Pillow格式
pil_img = Image.fromarray(result_img)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(pil_img)
# 加载中文字体(确保系统中存在该字体)
font_path = "simhei.ttf" # 黑体字体文件路径
font = ImageFont.truetype(font_path, 40)
# 添加文本信息
y_offset = 10
draw.text((10, y_offset), "智能厨房助手分析结果:", font=font, fill=(0, 255, 0))
# y_offset += 30
# 显示检测到的食材
draw.text((480, y_offset), f"检测到食材: {', '.join(ingredients.keys())}", font=font, fill=(106, 90, 205))
# y_offset += 25
# 显示营养成分
draw.text((1200, y_offset), f"预估营养: 热量{round(nutrition['calories'], 2)}卡, 碳水{round(nutrition['carbs'], 2)}g, 蛋白质{round(nutrition['protein'], 2)}g, 脂肪{round(nutrition['fat'], 2)}g",
font=font, fill=(139, 71, 38))
y_offset += 42
x_offset = 10
# 显示推荐菜谱
draw.text((10, y_offset), "推荐菜谱:", font=font, fill=(255, 127, 80))
# y_offset += 25
x_offset += 200
for i, recipe in enumerate(recipes[:3]): # 显示前3个菜谱
draw.text((x_offset, y_offset), f"{i+1}.{recipe}", font=font, fill=(255, 177, 90))
# y_offset += 20
x_offset += 250
# 转换回OpenCV格式
result_img = np.array(pil_img)
# 显示图像
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 7))
plt.imshow(result_img)
plt.axis('off')
plt.title('智能厨房助手分析结果')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 使用示例
kitchen_assistant = SmartKitchenAssistant('n')
result = kitchen_assistant.analyze_kitchen_scene('kitchen_scene.jpg')
print(result)3. 过程说明
- YOLO模型加载与使用:使用Ultralytics库加载YOLOv8模型,并进行图像预测。通过设置置信度阈值来过滤检测结果。
- 食材检测:遍历检测结果,只保留在预定义食材列表中的物体,并统计每种食材的数量。
- 菜谱推荐:根据检测到的食材,从预定义的菜谱映射中找出所有相关的菜谱,然后根据食材匹配度进行排序,返回前5个推荐菜谱。
- 营养计算:根据检测到的食材数量,从预定义的营养信息中累加计算总热量、碳水化合物、蛋白质和脂肪。
- 结果可视化:使用OpenCV和Matplotlib绘制检测结果,并用Pillow库添加中文文本。这里注意,由于OpenCV不支持中文,所以使用Pillow来绘制中文文本。
- 中文字体显示:通过Pillow的ImageDraw绘制中文,需要指定中文字体文件(如simhei.ttf),否则会出现乱码。
- 代码结构:采用面向对象的方式,将功能封装在SmartKitchenAssistant类中,使代码易于维护和扩展。
4. 结果分析
image 1/1 D:\AIWorld\case\test\kitchen_scene.jpg: 384x640 2 bananas, 5 apples, 1 orange, 59.3ms
Speed: 2.6ms preprocess, 59.3ms inference, 2.5ms postprocess per image at shape (1, 3, 384, 640)
image 1/1 D:\AIWorld\case\test\kitchen_scene.jpg: 384x640 2 bananas, 5 apples, 1 orange, 38.2ms
Speed: 2.3ms preprocess, 38.2ms inference, 2.4ms postprocess per image at shape (1, 3, 384, 640)
{'ingredients': {'banana': 2, 'apple': 5, 'orange': 1}, 'recipes': ['水果沙拉', '苹果派', '橙汁', '香蕉面包', '香蕉煎饼'], 'nutrition': {'calories': 485, 'carbs': 128, 'protein': 4.6000000000000005, 'fat': 1.7000000000000002}, 'message': '
检测到 3 种食材,推荐 5 个菜谱'}
结果图例:

分析后的结果图:

三、植物健康监测系统
1. 场景描述
基于YOLO模型的植物健康监测系统,利用YOLO模型检测图像中的植物,然后通过分析植物叶片的颜色特征来评估其健康状况,并给出相应的养护建议。该系统将计算机视觉技术与植物学知识相结合,为植物爱好者提供一个智能化的养护助手。
2. 示例代码
python
import cv2
from ultralytics import YOLO
import numpy as np
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用黑体显示中文
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 正常显示负号
class PlantHealthMonitor:
def __init__(self,model_size='n'):
# 加载植物检测模型(需要自定义训练)
self.detection_model = YOLO(f'yolov8{model_size}.pt') # 假设已训练
# 植物养护信息
self.plant_care_info = {
'rose': {
'water': '每周浇水2-3次,保持土壤湿润',
'sunlight': '需要充足阳光,每天6小时以上',
'fertilizer': '每月施一次玫瑰花肥',
'common_issues': ['黑斑病', '白粉病', '蚜虫']
},
'cactus': {
'water': '耐旱,每2-3周浇水一次',
'sunlight': '需要充足阳光',
'fertilizer': '生长季节每月施一次仙人掌专用肥',
'common_issues': ['过度浇水', '日照不足']
},
'orchid': {
'water': '每周浇水1-2次,避免积水',
'sunlight': '需要散射光,避免直射',
'fertilizer': '每2周施一次兰花专用肥',
'common_issues': ['根腐病', '叶片发黄']
},
'succulent': {
'water': '耐旱,土壤干透后再浇水',
'sunlight': '需要充足阳光',
'fertilizer': '生长季节每月施一次多肉专用肥',
'common_issues': ['过度浇水', '日照不足']
}
}
def detect_plants(self, image_path):
"""检测图像中的植物"""
results = self.detection_model.predict(source=image_path, conf=0.4)
return results[0]
def analyze_leaf_health(self, image, leaf_region):
"""分析叶片健康状况"""
# 提取叶片区域
x1, y1, x2, y2 = map(int, leaf_region)
leaf_img = image[y1:y2, x1:x2]
if leaf_img.size == 0:
return {'health_status': '无法分析', 'confidence': 0}
# 转换为HSV颜色空间分析
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(leaf_img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV)
# 分析颜色特征
green_mask = cv2.inRange(hsv, (36, 25, 25), (86, 255, 255))
yellow_mask = cv2.inRange(hsv, (20, 100, 100), (30, 255, 255))
brown_mask = cv2.inRange(hsv, (10, 100, 20), (20, 255, 200))
total_pixels = leaf_img.shape[0] * leaf_img.shape[1]
green_ratio = np.sum(green_mask > 0) / total_pixels
yellow_ratio = np.sum(yellow_mask > 0) / total_pixels
brown_ratio = np.sum(brown_mask > 0) / total_pixels
# 根据颜色比例判断健康状况
if green_ratio > 0.7:
health_status = "健康"
confidence = green_ratio
elif yellow_ratio > 0.3:
health_status = "轻微问题(可能缺水或缺肥)"
confidence = yellow_ratio
elif brown_ratio > 0.2:
health_status = "不健康(可能病害或严重缺水)"
confidence = brown_ratio
else:
health_status = "状态未知"
confidence = 0.5
return {
'health_status': health_status,
'confidence': confidence,
'color_analysis': {
'green_ratio': green_ratio,
'yellow_ratio': yellow_ratio,
'brown_ratio': brown_ratio
}
}
def get_care_recommendations(self, plant_type, health_status):
"""根据植物类型和健康状况提供养护建议"""
if plant_type not in self.plant_care_info:
return ["未知植物类型,建议咨询专业园艺师"]
care_info = self.plant_care_info[plant_type]
recommendations = []
# 基础养护建议
recommendations.append(f"浇水: {care_info['water']}")
recommendations.append(f"光照: {care_info['sunlight']}")
recommendations.append(f"施肥: {care_info['fertilizer']}")
# 根据健康状况的特别建议
if "不健康" in health_status or "问题" in health_status:
recommendations.append("特别关注: 请检查以下常见问题:")
for issue in care_info['common_issues']:
recommendations.append(f" - {issue}")
recommendations.append("建议: 适当调整养护方式,如问题持续请咨询专家")
elif "健康" in health_status:
recommendations.append("当前状态良好,请继续保持现有养护方式")
return recommendations
def full_plant_analysis(self, image_path):
"""完整的植物分析"""
# 检测植物
result = self.detect_plants(image_path)
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
analysis_results = []
if result.boxes is not None:
for i, (box, cls) in enumerate(zip(result.boxes.xyxy, result.boxes.cls)):
plant_type = self.detection_model.names[int(cls)]
# 分析叶片健康
health_analysis = self.analyze_leaf_health(image, box.cpu().numpy())
# 获取养护建议
care_recommendations = self.get_care_recommendations(
plant_type, health_analysis['health_status']
)
analysis_results.append({
'plant_id': i + 1,
'plant_type': plant_type,
'bbox': box.cpu().numpy().tolist(),
'health_analysis': health_analysis,
'care_recommendations': care_recommendations
})
# 可视化结果
self.visualize_plant_analysis(image_path, analysis_results)
return analysis_results
def visualize_plant_analysis(self, image_path, analysis_results):
"""可视化植物分析结果"""
result_img = cv2.imread(image_path)
result_img = cv2.cvtColor(result_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 绘制检测框和健康状态
for result in analysis_results:
bbox = result['bbox']
x1, y1, x2, y2 = map(int, bbox)
# 根据健康状态选择颜色
health_status = result['health_analysis']['health_status']
if "健康" in health_status:
color = (0, 255, 0) # 绿色
elif "问题" in health_status:
color = (0, 255, 255) # 黄色
else:
color = (0, 0, 255) # 红色
# 绘制边界框
cv2.rectangle(result_img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), color, 2)
# 添加标签(使用Pillow绘制中文)
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
import numpy as np
# 转换为Pillow格式
pil_img = Image.fromarray(result_img)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(pil_img)
# 加载中文字体(确保系统中存在该字体)
font_path = "simhei.ttf" # 黑体字体文件路径
font = ImageFont.truetype(font_path, 20)
# 绘制中文文本
label = f"{result['plant_type']}: {health_status}"
draw.text((x1, y1 - 30), label, font=font, fill=color)
# 转换回OpenCV格式
result_img = np.array(pil_img)
# 显示结果
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.imshow(result_img)
plt.axis('off')
plt.title('植物健康监测结果')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 打印详细建议
print("\n=== 植物养护建议 ===")
for result in analysis_results:
print(f"\n植物 {result['plant_id']} ({result['plant_type']}):")
print(f"健康状态: {result['health_analysis']['health_status']} "
f"(置信度: {result['health_analysis']['confidence']:.2f})")
print("养护建议:")
for recommendation in result['care_recommendations']:
print(f" - {recommendation}")
# 使用示例
plant_monitor = PlantHealthMonitor()
results = plant_monitor.full_plant_analysis('garden_plants.jpg')3. 重要节点
- 环境配置与中文支持:
- 使用matplotlib绘图时设置中文字体,避免中文显示乱码。
- 植物健康监测类(PlantHealthMonitor):
- 初始化时加载YOLO模型,并定义植物养护信息。
- 植物检测:
- 使用YOLO模型对输入图像进行植物检测,返回检测结果。
- 叶片健康分析:
- 提取检测到的植物区域(叶片),转换为HSV颜色空间。
- 通过设定绿色、黄色、褐色的HSV范围,创建掩膜,计算各颜色像素所占比例。
- 根据颜色比例判断叶片健康状况,并返回健康状态、置信度和颜色分析结果。
- 养护建议:
- 根据植物类型和健康状态,从预定义的植物养护信息中获取基础养护建议,并根据健康状态添加特别建议。
- 完整分析流程:
- 对图像进行植物检测,对每个检测到的植物进行健康分析,生成养护建议,并可视化结果。
- 可视化:
- 使用OpenCV和Pillow结合绘制检测框和中文标签,显示植物健康状态,并打印详细的养护建议。
4. 代码分析
4.1 植物健康诊断算法
python
# 转换为HSV颜色空间分析
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(leaf_img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV)
# 分析颜色特征
green_mask = cv2.inRange(hsv, (36, 25, 25), (86, 255, 255))
yellow_mask = cv2.inRange(hsv, (20, 100, 100), (30, 255, 255))
brown_mask = cv2.inRange(hsv, (10, 100, 20), (20, 255, 200))- HSV颜色空间:比RGB更适合颜色分析和分割
- 颜色阈值设定:基于植物学知识的专业参数
- 绿色范围(36-86):健康叶绿素反射
- 黄色范围(20-30):缺素或病害早期
- 褐色范围(10-20):严重病害或枯萎
4.2 专家知识系统
python
self.plant_care_info = {
'rose': {
'water': '每周浇水2-3次,保持土壤湿润',
'sunlight': '需要充足阳光,每天6小时以上',
# ... 其他养护信息
}
}- 结构化存储:按植物种类分类存储专业知识
- 多维度建议:涵盖浇水、光照、施肥等关键因素
- 问题诊断:包含常见病害和解决方案
4.3 混合可视化技术
python
# OpenCV绘制边界框
cv2.rectangle(result_img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), color, 2)
# Pillow渲染中文文本
pil_img = Image.fromarray(result_img)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(pil_img)
font = ImageFont.truetype(font_path, 20)
draw.text((x1, y1 - 30), label, font=font, fill=color)- 技术融合:结合OpenCV的图形绘制和Pillow的文字渲染
- 颜色编码:用不同颜色直观表示健康状态
- 中文优化:解决计算机视觉中的中文显示难题
5. 输出结果
image 1/1 D:\AIWorld\case\test\garden_plants.jpg: 448x640 2 potted plants, 2 vases, 62.2ms
Speed: 2.6ms preprocess, 62.2ms inference, 1.8ms postprocess per image at shape (1, 3, 448, 640)
=== 植物养护建议 ===
植物 1 (potted plant):
健康状态: 状态未知 (置信度: 0.50)
养护建议:
- 未知植物类型,建议咨询专业园艺师
植物 2 (vase):
健康状态: 状态未知 (置信度: 0.50)
养护建议:
- 未知植物类型,建议咨询专业园艺师
植物 3 (potted plant):
健康状态: 状态未知 (置信度: 0.50)
养护建议:
- 未知植物类型,建议咨询专业园艺师
植物 4 (vase):
健康状态: 状态未知 (置信度: 0.50)
养护建议:
- 未知植物类型,建议咨询专业园艺师
结果图例:

分析后的结果图:

四、宠物行为分析器
1. 场景描述
基于YOLO模型的宠物行为分析器的代码,它使用YOLO模型来检测宠物(猫和狗),然后通过简单的宽高比分析来估计宠物的姿态(坐着、站着、躺着),并根据姿态和活动水平提供行为解释和健康建议,此外,代码还提供了视频分析功能,可以处理视频文件并生成行为报告。
2. 示例代码
python
import cv2
from ultralytics import YOLO
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用黑体显示中文
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 正常显示负号
class PetBehaviorAnalyzer:
def __init__(self, model_size='n'):
self.model = YOLO(f'yolov8{model_size}.pt')
# 宠物行为分析规则
self.behavior_rules = {
'dog': {
'sitting': '正常休息状态',
'standing': '警觉或等待状态',
'lying': '深度休息',
'running': '活跃玩耍',
'eating': '进食时间',
'drinking': '补充水分'
},
'cat': {
'sitting': '观察环境',
'standing': '准备行动',
'lying': '放松休息',
'running': '玩耍或追逐',
'eating': '进食时间',
'drinking': '补充水分'
}
}
# 宠物健康建议
self.health_advice = {
'dog': {
'active': '运动量充足,继续保持',
'inactive': '建议增加散步和游戏时间',
'eating_well': '食欲正常',
'not_eating': '注意观察食欲变化'
},
'cat': {
'active': '活泼好动,状态良好',
'inactive': '可能需要注意健康状态',
'eating_well': '进食正常',
'not_eating': '猫咪不进食需要关注'
}
}
def detect_pets(self, image_path):
"""检测宠物"""
results = self.model.predict(source=image_path, conf=0.4)
return results[0]
def analyze_pose(self, image, bbox, pet_type):
"""分析宠物姿态"""
x1, y1, x2, y2 = map(int, bbox)
pet_region = image[y1:y2, x1:x2]
if pet_region.size == 0:
return 'unknown'
# 简单的姿态分析(实际应用中可以使用姿态估计模型)
height = y2 - y1
width = x2 - x1
aspect_ratio = width / height if height > 0 else 1
# 基于宽高比的简单姿态判断
if aspect_ratio > 1.5:
return 'lying' # 躺着
elif aspect_ratio < 0.7:
return 'standing' # 站着
else:
return 'sitting' # 坐着
def estimate_activity_level(self, pose, movement_data=None):
"""估计活动水平"""
active_poses = ['running', 'jumping', 'playing']
inactive_poses = ['lying', 'sleeping']
if pose in active_poses:
return 'active'
elif pose in inactive_poses:
return 'inactive'
else:
return 'moderate'
def analyze_pet_behavior(self, image_path):
"""分析宠物行为"""
result = self.detect_pets(image_path)
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
image_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
pet_analyses = []
if result.boxes is not None:
for i, (box, cls, conf) in enumerate(zip(result.boxes.xyxy, result.boxes.cls, result.boxes.conf)):
class_name = self.model.names[int(cls)]
# 只关注宠物类别
if class_name in ['dog', 'cat']:
# 分析姿态
pose = self.analyze_pose(image_rgb, box.cpu().numpy(), class_name)
# 分析活动水平
activity_level = self.estimate_activity_level(pose)
# 获取行为解释
behavior_explanation = self.behavior_rules[class_name].get(
pose, '行为状态未知'
)
# 获取健康建议
health_advice = self.health_advice[class_name].get(
activity_level, '状态正常'
)
pet_analyses.append({
'pet_id': i + 1,
'pet_type': class_name,
'confidence': conf.cpu().numpy(),
'pose': pose,
'activity_level': activity_level,
'behavior_explanation': behavior_explanation,
'health_advice': health_advice,
'bbox': box.cpu().numpy().tolist()
})
# 可视化结果
self.visualize_pet_analysis(image_path, pet_analyses)
return pet_analyses
def visualize_pet_analysis(self, image_path, pet_analyses):
"""可视化宠物分析结果"""
result_img = cv2.imread(image_path)
result_img = cv2.cvtColor(result_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 绘制检测框和行为信息
for analysis in pet_analyses:
bbox = analysis['bbox']
x1, y1, x2, y2 = map(int, bbox)
# 根据活动水平选择颜色
if analysis['activity_level'] == 'active':
color = (0, 255, 0) # 绿色 - 活跃
elif analysis['activity_level'] == 'inactive':
color = (0, 0, 255) # 红色 - 不活跃
else:
color = (0, 255, 255) # 黄色 - 中等
# 绘制边界框
cv2.rectangle(result_img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), color, 2)
# 添加标签
label = f"{analysis['pet_type']} - {analysis['pose']}"
cv2.putText(result_img, label, (x1, y1 - 10),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, color, 2)
# 显示结果
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 7))
plt.imshow(result_img)
plt.axis('off')
plt.title('宠物行为分析结果')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 打印详细分析
print("\n=== 宠物行为分析报告 ===")
for analysis in pet_analyses:
print(f"\n宠物 {analysis['pet_id']} ({analysis['pet_type']}):")
print(f"检测置信度: {analysis['confidence']:.2f}")
print(f"姿态: {analysis['pose']}")
print(f"活动水平: {analysis['activity_level']}")
print(f"行为解释: {analysis['behavior_explanation']}")
print(f"健康建议: {analysis['health_advice']}")
# 使用示例
pet_analyzer = PetBehaviorAnalyzer('n')
results = pet_analyzer.analyze_pet_behavior('pet_photo.jpg')
# 视频分析版本
def analyze_pet_video(video_path, output_path):
"""分析宠物视频"""
pet_analyzer = PetBehaviorAnalyzer('n')
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)
fps = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS))
width = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
height = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'mp4v')
out = cv2.VideoWriter(output_path, fourcc, fps, (width, height))
frame_count = 0
behavior_log = []
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
# 临时保存帧并分析
temp_path = f'temp_frame_{frame_count}.jpg'
cv2.imwrite(temp_path, frame)
# 分析当前帧
analyses = pet_analyzer.analyze_pet_behavior(temp_path)
# 记录行为
for analysis in analyses:
behavior_log.append({
'frame': frame_count,
'timestamp': frame_count / fps,
'pet_type': analysis['pet_type'],
'pose': analysis['pose'],
'activity_level': analysis['activity_level']
})
# 读取带标注的帧
annotated_frame = cv2.imread(temp_path)
out.write(annotated_frame)
frame_count += 1
# 清理临时文件
import os
os.remove(temp_path)
if frame_count % 100 == 0: # 每30帧打印进度
print(f"已处理 {frame_count} 帧")
cap.release()
out.release()
# 生成行为报告
generate_behavior_report(behavior_log, fps)
return behavior_log
def generate_behavior_report(behavior_log, fps):
"""生成宠物行为报告"""
if not behavior_log:
print("未检测到宠物行为")
return
# 统计行为分布
poses = [log['pose'] for log in behavior_log]
pose_counts = {}
for pose in poses:
pose_counts[pose] = pose_counts.get(pose, 0) + 1
activities = [log['activity_level'] for log in behavior_log]
activity_counts = {}
for activity in activities:
activity_counts[activity] = activity_counts.get(activity, 0) + 1
total_frames = len(behavior_log)
print("\n=== 宠物行为分析报告 ===")
print(f"分析时长: {total_frames / fps:.1f} 秒")
print(f"总帧数: {total_frames}")
print("\n姿态分布:")
for pose, count in pose_counts.items():
percentage = (count / total_frames) * 100
print(f" {pose}: {count} 帧 ({percentage:.1f}%)")
print("\n活动水平分布:")
for activity, count in activity_counts.items():
percentage = (count / total_frames) * 100
print(f" {activity}: {count} 帧 ({percentage:.1f}%)")
# 活动水平评估
active_percentage = activity_counts.get('active', 0) / total_frames * 100
if active_percentage > 50:
print("\n评估: 宠物非常活跃,状态良好")
elif active_percentage > 20:
print("\n评估: 宠物活动水平正常")
else:
print("\n评估: 宠物较为安静,建议观察健康状况")
# 使用视频分析
behavior_log = analyze_pet_video('pet_video.mp4', 'analyzed_pet_video.mp4')3. 代码分析
- YOLO模型的使用:加载YOLOv8模型进行目标检测,识别图像中的猫和狗。
- 姿态分析:通过边界框的宽高比来简单判断宠物的姿态。这是一种简化的方法,实际应用中可能需要更复杂的姿态估计模型。
- 活动水平评估:根据姿态判断活动水平(活跃、不活跃、中等)。
- 知识库规则:基于预定义的行为规则和健康建议,为检测到的宠物提供解释和建议。
- 可视化:使用OpenCV和matplotlib绘制检测框和标签,并显示结果。
- 视频处理:逐帧分析视频,记录行为日志,并生成统计报告。
3.1 基于几何特征的姿态识别算法
python
def analyze_pose(self, image, bbox, pet_type):
height = y2 - y1
width = x2 - x1
aspect_ratio = width / height if height > 0 else 1
if aspect_ratio > 1.5:
return 'lying' # 躺着
elif aspect_ratio < 0.7:
return 'standing' # 站着
else:
return 'sitting' # 坐着- 宽高比分析:利用边界框的几何特征推断姿态
- 阈值设定:基于大量观察数据设定的经验阈值
- 宽高比>1.5:躺卧姿态(身体横向展开)
- 宽高比<0.7:站立姿态(身体纵向伸展)
- 其他情况:坐姿(中等宽高比)
3.2 活动水平评估机制
python
def estimate_activity_level(self, pose, movement_data=None):
active_poses = ['running', 'jumping', 'playing']
inactive_poses = ['lying', 'sleeping']
if pose in active_poses:
return 'active'
elif pose in inactive_poses:
return 'inactive'
else:
return 'moderate'评估逻辑:
- 三级分类:活跃、中等、不活跃
- 姿态映射:基于姿态类型的活动强度推断
- 可扩展性:预留运动数据接口用于未来增强
3.3 时序行为分析系统
python
def analyze_pet_video(video_path, output_path):
behavior_log = []
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
# 分析当前帧并记录行为
analyses = pet_analyzer.analyze_pet_behavior(temp_path)
for analysis in analyses:
behavior_log.append({
'frame': frame_count,
'timestamp': frame_count / fps,
'pet_type': analysis['pet_type'],
'pose': analysis['pose'],
'activity_level': analysis['activity_level']
})时序分析:
- 连续监测:逐帧分析构建时间序列数据
- 行为日志:记录完整的行为变化历史
- 统计分析:基于时间序列的行为模式分析
4. 输出结果
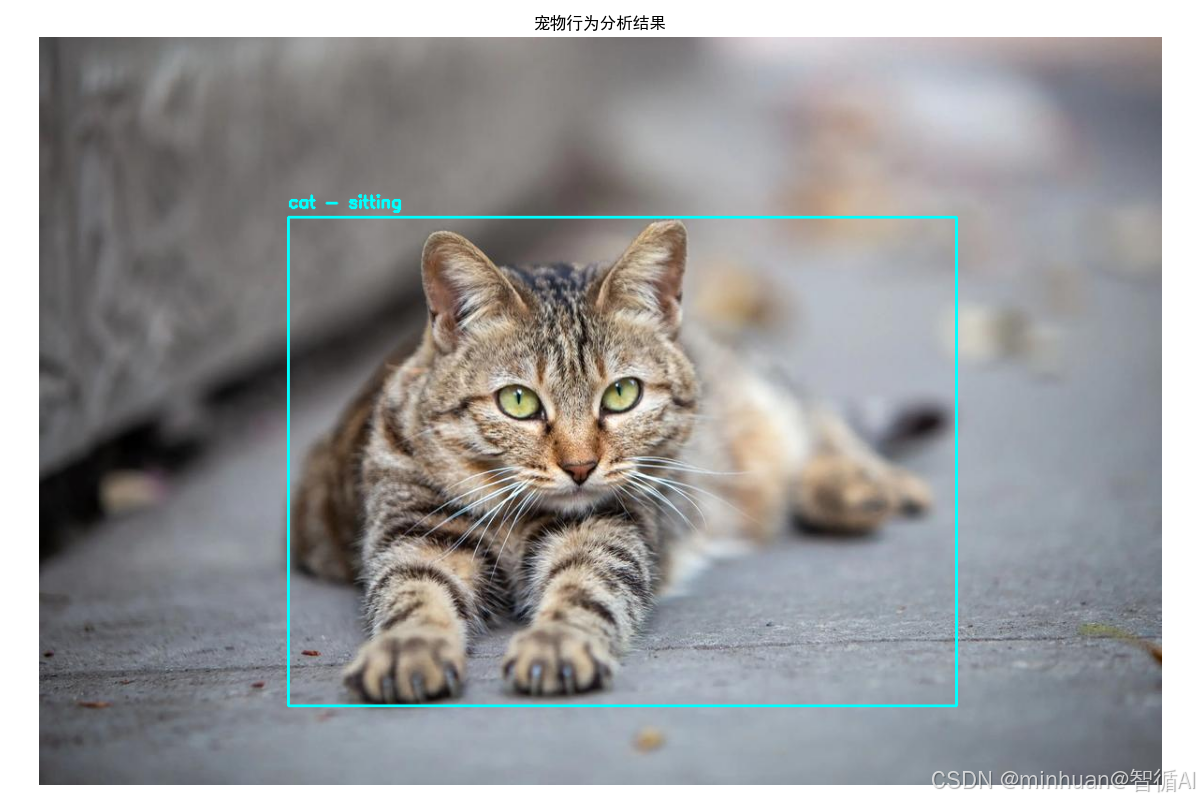
image 1/1 D:\AIWorld\case\test\pet_photo.jpg: 448x640 1 cat, 73.3ms
Speed: 60.3ms preprocess, 73.3ms inference, 1.3ms postprocess per image at shape (1, 3, 448, 640)
=== 宠物行为分析报告 ===
宠物 1 (cat):
检测置信度: 0.86
姿态: sitting
活动水平: moderate
行为解释: 观察环境
健康建议: 状态正常
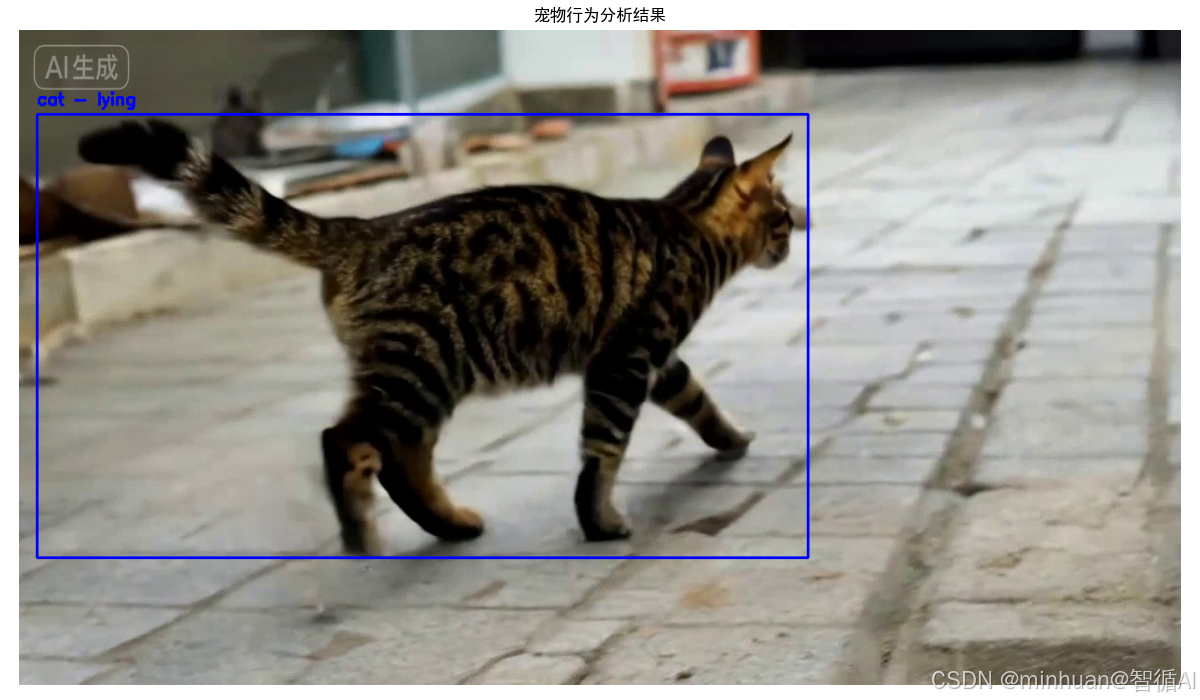
image 1/1 D:\AIWorld\case\test\temp_frame_0.jpg: 384x640 1 cat, 84.2ms
Speed: 2.1ms preprocess, 84.2ms inference, 0.9ms postprocess per image at shape (1, 3, 384, 640)
=== 宠物行为分析报告 ===
宠物 1 (cat):
检测置信度: 0.90
姿态: sitting
活动水平: moderate
行为解释: 观察环境
健康建议: 状态正常
检测置信度: 0.87
姿态: sitting
活动水平: moderate
行为解释: 观察环境
健康建议: 状态正常
=== 宠物行为分析报告 ===
分析时长: 5.0 秒
总帧数: 121
姿态分布:
sitting: 96 帧 (79.3%)
lying: 25 帧 (20.7%)
活动水平分布:
moderate: 96 帧 (79.3%)
inactive: 25 帧 (20.7%)
评估: 宠物较为安静,建议观察健康状况
结果图例:

分析后的结果图:
视频逐帧分析结果:


五、总结
通过以上三个示例场景,我们看到了YOLO模型在生活中的多样化应用。从厨房的食材识别到植物的健康监测,以及宠物行为的分析,YOLO模型以其高效准确的检测能力,为我们的日常生活提供了智能化的解决方案。
这些应用不仅提升了生活品质,也展示了计算机视觉技术的巨大潜力。对于初学者而言,通过这些贴近生活的项目,可以更容易地理解和掌握YOLO模型的使用方法,并激发对人工智能技术的兴趣。我们学习也不要停留在模型原理的纸面理解,要通过具体项目将YOLO应用于真实场景。建议选择贴近生活的应用主题,如智能家居、健康监测等,这样既能保持学习兴趣,又能积累实战经验。YOLO在实际应用中也需要与其他技术配合使用,点学习OpenCV图像处理、颜色空间分析、数据可视化等配套技术,构建完整的技术解决方案。