背景介绍
应用开发中的用户界面(UI)布局是用户与应用程序交互的关键部分。使用不同类型的布局可以将页面排布的更加美观,但也容易带来不合理的布局。不合理的布局虽然能在界面显示上达到相同效果,但是过度的布局计算,界面嵌套带来了渲染和计算的大量开销,造成性能的衰退,本文重点介绍了几种常见的布局功能和适用场景,同时提供了几种优化布局结构的方法。
常用布局
布局是UI的必要元素,它定义了组件在界面中的位置。ArkUI框架提供了多种布局方式,除了基础的线性布局(Row/Column)、层叠布局(Stack)、弹性布局(Flex)、相对布局(RelativeContainer)、栅格布局(GridRow/GridCol)外,也提供了相对复杂的列表(List)、网格(Grid/GridItem)、轮播(Swiper)。
优化布局结构
减少嵌套层级
布局的嵌套层次过深会导致在创建节点及进行布局时耗费更多时间。因此开发者在开发时,应避免冗余的嵌套或者使用扁平化布局来优化嵌套层次。
避免冗余的嵌套
冗余的嵌套会带来不必要的组件节点,加深组件树的层级。例如,内部容器和外部容器是相同的布局方向,内部容器形成的布局效果可以用外部容器代替,对于这类冗余的容器,应该尽量优化,减少嵌套深度。
反例:
使用了Grid来实现一个网格,但在外层套了3层包含不同属性参数的Stack容器:
@Entry
@Component
struct AspectRatioExample12 {
@State children: Number[] = Array.from(Array<number>(900), (v, k) => k);
build() {
Scroll() {
Grid() {
ForEach(this.children, (item: Number[]) => {
GridItem() {
Stack() {
Stack() {
Stack() {
Text(item.toString())
}.size({ width: "100%"})
}.backgroundColor(Color.Yellow)
}.backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
}
}, (item: string) => item)
}
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr 1fr 1fr')
.columnsGap(0)
.rowsGap(0)
.size({ width: "100%", height: "100%" })
}
}
}通过查看组件树结构,发现三层Stack容器设置了不同的属性参数,可以使用GridItem的属性参数实现同样的UI效果。因此,三层Stack容器是冗余的容器,可以去掉,只留下GridItem作为组件节点。
└─┬Scroll
└─┬Grid
├─┬GridItem
│ └─┬Stack
│ └─┬Stack
│ └─┬Stack
│ └──Text
├──GridItem
├──GridItem通过Trace图可以看到,创建页面耗时149ms左右。
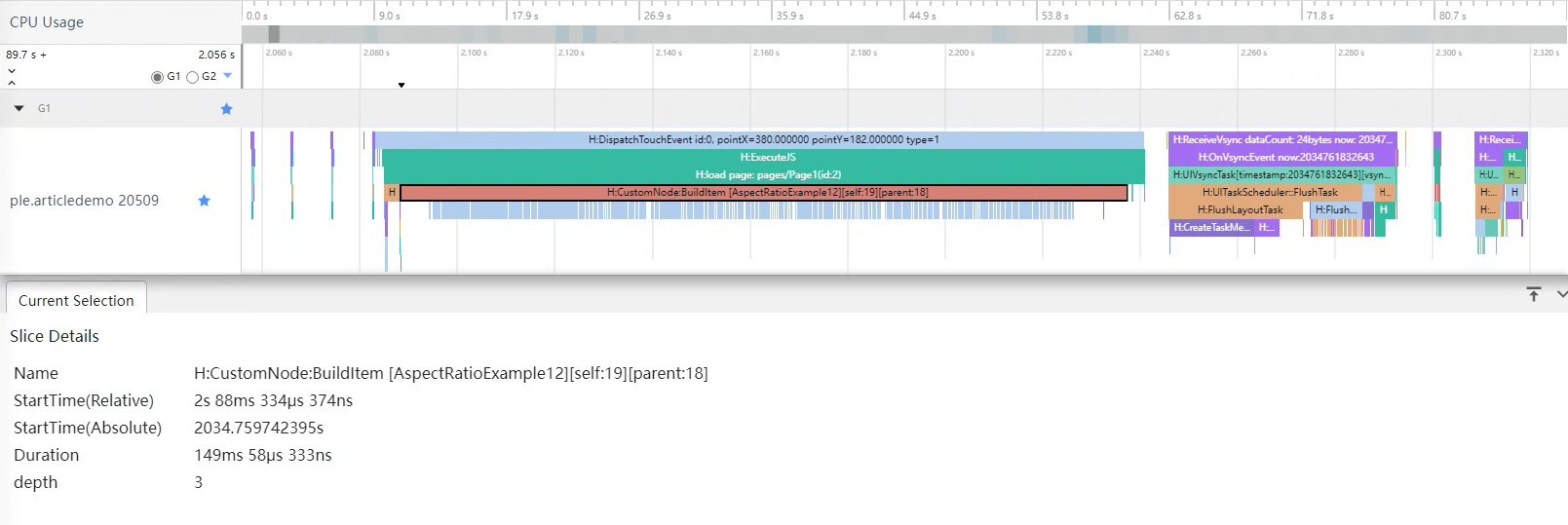
正例:
通过减少冗余的Stack容器嵌套,每个GridItem的组件数比上面少了3个:
@Entry
@Component
struct AspectRatioExample11 {
@State children: Number[] = Array.from(Array<number>(900), (v, k) => k);
build() {
Scroll() {
Grid() {
ForEach(this.children, (item: Number[]) => {
GridItem() {
Text(item.toString())
}.backgroundColor(Color.Yellow)
}, (item: string) => item)
}
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr 1fr 1fr')
.columnsGap(0)
.rowsGap(0)
.size({ width: "100%", height: "100%" })
}
}
}通过查看该组件树层级结构如下:
└─┬Scroll
└─┬Grid
├─┬GridItem
│ └──Text
├──GridItem
├──GridItem通过Trace图可以看到,创建页面耗时99ms左右,减少了大概33%的时间。
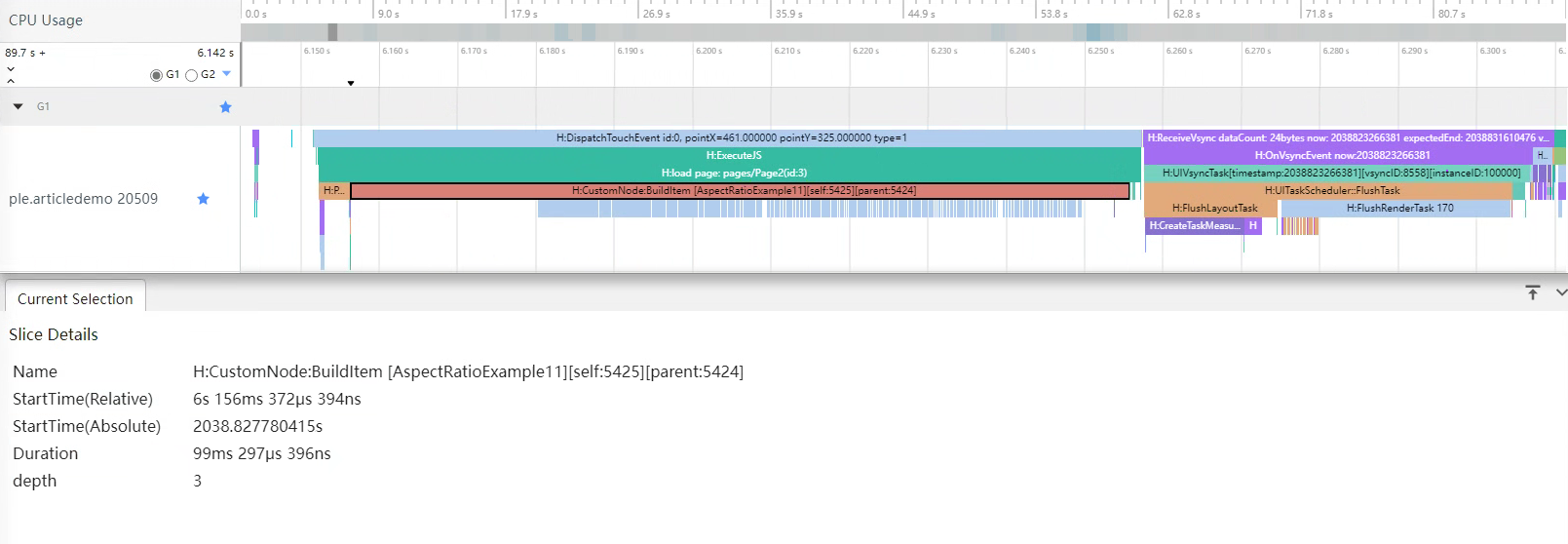
使用扁平化布局优化嵌套层级
开发者在实现自适应布局的时候,常使用Flex来达到弹性效果,这可能会造成多级嵌套。建议采用相对布局RelativeContainer进行扁平化布局,有效减少容器的嵌套层级,减少组件的创建时间。
例如,以下是一个自适应的效果:

反例:
下述代码使用线性布局实现以上UI:
@Entry
@Component
struct MyComponent3 {
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Flex({ justifyContent: FlexAlign.Center, alignItems: ItemAlign.Center }) {
Text('张')
// 属性参数见正例
}
.width("40vp")
.height("40vp")
}.height("100%").justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
//body
Flex({ direction: FlexDirection.Column, justifyContent: FlexAlign.Start }) {
Flex({ direction: FlexDirection.Column, justifyContent: FlexAlign.Center }) {
Flex({ direction: FlexDirection.Row,
justifyContent: FlexAlign.SpaceBetween, alignItems: ItemAlign.Center }) {
//Phone number or first name
Text('张三')
// 属性参数见正例
//Date Time
Text('2分钟前')
// 属性参数见正例
}
.width("100%").height(22)
Row() {
Text() {
//Content Abbreviations for Latest News
Span('Hello World'.replace(new RegExp("/[\r\n]/g"), " "))
.fontSize("14fp")
.fontColor('# 66182431')
}
.maxLines(1)
.textOverflow({ overflow: TextOverflow.Ellipsis })
}
.alignSelf(ItemAlign.Start)
.alignItems(VerticalAlign.Top)
.width("100%")
.height(19)
.margin({ top: "2vp" })
}.width("100%")
.height("100%")
}
.layoutWeight(1)
.height("100%")
.padding({ left: "12vp" })
}
.alignItems(VerticalAlign.Top)
.width("100%")
.height("100%")
}
}通过查看该组件树层级结构如下:
└─┬Row
├──┬Column
│ └─┬Flex
│ └──Text
└─┬Flex
└─┬Flex
│ └─┬Flex
│ ├──Text
│ └──Text
└─┬Row
└──Text通过Trace图,可以看到创建页面耗时3.5ms左右。
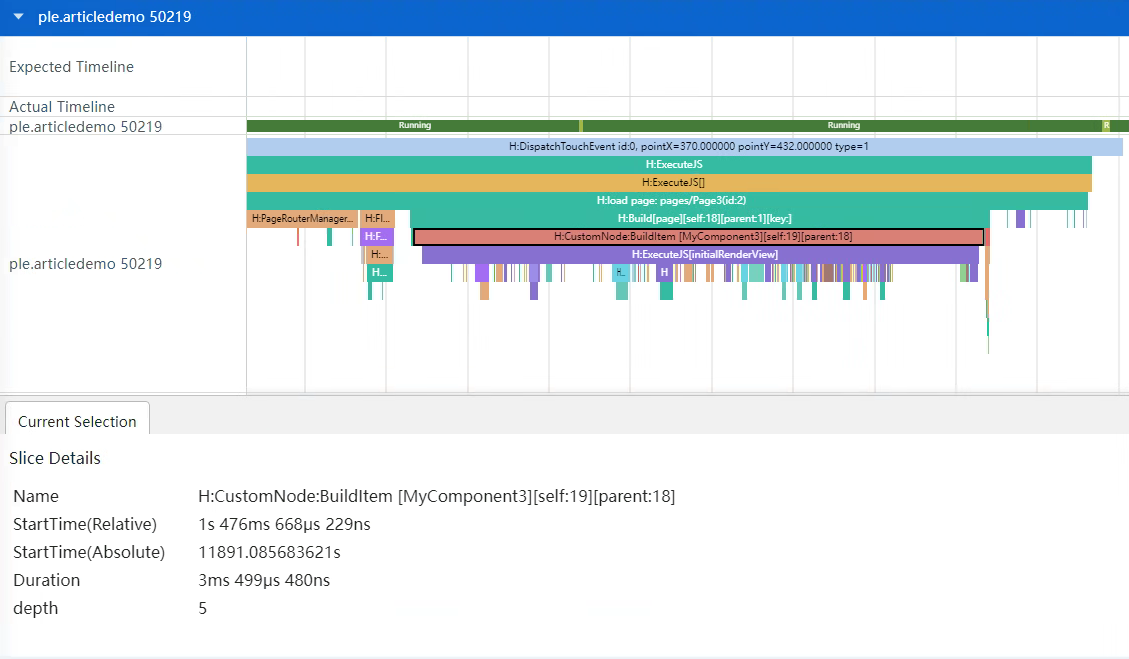
为了将4个元素放到合适的位置,开发者使用了11个组件,树深度为5,实际上是不合理的。
分析元素之间的布局关系可以得到如下:

正例:
从上图得到一个明确的相对布局位置关系,该场景可以使用相对布局的形式来优化,具体代码实现如下:
@Entry
@Component
struct MyComponent4 {
build() {
Row() {
RelativeContainer() {
Text('张')
.fontSize('20.0vp')
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.fontColor(Color.White)
.height('40vp')
.width('40vp')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
.clip(new Circle({ width: '40vp', height: '40vp' }))
.backgroundColor(Color.Green)
.alignRules({
center: { anchor: "__container__", align: VerticalAlign.Center },
left: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.Start }
})
.id('head')
Text('张三')
.fontSize('16.0fp')
.textOverflow({ overflow: TextOverflow.Ellipsis })
.fontColor('# ff182431')
.maxLines(1)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Medium)
.padding({ left: '12vp' })
.height(22)
.alignRules({
top: { anchor: 'head', align: VerticalAlign.Top },
left: { anchor: 'head', align: HorizontalAlign.End }
})
.id('name')
Text('2分钟前')
.fontColor('# 66182431')
.fontSize('12fp')
.maxLines(1)
.height(22)
.alignRules({
top: { anchor: 'head', align: VerticalAlign.Top },
right: { anchor: '__container__', align: HorizontalAlign.End }
})
.id("time")
Text() {
//Content Abbreviations for Latest News
Span('Hello World'.replace(new RegExp("/[\r\n]/g"), " "))
.fontSize('14fp')
.fontColor('# 66182431')
}
.maxLines(1)
.textOverflow({ overflow: TextOverflow.Ellipsis })
.width('100%')
.height(19)
.margin({ top: '2vp' })
.padding({ left: '12vp' })
.alignRules({
top: { anchor: 'name', align: VerticalAlign.Bottom },
left: { anchor: 'head', align: HorizontalAlign.End }
})
.id('content')
}
.width('100%').height('100%')
.border({ width: 1, color: "# 6699FF" })
}
.height('100%')
}
}通过减少嵌套层数后可以发现,布局实现了相同的效果,但是组件层级减少了3层,使用组件数也减少了6个。
└─┬RelativeContainer
├──Text
├──Text
├──Text
└──Text通过Trace图可以看到,创建页面耗时只有2.9ms左右,相较于反例代码,耗时减少了14%。
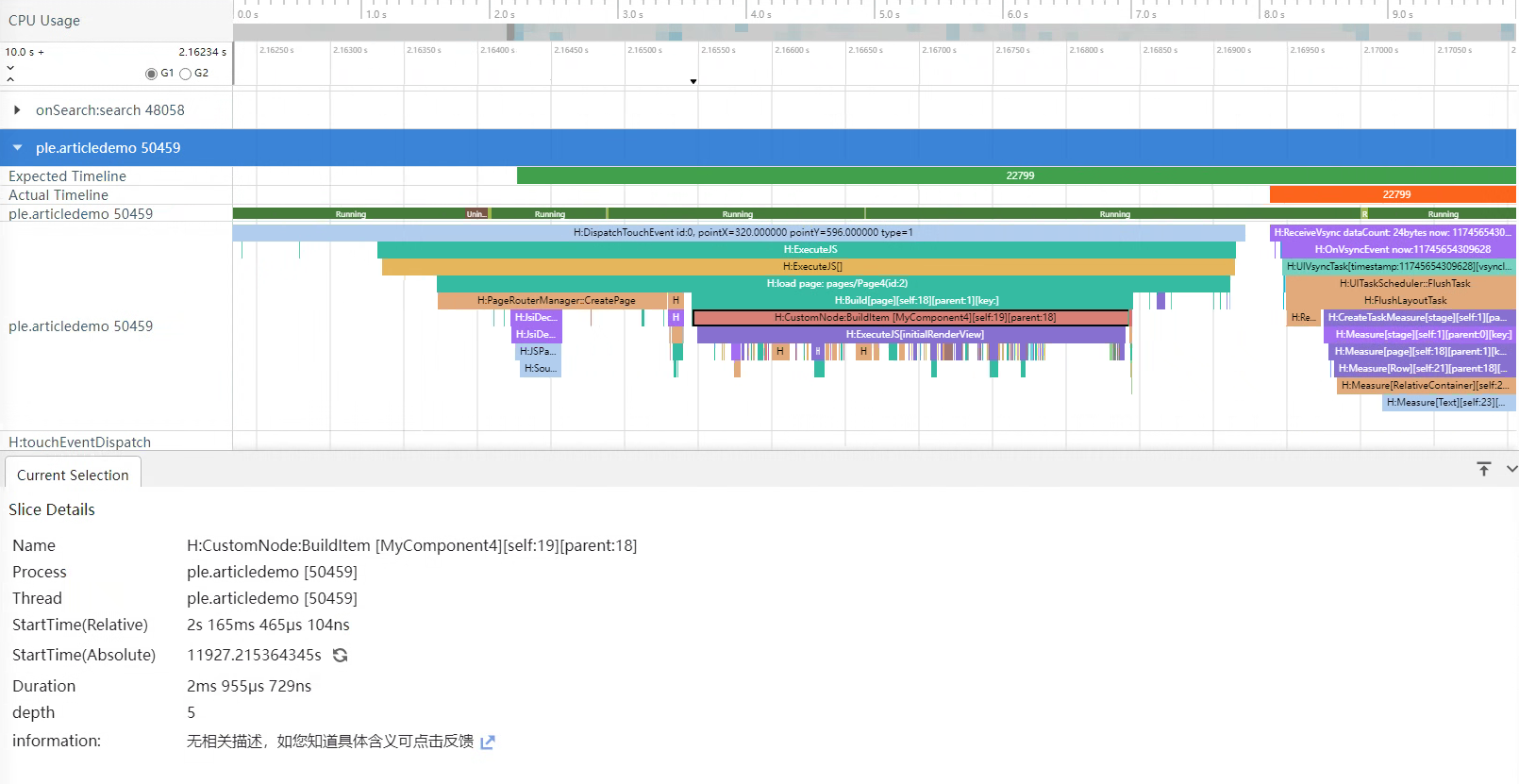
从上述案例中可以看到,使用扁平化布局逻辑概念设计更清晰,避免使用不参与绘制的布局组件,优化性能并减少占用内存。这种将一棵深度很高的UI树,改造为将内容排布到同一个节点下的思路,为扁平化布局。如下图所示,采用扁平化布局去除了中间冗余的两层布局节点。
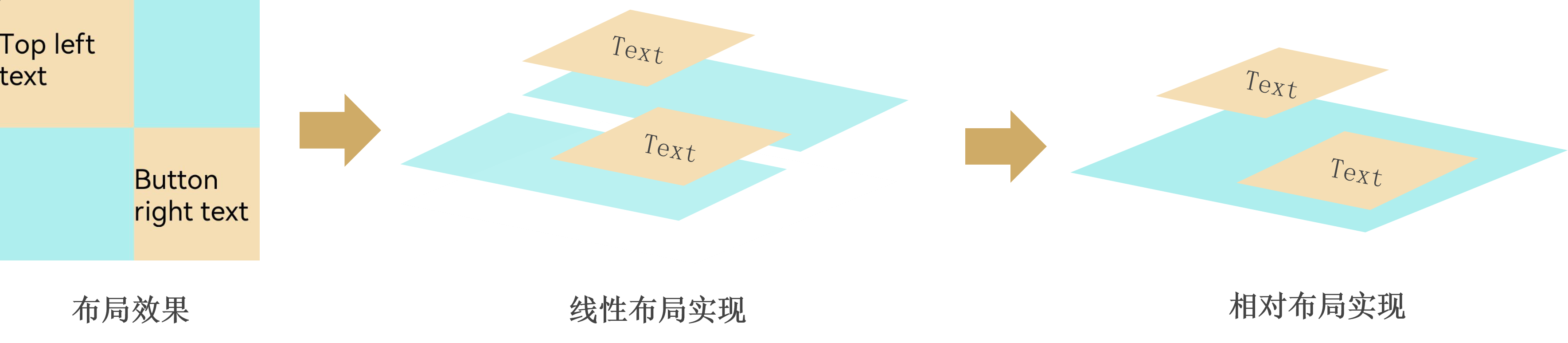
使用扁平化布局推荐使用RelativeContainer、绝对定位、自定义布局、Grid组件等
使用高性能布局组件
使用Column/Row替换Flex容器
如果使用Flex布局容器,只是为了实现横向或者纵向的布局。那直接使用Row、Column容器反而能够提升渲染性能。关于Flex带来的性能影响可以参考《Flex布局性能提升使用指导》。
使用Column、Row替换Flex容器组件避免二次渲染的案例见:《性能提升的其他方法》
适当减少使用if/else条件渲染
在ArkUI的build函数里,if/else也会被当成一个组件,在组件树上也是一个节点。对于一些在不同条件下展示不同效果的场景,基本布局不变,能够通过改变属性来进行控制界面变更的场景下,尽量减少if/else的方式来进行界面内容的切换,因为使用if/else不仅会增加一层节点,而且还有可能造成界面的重排与重绘。
反例:
下述代码中通过判断isVisible的值控制Image组件显示,这会导致在切换选择的过程中,不停创建和销毁Image组件元素。
@Entry
@Component
struct TopicItem {
@State isVisible : Boolean = true;
build() {
Stack() {
Column(){
if (this.isVisible) {
Image($r('app.media.icon')).width('25%').height('12.5%')
Image($r('app.media.icon')).width('25%').height('12.5%')
Image($r('app.media.icon')).width('25%').height('12.5%')
Image($r('app.media.icon')).width('25%').height('12.5%')
}
}
Column() {
Row().width(300).height(200).backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
}
}
}
}下图为isVisible值不同时组件树的情况:
isVisible为true:
└─┬Stack
├─┬Column
│ ├──Image
│ ├──Image
│ ├──Image
│ └──Image
└─┬Column
└──Row
isVisible为false:
└─┬Stack
├──Column
└─┬Column
└──Row正例:
下面例子通过visibility属性来控制图片的显隐,避免if/else条件渲染可能带来的重排与重绘。
@Entry
@Component
struct TopicItem {
@State isVisible : Boolean = true;
build() {
Stack() {
Column(){
Image($r('app.media.icon'))
.width('25%').height('12.5%').visibility(this.isVisible ? Visibility.Visible : Visibility.None)
Image($r('app.media.icon'))
.width('25%').height('12.5%').visibility(this.isVisible ? Visibility.Visible : Visibility.None)
Image($r('app.media.icon'))
.width('25%').height('12.5%').visibility(this.isVisible ? Visibility.Visible : Visibility.None)
Image($r('app.media.icon'))
.width('25%').height('12.5%').visibility(this.isVisible ? Visibility.Visible : Visibility.None)
}
Column() {
Row().width(300).height(200).backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
}
}
}
}说明:上述情况考虑的是性能优先的场景,而当开发者优先考虑内存时,建议使用if/else控制图片的显隐。
优化布局时间
布局的嵌套层次过深会导致在创建节点及进行布局时耗费更多时间。因此开发者在开发时,应避免冗余的嵌套或者使用扁平化布局来优化嵌套层次。
反例:
@Entry
@Component
struct PerformanceRelative {
@State message: string = 'Hello World'
@State textWidth: string = "";
build() {
Column() {
Image($r("app.media.app_icon")).width("100%").height(300).margin({ bottom: 20 })
Row() {
Blank()
Column() {
Image($r("app.media.app_icon")).margin({ bottom: 4 }).width(40).aspectRatio(1)
Text("Name")
}.margin({ left: 8, right: 8 })
}.position({ y: 280 }).width("100%")
// Empty row
Row().height(this.textWidth)
Column() {
Row() {
Text("Singapore").fontSize(20).fontWeight(FontWeight.Bolder)
.margin(8)
.textAlign(TextAlign.Start)
}.width("100%").justifyContent(FlexAlign.Start)
Flex({ alignItems: ItemAlign.Center }) {
Text("Camera").flexShrink(0)
.margin({ right: 8 })
TextInput()
}.margin(8)
Flex({ alignItems: ItemAlign.Center }) {
Text("Settings").flexShrink(0)
.margin({ right: 8 })
TextInput()
}.margin(8)
Row() {
Column() {
Image($r("app.media.app_icon")).width(80).aspectRatio(1).margin({ bottom: 8 })
Text("Description")
}.margin(8)
Column() {
Text("Title").fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold).margin({ bottom: 8 })
Text("Long Text")
}.margin(8).layoutWeight(1).alignItems(HorizontalAlign.Start)
}.margin(8).width("100%").alignItems(VerticalAlign.Top)
}.layoutWeight(1)
Flex({ justifyContent: FlexAlign.End }) {
Button("Upload").margin(8)
Button("Discard").margin(8)
}
}
.width("100%").height("100%")
}
}通过Trace图可以看到,使用线性布局时,从创建到布局完成,耗时大概是103.89ms。
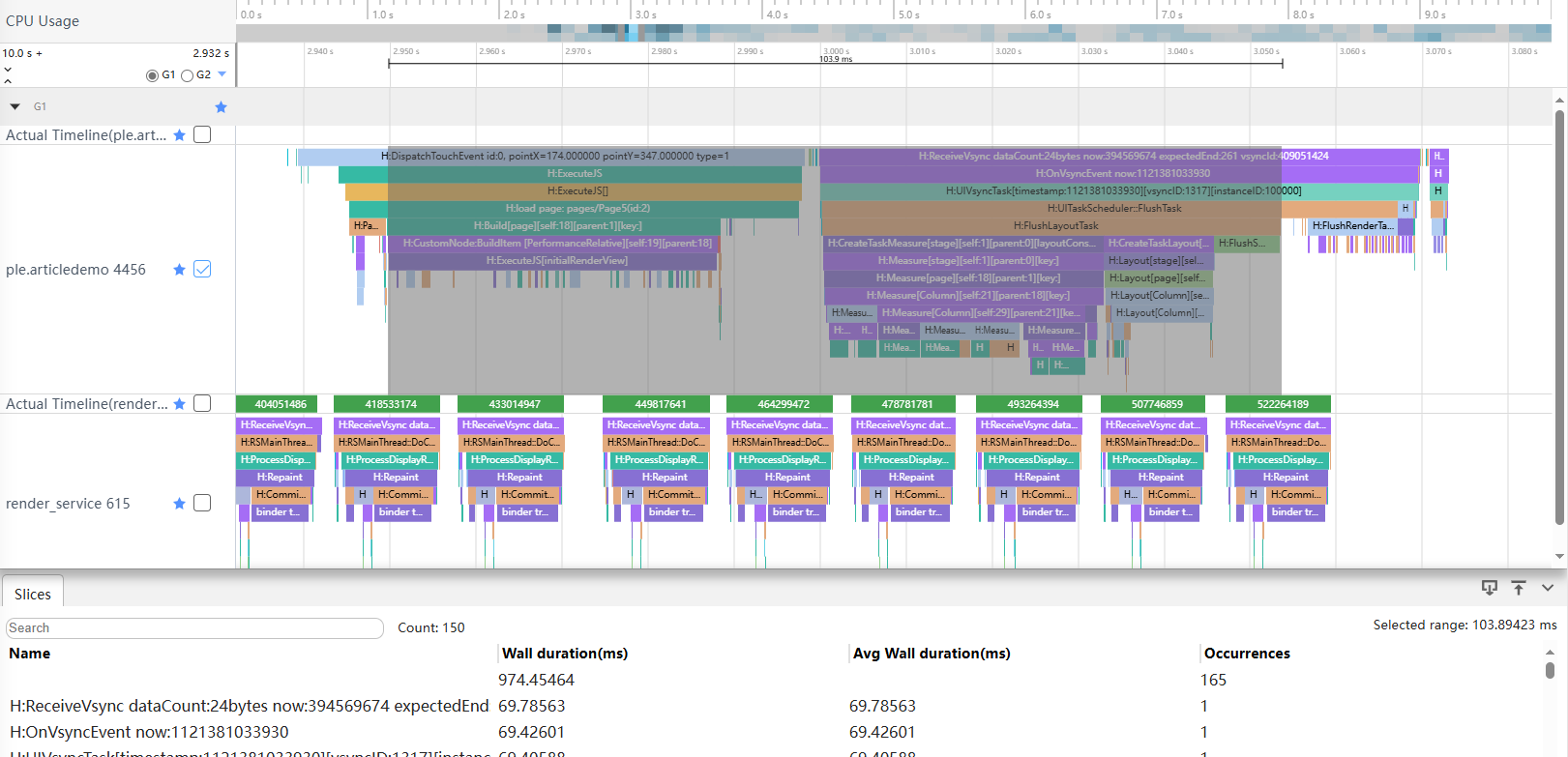
正例:
@Entry
@Component
struct RelativePerformance {
@State message: string = 'Hello World'
build() {
RelativeContainer(){
Image($r("app.media.app_icon"))
.height(300)
.width("100%")
.id("topImage")
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
top: {anchor: "__container__", align: VerticalAlign.Top }
})
Image($r("app.media.app_icon"))
.width(40)
.aspectRatio(1)
.margin(4)
.id("topCornerImage")
.alignRules({
right: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
center: {anchor: "topImage", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
})
Text("Name")
.id("name")
.margin(4)
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "topCornerImage", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
top: {anchor: "topCornerImage", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
})
Text("Singapore")
.margin(8)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bolder)
.fontSize(20)
.id("singapore")
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
top: {anchor: "name", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
})
Text("Camera")
.margin(8)
.id("camera")
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
top: {anchor: "singapore", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
})
TextInput()
.id("cameraInput")
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "camera", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
right:{ anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
top: {anchor: "camera", align: VerticalAlign.Top },
bottom: { anchor: "camera", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
})
Text("Settings")
.margin(8)
.id("settings")
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
top: {anchor: "camera", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
})
TextInput()
.id("settingInput")
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "settings", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
right:{ anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
top: {anchor: "settings", align: VerticalAlign.Top },
bottom: { anchor: "settings", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
})
Image($r("app.media.app_icon"))
.id("descriptionIcon")
.margin(8)
.width(80)
.aspectRatio(1)
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
top: {anchor: "settings", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
})
Text("Description")
.id("description")
.margin(8)
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
top: {anchor: "descriptionIcon", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
})
Text("Title")
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.id("title")
.margin(8)
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "description", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
top: {anchor: "descriptionIcon", align: VerticalAlign.Top }
})
Text("Long Text")
.id("longText")
.margin(8)
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "description", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
right: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
top: {anchor: "title", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
})
Button("Discard")
.id("discard")
.margin(8)
.alignRules({
right: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
bottom: {anchor: "__container__", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
})
Button("Upload")
.id("upload")
.margin(8)
.alignRules({
right: { anchor: "discard", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
bottom: {anchor: "__container__", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
})
}.width("100%").height("100%")
}
}使用相对布局实现上述界面,减少了组件的嵌套深度以及组件个数,从创建到布局完成耗时69.97ms,相对于线性布局,减少了30%左右。

应用节点数优化
自定义组件引起新增节点
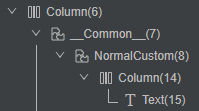
自定义组件自身为非渲染节点,仅是组件树和状态数据的组合。因此常规使用自定义组件时并不会产生多余的节点。但是当自定义组件自身设置通用属性后,会作为一个整体节点进行处理。此时,在自定义组件内部会创建一个__Common__节点,用于对内部的组件树进行操作,如背景色绘制、圆角绘制等指令,都会作用在该节点上,此时会出现多一个节点的问题。
反例
创建自定义组件NormalCustom,在页面中调用时添加全局属性height、width、backgroundColor。
@Entry
@Component
struct CustomComponentNormal {
build() {
Column() {
NormalCustom()
.height(100)
.width(100)
.backgroundColor(Color.Blue)
}
}
}
@Component
struct NormalCustom {
build() {
Column() {
Text('Hello Word')
}
}
}通过DevEco Studio内置ArkUI Inspector工具,查看组件树结构,会发现在自定义组件的外部,会多出一层__Common__节点。如图1所示。通常情况下,可以通过将属性设置内移的方式减少这一层节点。但是在应用开发中,会遇到需要给整个自定义组件设置统一属性的需求,如果将所有的属性设置都内移,就会出现传递参数过多的问题,同时也会创建更多状态变量,并且增加参数的传递耗时。虽然降低了节点数量,但是却牺牲了性能。
图1 常规设置自定义组件全局属性
正例
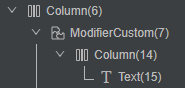
ArkUI提供了动态属性设置(Modifier)的接口,支持使用自定义Modifier构建组件并配置属性。
@Entry
@Component
struct CustomComponentModifier {
modifier: ColumnModifier = new ColumnModifier();
aboutToAppear(): void {
this.modifier.width = 100;
this.modifier.height = 100;
this.modifier.backgroundColor = Color.Red;
}
build() {
Column() {
ModifierCustom({ modifier: this.modifier })
}
}
}
@Component
struct ModifierCustom {
@Require @Prop modifier: AttributeModifier<ColumnAttribute>;
build() {
Column() {
Text('Hello Word')
}.attributeModifier(this.modifier)
}
}
// 使用动态属性设置时,需要继承AttributeModifier,自行实现一个Modifier,然后设置到需要的组件上
class ColumnModifier implements AttributeModifier<ColumnAttribute> {
width: number = 0;
height: number = 0;
backgroundColor: ResourceColor | undefined = undefined;
applyNormalAttribute(instance: ColumnAttribute): void {
instance.width(this.width);
instance.height(this.height);
instance.backgroundColor(this.backgroundColor);
}
}通过DevEco Studio内置ArkUI Inspector工具,查看组件树结构,会发现在自定义组件的外部并没有多出__Common__节点。如图2所示。
图2 使用Modifier设置自定义组件全局属性
布局嵌套场景
在应用代码中,由于业务需求,经常会出现布局嵌套的情况。
反例
通常情况下,会使用Stack布局,将一个组件覆盖到另一个组件上。
@Entry
@Component
struct ComponentStackNormal {
build() {
Column() {
Stack() {
Image($r('app.media.image_1'))
.objectFit(ImageFit.Contain)
Text("This is overlayNode")
.fontSize(20)
.fontColor(Color.Black)
}
}
}
}通过DevEco Studio内置ArkUI Inspector工具,查看组件树结构,如图3所示。
图3 使用Stack实现遮罩效果
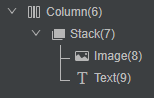
正例
ArkUI提供了overlay接口,可以直接给组件添加一个无交互、无动画场景的浮层,实现堆叠的效果。
@Entry
@Component
struct ComponentStackOverlay {
@Builder
OverlayNode() {
Text("This is overlayNode").fontSize(20).fontColor(Color.Black)
}
build() {
Column() {
Image($r('app.media.image_1'))
.overlay(this.OverlayNode(), { align: Alignment.Center })
.objectFit(ImageFit.Contain)
}
}
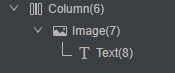
}通过DevEco Studio内置ArkUI Inspector工具,查看组件树结构,如图4所示。和反例中的代码相比,虽然组件树层数相同,但是减少了Stack组件的创建,优化了性能。
按压态效果
反例
应用为了实现按压遮罩效果,通常需要使用Stack,在组件上方增加遮罩层。
@Entry
@Component
struct MaskNormal {
build() {
Column() {
GrayScaleNormalCustom({ isGrayIcon: true })
}
}
}
@Component
struct GrayScaleNormalCustom {
@State isGrayIcon: boolean = true;
build() {
Stack() {
Column()
.width('90%')
.height(150)
.backgroundImage($r('app.media.image_1'))
Column()
.width('90%')
.height(150)
.backgroundColor(Color.Grey)
.opacity(this.isGrayIcon ? 0.5 : 0)
}
}
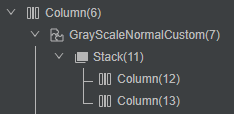
}通过DevEco Studio内置ArkUI Inspector工具,查看组件树结构,如图5所示。
图5 常规遮罩实现
正例
可以通过组件效果实现遮罩,而非直接通过组件实现。
@Entry
@Component
struct MaskGrayScale {
build() {
Column() {
GrayScaleCustom({ isGrayIcon: true })
}
}
}
@Component
struct GrayScaleCustom {
@State isGrayIcon: boolean = true;
build() {
Column()
.width('90%')
.height(150)
.backgroundImage($r('app.media.image_1'))
.grayscale(this.isGrayIcon ? 0.5 : 0)
}
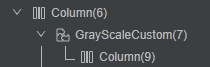
}通过DevEco Studio内置ArkUI Inspector工具,查看组件树结构,如图6所示,可以减少一层Stack组件的创建。
图6 通过组件效果实现遮罩
颜色叠加效果
在应用开发中,有使用到颜色叠加显示的需求。通常情况下,会通过将2个组件放在Stack中叠加的方式实现,这样不仅会多出一层布局节点,还会因为绘制了两个除颜色外其他属性都相同的组件导致了重复绘制。
反例
@Component
struct ColorNormal {
@Prop isSelected: boolean = false;
build() {
Stack() {
Column()
.width('100%')
.height(100)
.backgroundColor(this.isSelected ? Color.Blue : Color.Grey)
.borderRadius(12)
.alignItems(HorizontalAlign.Center)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
Column()
.width('100%')
.height(100)
.backgroundColor(this.isSelected ? "#99000000" : Color.Grey)
.borderRadius(12)
.alignItems(HorizontalAlign.Center)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
}
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State isSelected: boolean = false;
build() {
Scroll() {
Column() {
ColorNormal({ isSelected: this.isSelected })
.onClick(() => {
this.isSelected = !this.isSelected;
})
}
}
}
}通过DevEco Studio内置ArkUI Inspector工具,查看组件树结构,如图7所示。
图7
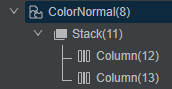
正例
系统中提供了颜色计算的API,可以通过计算的方式,将两个颜色合并为一个,省去Stack层的布局节点,并且可以少绘制一个组件,减少重复绘制的情况发生。
@Component
struct ColorMeasure {
@Prop isSelected: boolean = false;
build() {
Column()
.width('100%')
.height(100)
.backgroundColor(this.isSelected ? this.getBlendColor(Color.Blue, "#99000000").color : Color.Grey)
.borderRadius(12)
.alignItems(HorizontalAlign.Center)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
}
getBlendColor(baseColor: ResourceColor, addColor: ResourceColor): ColorMetrics {
let sourceColor: ColorMetrics;
try {
sourceColor = ColorMetrics.resourceColor(baseColor).blendColor(ColorMetrics.resourceColor(addColor));
} catch (error) {
console.log("getBlendColor failed, code = " + (error as BusinessError).code + ", message = " +
(error as BusinessError).message);
sourceColor = ColorMetrics.resourceColor(addColor);
}
return sourceColor;
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State isSelected: boolean = false;
build() {
Scroll() {
Column() {
ColorMeasure({ isSelected: this.isSelected })
.onClick(() => {
this.isSelected = !this.isSelected;
})
}
}
}
}通过DevEco Studio内置ArkUI Inspector工具,查看组件树结构,如图8所示。
图8
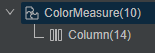
优化布局工具介绍
DevEco Studio内置ArkUI Inspector工具,开发者可以使用ArkUI Inspector,在DevEco Studio上查看应用在真机上的UI显示效果。利用ArkUI Inspector工具,开发者可以快速定位布局不理想或其他UI相关问题,同时也可以观察和了解不同组件之间的布局关系和属性。
最后
小编在之前的鸿蒙系统扫盲中,有很多朋友给我留言,不同的角度的问了一些问题,我明显感觉到一点,那就是许多人参与鸿蒙开发,但是又不知道从哪里下手,因为资料太多,太杂,教授的人也多,无从选择。有很多小伙伴不知道学习哪些鸿蒙开发技术?不知道需要重点掌握哪些鸿蒙应用开发知识点?而且学习时频繁踩坑,最终浪费大量时间。所以有一份实用的鸿蒙(HarmonyOS NEXT)文档用来跟着学习是非常有必要的。
为了确保高效学习,建议规划清晰的学习路线,涵盖以下关键阶段:
希望这一份鸿蒙学习文档能够给大家带来帮助~
鸿蒙(HarmonyOS NEXT)最新学习路线

该路线图包含基础技能、就业必备技能、多媒体技术、六大电商APP、进阶高级技能、实战就业级设备开发,不仅补充了华为官网未涉及的解决方案
路线图适合人群:
IT开发人员: 想要拓展职业边界
零基础小白: 鸿蒙爱好者,希望从0到1学习,增加一项技能。
**技术提升/进阶跳槽:**发展瓶颈期,提升职场竞争力,快速掌握鸿蒙技术
2.视频教程+学习PDF文档
(鸿蒙语法ArkTS、TypeScript、ArkUI教程......)

纯血版鸿蒙全套学习文档(面试、文档、全套视频等)
鸿蒙APP开发必备

总结
参与鸿蒙开发,你要先认清适合你的方向,如果是想从事鸿蒙应用开发方向的话,可以参考本文的学习路径,简单来说就是:为了确保高效学习,建议规划清晰的学习路线 