测试命令
java jar .\ZookeeperDemo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar bTest 192.168.206.100:2181 2
1. Barrier(阻塞原语)
1.1 概念
!quote\] A barrier is a primitive that enables a group of processes to synchronize the beginning and the end of a computation. The general idea of this implementation is to have a barrier node that serves the purpose of being a parent for individual process nodes. Suppose that we call the barrier node "/b1". Each process "p" then creates a node "/b1/p". Once enough processes have created their corresponding nodes, joined processes can start the computation.
- 阻塞是一个原语,它使一组进程能够同时开始计算。此实现的总体思想是拥有一个屏障节点,用于作为单个流程节点的父节点。
- 假设我们将障碍节点称为"/b1"。然后,每个进程" p"创建一个节点"/b1/p"。一旦有足够多的进程创建了相应的节点,联合进程就可以开始计算了。
- 场景:当有些操作需要所有参与者全部准备好之后才能开始执行,并且对每个参与者来说必须等待所有参与者全部执行完毕,才算执行完毕。于是就需要一个屏障,来控制所有参与者同时开始,并等待所有参与者全部结束。
1.2 设计
- 创建一个/b1的znode的持久化节点。
- enter() 模拟往阻塞里增加执行进程(Join barrier)。往znode下增加子节点,并判断子节点数是否满足指定的个数n。若未满足条件则继续等待;反之则返回true。
- leave() 模拟进程执行完毕后的离开(Wait until all reach barrier)。删除znode的子节点,并判断子节点是否大于0,若大于0则表示还有子进程没有执行完。
源码:
java
package com.agileluo.zookeeperdemo.barriers;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
import java.lang.Integer;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.RandomStringUtils;
import org.apache.zookeeper.CreateMode;
import org.apache.zookeeper.KeeperException;
import org.apache.zookeeper.WatchedEvent;
import org.apache.zookeeper.Watcher;
import org.apache.zookeeper.ZooKeeper;
import org.apache.zookeeper.ZooDefs.Ids;
import org.apache.zookeeper.data.Stat;
/**
* 1. Queue test * 1.1 Start a producer to create 100 elements * java SyncPrimitive qTest localhost 100 p * 1.2 Start a consumer to consume 100 elements * java SyncPrimitive qTest localhost 100 c * * 2.Barrier test * Start a barrier with 2 participants (start as many times as many participants you'd like to enter) * java SyncPrimitive bTest localhost 2 */public class SyncPrimitive implements Watcher {
static ZooKeeper zk = null;
static Integer mutex;
String root;
static{
System.setProperty("zookeeper.sasl.client", "false");
}
SyncPrimitive(String address) {
if(zk == null){
try {
System.out.println("Starting ZK:");
zk = new ZooKeeper(address, 3000, this);
mutex = Integer.parseInt("-1");
System.out.println("Finished starting ZK: " + zk);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
zk = null;
}
}
//else mutex = new Integer(-1);
}
synchronized public void process(WatchedEvent event) {
synchronized (mutex) {
//System.out.println("Process: " + event.getType());
mutex.notify();
}
}
/**
* Barrier(阻塞原语)
* A barrier is a primitive that enables a group of processes to synchronize the beginning and the end of a computation. The general idea of this implementation is to
* have a barrier node that serves the purpose of being a parent for individual process nodes. Suppose that we call the barrier node "/b1". Each process
* "p" then creates a node "/b1/p". Once enough processes have created their corresponding nodes, joined processes can start the computation.
* 阻塞是一个原语,它使一组进程能够同时开始计算。此实现的总体思想是拥有一个屏障节点,用于作为单个流程节点的父节点。
* 假设我们将障碍节点称为"/b1"。然后,每个进程" p"创建一个节点"/b1/p"。一旦有足够多的进程创建了相应的节点,联合进程就可以开始计算了。
* 场景:当有些操作需要所有参与者全部准备好之后才能开始执行,并且对每个参与者来说必须等待所有参与者全部执行完毕,才算执行完毕。于是就需要一个屏障,来控制所有参与者同时开始,并等待所有参与者全部结束。
*/
static public class Barrier extends SyncPrimitive {
//需要并行等待的子进程个数
int size;
/**
* 本参与者对应的子节点path
*/ String name;
/**
* Barrier constructor * * @param address
* @param root
* @param size
*/
Barrier(String address, String root, int size) {
super(address);
this.root = root;
this.size = size;
// Create barrier node(障碍节点必须是持久节点 CreateMode.PERSISTENT)
if (zk != null) {
try {
Stat s = zk.exists(root, false);
if (s == null) { // 如果根节点不存在,则创建
/**
* zk.create(String path, byte[] data, List<ACL> acl, CreateMode createMode) * 第1个参数: barrier节点的path
* 第2个参数: barrier节点的data
* 第3个参数: barrier节点的权限
* 第4个参数: barrier 节点的类型,持久节点 CreateMode.PERSISTENT,子节点必须是临时节点。
*/
zk.create(root, new byte[0], Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE,
CreateMode.PERSISTENT);
}
} catch (KeeperException e) {
System.out
.println("Keeper exception when instantiating queue: "
+ e.toString());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("Interrupted exception");
}
}
// My node name
try {
name = new String(InetAddress.getLocalHost().getCanonicalHostName().toString()+ ":"+ RandomStringUtils.randomAlphabetic(4));
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
}
/**
* Join barrier * * @return * @throws KeeperException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
boolean enter() throws KeeperException, InterruptedException{
zk.create(root + "/" + name, new byte[0], Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE,
CreateMode.EPHEMERAL); // EPHEMERAL 临时节点
while (true) {
synchronized (mutex) {
List<String> list = zk.getChildren(root, true);
if (list.size() < size) { //判断当前根下子节点的数量,若数量小于设定的进程数,则等待。
mutex.wait();
} else {
return true;
}
}
}
}
/**
* Wait until all reach barrier * * @return * @throws KeeperException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
boolean leave() throws KeeperException, InterruptedException{
zk.delete(root + "/" + name, 0); //模拟进程完成任务,删除子节点。
while (true) {
synchronized (mutex) {
List<String> list = zk.getChildren(root, true);
if (list.size() > 0) { //只要还存在子节点,就说明还有任务没有完成。
mutex.wait();
} else {
return true;
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* Producer-Consumer queue */ static public class Queue extends SyncPrimitive {
/**
* Constructor of producer-consumer queue * * @param address
* @param name
*/
Queue(String address, String name) {
super(address);
this.root = name;
// Create ZK node name
if (zk != null) {
try {
Stat s = zk.exists(root, false);
if (s == null) {
zk.create(root, new byte[0], Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE,
CreateMode.PERSISTENT);
}
} catch (KeeperException e) {
System.out
.println("Keeper exception when instantiating queue: "
+ e.toString());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("Interrupted exception");
}
}
}
/**
* Add element to the queue. * * @param i
* @return
*/
boolean produce(int i) throws KeeperException, InterruptedException{
ByteBuffer b = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
byte[] value;
// Add child with value i
b.putInt(i);
value = b.array();
zk.create(root + "/element", value, Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE,
CreateMode.PERSISTENT_SEQUENTIAL);
return true;
}
/**
* Remove first element from the queue. * * @return * @throws KeeperException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
int consume() throws KeeperException, InterruptedException{
int retvalue = -1;
Stat stat = null;
// Get the first element available
while (true) {
synchronized (mutex) {
List<String> list = zk.getChildren(root, true);
if (list.size() == 0) {
System.out.println("Going to wait");
mutex.wait();
} else {
Integer min = Integer.parseInt((list.get(0).substring(7)));
String minNode = list.get(0);
for(String s : list){
Integer tempValue = Integer.parseInt(s.substring(7));
//System.out.println("Temporary value: " + tempValue);
if(tempValue < min) {
min = tempValue;
minNode = s;
}
}
System.out.println("Temporary value: " + root + "/" + minNode);
byte[] b = zk.getData(root + "/" + minNode,
false, stat);
zk.delete(root + "/" + minNode, 0);
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(b);
retvalue = buffer.getInt();
return retvalue;
}
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
if (args[0].equals("qTest"))
queueTest(args);
else
barrierTest(args);
}
public static void queueTest(String args[]) {
Queue q = new Queue(args[1], "/app1");
System.out.println("Input: " + args[1]);
int i;
Integer max = Integer.parseInt(args[2]+"");
if (args[3].equals("p")) {
System.out.println("Producer");
for (i = 0; i < max; i++)
try{
q.produce(10 + i);
} catch (KeeperException e){
} catch (InterruptedException e){
}
} else {
System.out.println("Consumer");
for (i = 0; i < max; i++) {
try{
int r = q.consume();
System.out.println("Item: " + r);
} catch (KeeperException e){
i--;
} catch (InterruptedException e){
}
}
}
}
public static void barrierTest(String args[]) {
Barrier b = new Barrier(args[1], "/b1", Integer.parseInt(args[2]+""));
try{
boolean flag = b.enter();
System.out.println("Entered barrier: " + args[2]);
if(!flag) System.out.println("Error when entering the barrier");
} catch (KeeperException e){
} catch (InterruptedException e){
}
// Generate random integer
Random rand = new Random();
int r = rand.nextInt(100);
// Loop for rand iterations
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
try{
b.leave();
} catch (KeeperException e){
} catch (InterruptedException e){
}
System.out.println("Left barrier");
}
}1.3 测试步骤
- 第1步,打包 ZookeeperDemo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
xml
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-jar-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<archive>
<manifest>
<addClasspath>true</addClasspath>
<mainClass>com.xx.zookeeperdemo.barriers.SyncPrimitive</mainClass>
</manifest>
</archive>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>- 第2步,jar包目录下打开命令窗口,并执行 java -jar .\ZookeeperDemo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar bTest 192.168.206.100:2181 3
控制台输出:
执行后,查看zookeeper的znode情况: 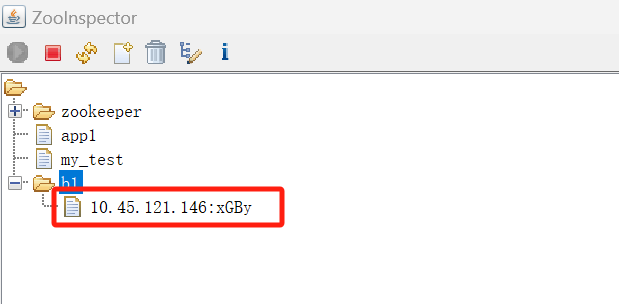
-
第3步,复制第2步操作,模拟启动第2个进程
执行后,查看zookeeper的znode情况:
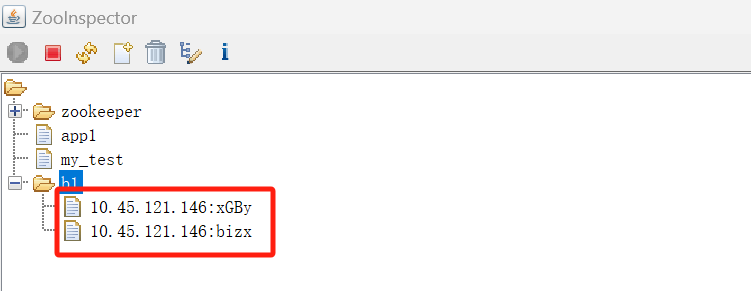
-
第4步,复制第2步操作,模拟启动第3个进程
执行后,第1个控制台输出:

第2个控制台输出:

第3个控制台输出:

然后所有进程在随机的整数时间后输出 Left barrier

查看zookeeper的znode情况: 所有子进程创建的临时子节点都已delete 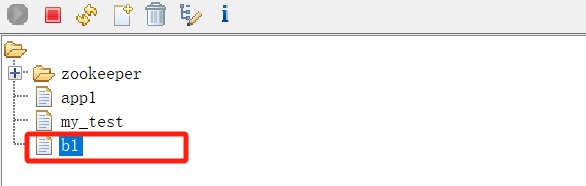
1.4 结果
能实现多个进程之间的并行协同。
1.5 注意事项
- 为了方便在同一台IP上模拟不同的进程,在官方提供的代码基础上增加了4位长度的随机字符串。
java
// 官方示例:
name = new String(InetAddress.getLocalHost().getCanonicalHostName().toString());
// 新增后的示例
name = new String(InetAddress.getLocalHost().getCanonicalHostName().toString()+ ":"+ RandomStringUtils.randomAlphabetic(4));- 关闭SASL安全验证
java
static{
System.setProperty("zookeeper.sasl.client", "false");
}2. 队列
2.1 概念
模拟向同一队列生产/消费消息。
2.2 设计
生产消息: 往znode新增子节点。
消费消息: 往znode中取first子节点,然后删除子节点。
2.3 源码
java
/**
* Producer-Consumer queue */static public class Queue extends SyncPrimitive {
/**
* Constructor of producer-consumer queue * * @param address
* @param name
*/
Queue(String address, String name) {
super(address);
this.root = name;
// Create ZK node name
if (zk != null) {
try {
Stat s = zk.exists(root, false);
if (s == null) {
zk.create(root, new byte[0], Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE,
CreateMode.PERSISTENT);
}
} catch (KeeperException e) {
System.out
.println("Keeper exception when instantiating queue: "
+ e.toString());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("Interrupted exception");
}
}
}
/**
* Add element to the queue. * * @param i
* @return
*/
boolean produce(int i) throws KeeperException, InterruptedException{
ByteBuffer b = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
byte[] value;
// Add child with value i
b.putInt(i);
value = b.array();
zk.create(root + "/element", value, Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE,
CreateMode.PERSISTENT_SEQUENTIAL);
return true;
}
/**
* Remove first element from the queue. * * @return * @throws KeeperException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
int consume() throws KeeperException, InterruptedException{
int retvalue = -1;
Stat stat = null;
// Get the first element available
while (true) {
synchronized (mutex) {
List<String> list = zk.getChildren(root, true);
if (list.size() == 0) {
System.out.println("Going to wait");
mutex.wait();
} else {
Integer min = Integer.parseInt((list.get(0).substring(7)));
String minNode = list.get(0);
for(String s : list){
Integer tempValue = Integer.parseInt(s.substring(7));
//System.out.println("Temporary value: " + tempValue);
if(tempValue < min) {
min = tempValue;
minNode = s;
}
}
System.out.println("Temporary value: " + root + "/" + minNode);
byte[] b = zk.getData(root + "/" + minNode,
false, stat);
zk.delete(root + "/" + minNode, 0);
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(b);
retvalue = buffer.getInt();
return retvalue;
}
}
}
}
}2.4 测试
生产消息: java SyncPrimitive qTest 192.168.206.100:2181 100 p
消费消息: java SyncPrimitive qTest 192.168.206.100:2181 100 c
2.5 结论
借助zookeeper实现消息队列的模拟。