一、服务雪崩与解决方案
1.1、服务雪崩问题
一句话:微服务之间相互调用,因为调用链中的一个服务故障,引起整个链路都无法访问的情况。
微服务中,服务间调用关系错综复杂,一个微服务往往依赖于多个其它微服务。
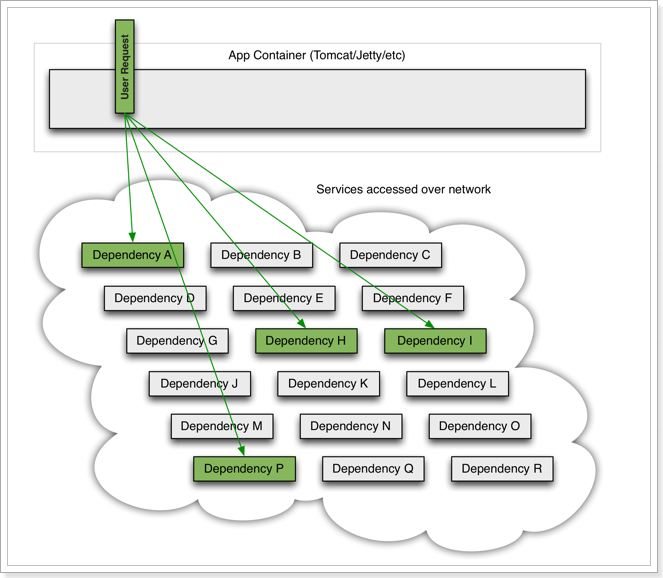
如图,如果服务提供者I发生了故障,当前的应用的部分业务因为依赖于服务I,因此也会被阻塞。此时,其它不依赖于服务I的业务似乎不受影响。
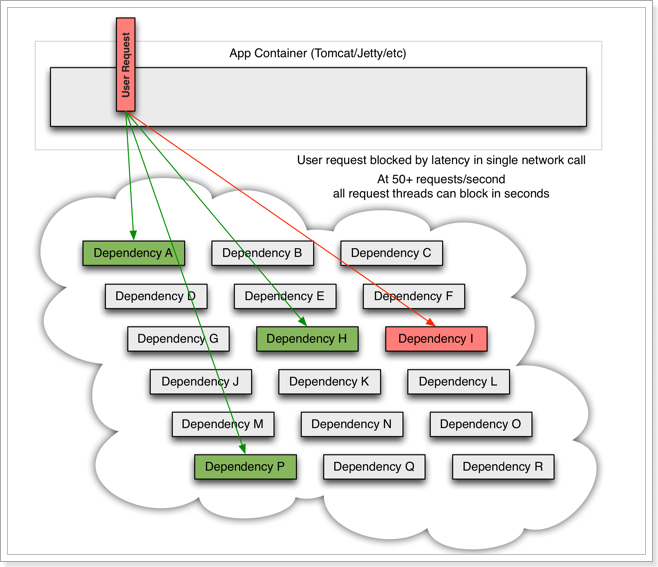
但是,依赖服务I的业务请求被阻塞,用户不会得到响应,则tomcat的这个线程不会释放,于是越来越多的用户请求到来,越来越多的线程会阻塞:
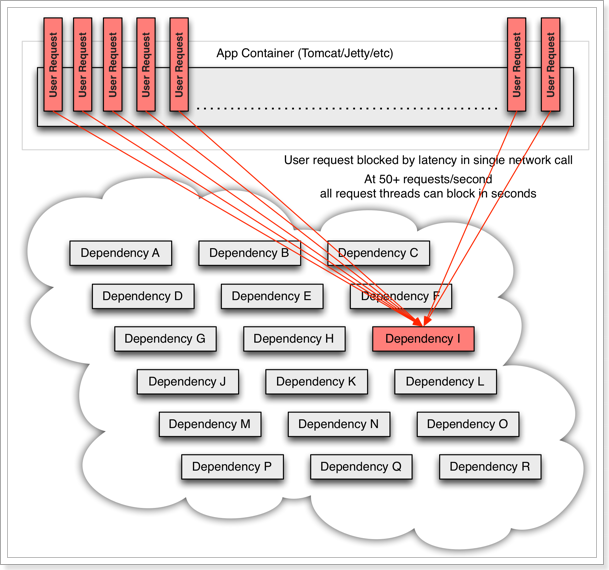
服务器支持的线程和并发数有限,请求一直阻塞,会导致服务器资源耗尽,从而导致所有其它服务都不可用,那么当前服务也就不可用了。
那么,依赖于当前服务的其它服务随着时间的推移,最终也都会变的不可用,形成级联失败,雪崩就发生了:
解决雪崩问题的常见方式有四种:
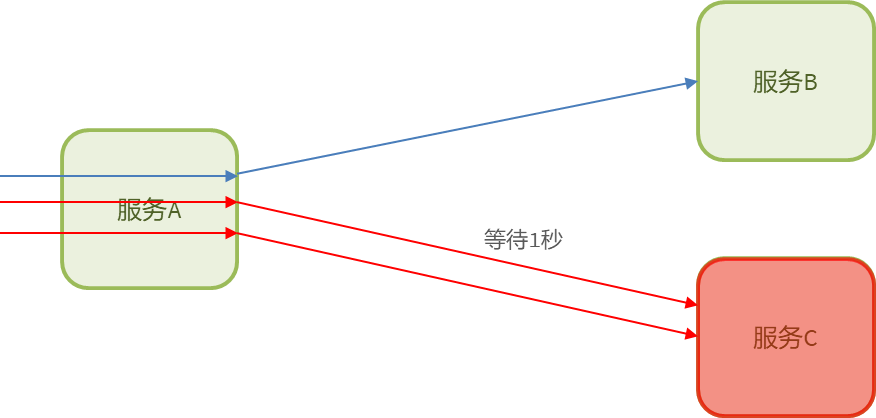
1.2、超时处理
超时处理:设定超时时间,请求超过一定时间没有响应就返回错误信息,不会无休止等待
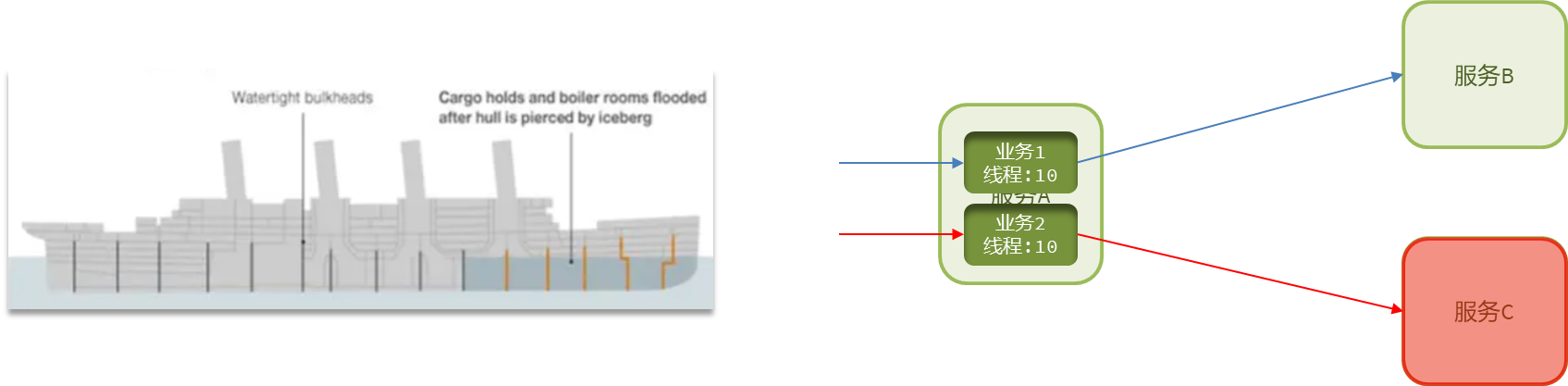
1.3、仓壁模式
仓壁模式来源于船舱的设计:
船舱都会被隔板分离为多个独立空间,当船体破损时,只会导致部分空间进入,将故障控制在一定范围内,避免整个船体都被淹没。
于此类似,我们可以限定每个业务能使用的线程数,避免耗尽整个tomcat的资源,因此也叫线程隔离。
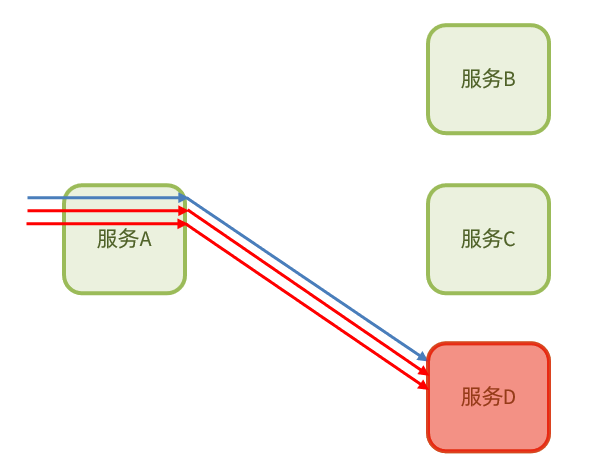
1.4、断路器
断路器模式:由断路器 统计业务执行的异常比例,如果超出阈值则会熔断该业务,拦截访问该业务的一切请求。
断路器会统计访问某个服务的请求数量,异常比例:
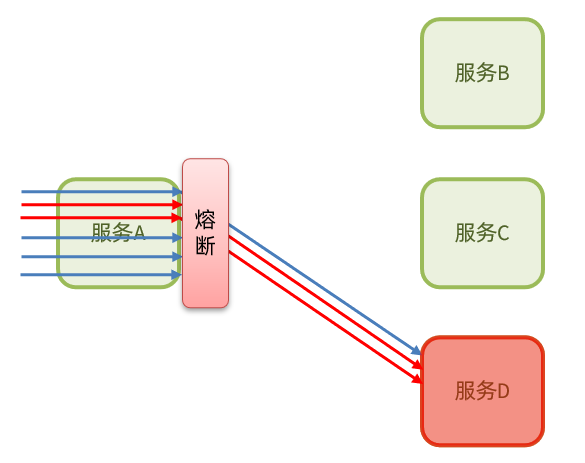
当发现访问服务D的请求异常比例过高时,认为服务D有导致雪崩的风险,会拦截访问服务D的一切请求,形成熔断:
1.5、限流
流量控制:限制业务访问的QPS,避免服务因流量的突增而故障。

1.6、总结
什么是雪崩问题?
- 微服务之间相互调用,因为调用链中的一个服务故障,引起整个链路都无法访问的情况。
可以认为:
限流 是对服务的保护,避免因瞬间高并发流量而导致服务故障,进而避免雪崩。是一种预防措施。
超时处理、线程隔离、降级熔断 是在部分服务故障时,将故障控制在一定范围,避免雪崩。是一种补救措施。
解决雪崩问题的常见方式有四种:
-
超时处理:设定超时时间,请求超过一定时间没有响应就返回错误信息,不会无休止等待
-
舱壁模式:限定每个业务能使用的线程数,避免耗尽整个tomcat的资源,因此也叫线程隔离。
-
熔断降级:由断路器 统计业务执行的异常比例,如果超出阈值则会熔断该业务,拦截访问该业务的一切请求。
-
流量控制:限制业务访问的QPS,避免服务因流量的突增而故障。
二、初识Sentinel
在SpringCloud当中支持多种服务保护技术:
早期比较流行的是Hystrix框架,但目前国内实用最广泛的还是阿里巴巴的Sentinel框架,这里我们做下对比:
| Sentinel | Hystrix | |
|---|---|---|
| 隔离策略 | 信号量隔离 | 线程池隔离/信号量隔离 |
| 熔断降级策略 | 基于慢调用比例或异常比例 | 基于失败比率 |
| 实时指标实现 | 滑动窗口 | 滑动窗口(基于 RxJava) |
| 规则配置 | 支持多种数据源 | 支持多种数据源 |
| 扩展性 | 多个扩展点 | 插件的形式 |
| 基于注解的支持 | 支持 | 支持 |
| 限流 | 基于 QPS,支持基于调用关系的限流 | 有限的支持 |
| 流量整形 | 支持慢启动、匀速排队模式 | 不支持 |
| 系统自适应保护 | 支持 | 不支持 |
| 控制台 | 开箱即用,可配置规则、查看秒级监控、机器发现等 | 不完善 |
| 常见框架的适配 | Servlet、Spring Cloud、Dubbo、gRPC 等 | Servlet、Spring Cloud Netflix |
http
https://sentinelguard.io/zh-cn/index.html
http
https://github.com/alibaba/SentinelSentinel是阿里巴巴开源的一款微服务流量控制组件。官网地址:https://sentinelguard.io/zh-cn/index.html
Sentinel 具有以下特征:
•丰富的应用场景:Sentinel 承接了阿里巴巴近 10 年的双十一大促流量的核心场景,例如秒杀(即突发流量控制在系统容量可以承受的范围)、消息削峰填谷、集群流量控制、实时熔断下游不可用应用等。
•完备的实时监控:Sentinel 同时提供实时的监控功能。您可以在控制台中看到接入应用的单台机器秒级数据,甚至 500 台以下规模的集群的汇总运行情况。
•广泛的开源生态:Sentinel 提供开箱即用的与其它开源框架/库的整合模块,例如与 Spring Cloud、Dubbo、gRPC 的整合。您只需要引入相应的依赖并进行简单的配置即可快速地接入 Sentinel。
•完善的 SPI 扩展点:Sentinel 提供简单易用、完善的 SPI 扩展接口。您可以通过实现扩展接口来快速地定制逻辑。例如定制规则管理、适配动态数据源等。
三、微服务整合Sentinel
3.1、改POM
xml
<dependencies>
<!--sentinel-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>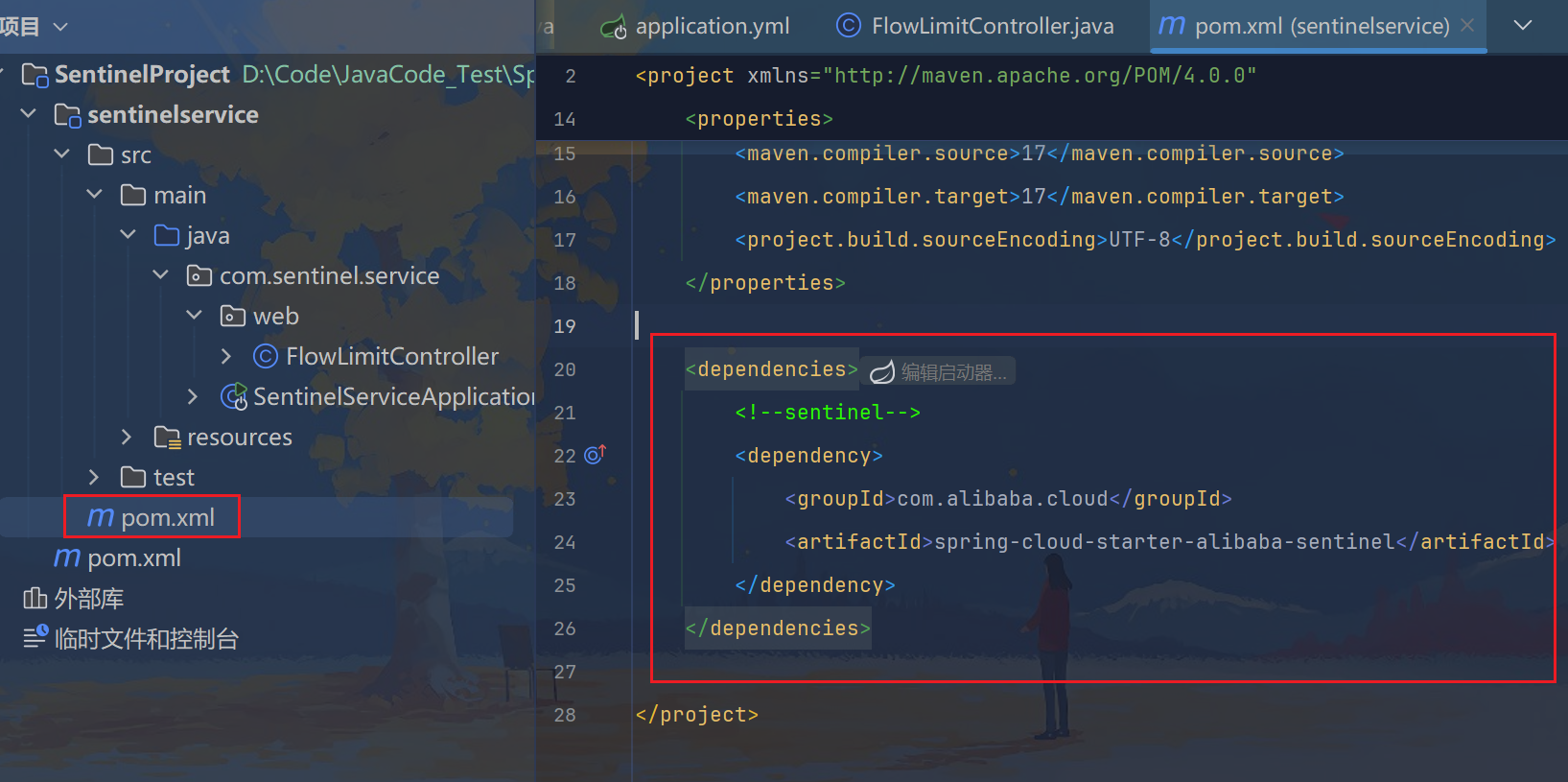
3.2、写YAML
yaml
server:
port: 9001
spring:
application:
name: sentinelservice
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: 192.168.200.129:8848 #配置Nacos地址
sentinel:
transport:
dashboard: 192.168.200.129:8858 #配置Sentinel dashboard控制台服务地址
port: 8719 #默认8719端口,假如被占用会自动从8719开始依次+1扫描,直至找到未被占用的端口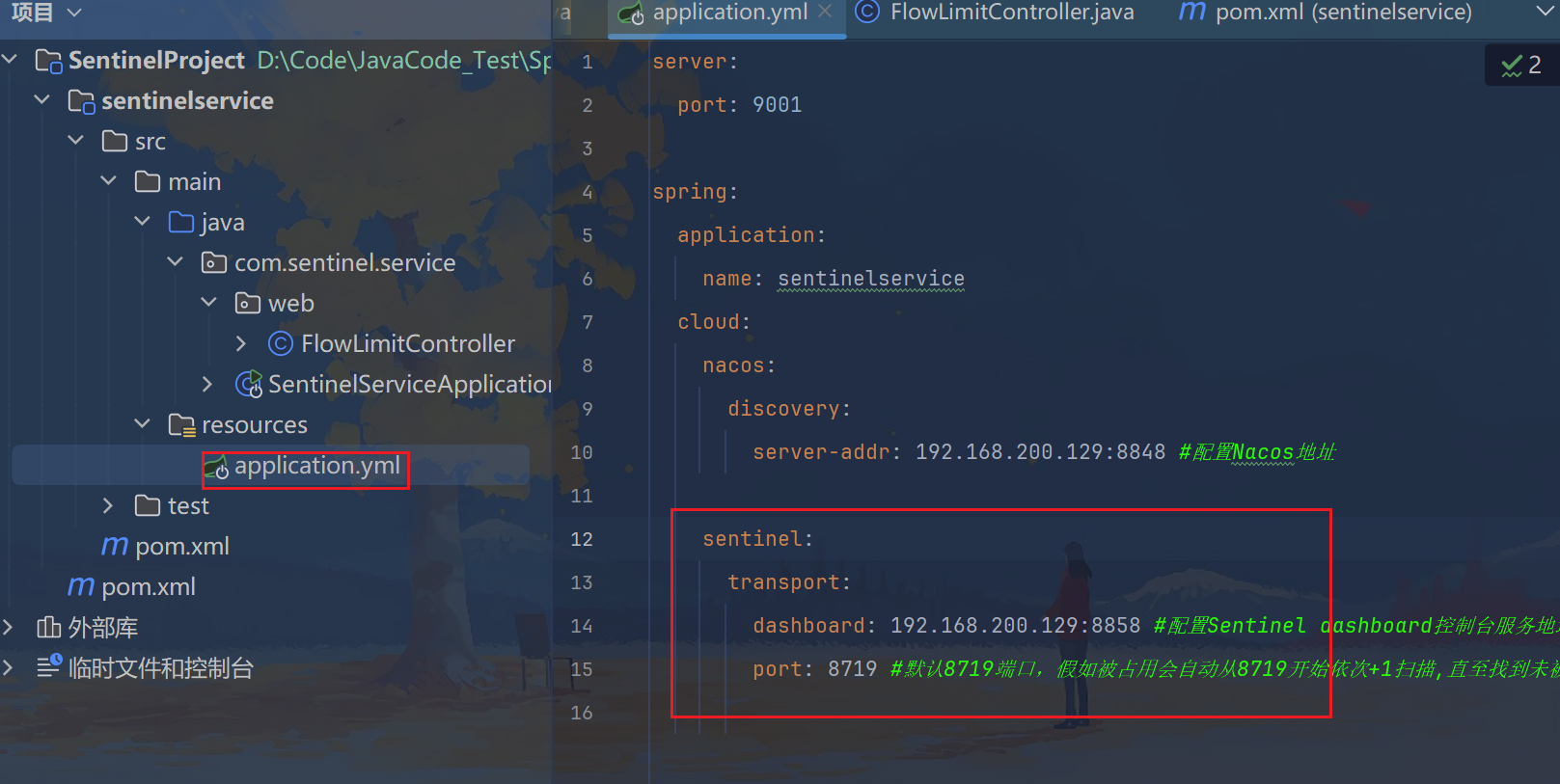
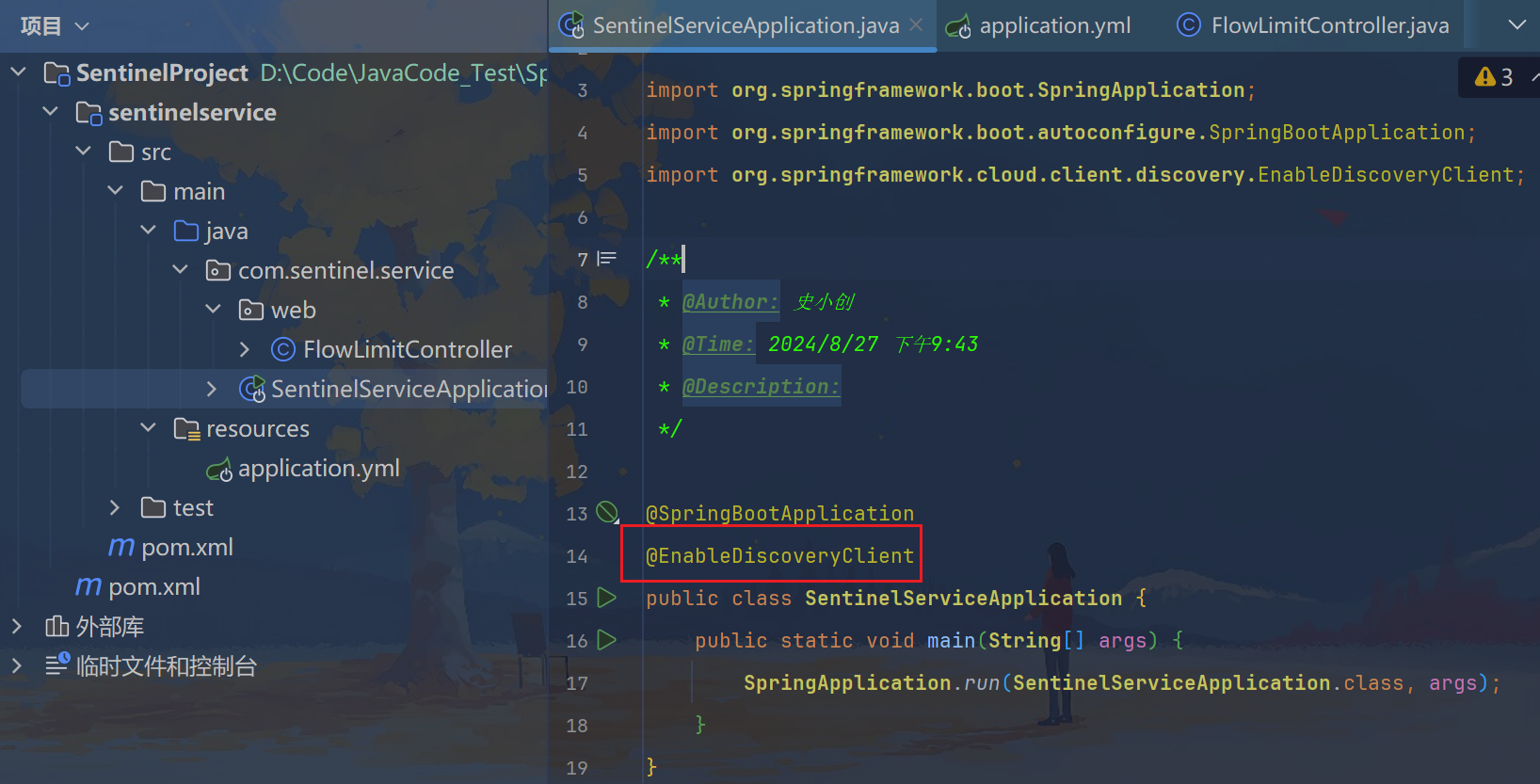
3.3、主启动
java
package com.sentinel.service;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
/**
* @Author: 史小创
* @Time: 2024/8/27 下午9:43
* @Description:
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class SentinelServiceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SentinelServiceApplication.class, args);
}
}
3.4、测试
原因:Sentinel采用的为懒加载的模式。想使用Sentinel对某个接口进行限流和降级等操作,一定要先访问下接口,使Sentinel检测出相应的接口
http
http://localhost:9001/testA
http
http://localhost:9001/testB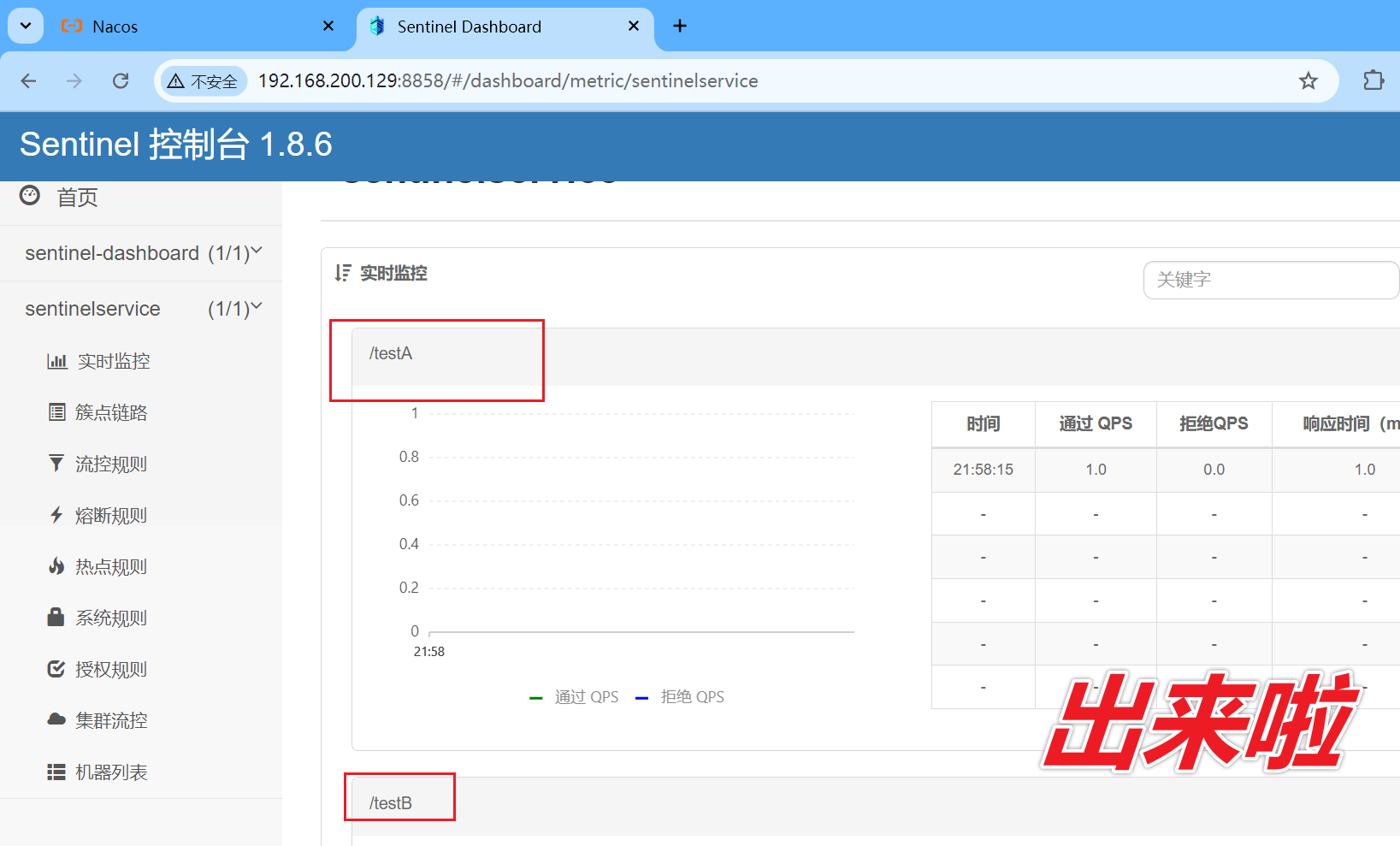
四、实战:流控规则
4.1、概述
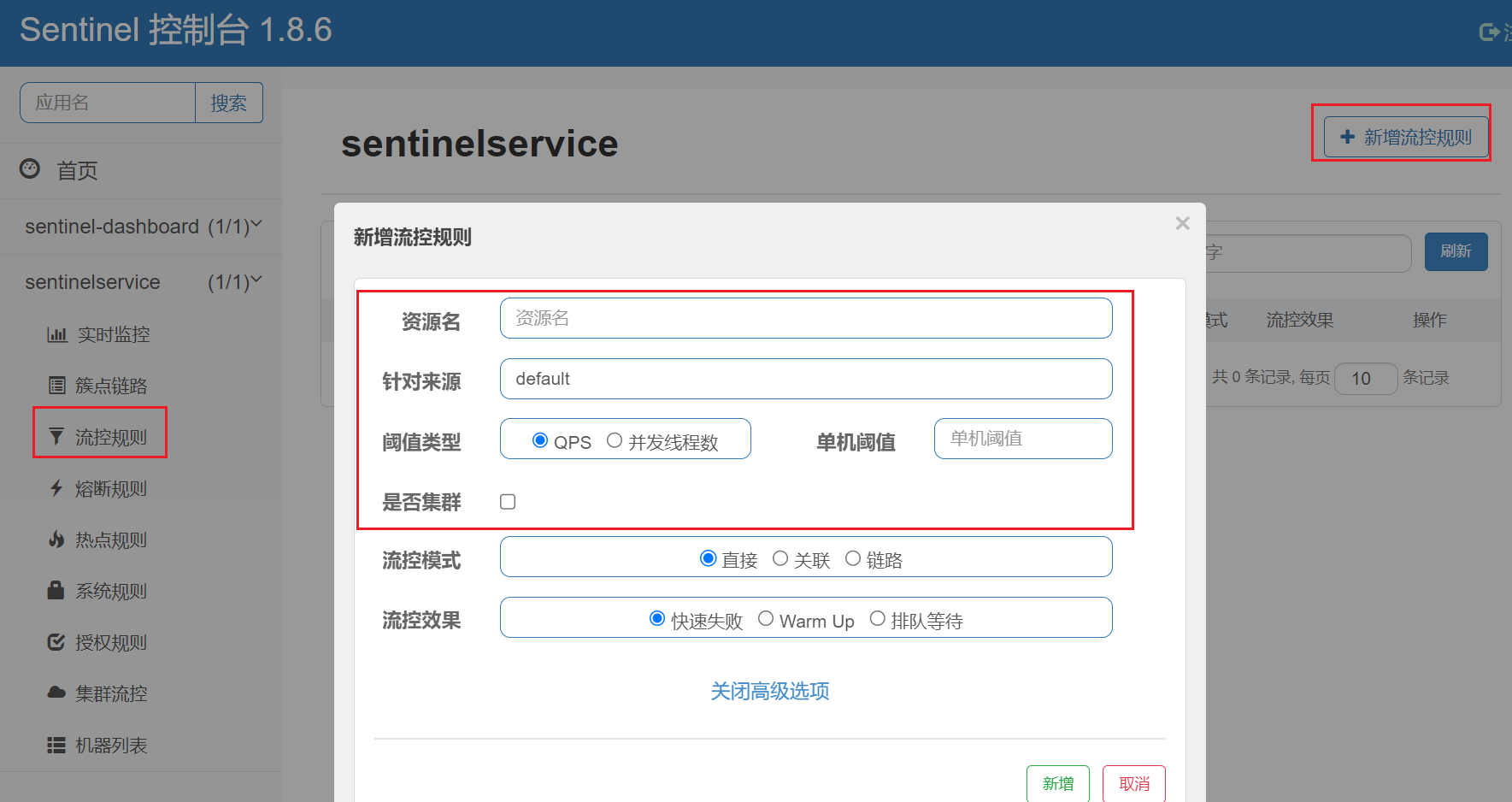
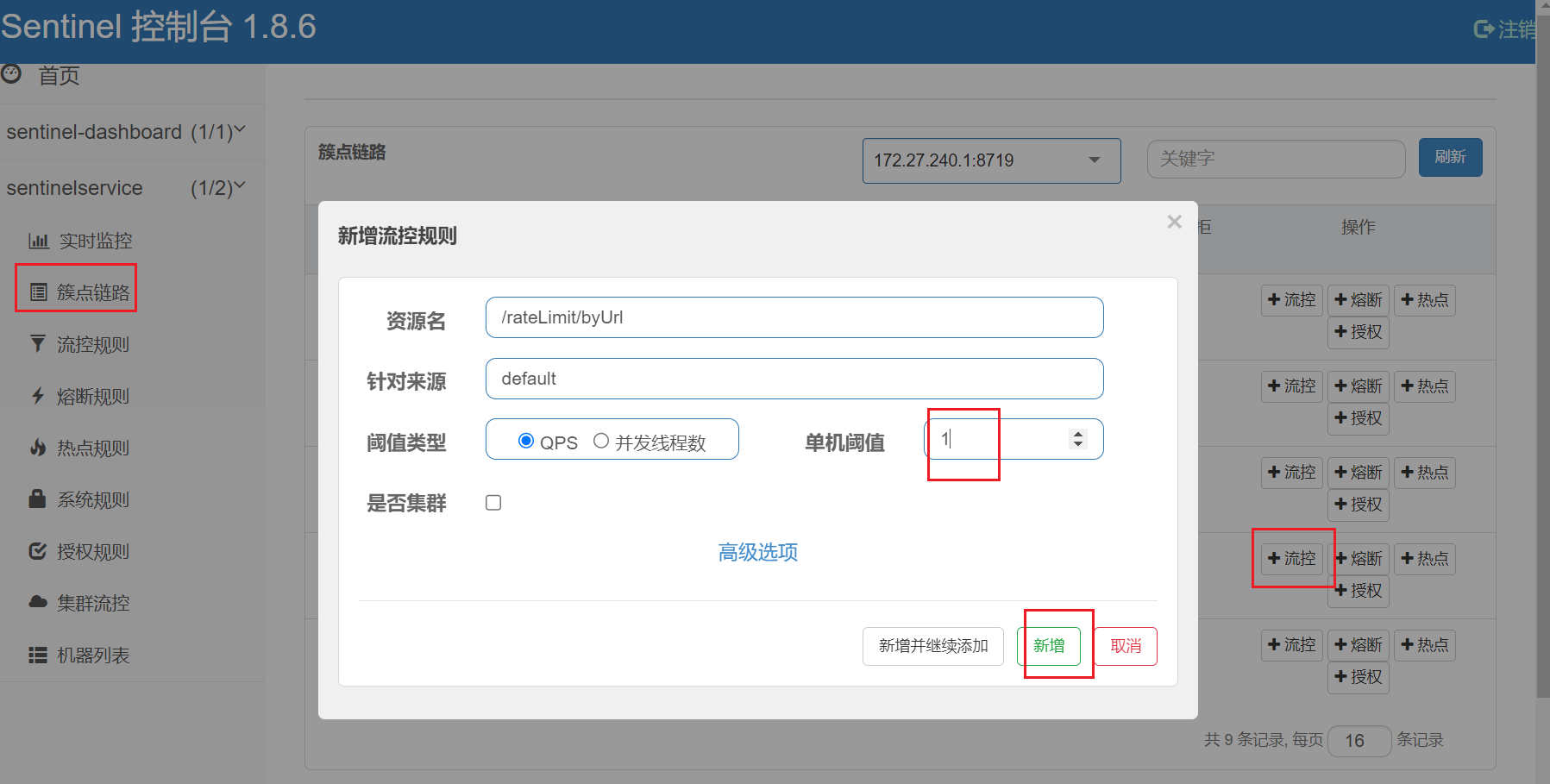
Sentinel能够对流量进行控制,主要是监控应用的QPS流量或者并发线程数等指标,如果达到指定的阈值时,就会被流量进行控制,以避免服务被瞬时的高并发流量击垮,保证服务的高可靠性。参数见最下方:
| 序号 | 名称 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 资源名 | 资源的唯一名称,默认就是请求的接口路径,可以自行修改,但是要保证唯一。 |
| 2 | 针对来源 | 具体针对某个微服务进行限流,默认值为default,表示不区分来源,全部限流。 |
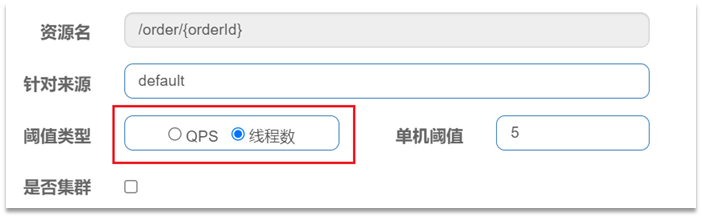
| 3 | 阈值类型 | QPS表示通过QPS进行限流,并发线程数表示通过并发线程数限流。 |
| 4 | 单机阈值 | 与阈值类型组合使用。如果阈值类型选择的是QPS,表示当调用接口的QPS达到阈值时,进行限流操作。如果阈值类型选择的是并发线程数,则表示当调用接口的并发线程数达到阈值时,进行限流操作。 |
| 5 | 是否集群 | 选中则表示集群环境,不选中则表示非集群环境。 |
4.2、流控模式

在添加限流规则时,点击高级选项,可以选择三种流控模式:
- 直接:统计当前资源的请求,触发阈值时对当前资源直接限流,也是默认的模式
- 关联:统计与当前资源相关的另一个资源,触发阈值时,对当前资源限流
- 链路:统计从指定链路访问到本资源的请求,触发阈值时,对指定链路限流
4.2.1、直连
默认的流控模式,当接口达到限流条件时,直接开启限流功能。
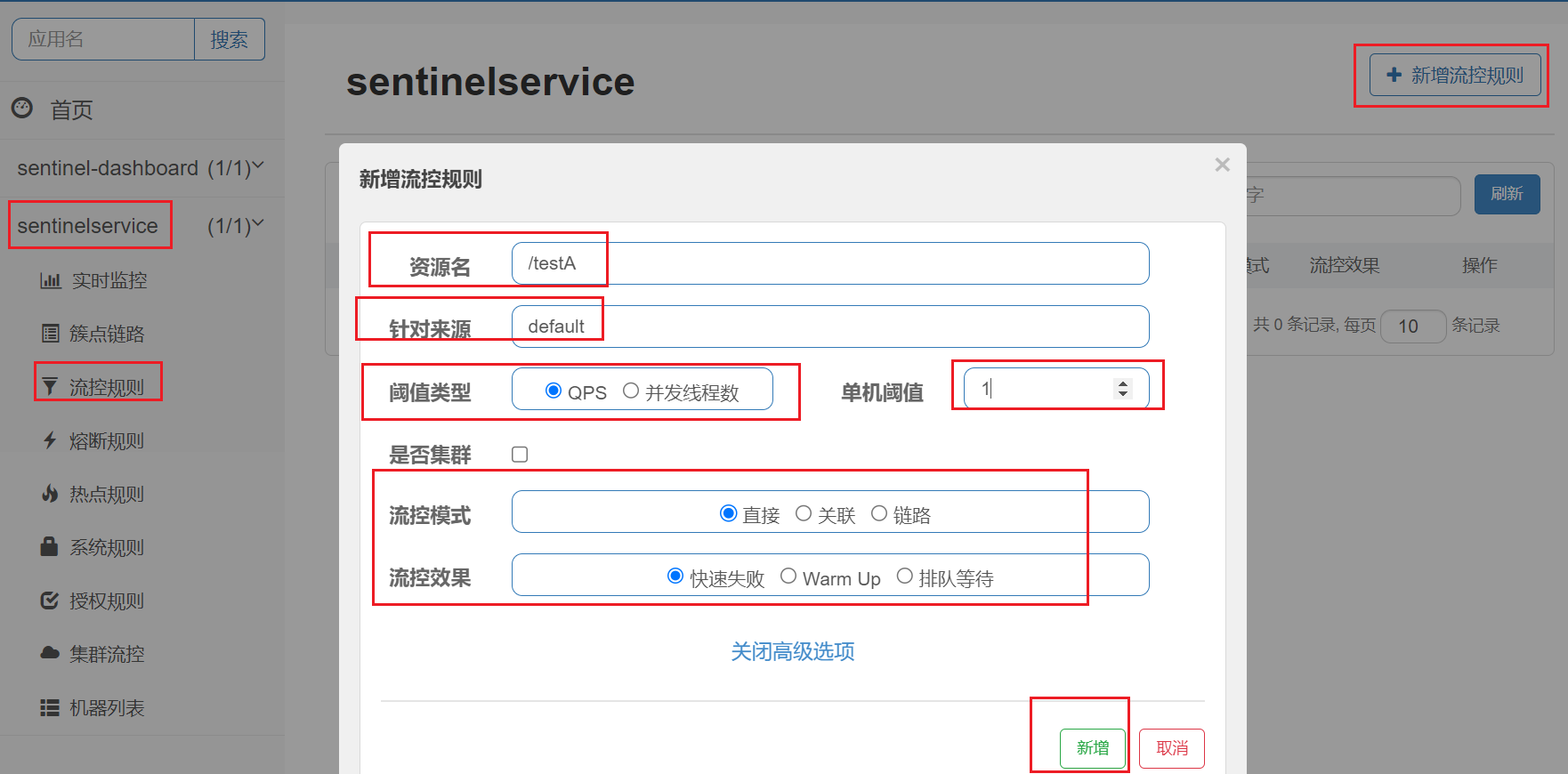

表示1秒钟内查询1次就是OK,若超过次数1,就直接-快速失败,报默认错误
http
http://localhost:9001/testA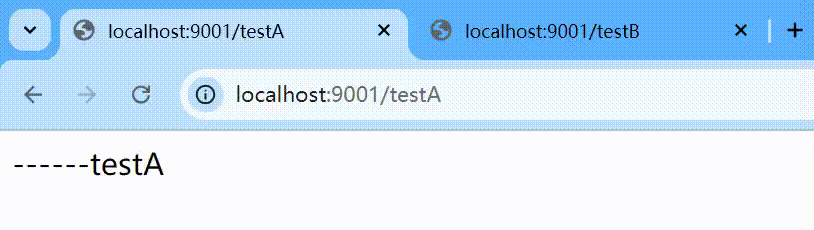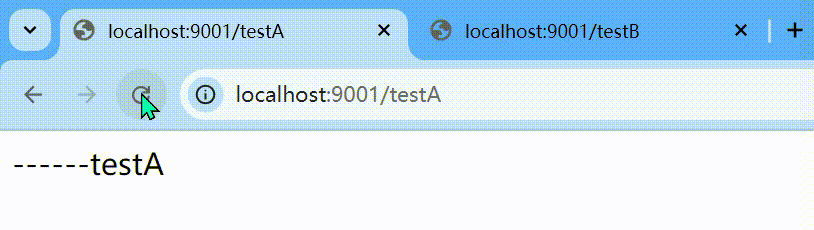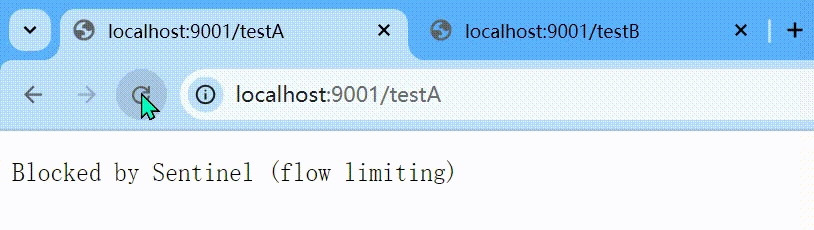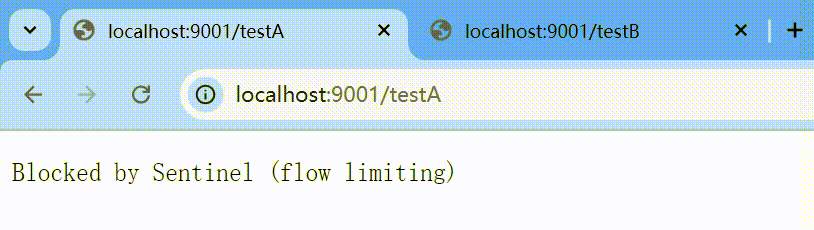
Blocked by Sentinel (flow limiting) 这样的方式貌似太丑,能否有美观一点呢
4.2.2、关联
关联模式:统计与当前资源相关的另一个资源,触发阈值时,对当前资源限流
使用场景:比如用户支付时需要修改订单状态,同时用户要查询订单。查询和修改操作会争抢数据库锁,产生竞争。业务需求是优先支付和更新订单的业务,因此当修改订单业务触发阈值时,需要对查询订单业务限流。
简单讲:当关联的资源达到阈值时,就限流自己。当与A关联的资源B达到阀值后,就限流A自己B惹事,A挂了。
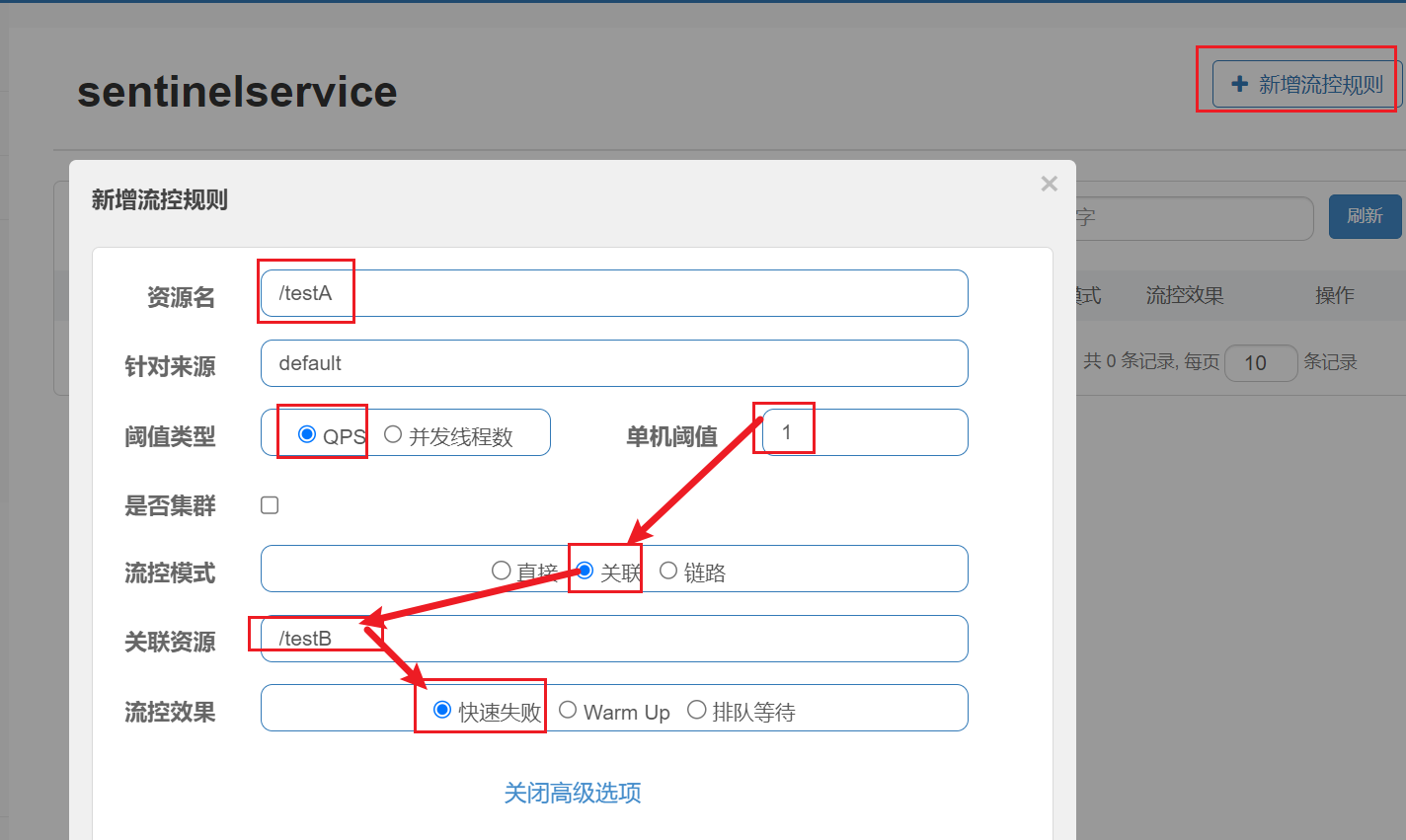
当关联资源/testB的qps阀值超过1时,就限流/testA的Rest访问地址,当关联资源到阈值后限制配置好的资源名,B惹事,A挂了
http
http://localhost:9001/testB
http
http://localhost:9001/testA
小结:
满足下面条件可以使用关联模式:
- 两个有竞争关系的资源
- 一个优先级较高,一个优先级较低
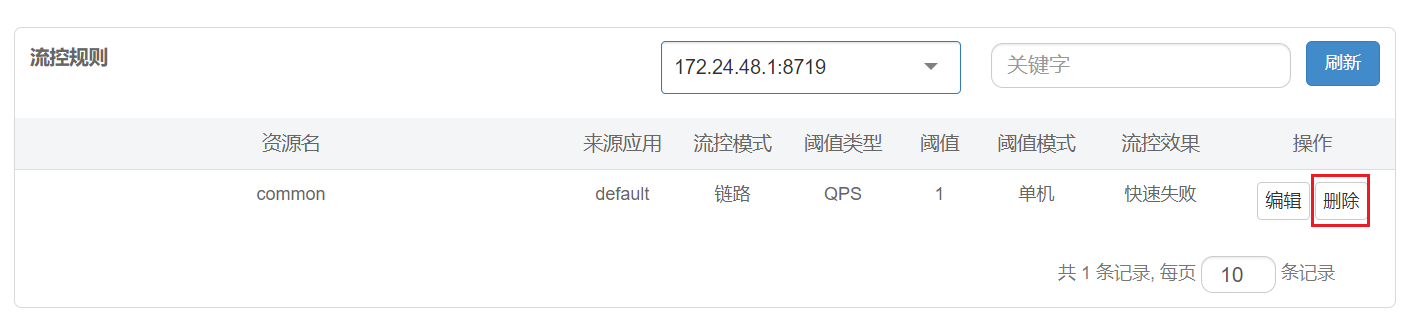
4.2.3、链路
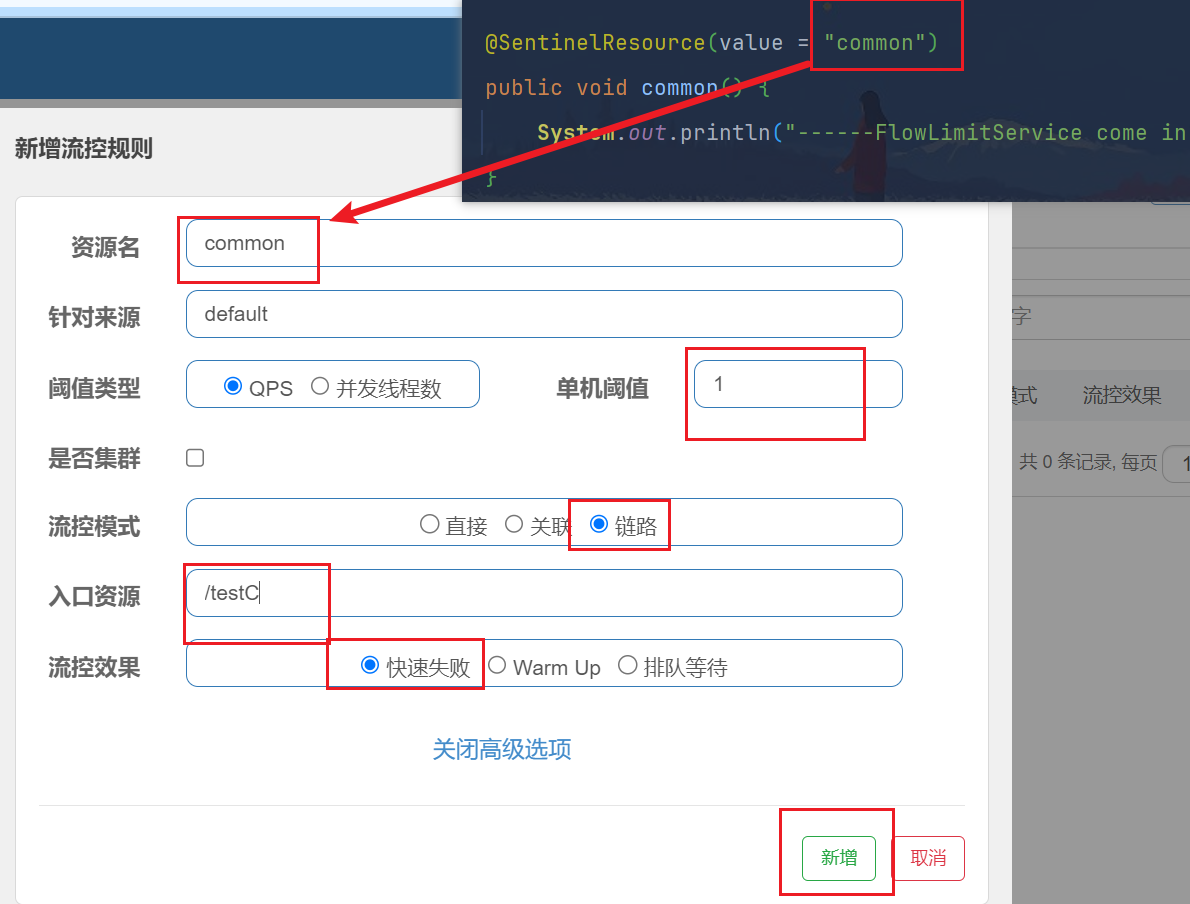
链路模式:只针对从指定链路访问到本资源的请求做统计,判断是否超过阈值。
来自不同链路的请求对同一个目标访问时,实施针对性的不同限流措施,比如C请求来访问就限流,D请求来访问就是OK
yaml
web-context-unify: false # controller层的方法对service层调用不认为是同一个根链路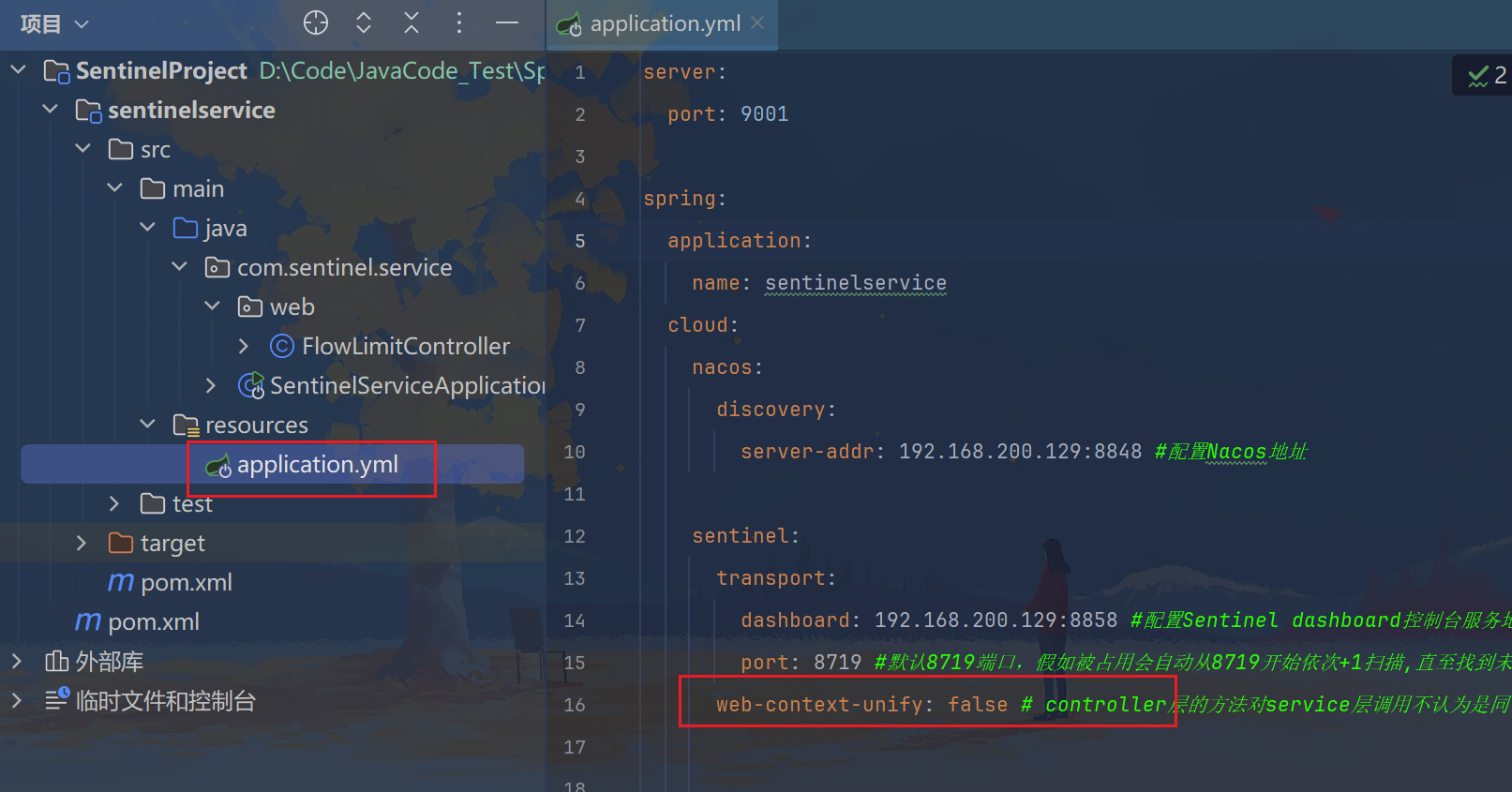
java
package com.sentinel.service.service;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.annotation.SentinelResource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @Author: 史小创
* @Time: 2024/8/27 下午10:43
* @Description:
*/
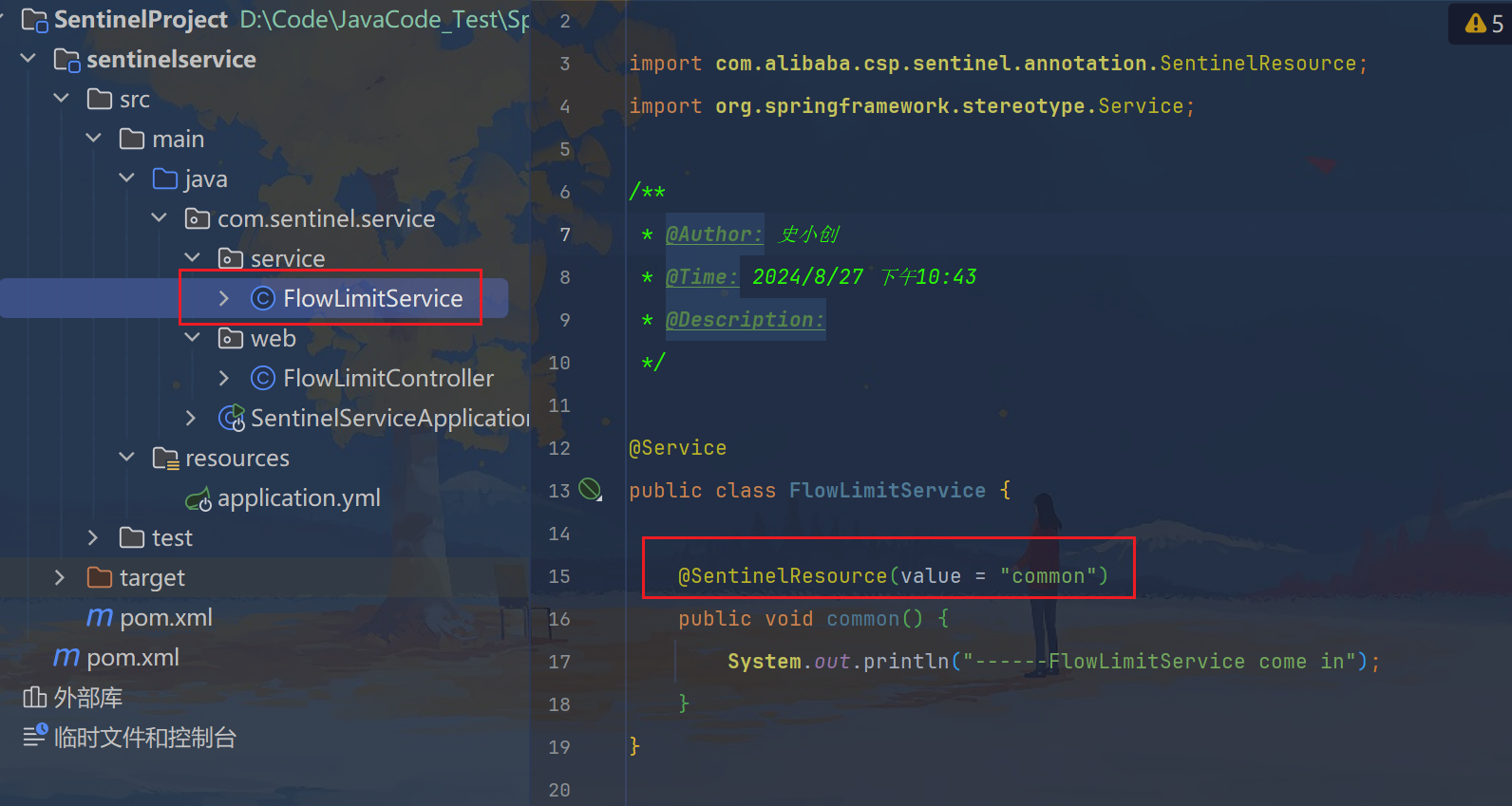
@Service
public class FlowLimitService {
@SentinelResource(value = "common")
public void common() {
System.out.println("------FlowLimitService come in");
}
}
java
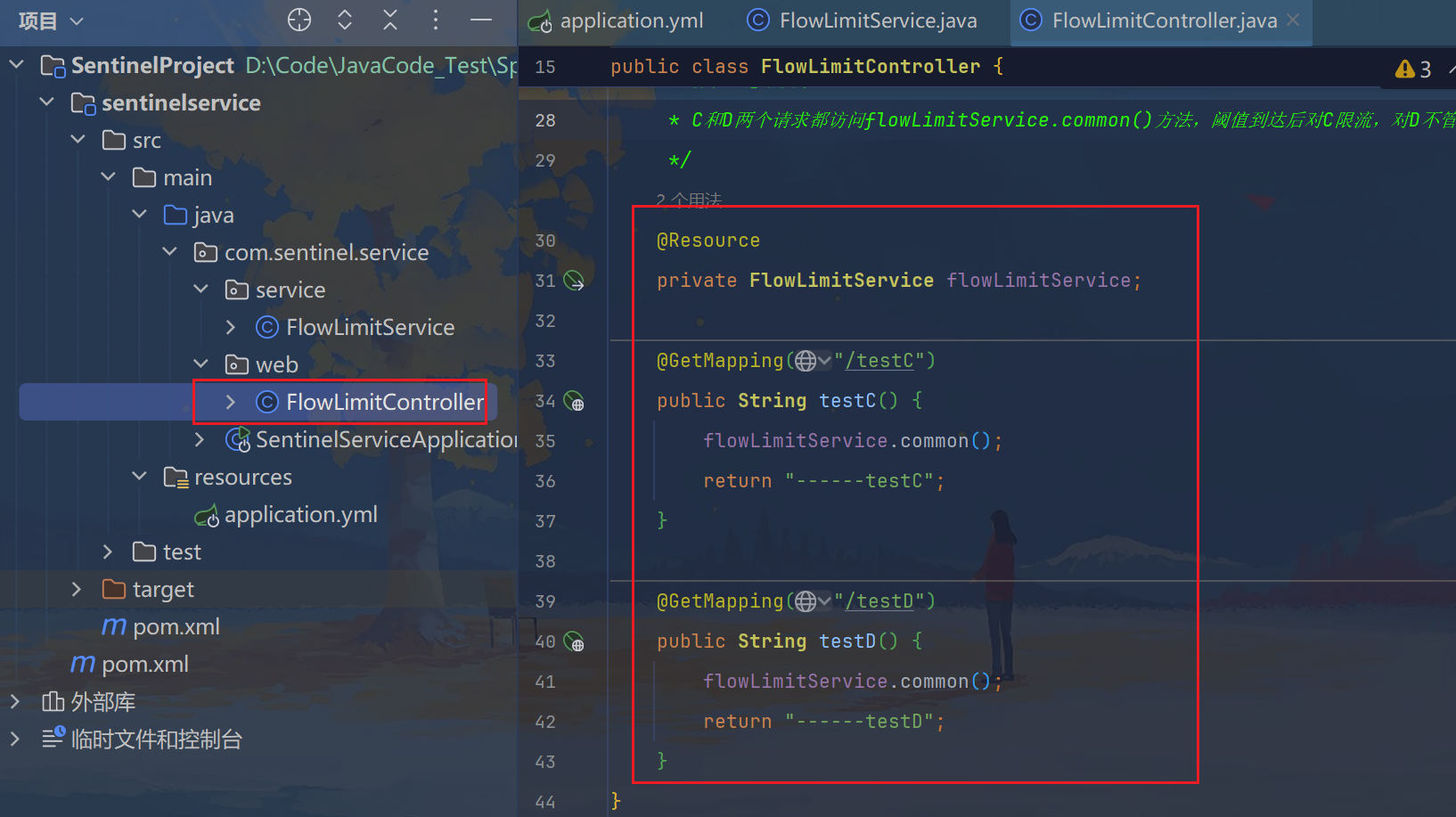
/**
* 流控-链路演示demo
* C和D两个请求都访问flowLimitService.common()方法,阈值到达后对C限流,对D不管
*/
@Resource
private FlowLimitService flowLimitService;
@GetMapping("/testC")
public String testC() {
flowLimitService.common();
return "------testC";
}
@GetMapping("/testD")
public String testD() {
flowLimitService.common();
return "------testD";
}
http
http://localhost:9001/testC
http
http://localhost:9001/testD
4.3、流控效果
在流控的高级选项中,还有一个流控效果选项:

流控效果是指请求达到流控阈值时应该采取的措施,包括三种:
-
快速失败:达到阈值后,新的请求会被立即拒绝并抛出FlowException异常。是默认的处理方式。
-
warm up:预热模式,对超出阈值的请求同样是拒绝并抛出异常。但这种模式阈值会动态变化,从一个较小值逐渐增加到最大阈值。
-
排队等待:让所有的请求按照先后次序排队执行,两个请求的间隔不能小于指定时长
4.3.1、快速失败
4.3.2、预热Warm up
http
https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/Flow-Control:-Warm-Up
http
https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/%E9%99%90%E6%B5%81---%E5%86%B7%E5%90%AF%E5%8A%A8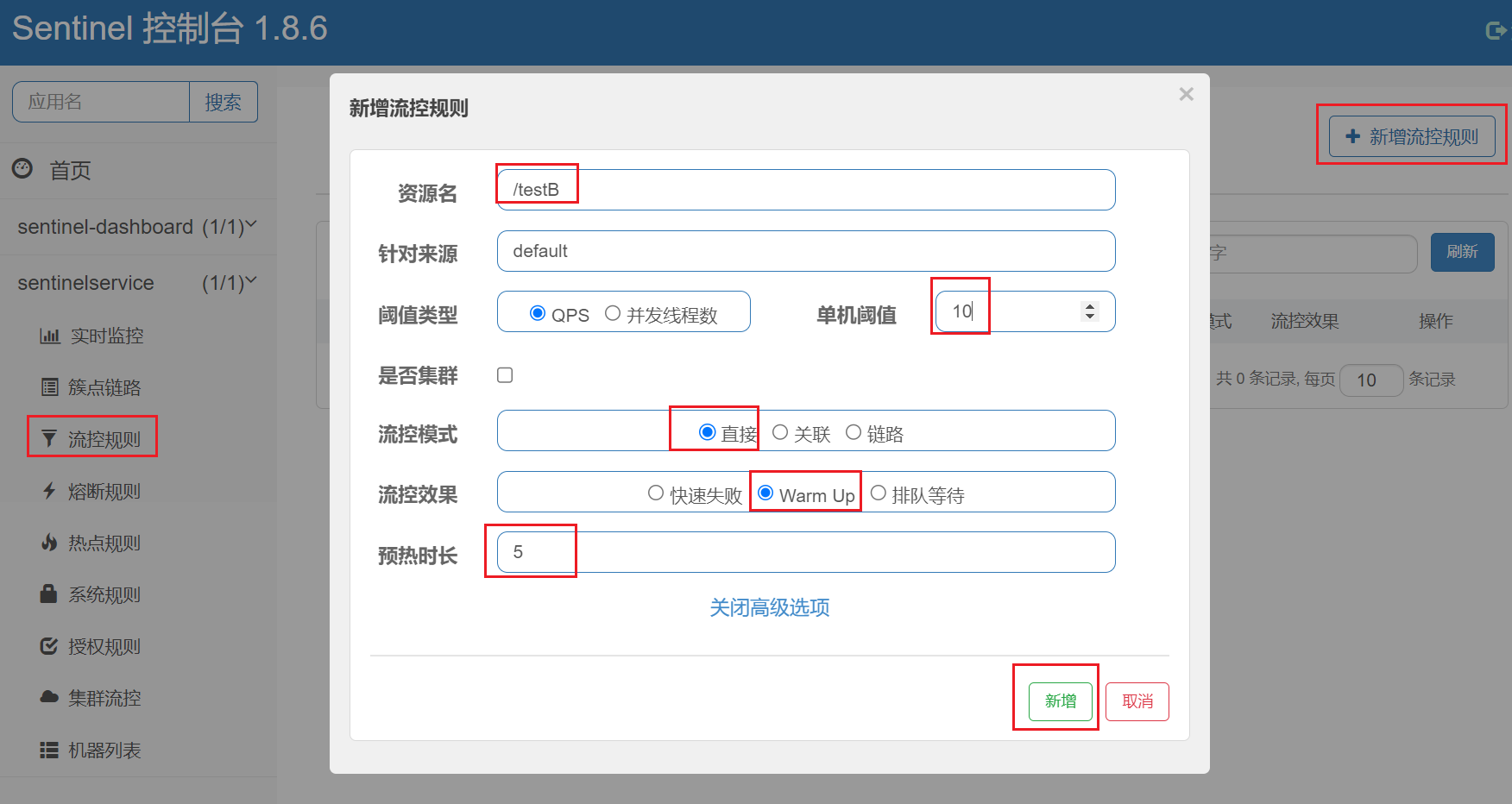
阈值一般是一个微服务能承担的最大QPS,但是一个服务刚刚启动时,一切资源尚未初始化(冷启动),如果直接将QPS跑到最大值,可能导致服务瞬间宕机。
warm up也叫预热模式,是应对服务冷启动的一种方案。请求阈值初始值是 maxThreshold / coldFactor,持续指定时长后,逐渐提高到maxThreshold值。而coldFactor的默认值是3.
例如,我设置QPS的maxThreshold为10,预热时间为5秒,那么初始阈值就是 10 / 3 ,也就是3,然后在5秒后逐渐增长到10.
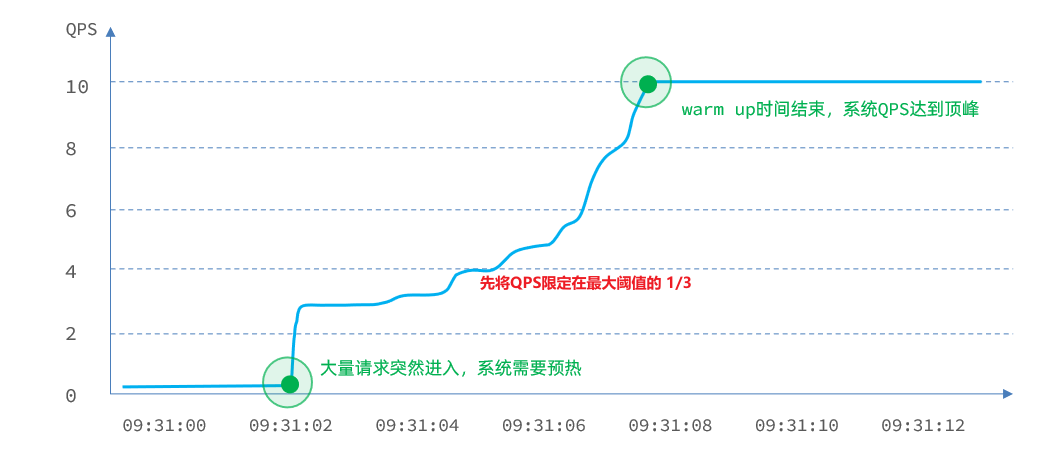
如:秒杀系统在开启的瞬间,会有很多流量上来,很有可能把系统打死,预热方式就是把为了保护系统,可慢慢的把流量放进来,慢慢的把阈值增长到设置的阈值。
默认 coldFactor 为 3,即请求 QPS 从 threshold / 3 开始,经预热时长逐渐升至设定的 QPS 阈值。
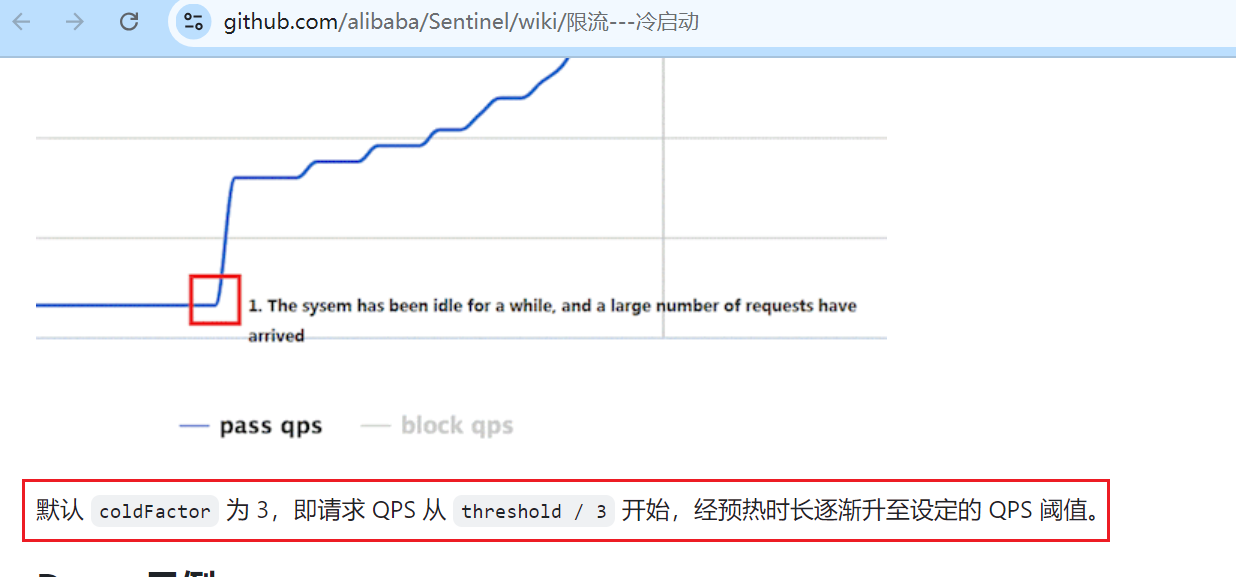
http
https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/blob/1.8/sentinel-core/src/main/java/com/alibaba/csp/sentinel/slots/block/flow/controller/WarmUpController.java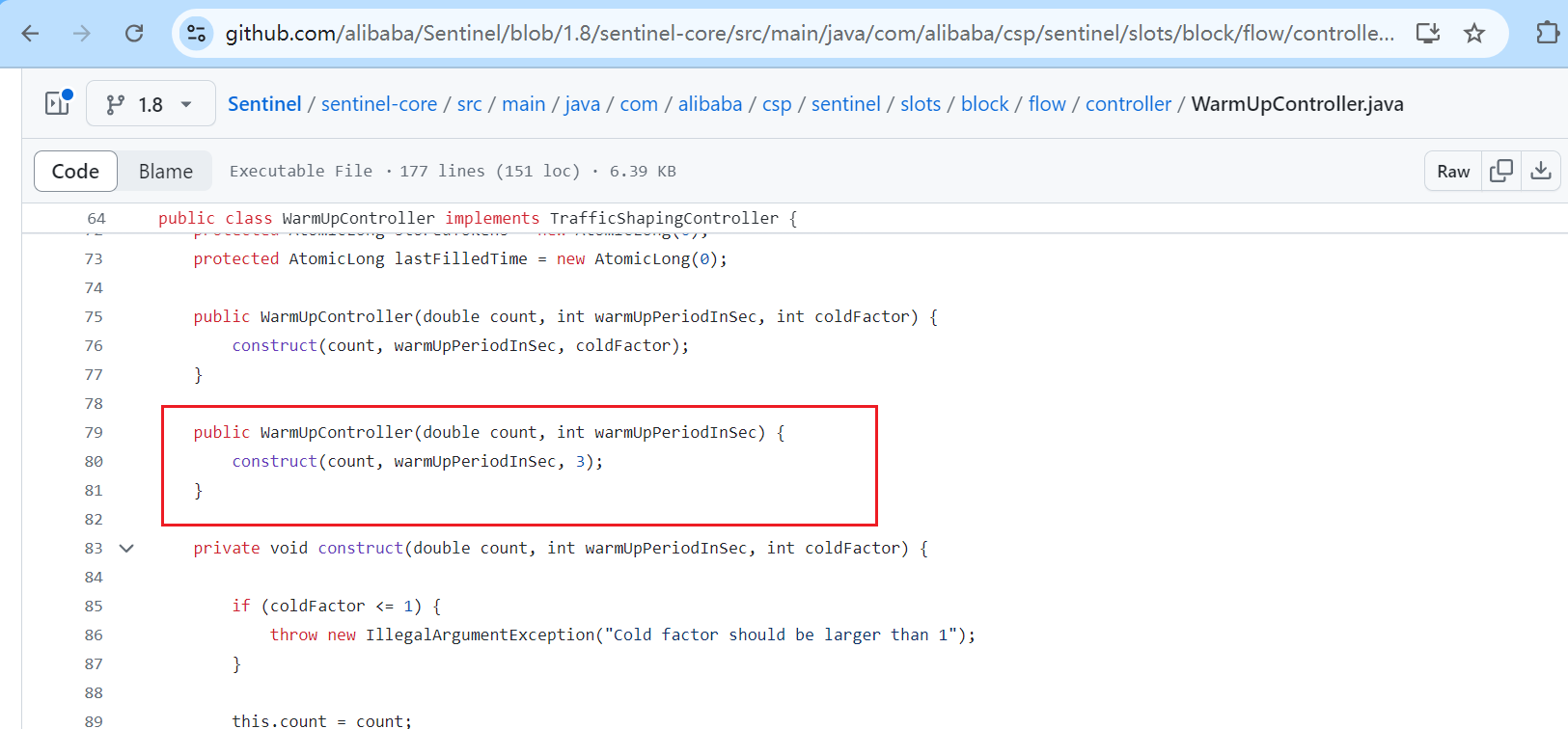
| 默认 coldFactor 为 3,即请求QPS从(threshold / 3) 开始,经多少预热时长才逐渐升至设定的 QPS 阈值。 |
|---|
| 案例,单机阈值为10,预热时长设置5秒。 系统初始化的阈值为10 / 3 约等于3,即单机阈值刚开始为3(我们人工设定单机阈值是10,sentinel计算后QPS判定为3开始); 然后过了5秒后阀值才慢慢升高恢复到设置的单机阈值10,也就是说5秒钟内QPS为3,过了保护期5秒后QPS为10 |

http
http://localhost:9001/testB
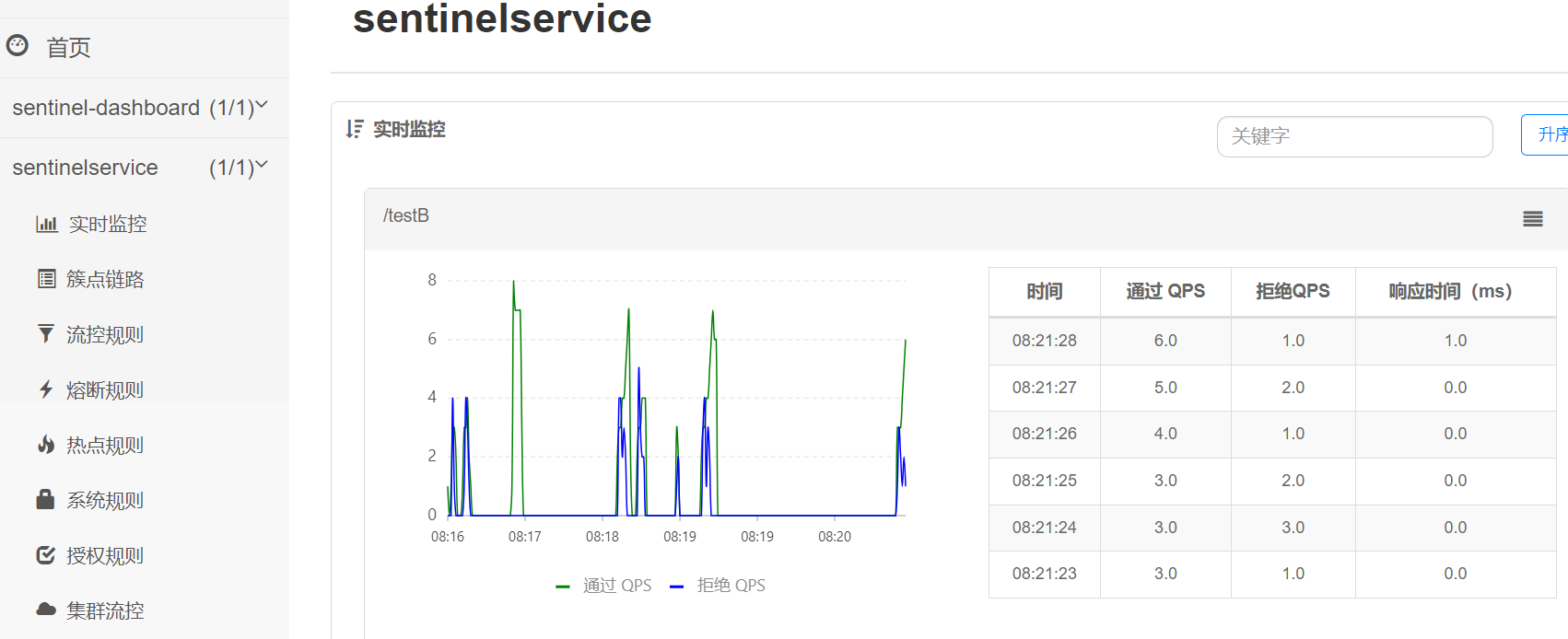
4.3.3、排队等待
当请求超过QPS阈值时,快速失败和warm up 会拒绝新的请求并抛出异常。
而排队等待则是让所有请求进入一个队列中,然后按照阈值允许的时间间隔依次执行。后来的请求必须等待前面执行完成,如果请求预期的等待时间超出最大时长,则会被拒绝。
工作原理
例如:QPS = 5,意味着每200ms处理一个队列中的请求;timeout = 2000,意味着预期等待时长超过2000ms的请求会被拒绝并抛出异常。
那什么叫做预期等待时长呢?
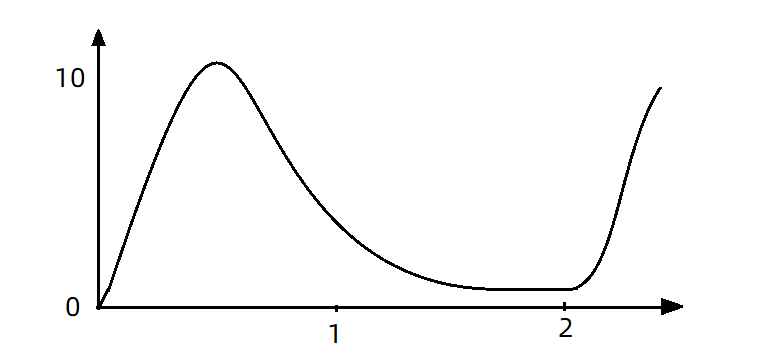
比如现在一下子来了12 个请求,因为每200ms执行一个请求,那么:
- 第6个请求的预期等待时长 = 200 * (6 - 1) = 1000ms
- 第12个请求的预期等待时长 = 200 * (12-1) = 2200ms
现在,第1秒同时接收到10个请求,但第2秒只有1个请求,此时QPS的曲线这样的:
如果使用队列模式做流控,所有进入的请求都要排队,以固定的200ms的间隔执行,QPS会变的很平滑:
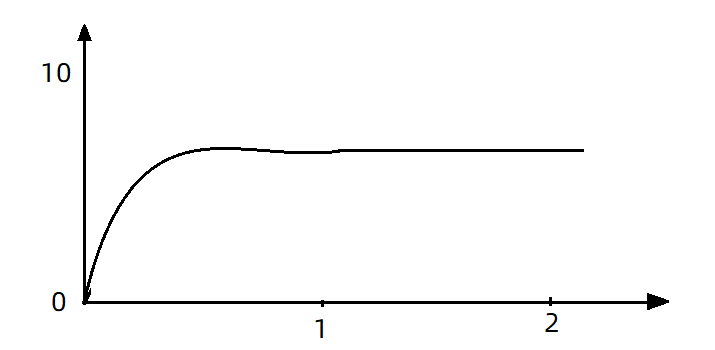
平滑的QPS曲线,对于服务器来说是更友好的。
java
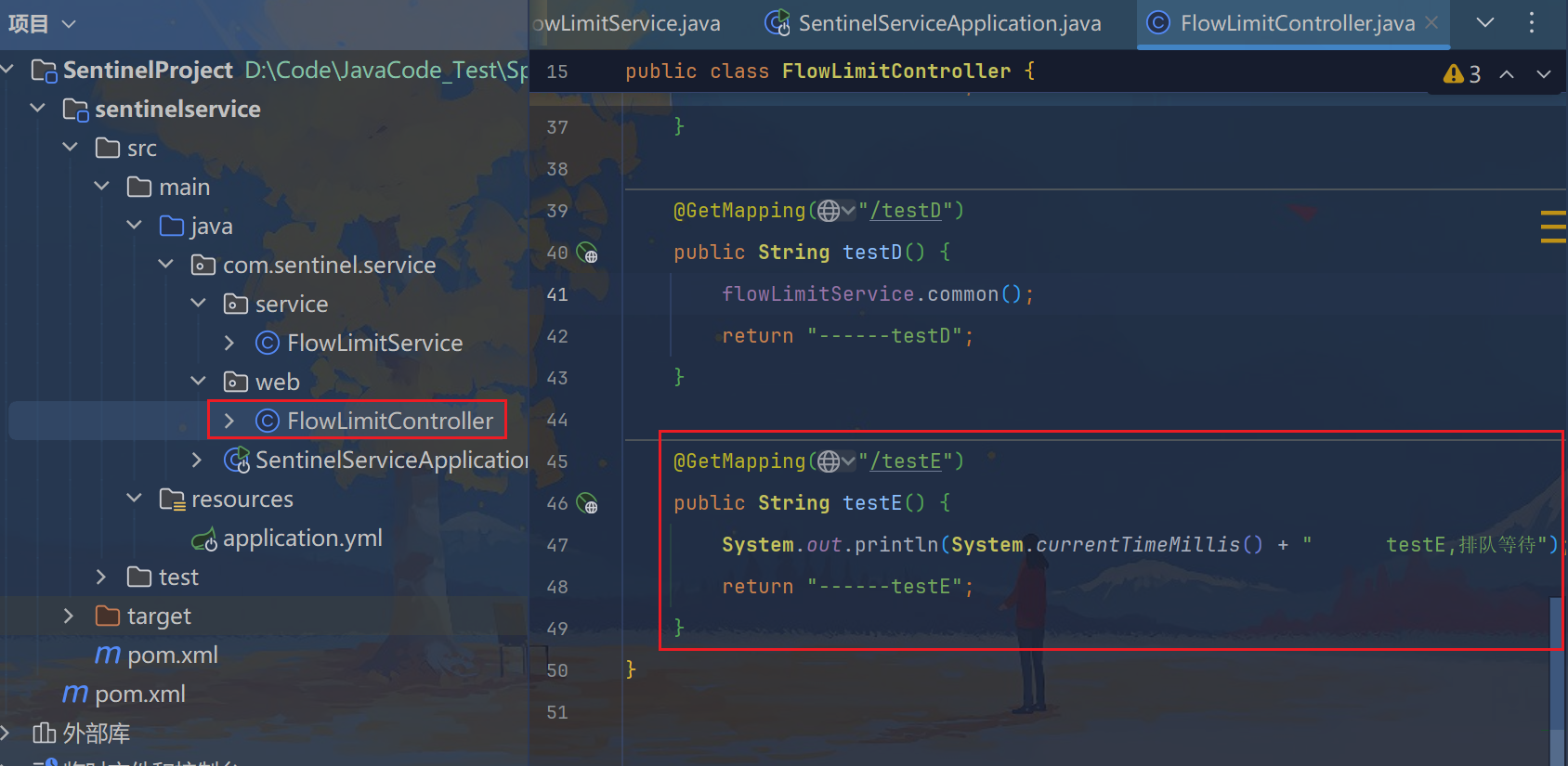
@GetMapping("/testE")
public String testE() {
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + " testE,排队等待");
return "------testE";
}
http
http://localhost:9001/testE
4.4.4、总结
流控效果有哪些?
-
快速失败:QPS超过阈值时,拒绝新的请求
-
warm up: QPS超过阈值时,拒绝新的请求;QPS阈值是逐渐提升的,可以避免冷启动时高并发导致服务宕机。
-
排队等待:请求会进入队列,按照阈值允许的时间间隔依次执行请求;如果请求预期等待时长大于超时时间,直接拒绝
4.4、线程隔离(舱壁模式)
线程隔离有两种方式实现:
-
线程池隔离
-
信号量隔离(Sentinel默认采用)
如图:
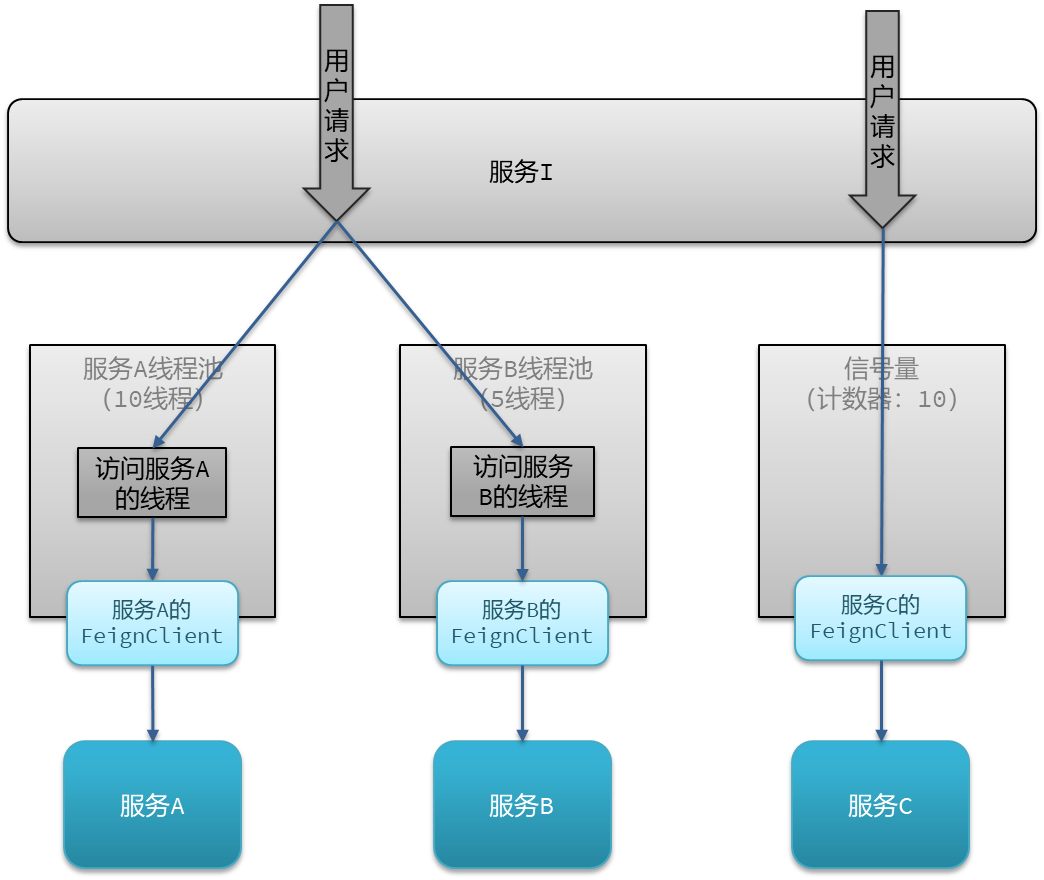
线程池隔离:给每个服务调用业务分配一个线程池,利用线程池本身实现隔离效果
信号量隔离:不创建线程池,而是计数器模式,记录业务使用的线程数量,达到信号量上限时,禁止新的请求。
两者的优缺点:

用法说明:
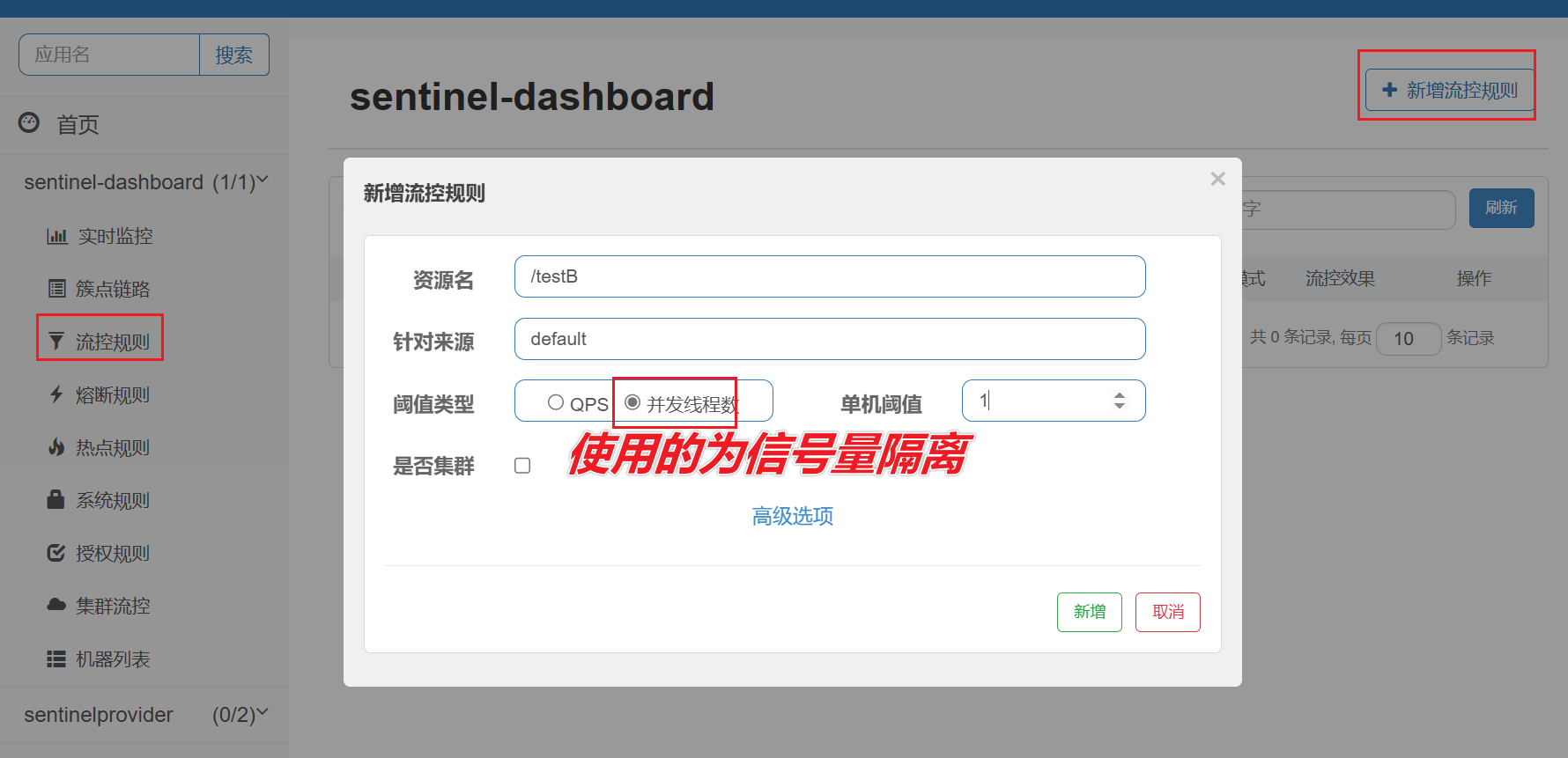
在添加限流规则时,可以选择两种阈值类型:
-
QPS:就是每秒的请求数,在快速入门中已经演示过
-
线程数:是该资源能使用用的tomcat线程数的最大值。也就是通过限制线程数量,实现线程隔离(舱壁模式)。
实操
Jmeter给它打满了,大部分我们自己访问都不好使,偶尔Jmeter线程切换系统判定没访问,我们自己的点击才有点机会
五、实战:熔断规则
熔断降级是解决雪崩问题的重要手段。其思路是由断路器 统计服务调用的异常比例、慢请求比例,如果超出阈值则会熔断该服务。即拦截访问该服务的一切请求;而当服务恢复时,断路器会放行访问该服务的请求。
断路器控制熔断和放行是通过状态机来完成的:
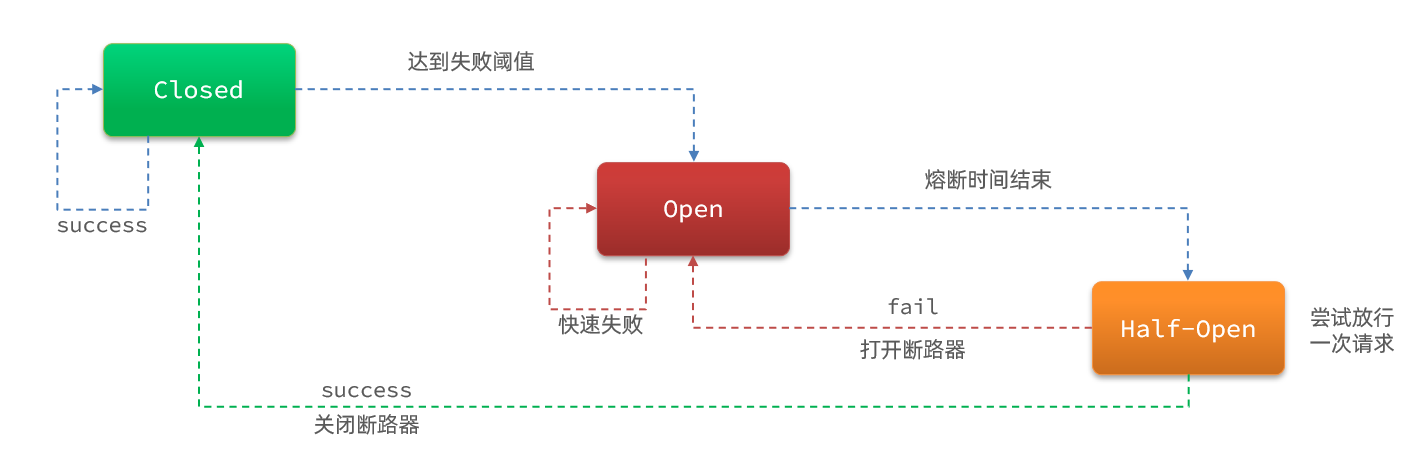
状态机包括三个状态:
- closed:关闭状态,断路器放行所有请求,并开始统计异常比例、慢请求比例。超过阈值则切换到open状态
- open:打开状态,服务调用被熔断,访问被熔断服务的请求会被拒绝,快速失败,直接走降级逻辑。Open状态5秒后会进入half-open状态
- half-open:半开状态,放行一次请求,根据执行结果来判断接下来的操作。
- 请求成功:则切换到closed状态
- 请求失败:则切换到open状态
断路器熔断策略有三种:慢调用、异常比例、异常数
http
https://sentinelguard.io/zh-cn/docs/circuit-breaking.html
http
https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/%E7%86%94%E6%96%AD%E9%99%8D%E7%BA%A7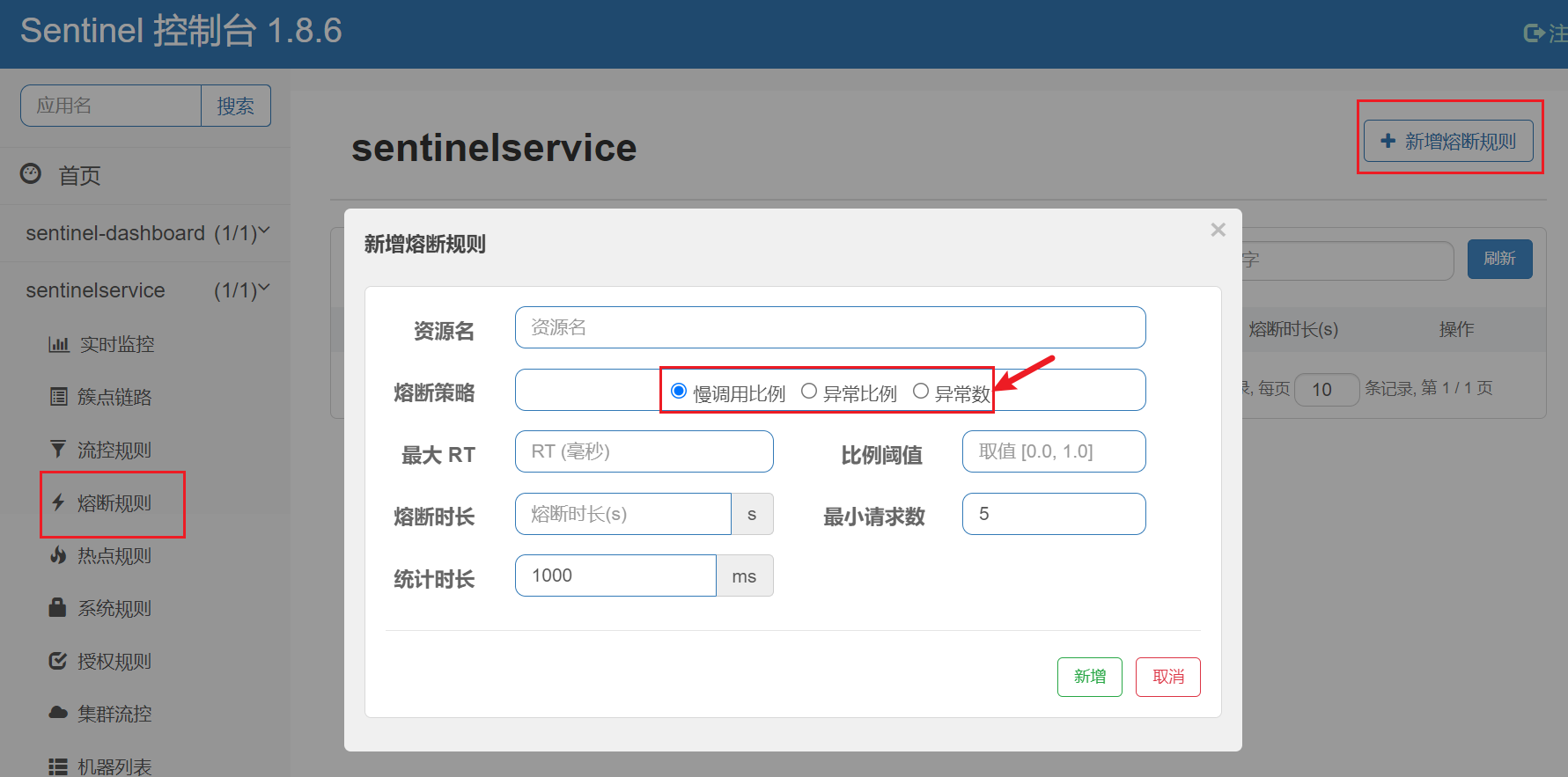
5.1、慢调用
慢调用:业务的响应时长(RT)大于指定时长的请求认定为慢调用请求。在指定时间内,如果请求数量超过设定的最小数量,慢调用比例大于设定的阈值,则触发熔断。
慢调用比例 (SLOW_REQUEST_RATIO):选择以慢调用比例作为阈值,需要设置允许的慢调用 RT(即最大的响应时间),请求的响应时间大于该值则统计为慢调用。当单位统计时长(statIntervalMs)内请求数目大于设置的最小请求数目,并且慢调用的比例大于阈值,则接下来的熔断时长内请求会自动被熔断。经过熔断时长后熔断器会进入探测恢复状态(HALF-OPEN 状态),若接下来的一个请求响应时间小于设置的慢调用 RT 则结束熔断,若大于设置的慢调用 RT 则会再次被熔断。
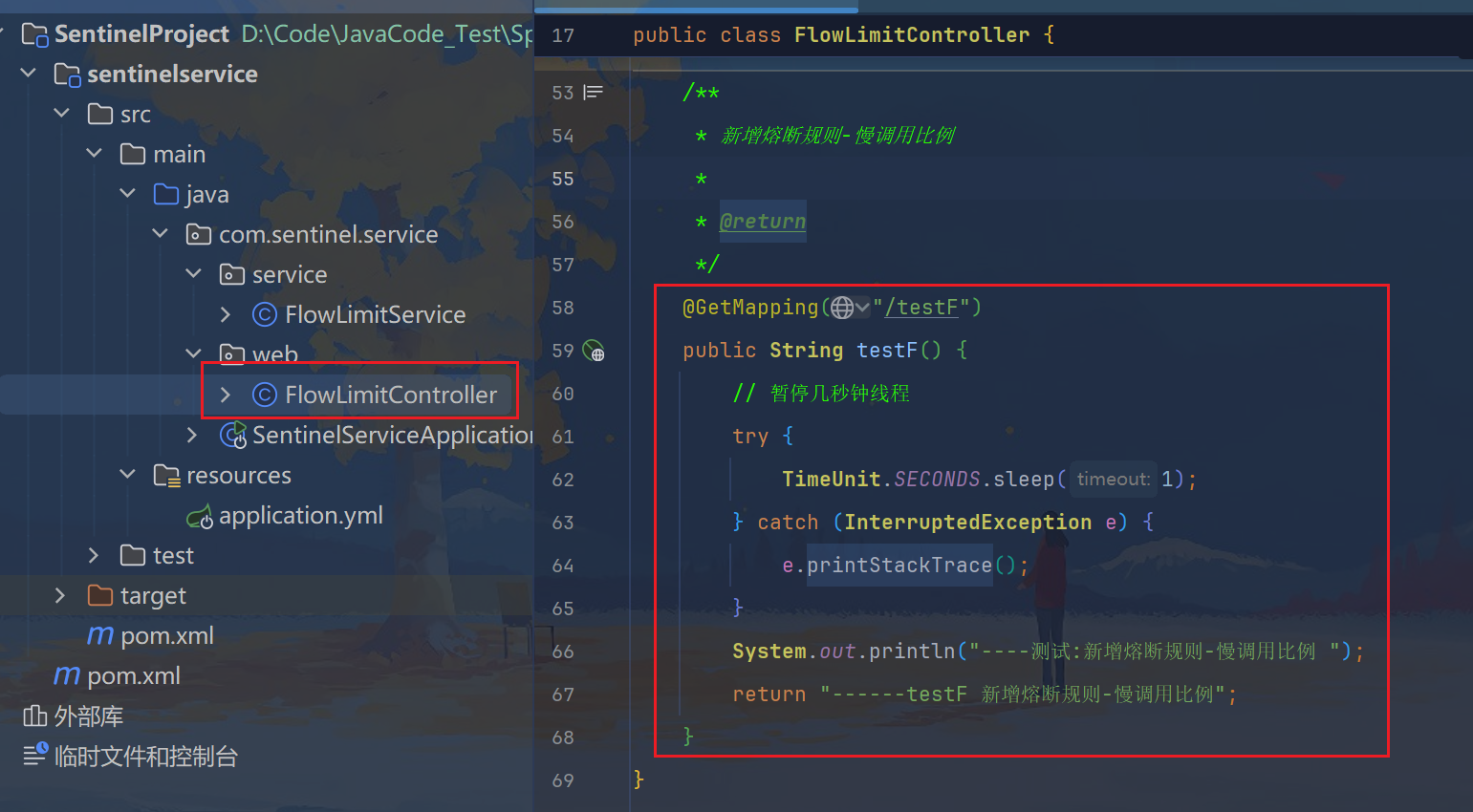
java
/**
* 新增熔断规则-慢调用比例
*
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/testF")
public String testF() {
// 暂停几秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("----测试:新增熔断规则-慢调用比例 ");
return "------testF 新增熔断规则-慢调用比例";
}
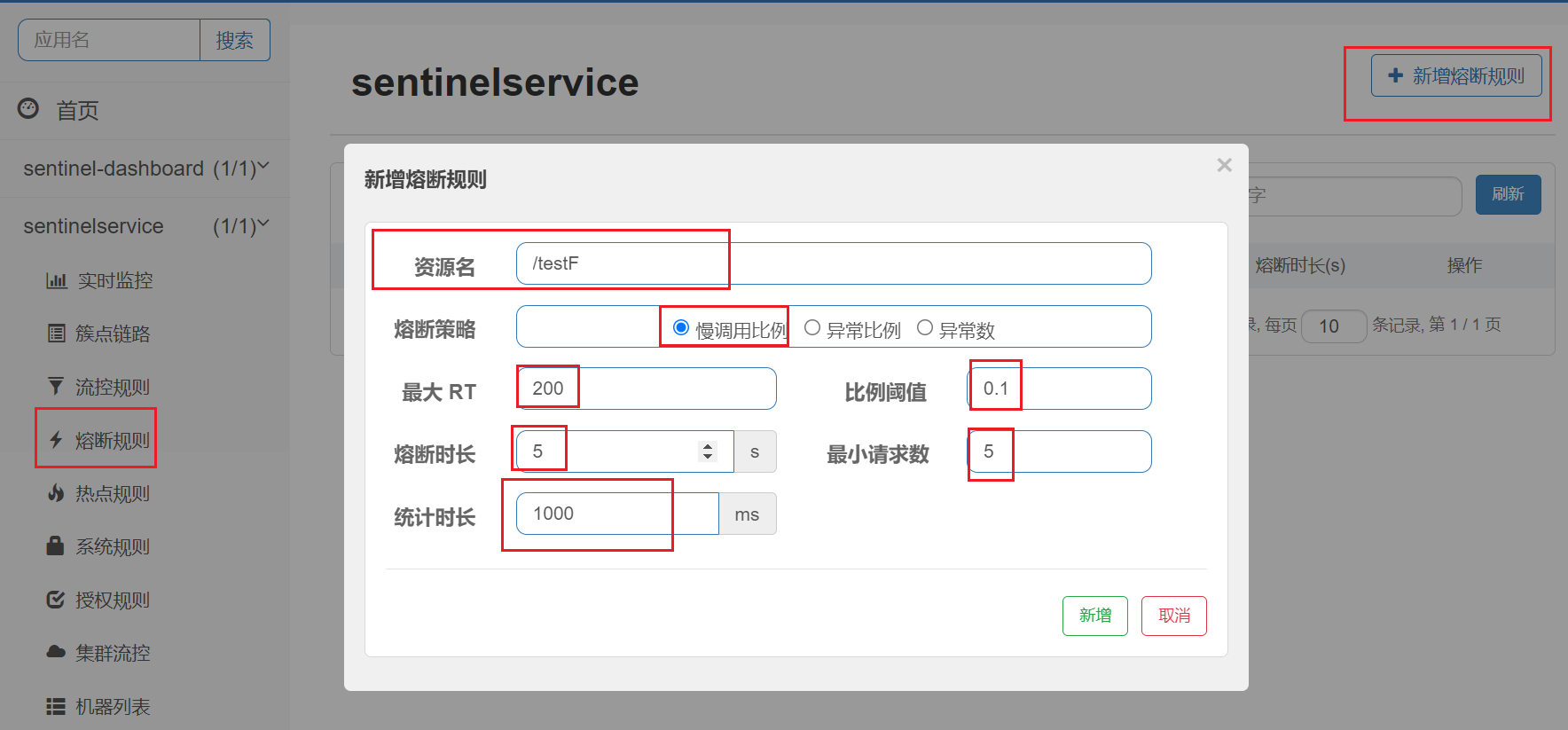
名词解释:
进入熔断状态判断依据:在统计时长内,实际请求数目>设定的最小请求数 且 实际慢调用比例>比例阈值 ,进入熔断状态。
1.调用:一个请求发送到服务器,服务器给与响应,一个响应就是一个调用。
2.最大RT:即最大的响应时间,指系统对请求作出响应的业务处理时间。
3.慢调用:处理业务逻辑的实际时间>设置的最大RT时间,这个调用叫做慢调用。
4.慢调用比例:在所以调用中,慢调用占有实际的比例=慢调用次数➗总调用次数
5.比例阈值:自己设定的 , 比例阈值=慢调用次数➗调用次数
6.统计时长:时间的判断依据
7.最小请求数:设置的调用最小请求数,上图比如1秒钟打进来10个线程(大于我们配置的5个了)调用被触发
触发条件+熔断状态:
1熔断状态(保险丝跳闸断电,不可访问):在接下来的熔断时长内请求会自动被熔断
2探测恢复状态(探路先锋):熔断时长结束后进入探测恢复状态
3结束熔断(保险丝闭合恢复,可以访问):在探测恢复状态,如果接下来的一个请求响应时间小于设置的慢调用 RT,则结束熔断,否则继续熔断。
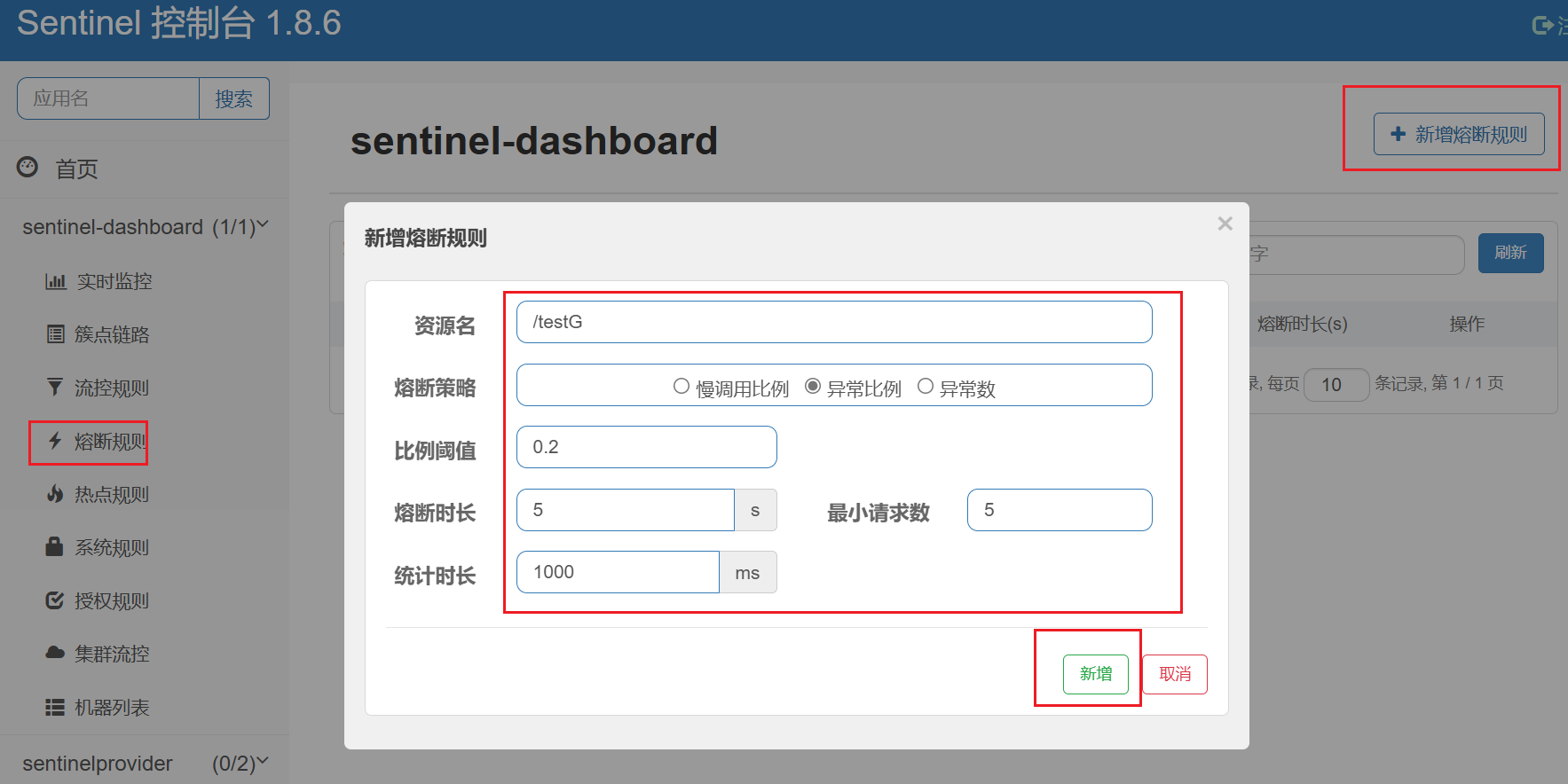
5.2、异常比例
异常比例 (ERROR_RATIO):当单位统计时长(statIntervalMs)内请求数目大于设置的最小请求数目,并且异常的比例大于阈值,则接下来的熔断时长内请求会自动被熔断。经过熔断时长后熔断器会进入探测恢复状态(HALF-OPEN 状态),若接下来的一个请求成功完成(没有错误)则结束熔断,否则会再次被熔断。异常比率的阈值范围是 [0.0, 1.0],代表 0% - 100%。
java
/**
* 新增熔断规则-异常比例
*
* @return
*/
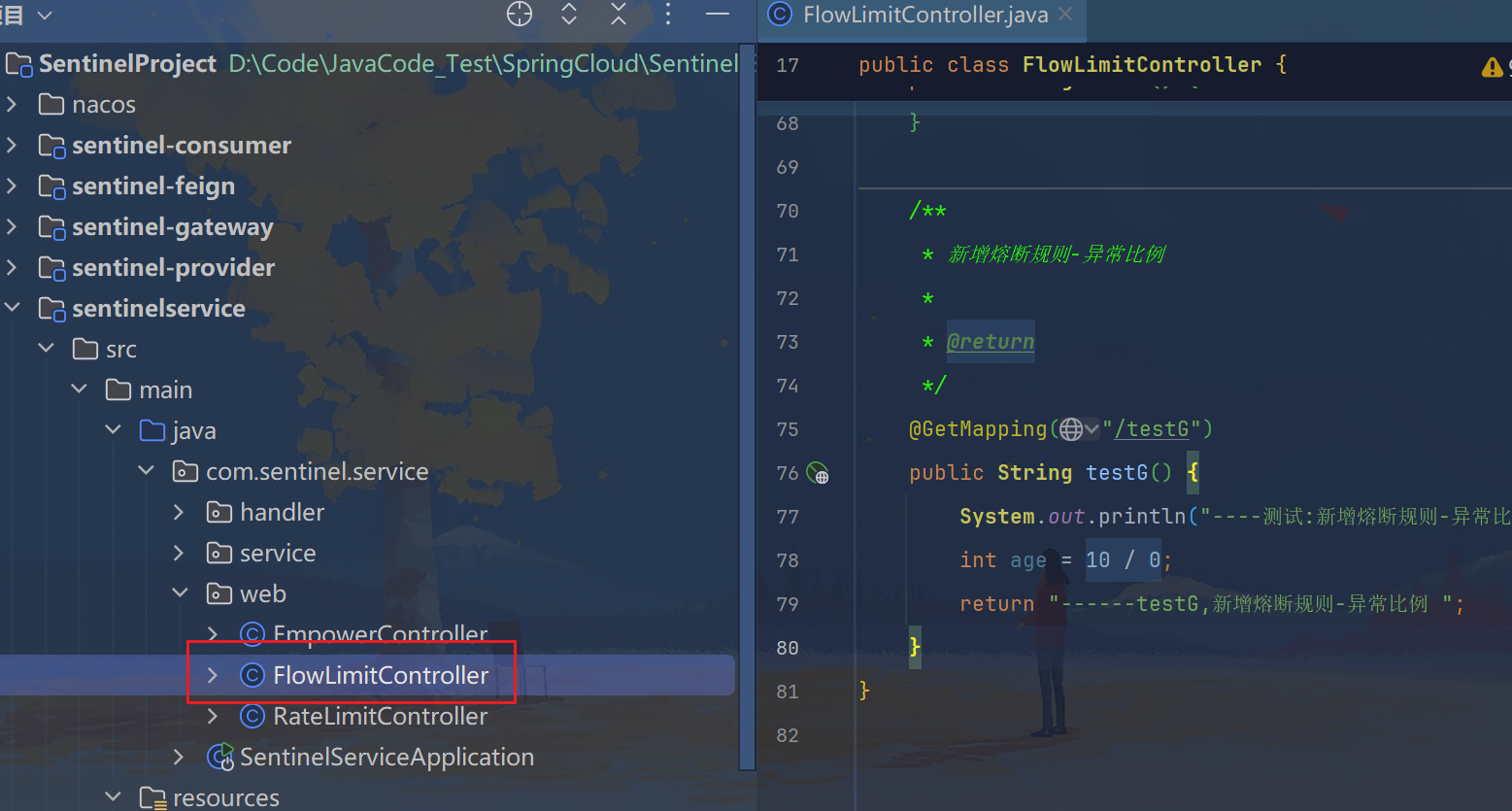
@GetMapping("/testG")
public String testG() {
System.out.println("----测试:新增熔断规则-异常比例 ");
int age = 10 / 0;
return "------testG,新增熔断规则-异常比例 ";
}
不配置Sentinel,对于int age=10/0,调一次错一次报错error,页面报【Whitelabel Error Page】或全局异常
配置Sentinel,对于int age=10/0,如符合如下异常比例启动熔断,页面报【Blocked by Sentinel (flow limiting)】
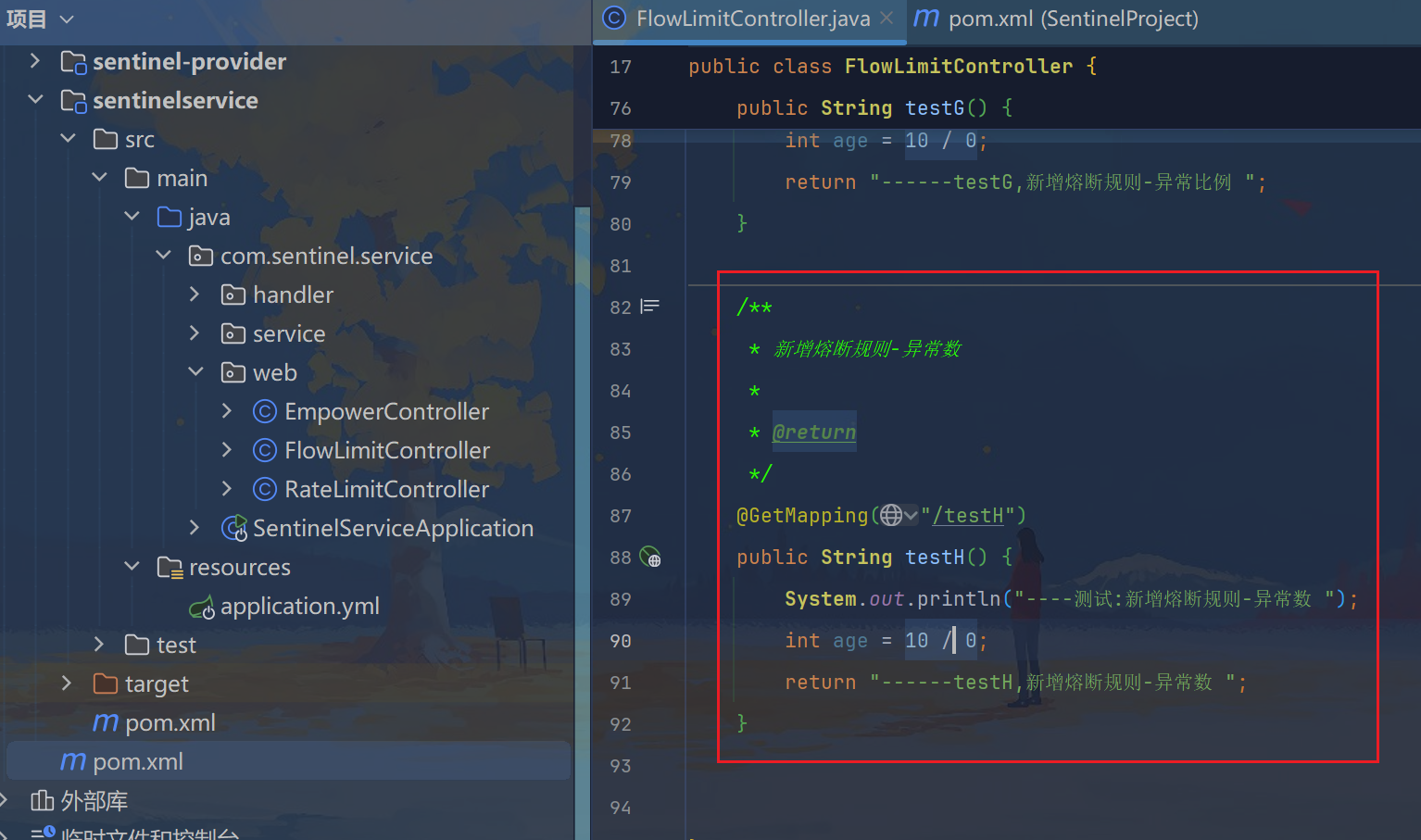
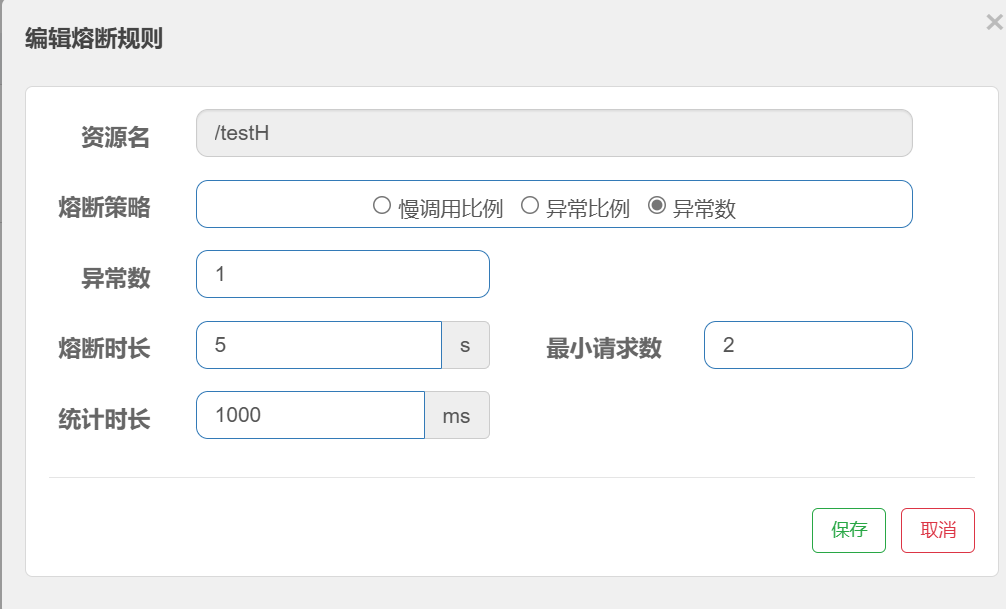
5.3、异常数
java
/**
* 新增熔断规则-异常数
*
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/testH")
public String testH() {
System.out.println("----测试:新增熔断规则-异常数 ");
int age = 10 / 0;
return "------testH,新增熔断规则-异常数 ";
}
六、SentinelResource注解
6.1、概述
SentinelResource是一个流量防卫防护组件注解,用于指定防护资源,对配置的资源进行流量控制、熔断降级等功能。
http
https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/blob/1.8/sentinel-core/src/main/java/com/alibaba/csp/sentinel/annotation/SentinelResource.java
java
package com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.annotation;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.EntryType;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* 该注解用于定义 Sentinel 资源。
*/
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
public @interface SentinelResource {
/**
* @return Sentinel 资源的名称
*/
String value() default "";
/**
* @return 进入类型(入站或出站),默认为出站
*/
EntryType entryType() default EntryType.OUT;
/**
* @return 资源的分类(类型)
* @自 1.7.0
*/
int resourceType() default 0;
/**
* @return 阻塞异常处理函数的名称,默认为空
*/
String blockHandler() default "";
/**
* 默认情况下,{@code blockHandler} 位于与原方法相同的类中。
* 但是,如果某些方法具有相同的签名并且打算设置相同的阻塞处理程序,
* 则用户可以设置阻塞处理程序所在的类。注意,阻塞处理程序方法必须是静态的。
*
* @return 阻塞处理程序所在的类,不应提供多个类
*/
Class<?>[] blockHandlerClass() default {};
/**
* @return 回退函数的名称,默认为空
*/
String fallback() default "";
/**
* {@code defaultFallback} 用作默认的通用回退方法。
* 它不应接受任何参数,并且返回类型应与原方法兼容。
*
* @return 默认回退方法的名称,默认为空
* @自 1.6.0
*/
String defaultFallback() default "";
/**
* 默认情况下,{@code fallback} 位于与原方法相同的类中。
* 但是,如果某些方法具有相同的签名并且打算设置相同的回退,
* 则用户可以设置回退函数所在的类。注意,共享的回退方法必须是静态的。
*
* @return 回退方法所在的类(仅单个类)
* @自 1.6.0
*/
Class<?>[] fallbackClass() default {};
/**
* @return 要跟踪的异常类列表,默认是 {@link Throwable}
* @自 1.5.1
*/
Class<? extends Throwable>[] exceptionsToTrace() default {Throwable.class};
/**
* 指示要忽略的异常。注意,{@code exceptionsToTrace} 和 {@code exceptionsToIgnore}
* 不应同时出现,否则 {@code exceptionsToIgnore} 将具有更高优先级。
*
* @return 要忽略的异常类列表,默认为空
* @自 1.6.0
*/
Class<? extends Throwable>[] exceptionsToIgnore() default {};
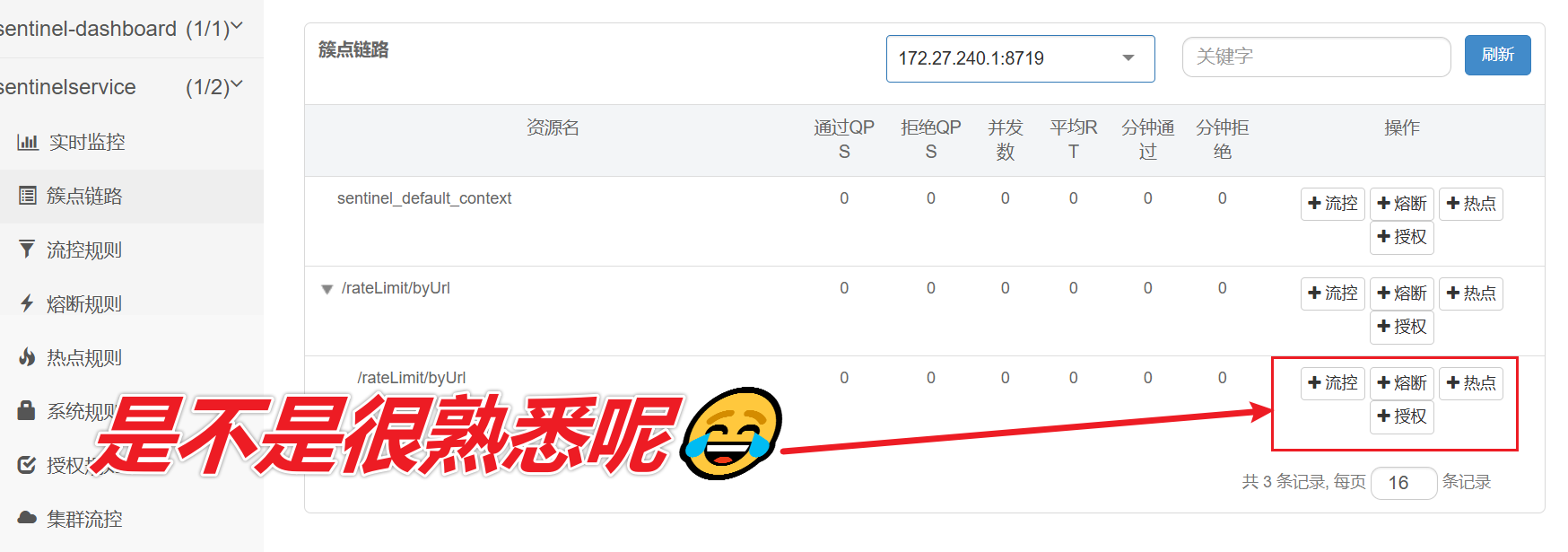
}当请求进入微服务时,首先会访问DispatcherServlet,然后进入Controller、Service、Mapper,这样的一个调用链就叫做簇点链路 。簇点链路中被监控的每一个接口就是一个资源。
默认情况下sentinel会监控SpringMVC的每一个端点(Endpoint,也就是controller中的方法),因此SpringMVC的每一个端点(Endpoint)就是调用链路中的一个资源。
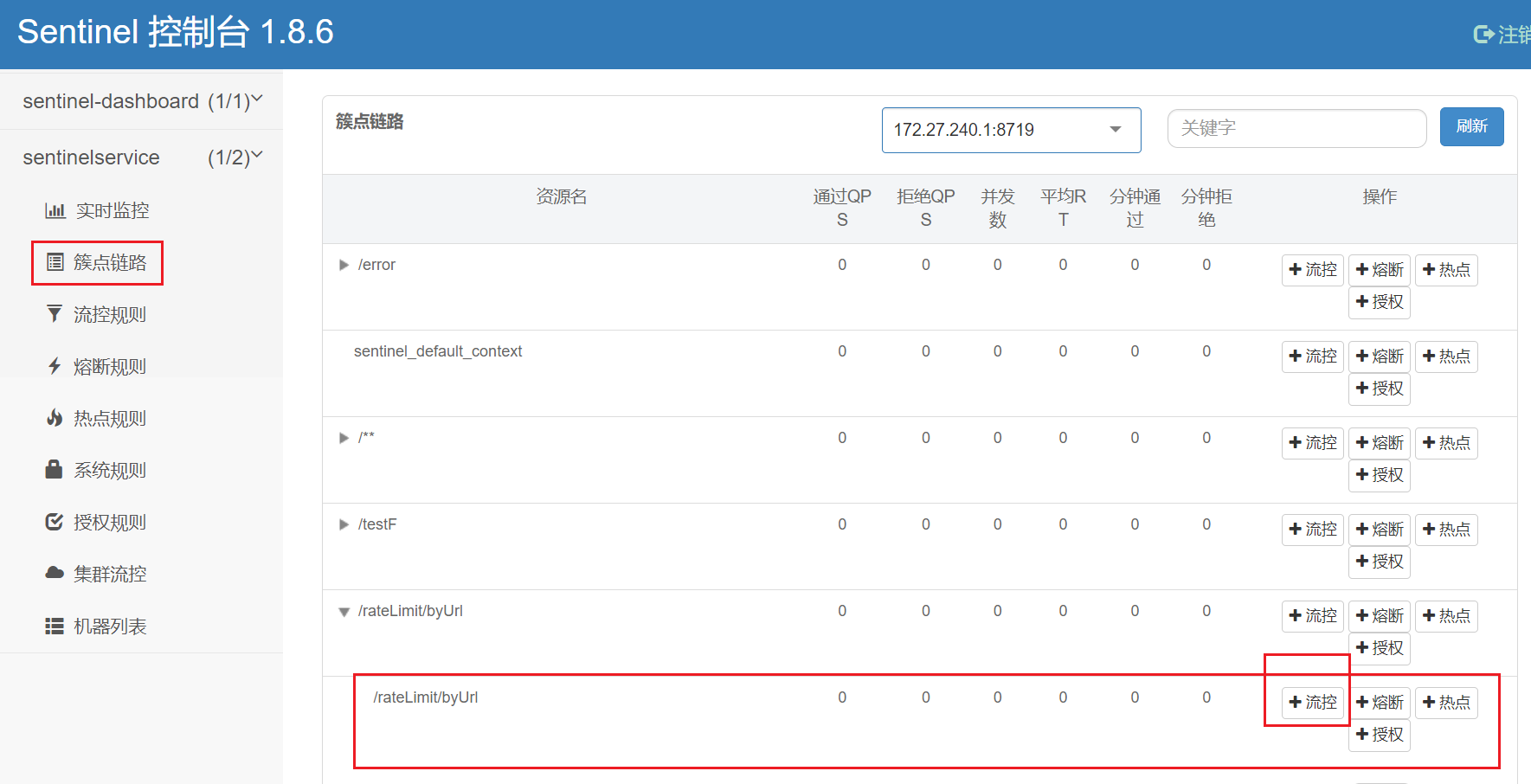
流控、熔断等都是针对簇点链路中的资源来设置的,因此我们可以点击对应资源后面的按钮来设置规则:
- 流控:流量控制
- 降级:降级熔断
- 热点:热点参数限流,是限流的一种
- 授权:请求的权限控制
6.2、按照rest地址限流+默认限流返回
通过访问res地址来限流,会返回Sentinel自带默认的限流处理信息。
java
package com.sentinel.service.web;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @Author: 史小创
* @Time: 2024/8/28 下午2:20
* @Description:
*/
@RestController
public class RateLimitController {
@GetMapping("/rateLimit/byUrl")
public String byUrl() {
return "按rest地址限流测试OK";
}
}
先访问一下:
http
http://localhost:9001/rateLimit/byUrl
http
http://localhost:9001/rateLimit/byUrl
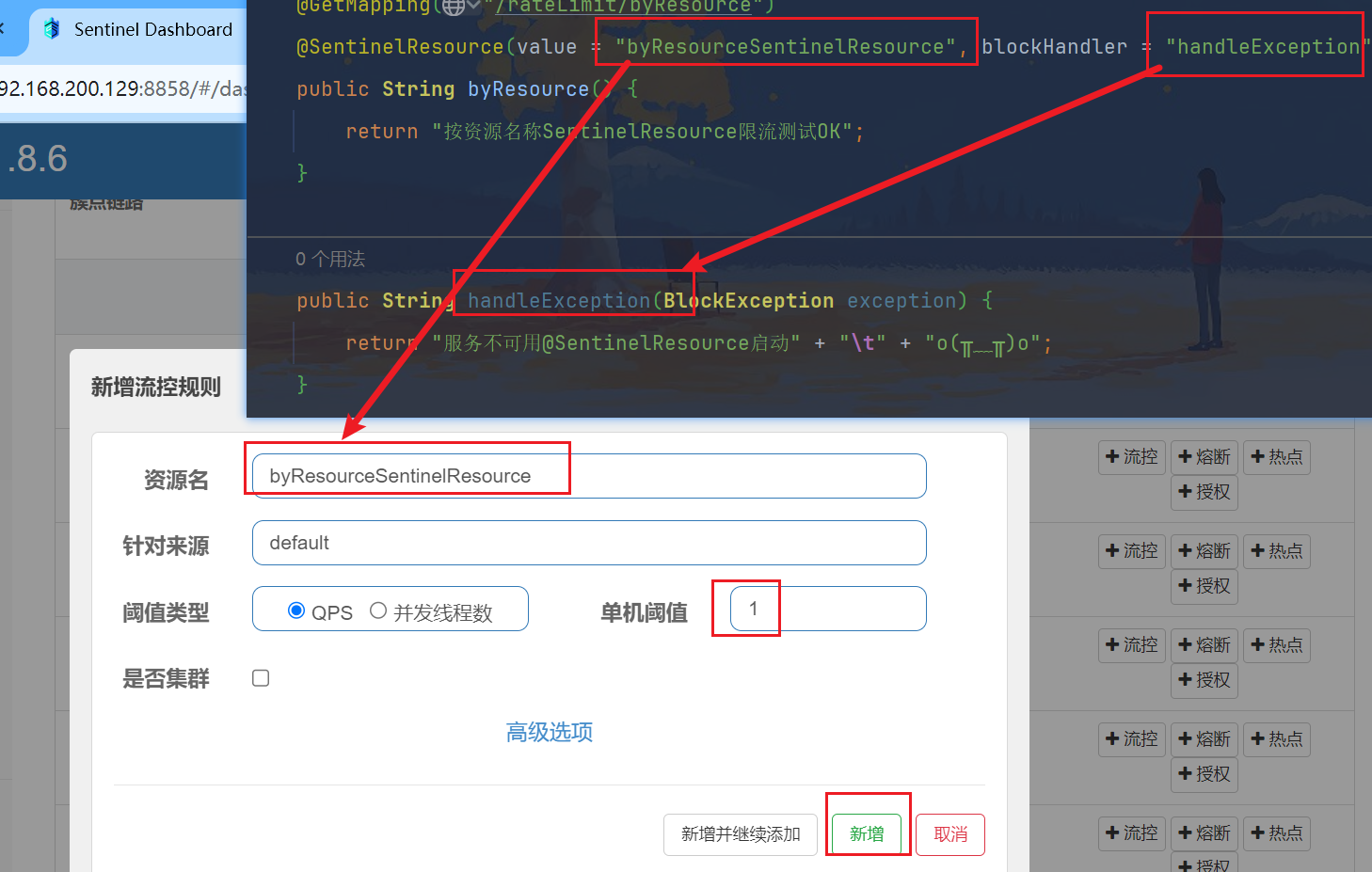
6.3、按SentinelResource资源名称限流+自定义限流返回
不想用默认的限流提示(Blocked by Sentinel (flow limiting)),想返回自定义限流的提示
java
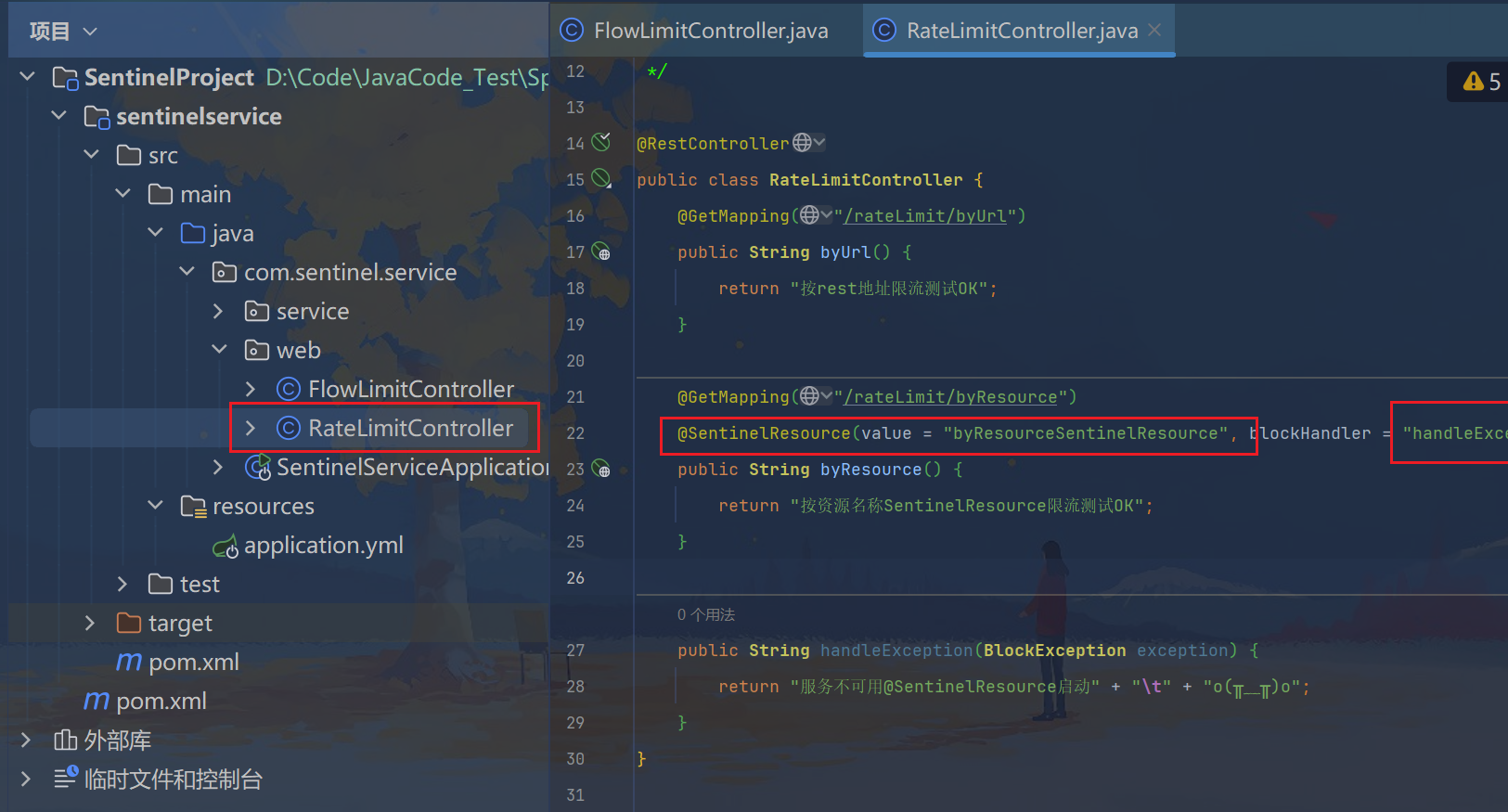
@GetMapping("/rateLimit/byResource")
@SentinelResource(value = "byResourceSentinelResource", blockHandler = "handleException")
public String byResource() {
return "按资源名称SentinelResource限流测试OK";
}
public String handleException(BlockException exception) {
return "服务不可用@SentinelResource启动" + "\t" + "o(╥﹏╥)o";
}
http
http://localhost:9001/rateLimit/byResource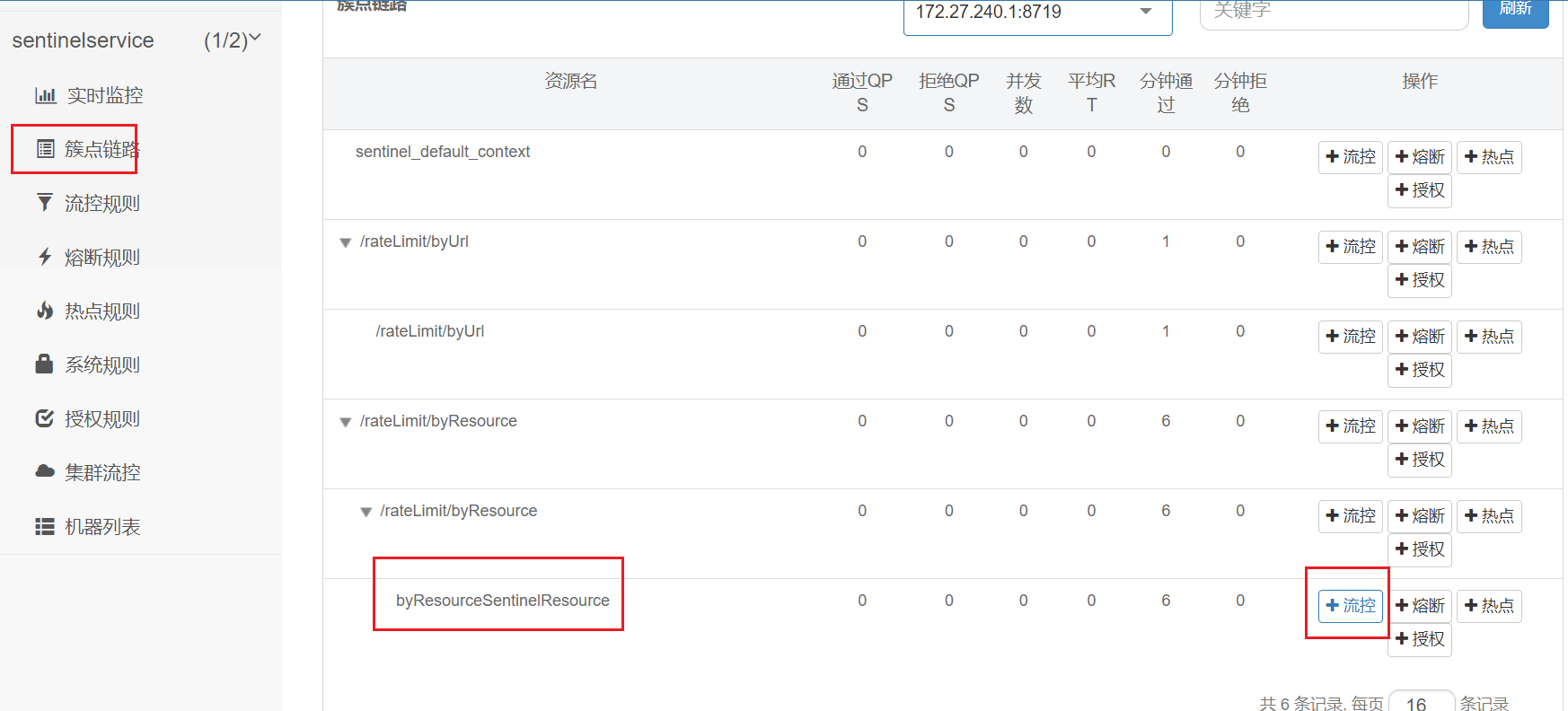
http
http://localhost:9001/rateLimit/byResource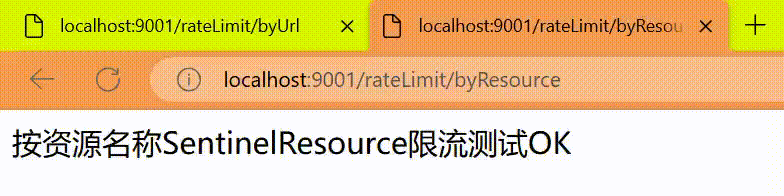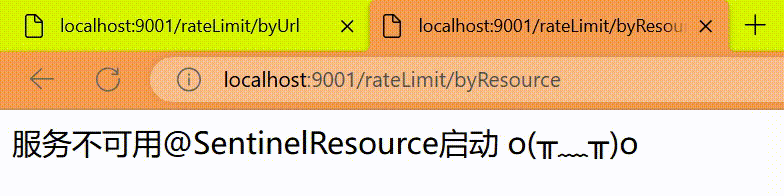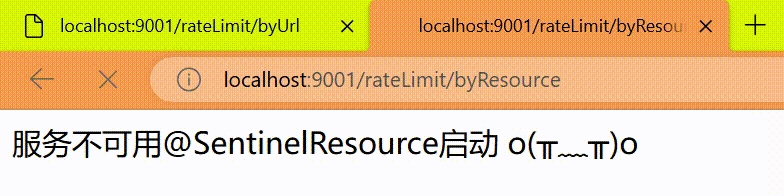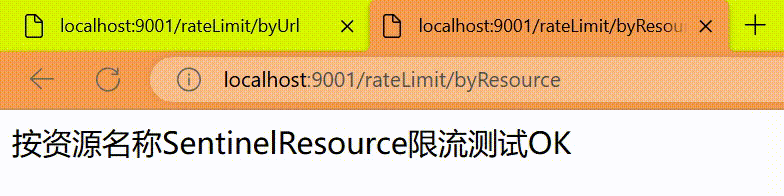
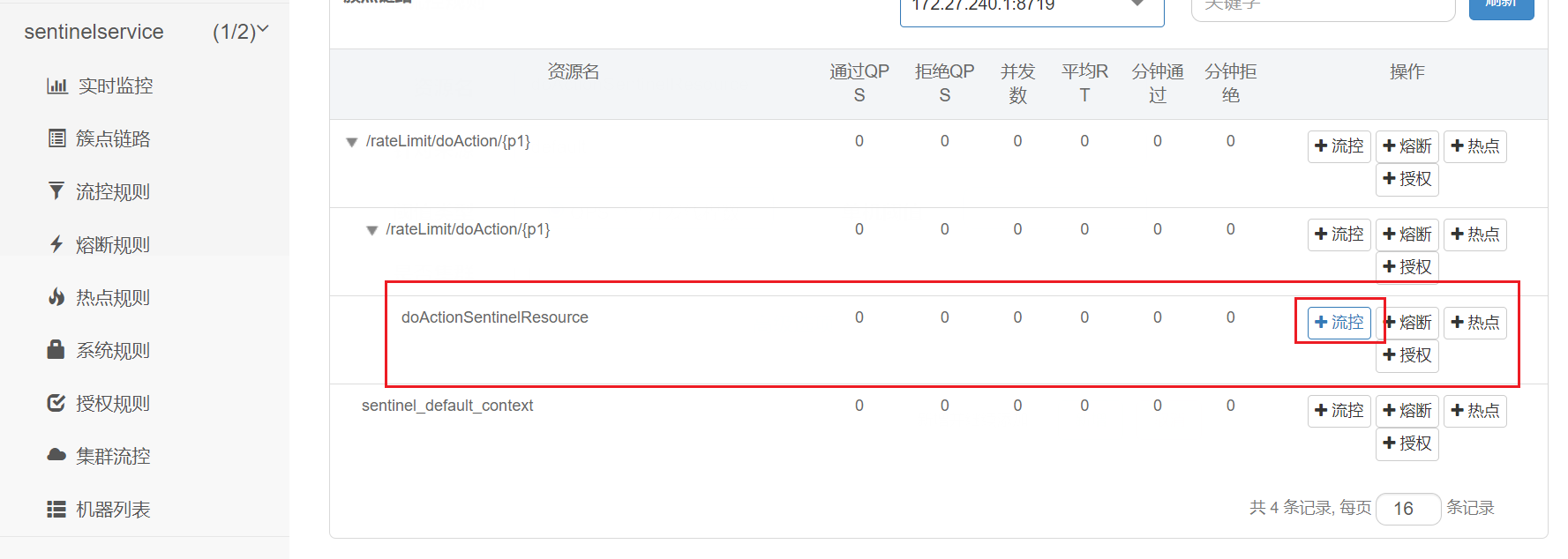
6.4、按SentinelResource资源名称限流+自定义限流返回+服务降级处理
按SentinelResource配置,点击超过限流配置返回自定义限流提示+程序异常返回fallback服务降级
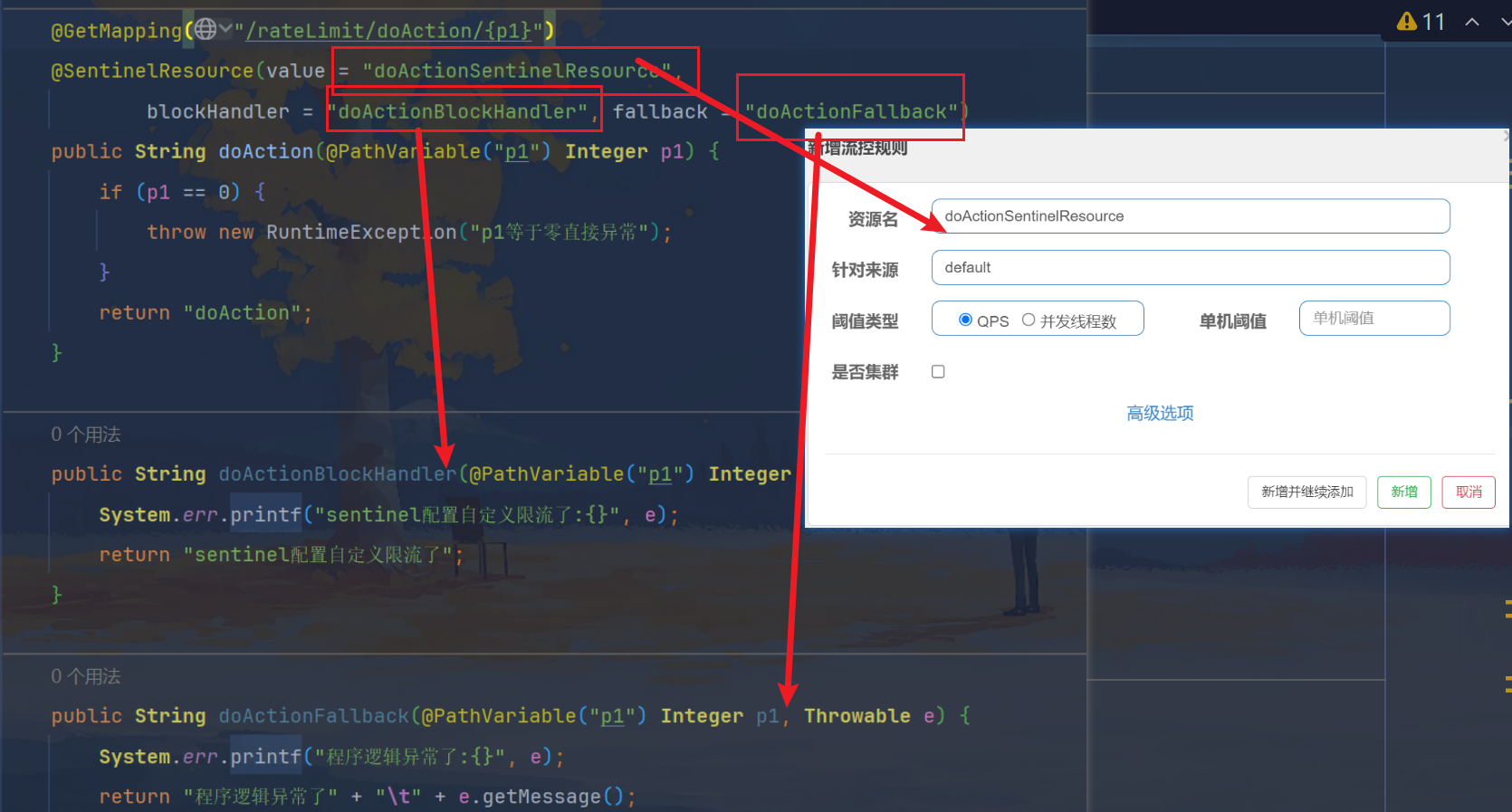
java
@GetMapping("/rateLimit/doAction/{p1}")
@SentinelResource(value = "doActionSentinelResource",
blockHandler = "doActionBlockHandler", fallback = "doActionFallback")
public String doAction(@PathVariable("p1") Integer p1) {
if (p1 == 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("p1等于零直接异常");
}
return "doAction";
}
public String doActionBlockHandler(@PathVariable("p1") Integer p1, BlockException e) {
System.err.printf("sentinel配置自定义限流了:{}", e);
return "sentinel配置自定义限流了";
}
public String doActionFallback(@PathVariable("p1") Integer p1, Throwable e) {
System.err.printf("程序逻辑异常了:{}", e);
return "程序逻辑异常了" + "\t" + e.getMessage();
}
http
http://localhost:9001/rateLimit/doAction/99
http
http://localhost:9001/rateLimit/doAction/99
http
http://localhost:9001/rateLimit/doAction/0
七、实战:热点规则
7.1、概述
热点即经常访问的数据,很多时候我们希望统计或者限制某个热点数据中访问频次最高的TopN数据,并对其访问进行限流或者其它操作
http
https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/%E7%83%AD%E7%82%B9%E5%8F%82%E6%95%B0%E9%99%90%E6%B5%81
7.2、全局参数限流
方法testHotKey里面第一个参数P1只要QPS超过每秒1次,马上降级处理
java
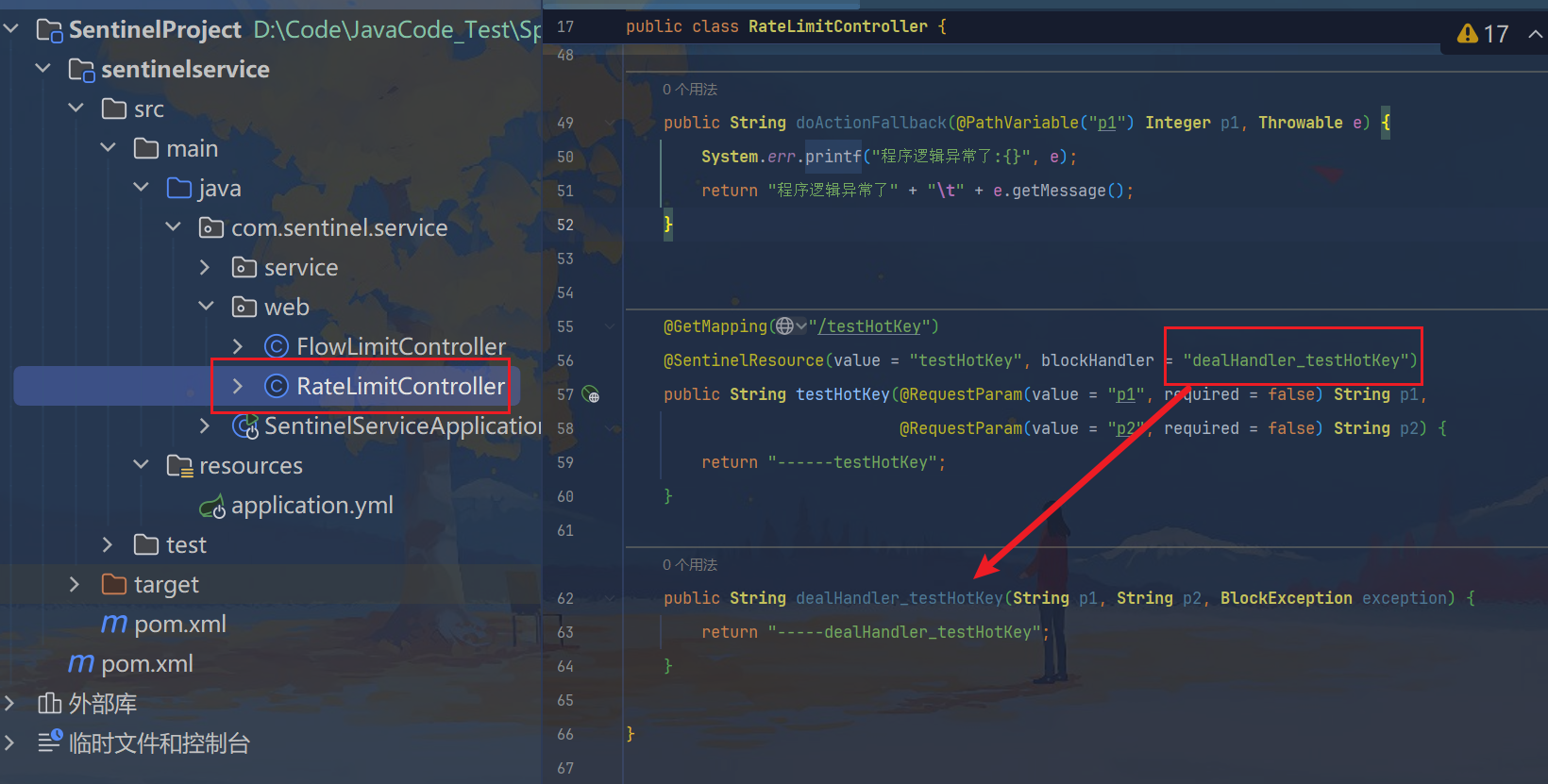
@GetMapping("/testHotKey")
@SentinelResource(value = "testHotKey", blockHandler = "dealHandler_testHotKey")
public String testHotKey(@RequestParam(value = "p1", required = false) String p1,
@RequestParam(value = "p2", required = false) String p2) {
return "------testHotKey";
}
public String dealHandler_testHotKey(String p1, String p2, BlockException exception) {
return "-----dealHandler_testHotKey";
}
http
http://localhost:9001/testHotkey
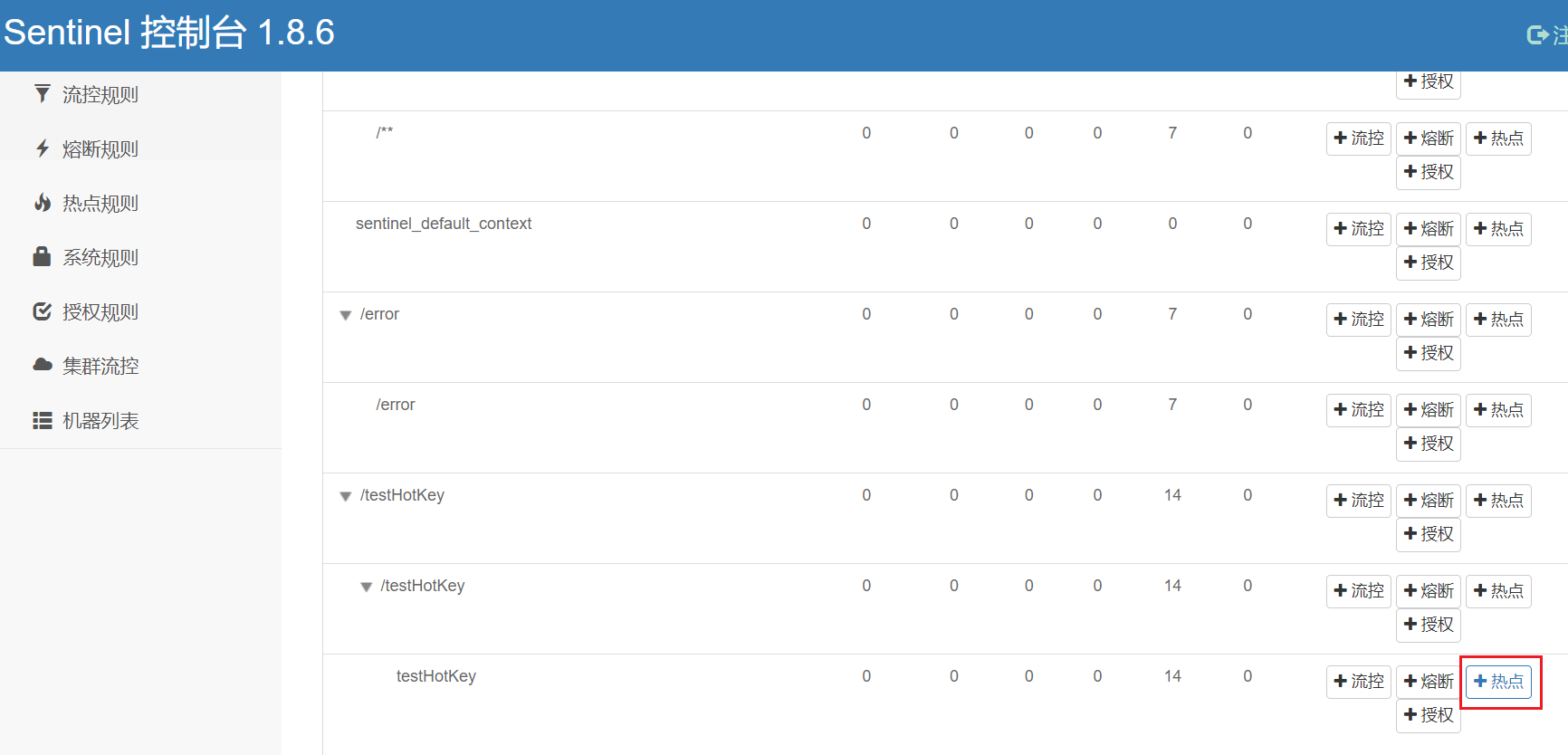
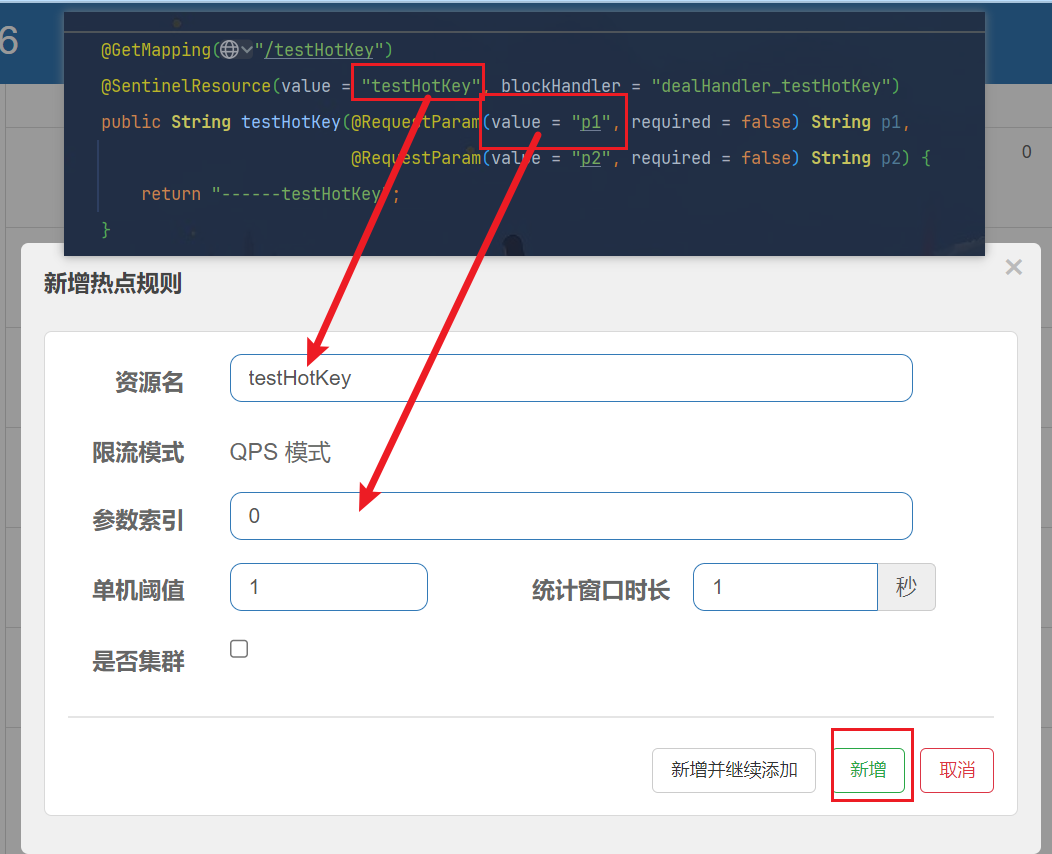
限流模式只支持QPS模式,固定写死了。(这才叫热点)
@SentinelResource注解的方法参数索引,0代表第一个参数,1代表第二个参数,以此类推
单机阀值以及统计窗口时长表示在此窗口时间超过阀值就限流。
上面的抓图就是第一个参数有值的话,1秒的QPS为1,超过就限流,限流后调用dealHandler_testHotKey支持方法。
http
http://localhost:9001/testHotkey?p1=abc
http
http://localhost:9001/testHotkey?p1=abc
http
http://localhost:9001/testHotKey?p2=99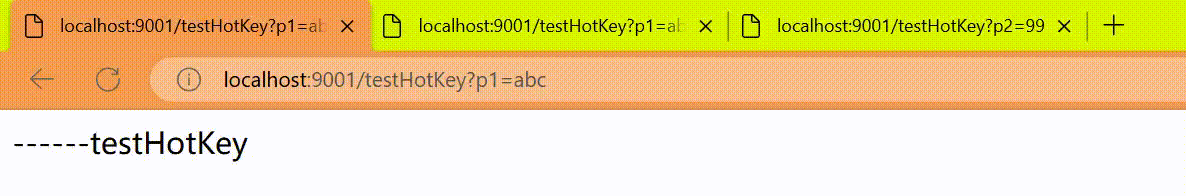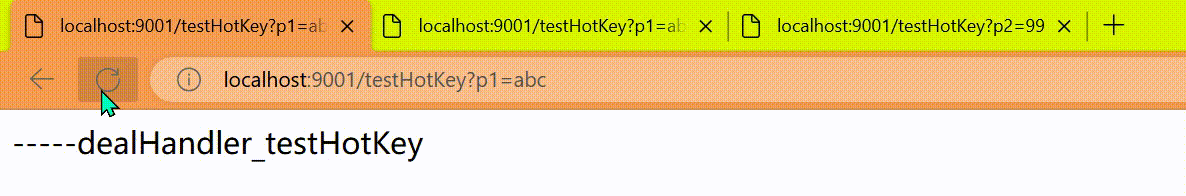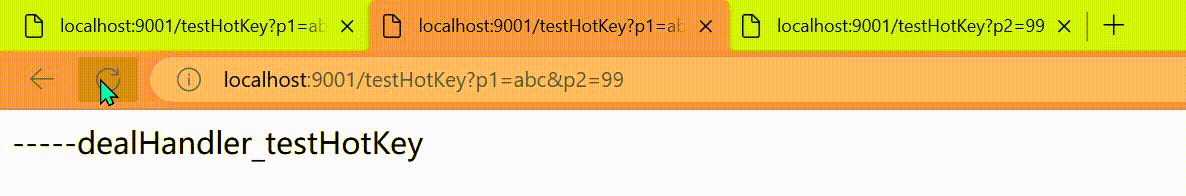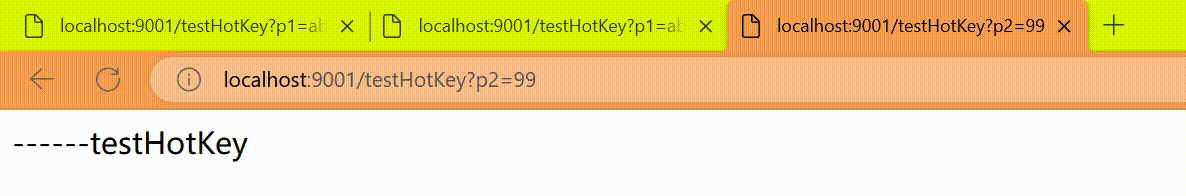
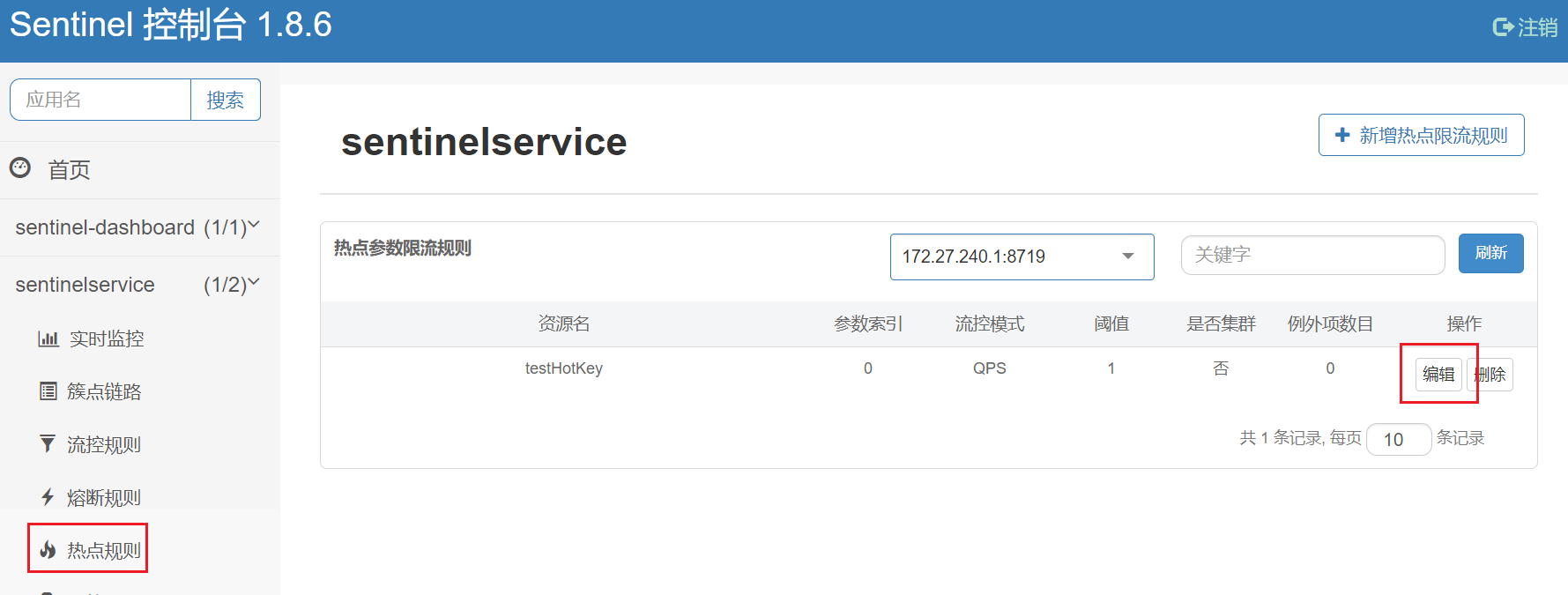
7.3、测试例外项(热点参数限流)
上述案例演示了第一个参数p1,当QPS超过1秒1次点击后马上被限流
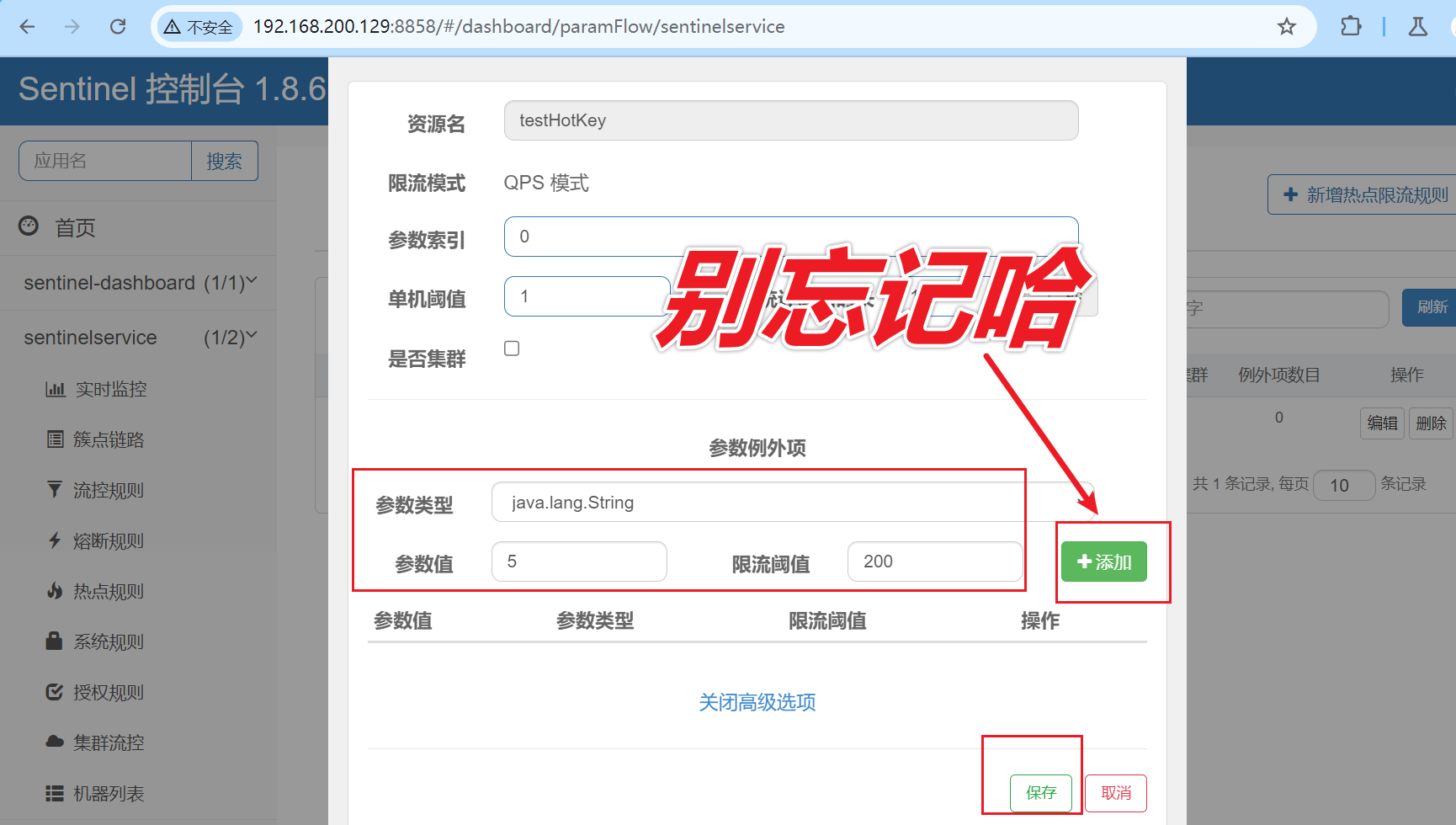
我们期望p1参数当它是某个特殊值时,到达某个约定值后【普通正常限流】规则突然例外、失效了,它的限流值和平时不一样,假如当p1的值等于5时,它的阈值可以达到200或其它值
http
http://localhost:9001/testHotKey?p1=abc
http
http://localhost:9001/testHotKey?p1=5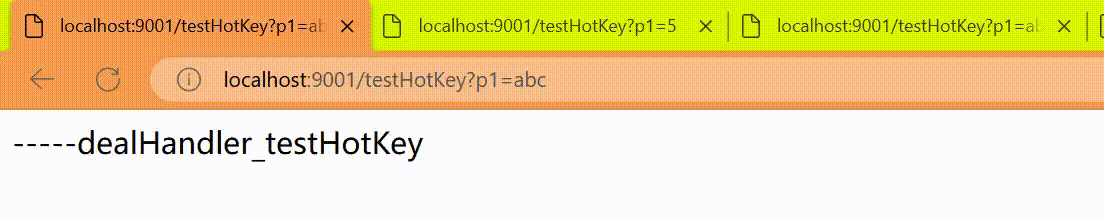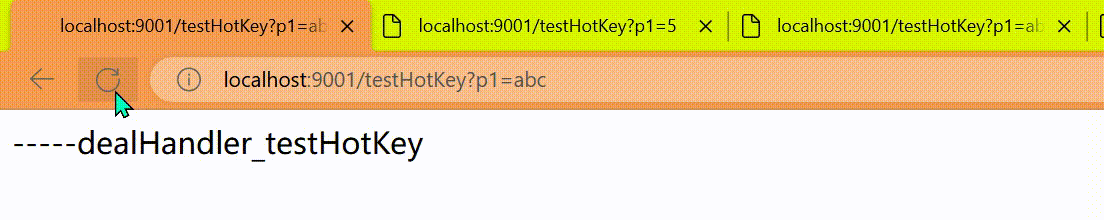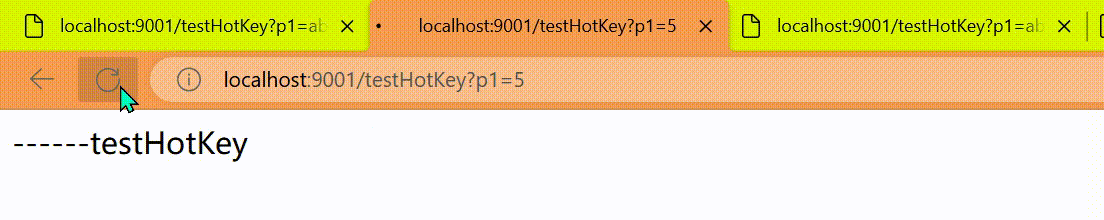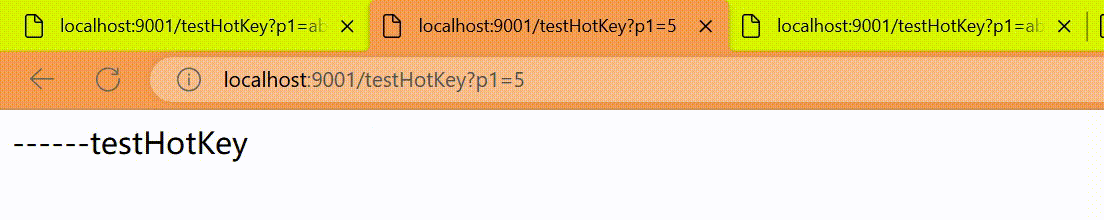
注意:热点参数的注意点,参数必须是基本类型或者String
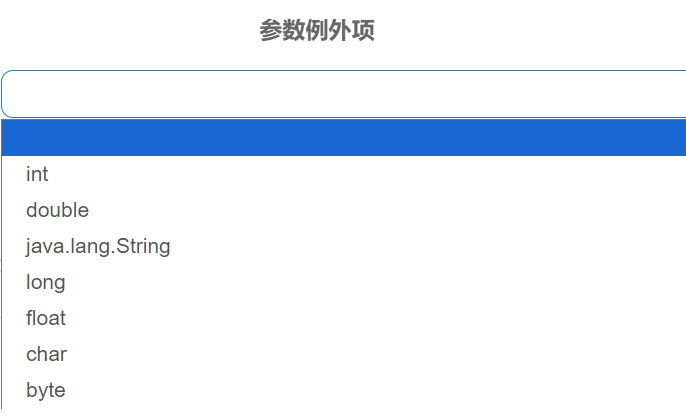
八、实战:授权规则
8.1、概述
http
https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/%E5%A6%82%E4%BD%95%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8#%E8%AE%BF%E9%97%AE%E6%8E%A7%E5%88%B6%E8%A7%84%E5%88%99-authorityrule
在Sentinel的授权规则中,提供了 白名单与黑名单 两种授权类型。白放行、黑禁止
授权规则可以对调用方的来源做控制,有白名单和黑名单两种方式。
-
白名单:来源(origin)在白名单内的调用者允许访问
-
黑名单:来源(origin)在黑名单内的调用者不允许访问
点击左侧菜单的授权,可以看到授权规则:
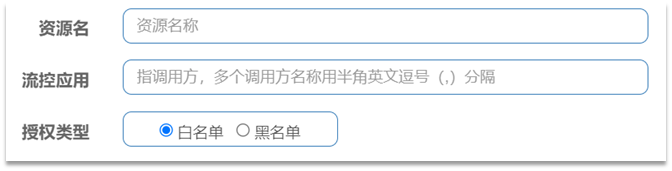
-
资源名:就是受保护的资源,例如/order/{orderId}
-
流控应用:是来源者的名单,
- 如果是勾选白名单,则名单中的来源被许可访问。
- 如果是勾选黑名单,则名单中的来源被禁止访问。
比如:
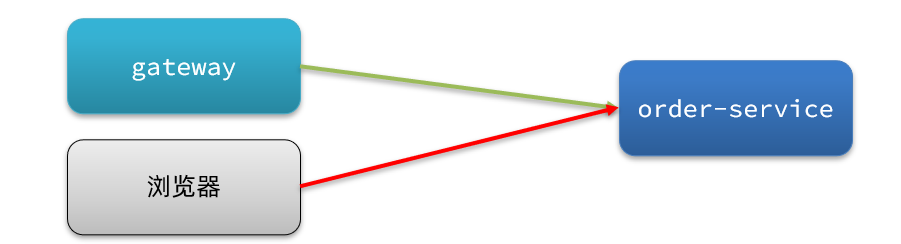
我们允许请求从gateway到order-service,不允许浏览器访问order-service,那么白名单中就要填写网关的来源名称(origin)。
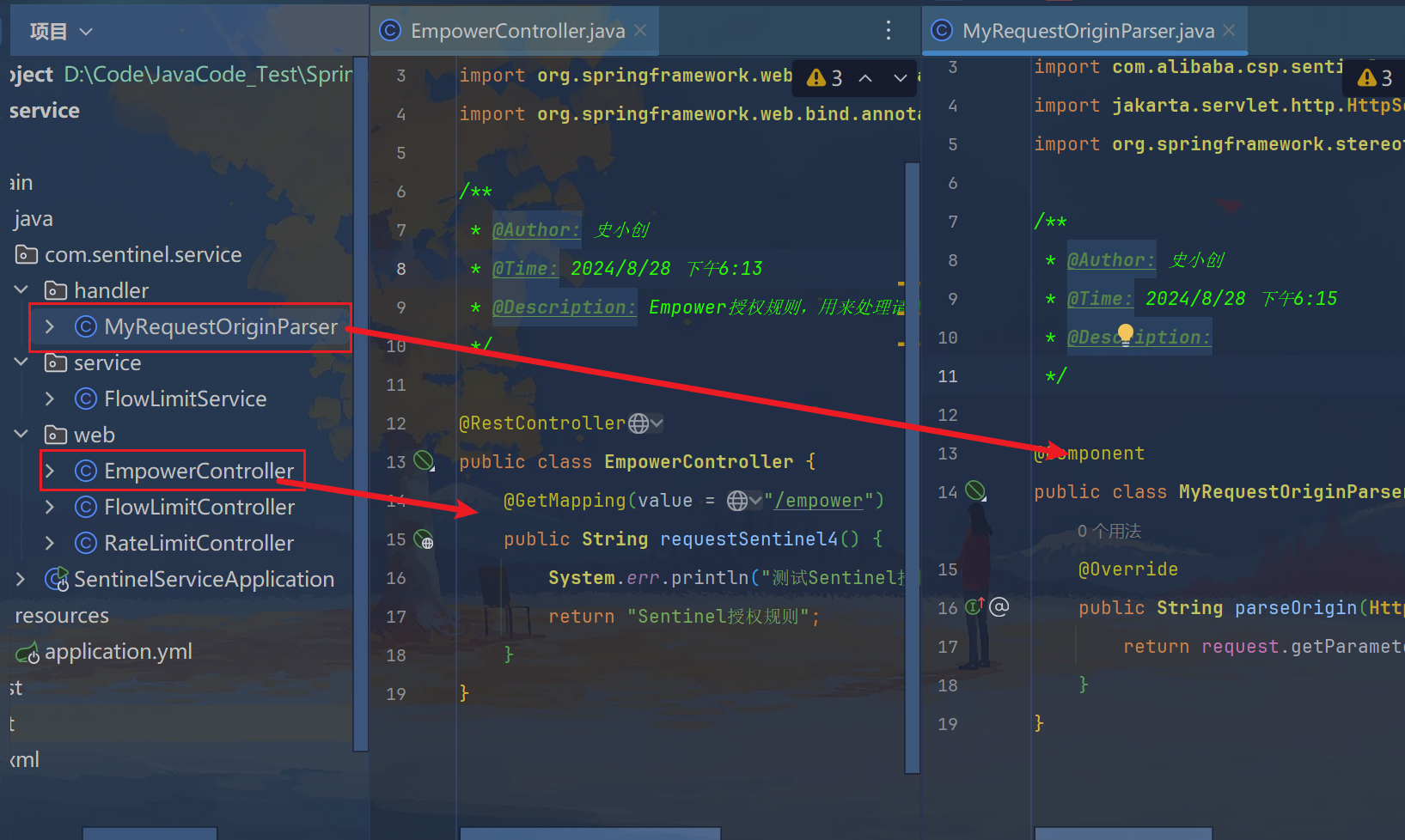
8.2、代码
java
package com.sentinel.service.web;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @Author: 史小创
* @Time: 2024/8/28 下午6:13
* @Description: Empower授权规则,用来处理请求的来源
*/
@RestController
public class EmpowerController {
@GetMapping(value = "/empower")
public String requestSentinel4() {
System.err.println("测试Sentinel授权规则empower");
return "Sentinel授权规则";
}
}
java
package com.sentinel.service.handler;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.adapter.spring.webmvc.callback.RequestOriginParser;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @Author: 史小创
* @Time: 2024/8/28 下午6:15
* @Description:
*/
@Component
public class MyRequestOriginParser implements RequestOriginParser {
@Override
public String parseOrigin(HttpServletRequest request) {
return request.getParameter("serverName");
}
}
8.3、测试
http
http://localhost:9001/empower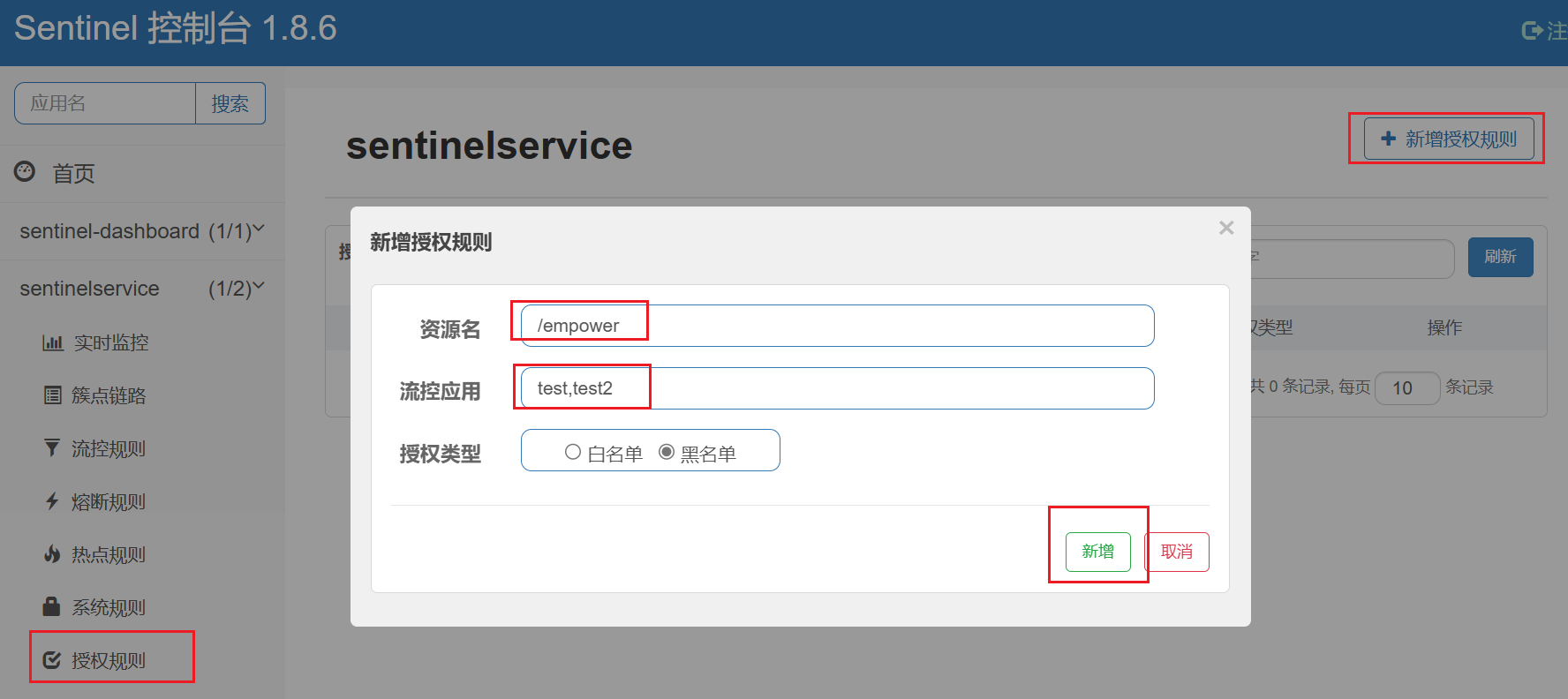
http
http://localhost:9001/empower?serverName=abc
http
http://localhost:9001/empower?serverName=test2
http
http://localhost:9001/empower?serverName=test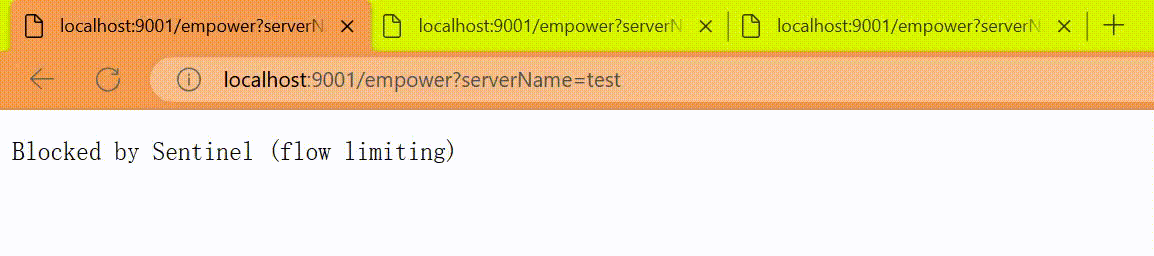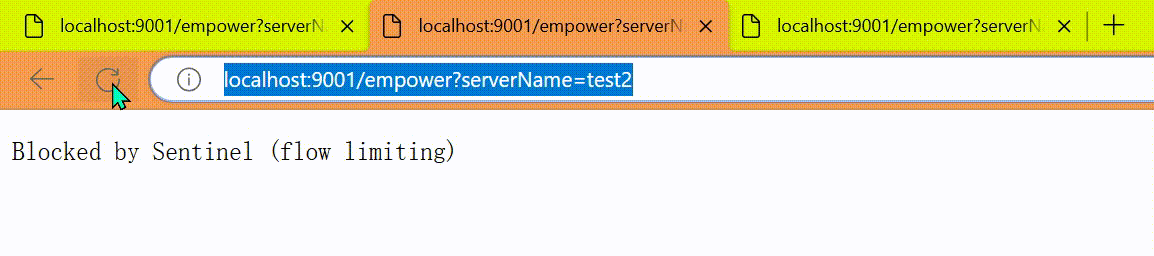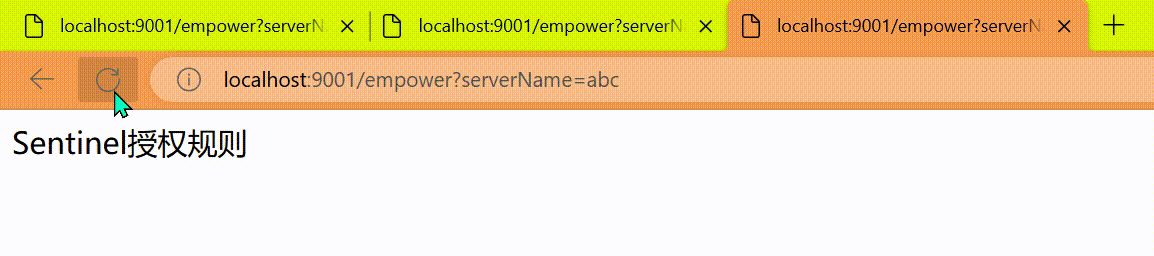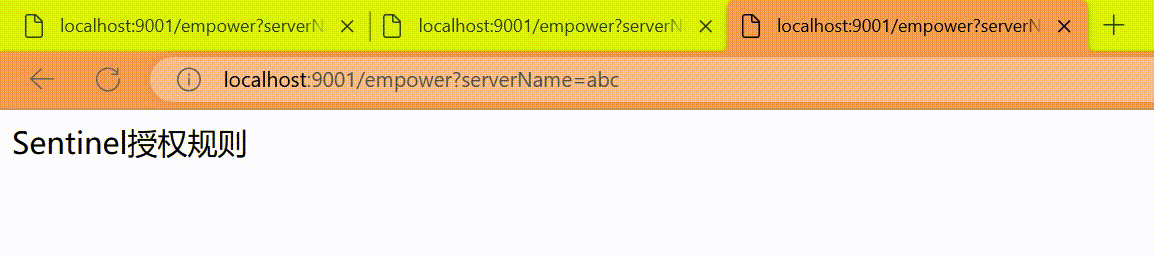
九、规则持久化
现在,sentinel的所有规则都是内存存储,重启后所有规则都会丢失。在生产环境下,我们必须确保这些规则的持久化,避免丢失。
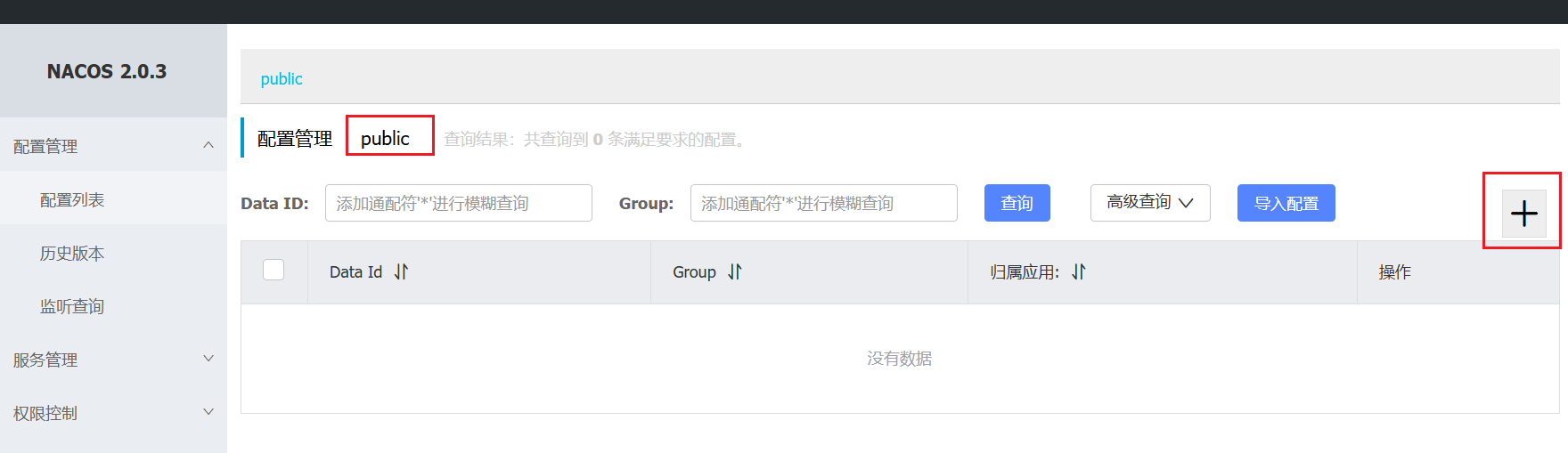
9.1、规则管理模式
规则是否能持久化,取决于规则管理模式,sentinel支持三种规则管理模式:
-
原始模式:Sentinel的默认模式,将规则保存在内存,重启服务会丢失。
-
pull模式
-
push模式
9.2、pull模式
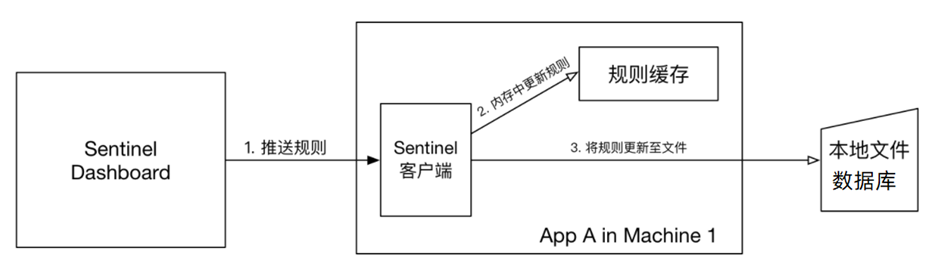
pull模式:控制台将配置的规则推送到Sentinel客户端,而客户端会将配置规则保存在本地文件或数据库中。以后会定时去本地文件或数据库中查询,更新本地规则。
9.3、push模式
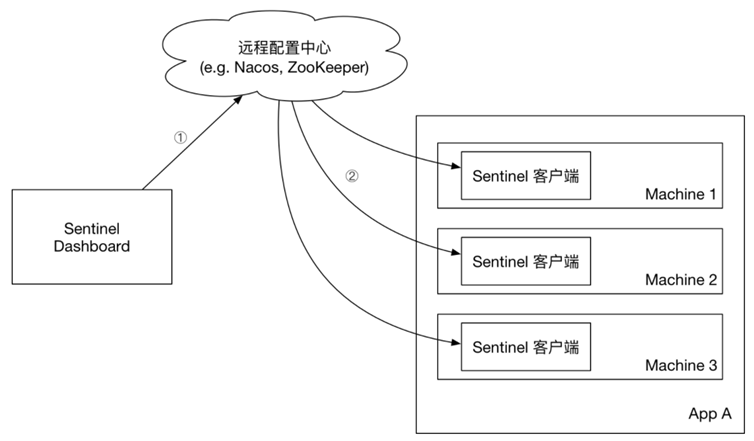
push模式:控制台将配置规则推送到远程配置中心,例如Nacos。Sentinel客户端监听Nacos,获取配置变更的推送消息,完成本地配置更新。
9.4、改POM
xml
<!--SpringCloud ailibaba sentinel-datasource-nacos -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-datasource-nacos</artifactId>
</dependency>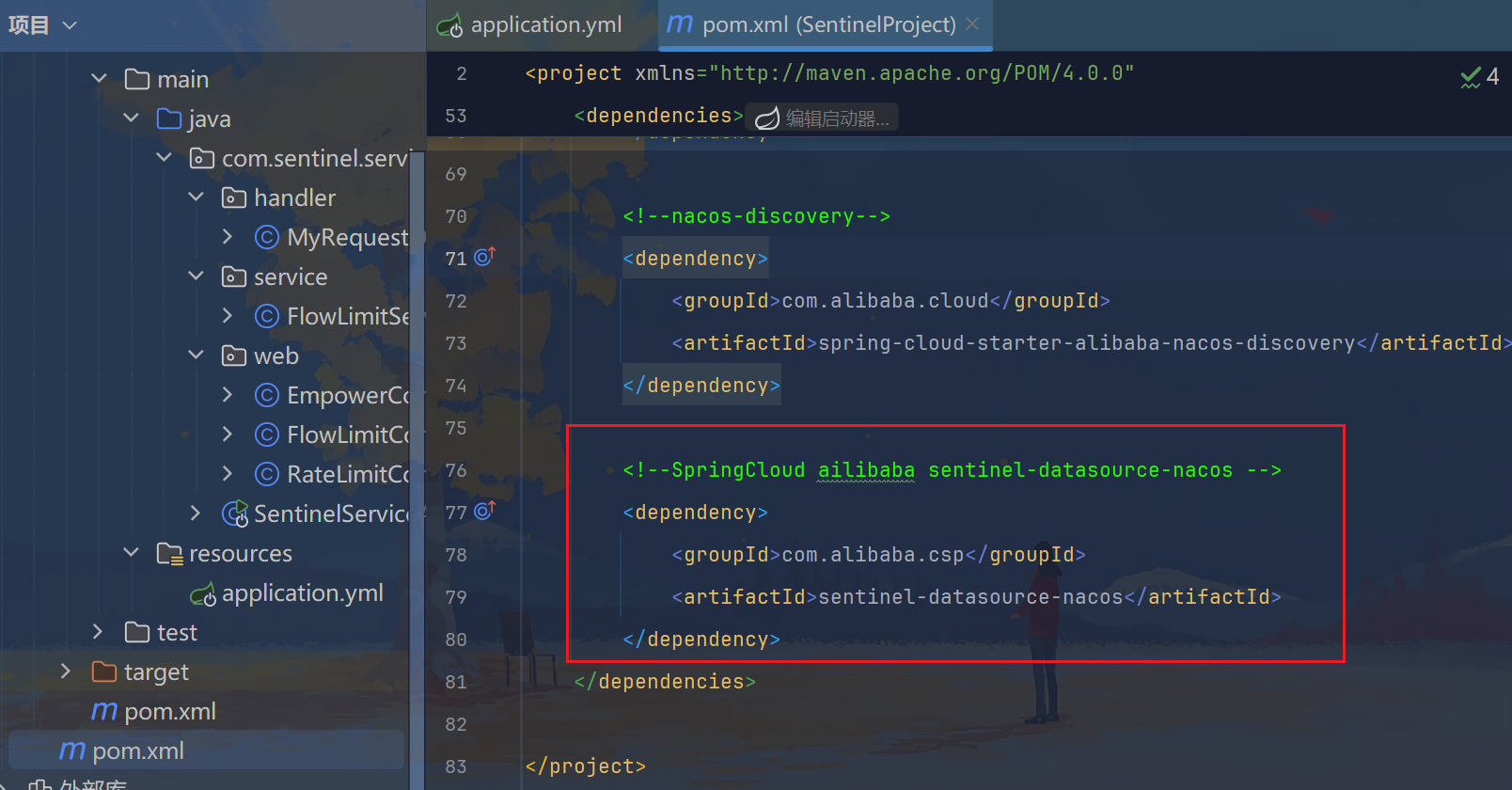
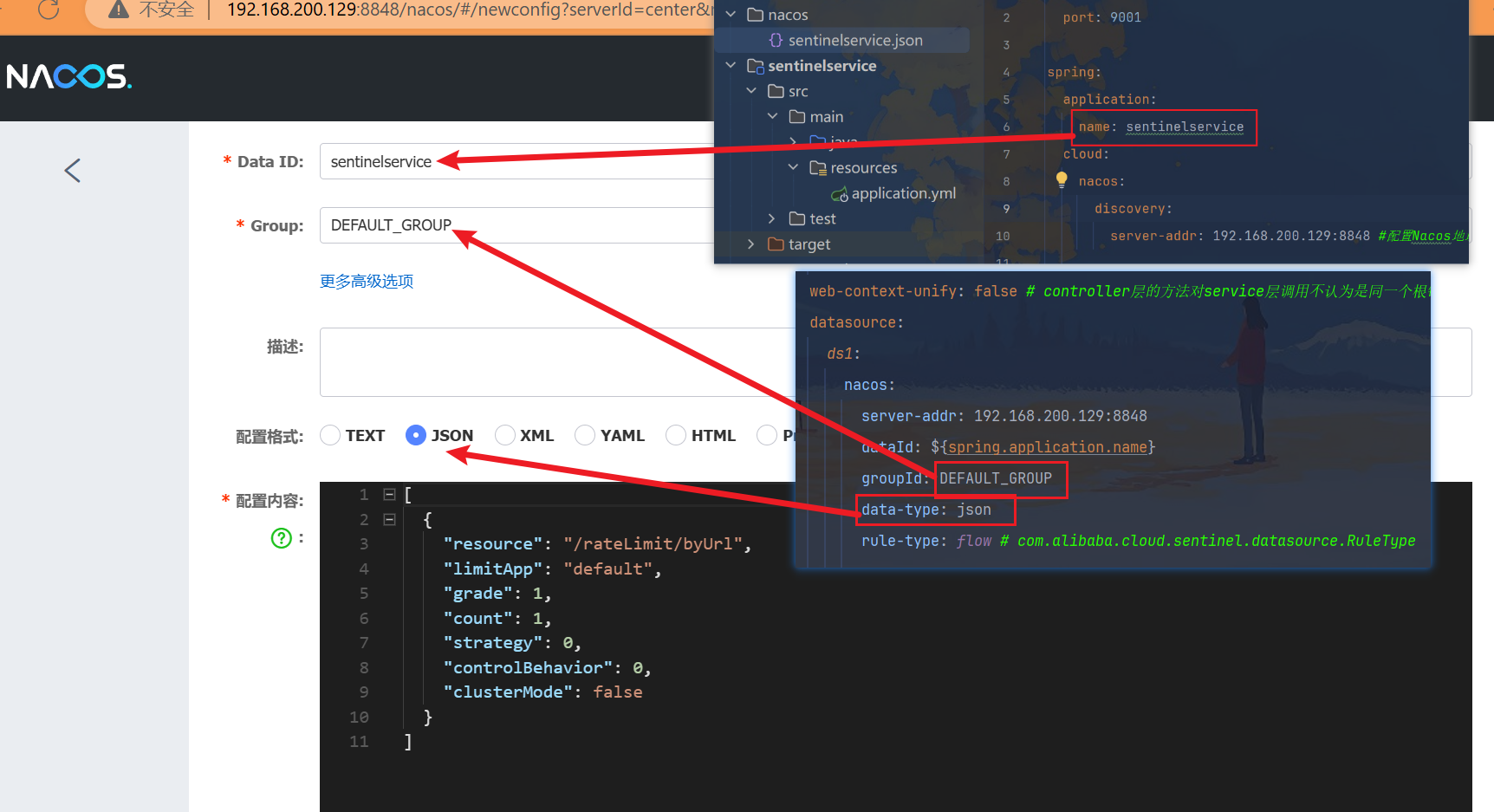
9.5、写Yaml
yaml
datasource:
ds1:
nacos:
server-addr: 192.168.200.129:8848
dataId: ${spring.application.name}
groupId: DEFAULT_GROUP
data-type: json
rule-type: flow # com.alibaba.cloud.sentinel.datasource.RuleType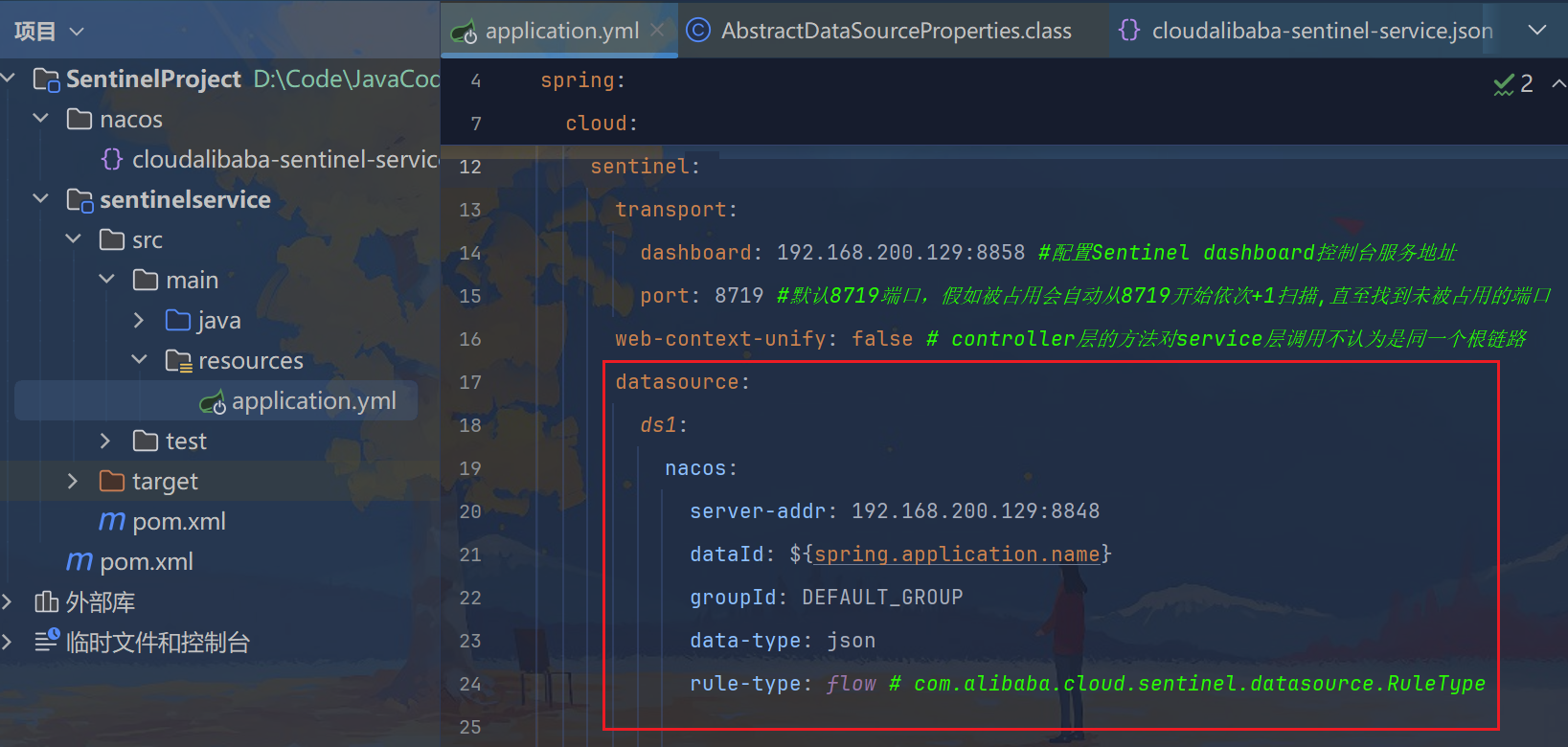
跟踪rule-type: flow

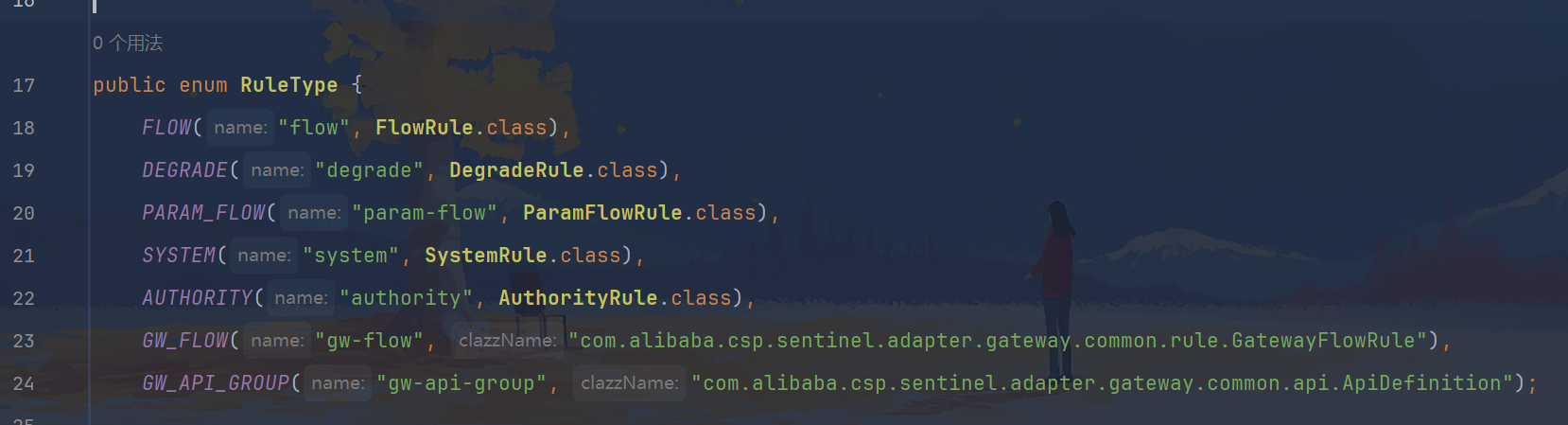
java
public enum RuleType {
FLOW("flow", FlowRule.class),
DEGRADE("degrade", DegradeRule.class),
PARAM_FLOW("param-flow", ParamFlowRule.class),
SYSTEM("system", SystemRule.class),
AUTHORITY("authority", AuthorityRule.class),
GW_FLOW("gw-flow", "com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.adapter.gateway.common.rule.GatewayFlowRule"),
GW_API_GROUP("gw-api-group", "com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.adapter.gateway.common.api.ApiDefinition");
}| 枚举常量 | 含义 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| FLOW | 限流规则 | 控制应用的QPS(每秒查询率),限制系统流量以避免过载。 |
| DEGRADE | 熔断降级规则 | 当响应时间过长或错误率过高时,触发降级,临时阻断流量以保护系统。 |
| PARAM_FLOW | 热点参数限流规则 | 针对特定参数值进行限流,例如限制某个用户或IP的访问频率。 |
| SYSTEM | 系统规则 | 根据CPU使用率、内存等指标调整流控策略,保护系统整体稳定性。 |
| AUTHORITY | 授权规则 | 基于黑白名单控制访问权限,限制特定来源的流量。 |
| GW_FLOW | 网关流控规则 | 针对API网关的流量控制规则,细粒度控制通过网关的流量。 |
| GW_API_GROUP | 网关API分组规则 | 将API进行分组管理,定义一组API的流量控制策略。 |
我想多数据源配置呢??
yaml
spring:
application:
name: sentinel-project
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
# Nacos服务注册中心地址
server-addr: 10.20.30.227:9999
sentinel:
transport:
# 配置Sentinel dashboard地址
dashboard: 10.20.30.94:8080
# 默认8719端口,假如被占用会自动从8719开始依次+1扫描,直至找到未被占用的端口
port: 8719
datasource:
# sentinel持久化配置
ds1:
# 你是自定义key, 也可以做限流类型等
nacos:
server-addr: 10.20.30.227:9999 # nacos地址
dataId: flow # 你是nacos配置里面的
groupId: DEFAULT_GROUP # 就是nacos配置里面的
data-type: json # 你是nacos配置里面的
rule-type: flow # 也以为流量规则, 具体类型见com.alibaba.cloud.sentinel.datasource.RuleType
ds2:
# 你是自定义key, 也可以做限流类型等
nacos:
server-addr: 10.20.30.227:9999 # nacos地址
dataId: degrade # 你是nacos配置里面的
groupId: DEFAULT_GROUP # 就是nacos配置里面的
data-type: json # 你是nacos配置里面的
rule-type: degrade # 也以为熔断降级规则, 具体类型见com.alibaba.cloud.sentinel.datasource.RuleType9.6、Nacos配置
json
[
{
"resource": "/rateLimit/byUrl",
"limitApp": "default",
"grade": 1,
"count": 1,
"strategy": 0,
"controlBehavior": 0,
"clusterMode": false
}
]| 字段名称 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| resource | 资源名称 |
| limitApp | 来源应用 |
| grade | 阈值类型,0表示线程数,1表示QPS |
| count | 单机阈值 |
| strategy | 流控模式,0表示直接,1表示关联,2表示链路 |
| controlBehavior | 流控效果,0表示快速失败,1表示Warm Up,2表示排队等待 |
| clusterMode | 是否集群 |
9.7、测试
重启服务后一定要多刷几次就出来了哈:
http
http://localhost:9001/rateLimit/byUrl
十、OpenFeign和Sentinel集成实现fallback服务降级
SpringCloud中,微服务调用都是通过Feign来实现的,因此做客户端保护必须整合Feign和Sentinel。
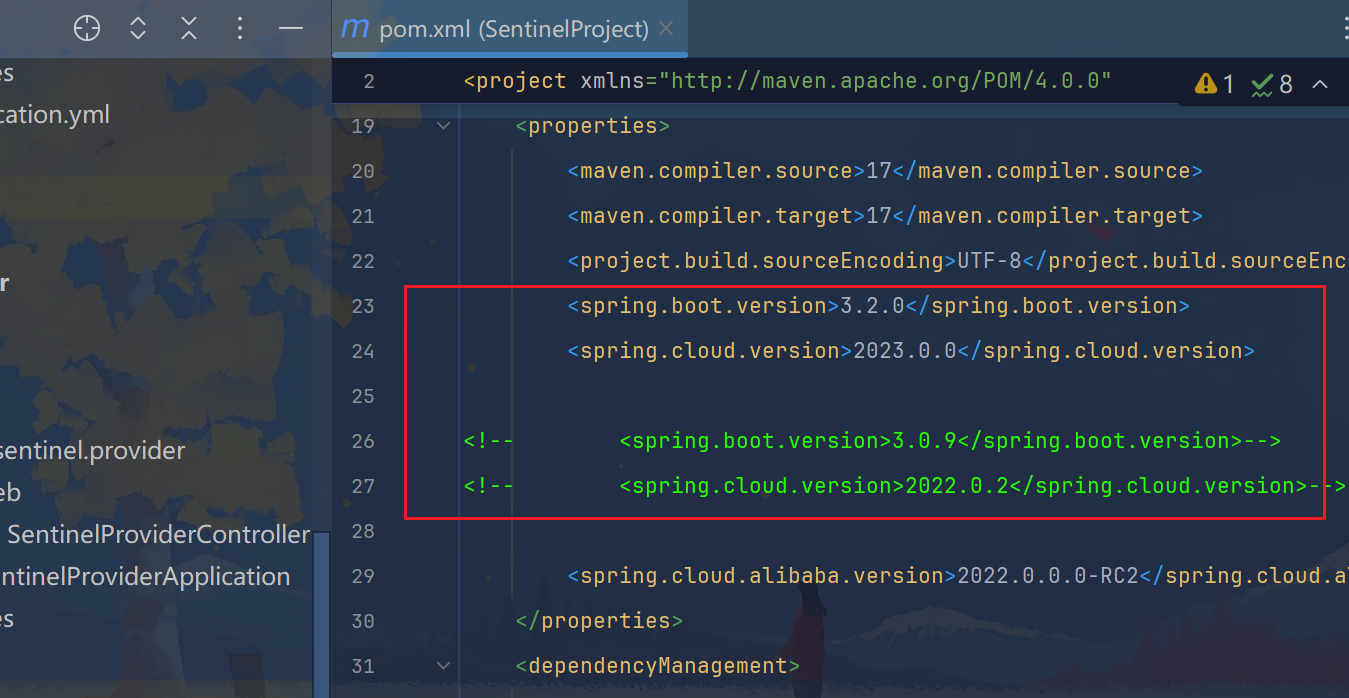
先降低版本:
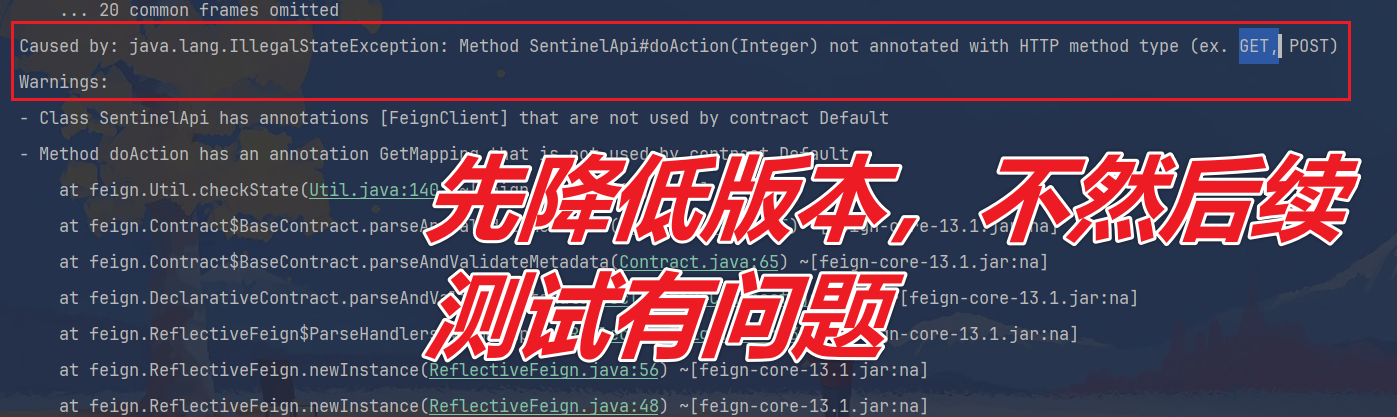
xml
<spring.boot.version>3.0.9</spring.boot.version>
<spring.cloud.version>2022.0.2</spring.cloud.version>
10.1、服务的提供者
101.1、YAML
yaml
server:
port: 9001
spring:
application:
name: sentinelprovider
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: 192.168.200.129:8848 #配置Nacos地址
sentinel:
transport:
dashboard: 192.168.200.129:8858 #配置Sentinel dashboard控制台服务地址
port: 8719 #默认8719端口,假如被占用会自动从8719开始依次+1扫描,直至找到未被占用的端口10.1.2、主启动
java
package com.sentinel.provider;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
/**
* @Author: 史小创
* @Time: 2024/8/28 下午7:56
* @Description:
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class SentinelProviderApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SentinelProviderApplication.class, args);
}
}10.1.3、业务类
java
package com.sentinel.provider.web;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.annotation.SentinelResource;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.BlockException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @Author: 史小创
* @Time: 2024/8/28 下午8:12
* @Description:
*/
@RestController
public class SentinelProviderController {
@GetMapping("/rateLimit/doAction/{p1}")
@SentinelResource(value = "doActionSentinelResource", blockHandler = "doActionBlockHandler")
public String doAction(@PathVariable("p1") Integer p1) {
if (p1 == 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("p1等于零直接异常");
}
return "doAction";
}
public String doActionBlockHandler(@PathVariable("p1") Integer p1, BlockException e) {
System.err.printf("sentinel配置自定义限流了:{}", e);
return "sentinel配置自定义限流了";
}
}10.1.4、测试
http
http://localhost:9001/rateLimit/doAction/1
10.2、OpenFeign
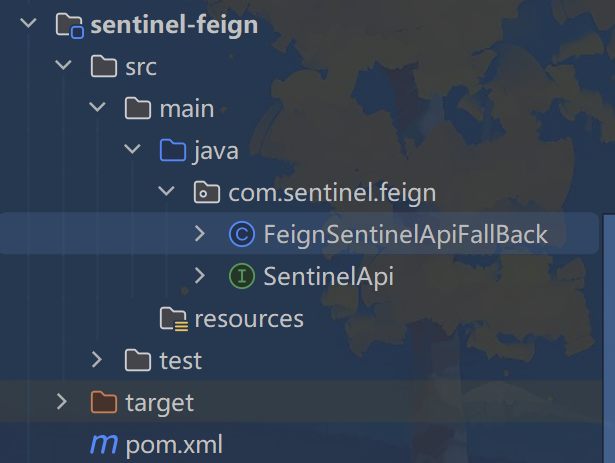
xml
<dependencies>
<!--openfeign-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
java
package com.sentinel.feign;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
@FeignClient(value = "sentinelprovider", fallback = FeignSentinelApiFallBack.class)
public interface SentinelApi {
@GetMapping("/rateLimit/doAction/{p1}")
public String doAction(@PathVariable("p1") Integer p1);
}
java
package com.sentinel.feign;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @Author: 史小创
* @Time: 2024/8/28 下午8:26
* @Description: 统一服务降级类
*/
@Component
public class FeignSentinelApiFallBack implements SentinelApi {
@Override
public String doAction(Integer p1) {
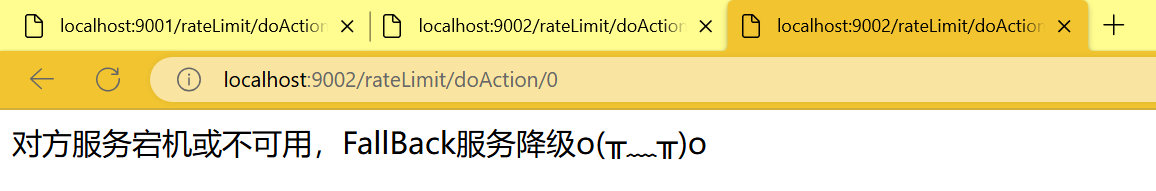
return "对方服务宕机或不可用,FallBack服务降级o(╥﹏╥)o";
}
}10.3、服务消费者
10.3.1、POM
xml
<dependencies>
<!-- 引入自己定义的api通用包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.sentinel</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-feign</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<!--openfeign-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>10.3.2、YAML
yaml
server:
port: 9002
spring:
application:
name: sentinelconsumer
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: 192.168.200.129:8848 #配置Nacos地址
# 激活Sentinel对Feign的支持
feign:
sentinel:
enabled: true10.3.3、主启动
java
package com.sentinel.consumer;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
/**
* @Author: 史小创
* @Time: 2024/8/28 下午7:56
* @Description:
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@EnableFeignClients(basePackages = "com.sentinel.feign")
@ComponentScan("com.sentinel")
public class SentinelConsumerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SentinelConsumerApplication.class, args);
}
}10.3.4、业务类
yaml
package com.sentinel.consumer.web;
import com.sentinel.feign.SentinelApi;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @Author: 史小创
* @Time: 2024/8/28 下午8:33
* @Description:
*/
@RestController
public class SentinelConsumerController {
@Autowired
private SentinelApi sentinelApi;
@GetMapping("/rateLimit/doAction/{p1}")
public String doAction(@PathVariable("p1") Integer p1) {
return sentinelApi.doAction(p1);
}
}10.3.5、测试
http
http://localhost:9002/rateLimit/doAction/1
http
http://localhost:9002/rateLimit/doAction/0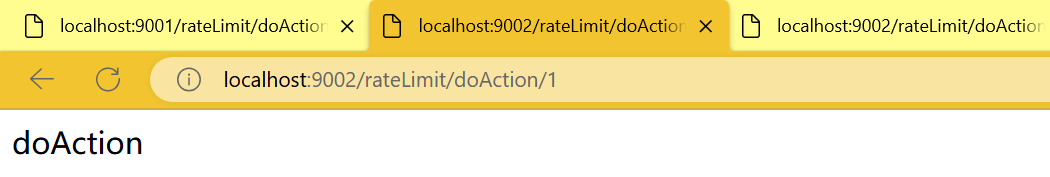
10.4、整合Sentinel
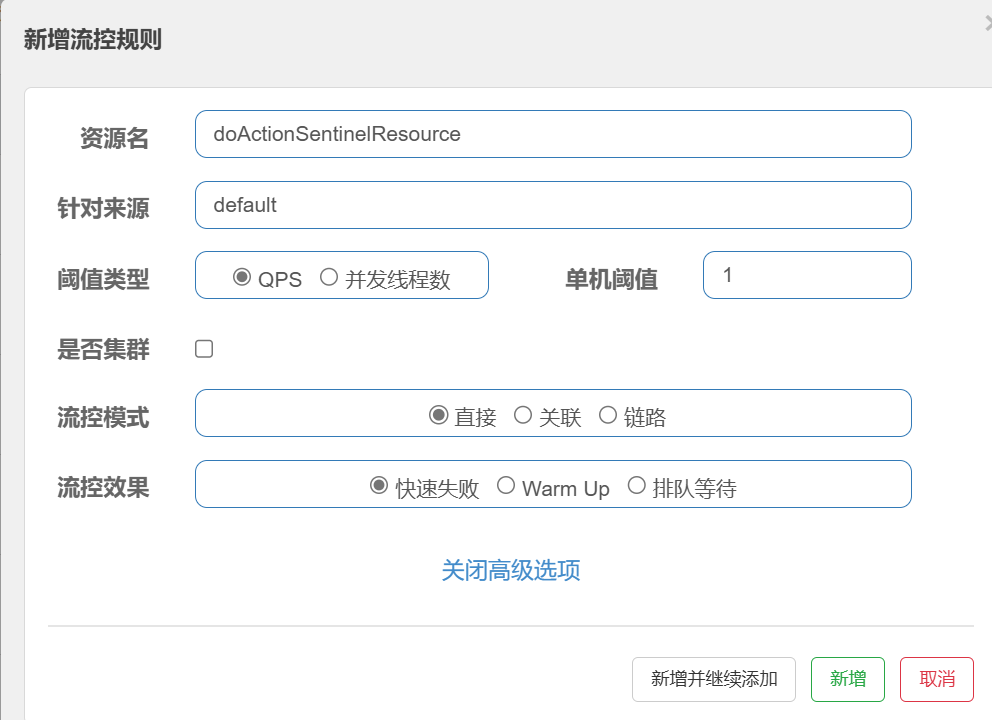
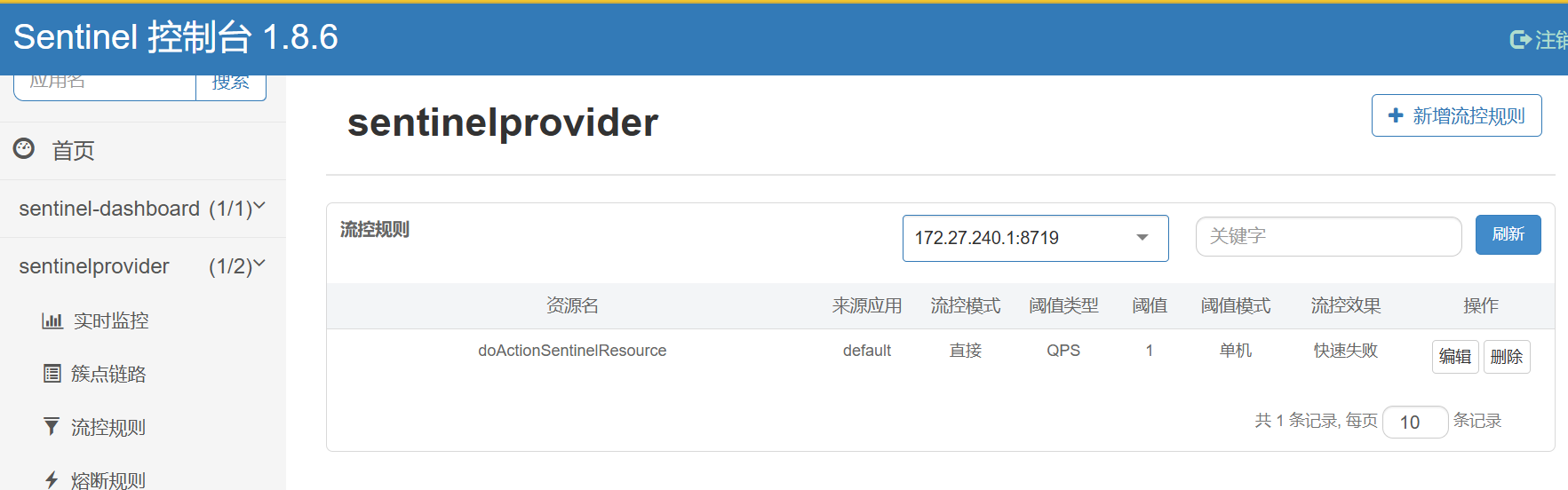
http
http://localhost:9002/rateLimit/doAction/1
http
http://localhost:9002/rateLimit/doAction/0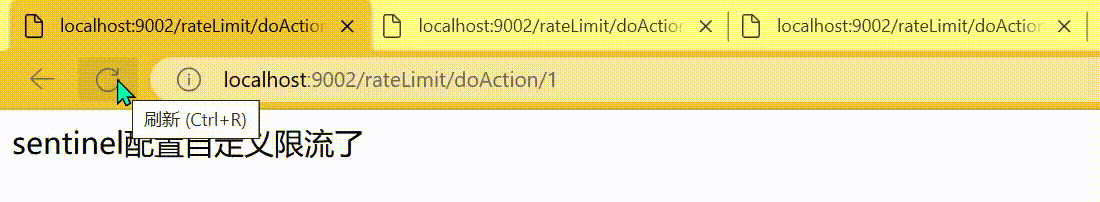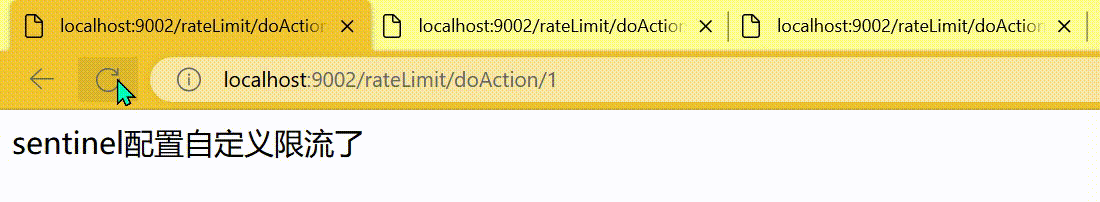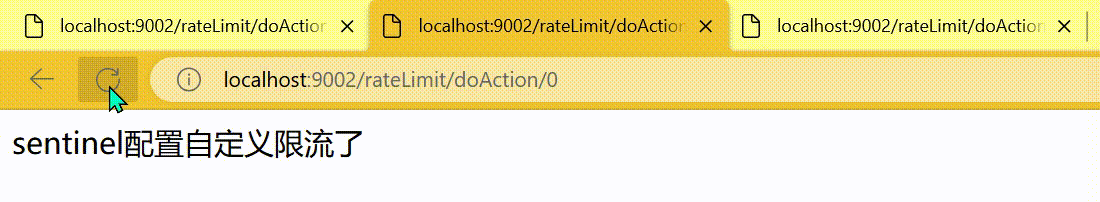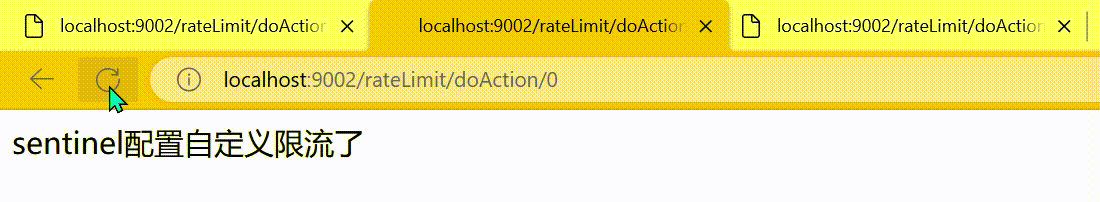
10.5、版本复原
十一、GateWay和Sentinel集成实现服务限流
11.1、POM
Spring Cloud Gateway确实是基于Spring WebFlux的反应式框架构建的。因此,通常情况下,不需要也不应该同时包含spring-boot-starter-web依赖,因为spring-boot-starter-web是基于Servlet API的,而Spring WebFlux是基于反应式堆栈的。这两者使用不同的底层模型,不适合一起使用。
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-transport-simple-http</artifactId>
<version>1.8.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-spring-cloud-gateway-adapter</artifactId>
<version>1.8.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.annotation</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.annotation-api</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webflux</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
11.2、YAML
yaml
server:
port: 8888
spring:
application:
name: sentinelgateway # sentinel+gataway整合Case
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: 192.168.200.129:8848
gateway:
routes:
- id: pay_routh1 #pay_routh1 #路由的ID(类似mysql主键ID),没有固定规则但要求唯一,建议配合服务名
uri: lb://sentinelprovider #匹配后提供服务的路由地址
predicates:
- Path=/rateLimit/doAction/** # 断言,路径相匹配的进行路由11.3、启动
java
package com.sentinel.gateway;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
/**
* @Author: 史小创
* @Time: 2024/8/28 下午10:19
* @Description:
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class SentinelGatewayApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SentinelGatewayApplication.class, args);
}
}11.4、配置类
http
https://sentinelguard.io/zh-cn/docs/api-gateway-flow-control.html
java
package com.sentinel.gateway.config;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.adapter.gateway.common.rule.GatewayFlowRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.adapter.gateway.common.rule.GatewayRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.adapter.gateway.sc.SentinelGatewayFilter;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.adapter.gateway.sc.callback.BlockRequestHandler;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.adapter.gateway.sc.callback.GatewayCallbackManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.adapter.gateway.sc.exception.SentinelGatewayBlockExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.ObjectProvider;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.GlobalFilter;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.codec.ServerCodecConfigurer;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.BodyInserters;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.ServerResponse;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.result.view.ViewResolver;
import org.springframework.web.server.ServerWebExchange;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @Author: 史小创
* @Time: 2024/8/28 下午10:24
* @Description:
*/
@Configuration
public class GatewayConfiguration {
private final List<ViewResolver> viewResolvers;
private final ServerCodecConfigurer serverCodecConfigurer;
public GatewayConfiguration(ObjectProvider<List<ViewResolver>> viewResolversProvider,
ServerCodecConfigurer serverCodecConfigurer) {
this.viewResolvers = viewResolversProvider.getIfAvailable(Collections::emptyList);
this.serverCodecConfigurer = serverCodecConfigurer;
}
@Bean
@Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
public SentinelGatewayBlockExceptionHandler sentinelGatewayBlockExceptionHandler() {
// Register the block exception handler for Spring Cloud Gateway.
return new SentinelGatewayBlockExceptionHandler(viewResolvers, serverCodecConfigurer);
}
@Bean
@Order(-1)
public GlobalFilter sentinelGatewayFilter() {
return new SentinelGatewayFilter();
}
@PostConstruct
public void doInit() {
// 自己动手,丰衣足食
// initGatewayRules();
initBlockHandler();
}
// 处理+自定义返回的例外信息内容,类似我们的调用触发了流控规则保护
private void initBlockHandler() {
Set<GatewayFlowRule> rules = new HashSet<>();
rules.add(new GatewayFlowRule("pay_routh1").setCount(2).setIntervalSec(1));
GatewayRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
BlockRequestHandler handler = new BlockRequestHandler() {
@Override
public Mono<ServerResponse> handleRequest(ServerWebExchange exchange, Throwable t) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("errorCode", HttpStatus.TOO_MANY_REQUESTS.getReasonPhrase());
map.put("errorMessage", "请求太过频繁,系统忙不过来,触发限流(sentinel+gataway整合Case)");
return ServerResponse.status(HttpStatus.TOO_MANY_REQUESTS)
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.body(BodyInserters.fromValue(map));
}
};
GatewayCallbackManager.setBlockHandler(handler);
}
}11.5、测试
http
http://localhost:8888/rateLimit/doAction/1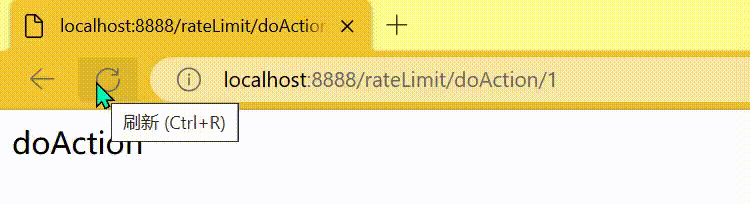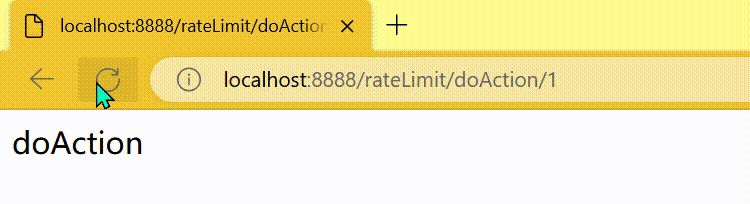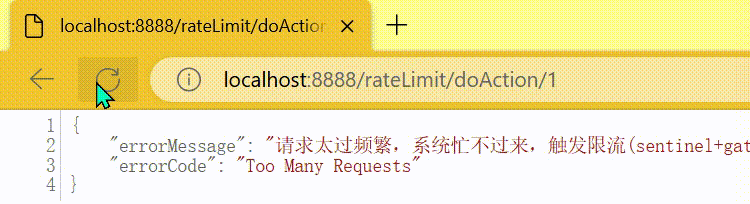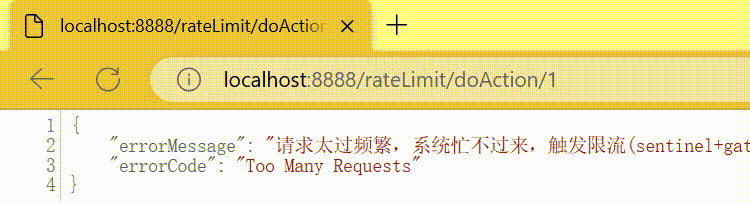
十二、环境搭建
SpringBoot+SpringCloud
xml
<spring.boot.version>3.2.0</spring.boot.version>
<spring.cloud.version>2023.0.0</spring.cloud.version>
<spring.cloud.alibaba.version>2022.0.0.0</spring.cloud.alibaba.version>docker
Nacos
bash
docker pull nacos/nacos-server:v2.0.3
bash
docker run --env MODE=standalone --name nacos --restart=always -d -p 8848:8848 -p 9848:9848 -p 9849:9849 -e JVM_XMS=512m -e JVM_XMX=512m -v /opt/nacos:/home/nacos/nacos-server-2.0.3/nacos/standalone/data nacos/nacos-server:v2.0.3
bash
http://192.168.200.129:8848/nacos/#/loginsentinel
bash
docker pull bladex/sentinel-dashboard:1.8.6
bash
docker run --name sentinel-dashboard --restart=always -p 8858:8858 -v /opt/sentinel:/opt/sentinel -d bladex/sentinel-dashboard:1.8.6
bash
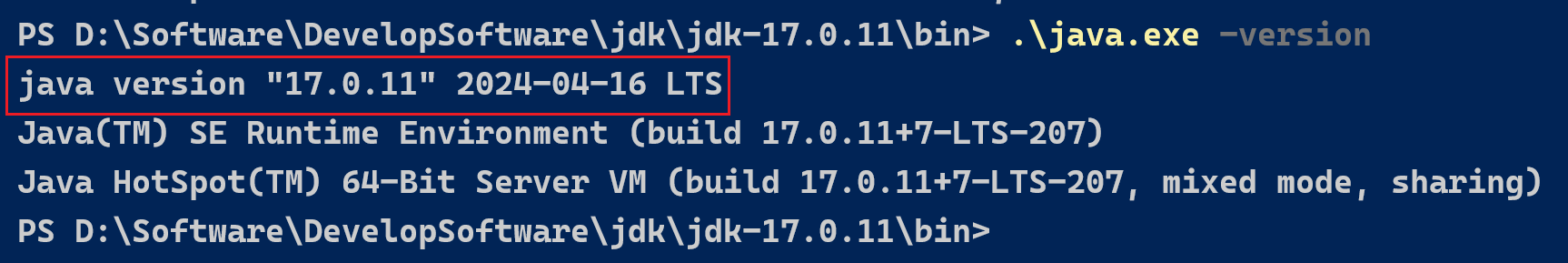
http://192.168.200.129:8858/#/loginjdk:
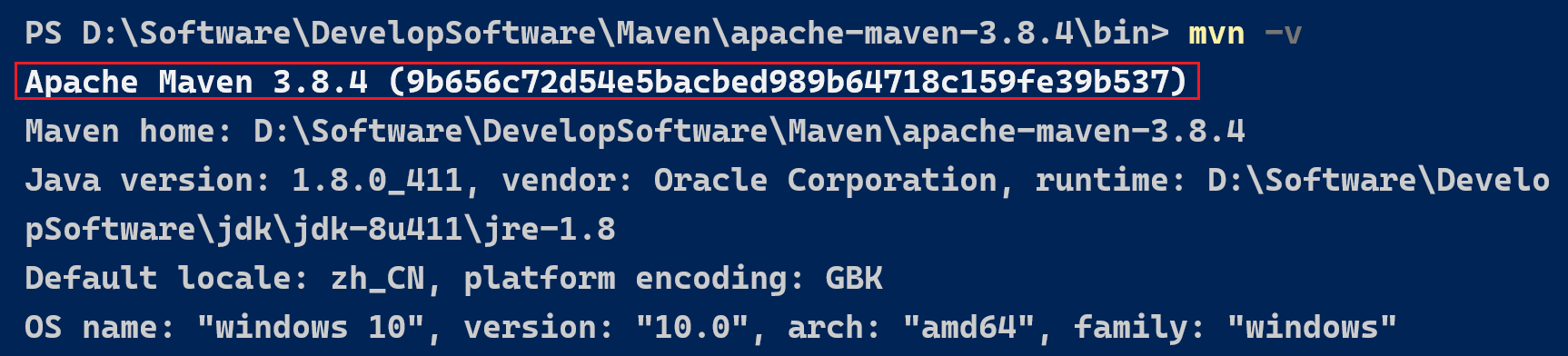
Maven
IDEA

代码汇总:
http
https://github.com/shixiaochuangjob/markdownfile/tree/main/20240828
http
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzkwOTczNzUxMQ==&mid=2247485129&idx=1&sn=6ff255ba38842473c025ada5ccd72182&chksm=c1376d81f640e49770514d2af99b21e9893c606c31fa9eefbd9483a9af3053901635d43a8c0e#rd