一、模型介绍
Qwen-Image 是阿里巴巴通义千问团队于 2025 年 8 月开源的首个图像生成基础模型,也是目前在复杂文本(尤其是中文)渲染方面表现最好的开源文生图大模型之一。
这是一个 20B MMDiT 图像基础模型,在复杂文本渲染 和精确图像编辑方面取得了重大进步。

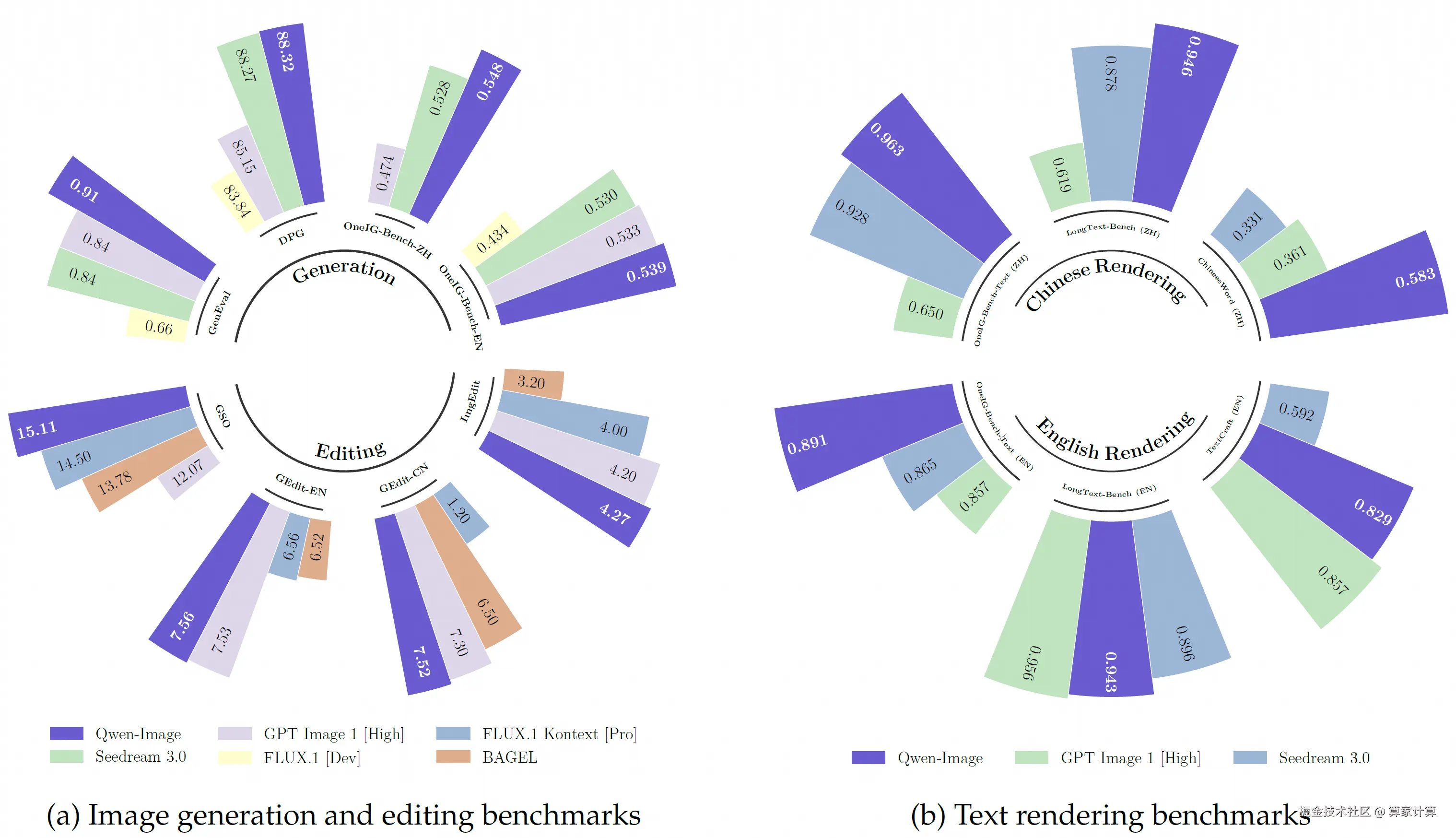
性能表现上,在多个公开基准上的对 Qwen-Image 的全面评估,包括用于通用图像生成的 GenEval、DPG 和 OneIG-Bench,以及用于图像编辑的 GEdit、ImgEdit 和 GSO。Qwen-Image 在所有基准测试中均取得了最先进的性能,展现出其在图像生成与图像编辑方面的强大能力。此外,在用于文本渲染的 LongText-Bench、ChineseWord 和 TextCraft 上的结果表明,Qwen-Image 在文本渲染方面表现尤为出色,特别是在中文文本渲染上,大幅领先现有的最先进模型。这凸显了 Qwen-Image 作为先进图像生成模型的独特地位,兼具广泛的通用能力与卓越的文本渲染精度。
主要特性包括:
- 卓越的文本渲染能力 : Qwen-Image 在复杂文本渲染方面表现出色,支持多行布局、段落级文本生成以及细粒度细节呈现。无论是英语还是中文,均能实现高保真输出。
- 一致性的图像编辑能力 : 通过增强的多任务训练范式,Qwen-Image 在编辑过程中能出色地保持编辑的一致性。
- 强大的跨基准性能表现 : 在多个公开基准测试中的评估表明,Qwen-Image 在各类生成与编辑任务中均获得 SOTA,是一个强大的图像生成基础模型。
更多详情请见:Qwen-Image · 模型库
二、模型部署
基础环境最低配置推荐
| 环境名称 | 版本信息 |
|---|---|
| Ubuntu | 22.04.4 LTS |
| Python | 3.12 |
| CUDA | 12.6 |
| NVIDIA Corporation | RTX 4090 * 3 |
注:该模型支持多卡并行而不支持多卡推理,若显卡配置较高,可先用A100;较低,则可选用3张4090显卡配置,不过需要对原代码进行修改。
1.更新基础软件包、配置镜像源
查看系统版本信息
bash
#查看系统的版本信息,包括 ID(如 ubuntu、centos 等)、版本号、名称、版本号 ID 等
cat /etc/os-release
更新软件包列表
csharp
#更新软件列表
apt-get update
配置国内镜像源(阿里云)
具体而言,vim 指令编辑文件 sources.list
bash
#编辑源列表文件
vim /etc/apt/sources.list
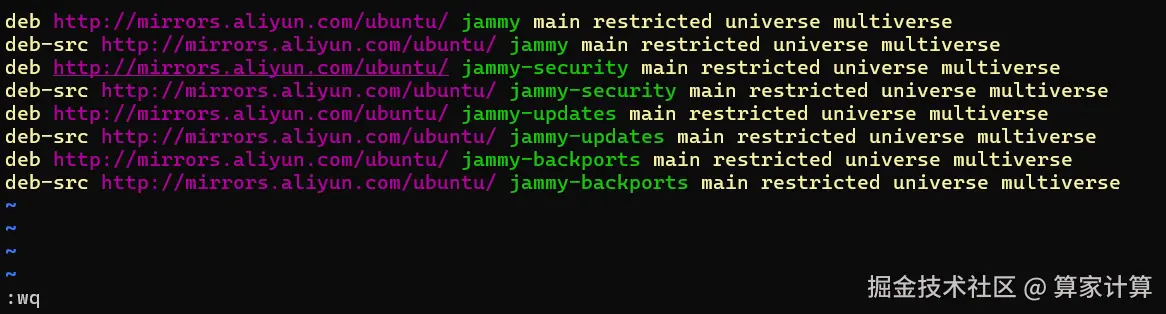
按 "i" 进入编辑模式,将如下内容插入至 sources.list 文件中
arduino
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ jammy main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ jammy main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ jammy-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ jammy-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ jammy-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ jammy-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ jammy-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ jammy-backports main restricted universe multiverse最后,按 "esc" 键退出编辑模式,输入 :wq 命令并按下 "enter" 键便可保存并退出 sources.list 文件
2.创建虚拟环境
创建虚拟环境
ini
#创建名为Qwen-Image的虚拟环境,python版本:3.12
conda create -n Qwen-Image python=3.12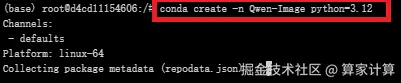
激活虚拟环境
conda activate Qwen-Image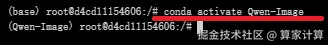
3.克隆项目
创建Qwen-Image文件夹
bash
#创建Qwen-Image文件夹
mkdir Qwen-Image

github(QwenLM/Qwen-Image:Qwen-Image 是一个强大的图像生成基础模型,能够进行复杂的文本渲染和精确的图像编辑。)中克隆项目代码文件至该目录
bash
#进入Qwen-Image目录
cd Qwen-Image
#克隆仓库
git clone https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen-Image.git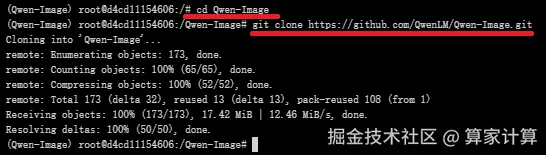
4.下载依赖
requirements.txt 文件
pip install -r requirements.txt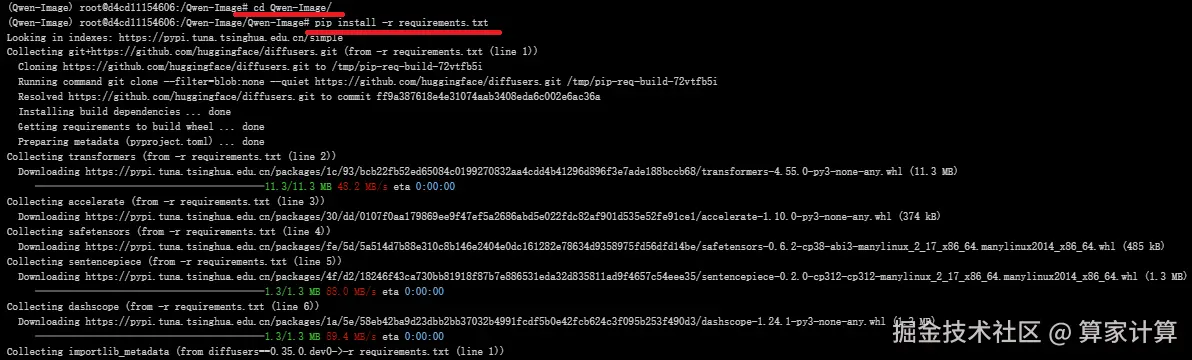
文件内容:
arduino
git+https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git
transformers
accelerate
safetensors
sentencepiece
dashscope5.模型下载
转到魔塔社区官网下载模型文件:Qwen-Image · 模型库
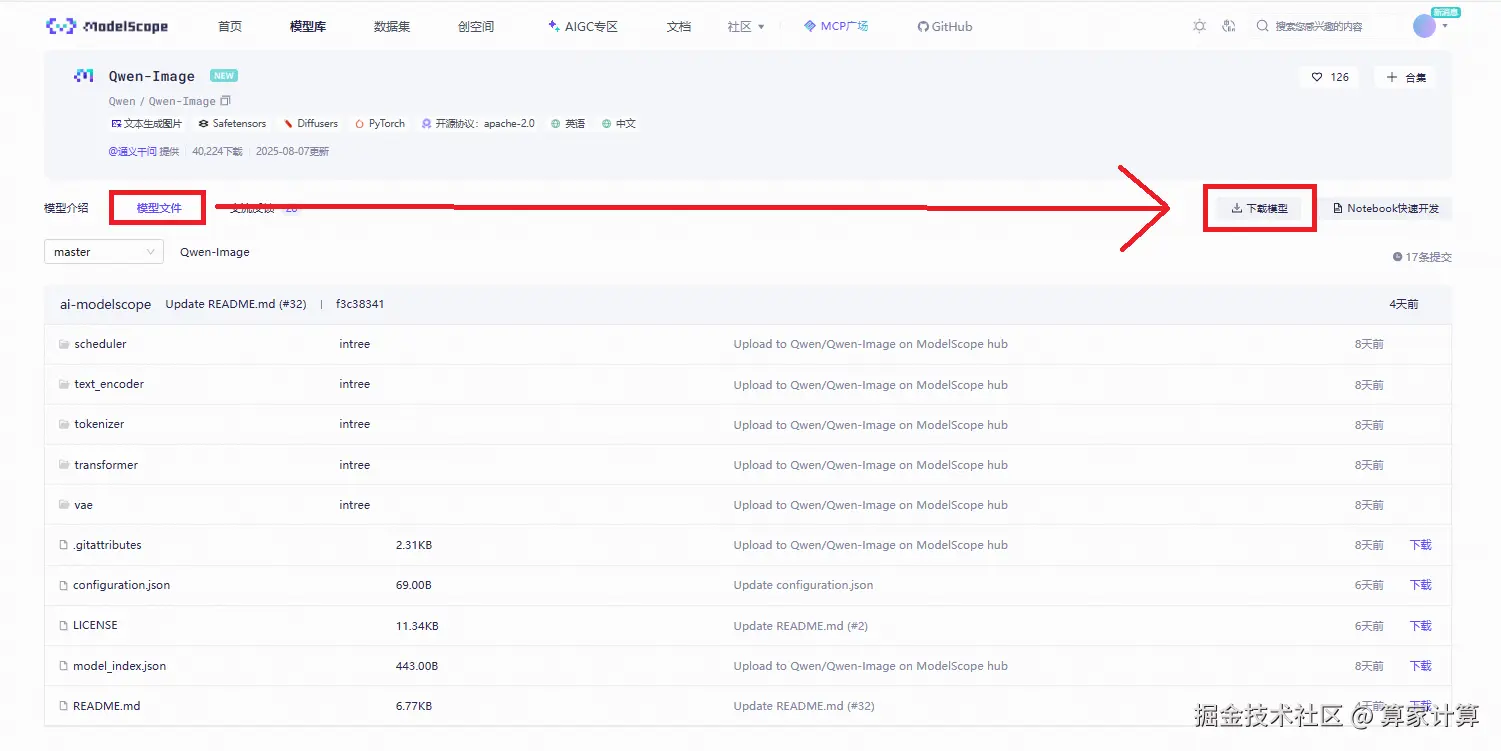
使用命令行下载完整模型库
bash
#在下载前,请先通过如下命令安装
pip install modelscope
#命令行下载(下载至当前文件夹)
modelscope download --model 'Qwen/Qwen-Image' --local_dir './'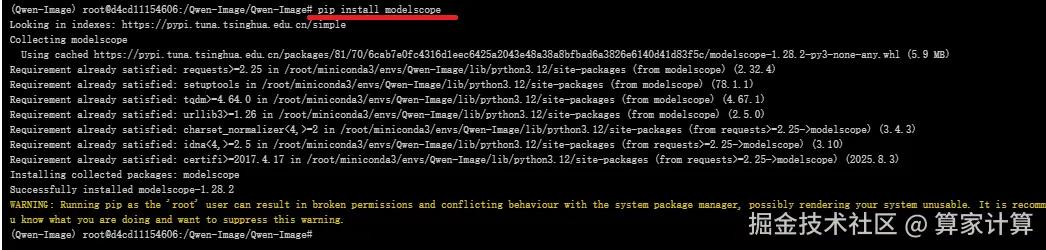
三、web页面启动
注:该模型支持多卡并行但不支持多卡推理,若要进行多卡推理,解决方案如1所示;若配置较高,显卡为A100,则可选用方案2,速度更快。
1.采用3 * 4090的显卡配置
官方文档中并没有具体给出多卡推理的实现代码,如下的app.py可用于实现多卡推理。
bash
#进入目录
cd Qwen-Image/src/examples/
#查看文件列表
ls
#编写app.py文件
vim app.py
ini
import torch
import numpy as np
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
from diffusers.pipelines.qwenimage import QwenImagePipeline
from diffusers.pipelines.qwenimage.pipeline_output import QwenImagePipelineOutput
from typing import Any, Callable, Dict, List, Optional, Union
from diffusers.pipelines.stable_diffusion.pipeline_stable_diffusion import retrieve_timesteps
from diffusers.utils import is_torch_xla_available
import gradio as gr
if is_torch_xla_available():
import torch_xla.core.xla_model as xm
XLA_AVAILABLE = True
else:
XLA_AVAILABLE = False
def calculate_shift(
image_seq_len,
base_seq_len: int = 256,
max_seq_len: int = 4096,
base_shift: float = 0.5,
max_shift: float = 1.15,
):
m = (max_shift - base_shift) / (max_seq_len - base_seq_len)
b = base_shift - m * base_seq_len
mu = image_seq_len * m + b
return mu
class CustomQwenImagePipeline(QwenImagePipeline):
@torch.no_grad()
def __call__(
self,
prompt: Union[str, List[str]] = None,
negative_prompt: Union[str, List[str]] = None,
true_cfg_scale: float = 4.0,
height: Optional[int] = None,
width: Optional[int] = None,
num_inference_steps: int = 50,
sigmas: Optional[List[float]] = None,
guidance_scale: float = 1.0,
num_images_per_prompt: int = 1,
generator: Optional[Union[torch.Generator, List[torch.Generator]]] = None,
latents: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
prompt_embeds: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
prompt_embeds_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
negative_prompt_embeds: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
negative_prompt_embeds_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
output_type: Optional[str] = "pil",
return_dict: bool = True,
attention_kwargs: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None,
callback_on_step_end: Optional[Callable[[int, int, Dict], None]] = None,
callback_on_step_end_tensor_inputs: List[str] = ["latents"],
max_sequence_length: int = 512,
):
r"""
Function invoked when calling the pipeline for generation.
Args:
prompt (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
The prompt or prompts to guide the image generation. If not defined, one has to pass `prompt_embeds`.
instead.
negative_prompt (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
The prompt or prompts not to guide the image generation. If not defined, one has to pass
`negative_prompt_embeds` instead. Ignored when not using guidance (i.e., ignored if `true_cfg_scale` is
not greater than `1`).
true_cfg_scale (`float`, *optional*, defaults to 1.0):
When > 1.0 and a provided `negative_prompt`, enables true classifier-free guidance.
height (`int`, *optional*, defaults to self.unet.config.sample_size * self.vae_scale_factor):
The height in pixels of the generated image. This is set to 1024 by default for the best results.
width (`int`, *optional*, defaults to self.unet.config.sample_size * self.vae_scale_factor):
The width in pixels of the generated image. This is set to 1024 by default for the best results.
num_inference_steps (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 50):
The number of denoising steps. More denoising steps usually lead to a higher quality image at the
expense of slower inference.
sigmas (`List[float]`, *optional*):
Custom sigmas to use for the denoising process with schedulers which support a `sigmas` argument in
their `set_timesteps` method. If not defined, the default behavior when `num_inference_steps` is passed
will be used.
guidance_scale (`float`, *optional*, defaults to 3.5):
Guidance scale as defined in [Classifier-Free Diffusion
Guidance](https://huggingface.co/papers/2207.12598). `guidance_scale` is defined as `w` of equation 2.
of [Imagen Paper](https://huggingface.co/papers/2205.11487). Guidance scale is enabled by setting
`guidance_scale > 1`. Higher guidance scale encourages to generate images that are closely linked to
the text `prompt`, usually at the expense of lower image quality.
num_images_per_prompt (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 1):
The number of images to generate per prompt.
generator (`torch.Generator` or `List[torch.Generator]`, *optional*):
One or a list of [torch generator(s)](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.Generator.html)
to make generation deterministic.
latents (`torch.Tensor`, *optional*):
Pre-generated noisy latents, sampled from a Gaussian distribution, to be used as inputs for image
generation. Can be used to tweak the same generation with different prompts. If not provided, a latents
tensor will be generated by sampling using the supplied random `generator`.
prompt_embeds (`torch.Tensor`, *optional*):
Pre-generated text embeddings. Can be used to easily tweak text inputs, *e.g.* prompt weighting. If not
provided, text embeddings will be generated from `prompt` input argument.
negative_prompt_embeds (`torch.Tensor`, *optional*):
Pre-generated negative text embeddings. Can be used to easily tweak text inputs, *e.g.* prompt
weighting. If not provided, negative_prompt_embeds will be generated from `negative_prompt` input
argument.
output_type (`str`, *optional*, defaults to `"pil"`):
The output format of the generate image. Choose between
[PIL](https://pillow.readthedocs.io/en/stable/): `PIL.Image.Image` or `np.array`.
return_dict (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `True`):
Whether or not to return a [`~pipelines.qwenimage.QwenImagePipelineOutput`] instead of a plain tuple.
attention_kwargs (`dict`, *optional*):
A kwargs dictionary that if specified is passed along to the `AttentionProcessor` as defined under
`self.processor` in
[diffusers.models.attention_processor](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/attention_processor.py).
callback_on_step_end (`Callable`, *optional*):
A function that calls at the end of each denoising steps during the inference. The function is called
with the following arguments: `callback_on_step_end(self: DiffusionPipeline, step: int, timestep: int,
callback_kwargs: Dict)`. `callback_kwargs` will include a list of all tensors as specified by
`callback_on_step_end_tensor_inputs`.
callback_on_step_end_tensor_inputs (`List`, *optional*):
The list of tensor inputs for the `callback_on_step_end` function. The tensors specified in the list
will be passed as `callback_kwargs` argument. You will only be able to include variables listed in the
`._callback_tensor_inputs` attribute of your pipeline class.
max_sequence_length (`int` defaults to 512): Maximum sequence length to use with the `prompt`.
Examples:
Returns:
[`~pipelines.qwenimage.QwenImagePipelineOutput`] or `tuple`:
[`~pipelines.qwenimage.QwenImagePipelineOutput`] if `return_dict` is True, otherwise a `tuple`. When
returning a tuple, the first element is a list with the generated images.
"""
height = height or self.default_sample_size * self.vae_scale_factor
width = width or self.default_sample_size * self.vae_scale_factor
# 1. Check inputs. Raise error if not correct
self.check_inputs(
prompt,
height,
width,
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
prompt_embeds=prompt_embeds,
negative_prompt_embeds=negative_prompt_embeds,
prompt_embeds_mask=prompt_embeds_mask,
negative_prompt_embeds_mask=negative_prompt_embeds_mask,
callback_on_step_end_tensor_inputs=callback_on_step_end_tensor_inputs,
max_sequence_length=max_sequence_length,
)
self._guidance_scale = guidance_scale
self._attention_kwargs = attention_kwargs
self._current_timestep = None
self._interrupt = False
# 2. Define call parameters
if prompt is not None and isinstance(prompt, str):
batch_size = 1
elif prompt is not None and isinstance(prompt, list):
batch_size = len(prompt)
else:
batch_size = prompt_embeds.shape[0]
device = self._execution_device
has_neg_prompt = negative_prompt is not None or (
negative_prompt_embeds is not None and negative_prompt_embeds_mask is not None
)
do_true_cfg = true_cfg_scale > 1 and has_neg_prompt
prompt_embeds, prompt_embeds_mask = self.encode_prompt(
prompt=prompt,
prompt_embeds=prompt_embeds,
prompt_embeds_mask=prompt_embeds_mask,
device=device,
num_images_per_prompt=num_images_per_prompt,
max_sequence_length=max_sequence_length,
)
if do_true_cfg:
negative_prompt_embeds, negative_prompt_embeds_mask = self.encode_prompt(
prompt=negative_prompt,
prompt_embeds=negative_prompt_embeds,
prompt_embeds_mask=negative_prompt_embeds_mask,
device=device,
num_images_per_prompt=num_images_per_prompt,
max_sequence_length=max_sequence_length,
)
# 4. Prepare latent variables
num_channels_latents = self.transformer.config.in_channels // 4
latents, latent_image_ids = self.prepare_latents(
batch_size * num_images_per_prompt,
num_channels_latents,
height,
width,
prompt_embeds.dtype,
device,
generator,
latents,
)
img_shapes = [(1, height // self.vae_scale_factor // 2, width // self.vae_scale_factor // 2)] * batch_size
# 5. Prepare timesteps
sigmas = np.linspace(1.0, 1 / num_inference_steps, num_inference_steps) if sigmas is None else sigmas
image_seq_len = latents.shape[1]
mu = calculate_shift(
image_seq_len,
self.scheduler.config.get("base_image_seq_len", 256),
self.scheduler.config.get("max_image_seq_len", 4096),
self.scheduler.config.get("base_shift", 0.5),
self.scheduler.config.get("max_shift", 1.15),
)
timesteps, num_inference_steps = retrieve_timesteps(
self.scheduler,
num_inference_steps,
device,
sigmas=sigmas,
mu=mu,
)
num_warmup_steps = max(len(timesteps) - num_inference_steps * self.scheduler.order, 0)
self._num_timesteps = len(timesteps)
# handle guidance
if self.transformer.config.guidance_embeds:
guidance = torch.full([1], guidance_scale, device=device, dtype=torch.float32)
guidance = guidance.expand(latents.shape[0])
else:
guidance = None
if self.attention_kwargs is None:
self._attention_kwargs = {}
# 6. Denoising loop
self.scheduler.set_begin_index(0)
with self.progress_bar(total=num_inference_steps) as progress_bar:
for i, t in enumerate(timesteps):
if self.interrupt:
continue
self._current_timestep = t
# broadcast to batch dimension in a way that's compatible with ONNX/Core ML
timestep = t.expand(latents.shape[0]).to(latents.dtype)
# with self.transformer.cache_context("cond"):
# noise_pred = self.transformer(
# hidden_states=latents,
# timestep=timestep / 1000,
# guidance=guidance,
# encoder_hidden_states_mask=prompt_embeds_mask,
# encoder_hidden_states=prompt_embeds,
# img_shapes=img_shapes,
# txt_seq_lens=prompt_embeds_mask.sum(dim=1).tolist(),
# attention_kwargs=self.attention_kwargs,
# return_dict=False,
# )[0]
######################################TODO version1####################################
with self.transformer.cache_context("cond"):
hidden_states = self.transformer.img_in(latents).to("cuda:0")
encoder_hidden_states = self.transformer.txt_norm(prompt_embeds).to("cuda:0")
encoder_hidden_states = self.transformer.txt_in(encoder_hidden_states)
encoder_hidden_states_mask = prompt_embeds_mask.to("cuda:0")
# 计算共享参数
timestep_float = timestep.to("cuda:0") / 1000
temb = (
self.transformer.time_text_embed(timestep_float, hidden_states)
if guidance is None
else self.transformer.time_text_embed(timestep_float, guidance.to("cuda:0"), hidden_states)
)
image_rotary_emb = self.transformer.pos_embed(
img_shapes,
prompt_embeds_mask.sum(dim=1).tolist(),
device="cuda:0"
)
# # 前8层处理
# temb_c0 = temb.to("cuda:0", non_blocking=True)
# image_rotary_emb_c0 = tuple(item.to("cuda:0", non_blocking=True) for item in image_rotary_emb)
# torch.cuda.synchronize("cuda:0")
# for i, block in enumerate(self.transformer.transformer_blocks[:6]):
# # 只传输变化的hidden_states和encoder states
# hidden_states = hidden_states.to("cuda:0", non_blocking=True)
# encoder_hidden_states = encoder_hidden_states.to("cuda:0", non_blocking=True)
# encoder_hidden_states_mask = encoder_hidden_states_mask.to("cuda:0", non_blocking=True)
# torch.cuda.synchronize("cuda:0")
# encoder_hidden_states, hidden_states = block(
# hidden_states=hidden_states,
# encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
# encoder_hidden_states_mask=encoder_hidden_states_mask,
# temb=temb_c0,
# image_rotary_emb=image_rotary_emb_c0,
# joint_attention_kwargs=self.attention_kwargs,
# )
# 中间26层处理
temb_c1 = temb.to("cuda:1", non_blocking=True)
image_rotary_emb_c1 = tuple(item.to("cuda:1", non_blocking=True) for item in image_rotary_emb)
torch.cuda.synchronize("cuda:1")
for i, block in enumerate(self.transformer.transformer_blocks[:30]):
# 只传输变化的hidden_states和encoder states
hidden_states = hidden_states.to("cuda:1", non_blocking=True)
encoder_hidden_states = encoder_hidden_states.to("cuda:1", non_blocking=True)
encoder_hidden_states_mask = encoder_hidden_states_mask.to("cuda:1", non_blocking=True)
torch.cuda.synchronize("cuda:1")
encoder_hidden_states, hidden_states = block(
hidden_states=hidden_states,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_hidden_states_mask=encoder_hidden_states_mask,
temb=temb_c1,
image_rotary_emb=image_rotary_emb_c1,
joint_attention_kwargs=self.attention_kwargs,
)
# 后26层处理
temb_c2 = temb.to("cuda:2", non_blocking=True)
image_rotary_emb_c2 = tuple(item.to("cuda:2", non_blocking=True) for item in image_rotary_emb)
torch.cuda.synchronize("cuda:2")
for i, block in enumerate(self.transformer.transformer_blocks[30:], start=30):
hidden_states = hidden_states.to("cuda:2", non_blocking=True)
encoder_hidden_states = encoder_hidden_states.to("cuda:2", non_blocking=True)
encoder_hidden_states_mask = encoder_hidden_states_mask.to("cuda:2", non_blocking=True)
torch.cuda.synchronize("cuda:2")
encoder_hidden_states, hidden_states = block(
hidden_states=hidden_states,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_hidden_states_mask=encoder_hidden_states_mask,
temb=temb_c2,
image_rotary_emb=image_rotary_emb_c2,
joint_attention_kwargs=self.attention_kwargs,
)
# 最终处理
hidden_states = hidden_states.to("cuda:0", non_blocking=True)
torch.cuda.synchronize("cuda:0")
hidden_states = self.transformer.norm_out(hidden_states, temb)
noise_pred = self.transformer.proj_out(hidden_states)
if do_true_cfg:
# with self.transformer.cache_context("uncond"):
# neg_noise_pred = self.transformer(
# hidden_states=latents,
# timestep=timestep / 1000,
# guidance=guidance,
# encoder_hidden_states_mask=negative_prompt_embeds_mask,
# encoder_hidden_states=negative_prompt_embeds,
# img_shapes=img_shapes,
# txt_seq_lens=negative_prompt_embeds_mask.sum(dim=1).tolist(),
# attention_kwargs=self.attention_kwargs,
# return_dict=False,
# )[0]
with self.transformer.cache_context("uncond"):
# 初始化hidden_states在cuda:0 (使用相同的latents)
hidden_states = self.transformer.img_in(latents).to("cuda:0")
encoder_hidden_states = self.transformer.txt_norm(negative_prompt_embeds).to("cuda:0")
encoder_hidden_states = self.transformer.txt_in(encoder_hidden_states)
encoder_hidden_states_mask = negative_prompt_embeds_mask.to("cuda:0")
# 计算共享参数
timestep_float = timestep.to("cuda:0") / 1000
temb = (
self.transformer.time_text_embed(timestep_float, hidden_states)
if guidance is None
else self.transformer.time_text_embed(timestep_float, guidance.to("cuda:0"), hidden_states)
)
image_rotary_emb = self.transformer.pos_embed(
img_shapes,
negative_prompt_embeds_mask.sum(dim=1).tolist(),
device="cuda:0"
)
# # 前8层处理
# temb_c0 = temb.to("cuda:0", non_blocking=True)
# image_rotary_emb_c0 = tuple(item.to("cuda:0", non_blocking=True) for item in image_rotary_emb)
# torch.cuda.synchronize("cuda:0")
# for i, block in enumerate(self.transformer.transformer_blocks[:6]):
# # 只传输变化的hidden_states和encoder states
# hidden_states = hidden_states.to("cuda:0", non_blocking=True)
# encoder_hidden_states = encoder_hidden_states.to("cuda:0", non_blocking=True)
# encoder_hidden_states_mask = encoder_hidden_states_mask.to("cuda:0", non_blocking=True)
# torch.cuda.synchronize("cuda:0")
# encoder_hidden_states, hidden_states = block(
# hidden_states=hidden_states,
# encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
# encoder_hidden_states_mask=encoder_hidden_states_mask,
# temb=temb_c0,
# image_rotary_emb=image_rotary_emb_c0,
# joint_attention_kwargs=self.attention_kwargs,
# )
# 中间26层处理
temb_c1 = temb.to("cuda:1", non_blocking=True)
image_rotary_emb_c1 = tuple(item.to("cuda:1", non_blocking=True) for item in image_rotary_emb)
torch.cuda.synchronize("cuda:1")
for i, block in enumerate(self.transformer.transformer_blocks[:30]):
# 只传输变化的hidden_states和encoder states
hidden_states = hidden_states.to("cuda:1", non_blocking=True)
encoder_hidden_states = encoder_hidden_states.to("cuda:1", non_blocking=True)
encoder_hidden_states_mask = encoder_hidden_states_mask.to("cuda:1", non_blocking=True)
torch.cuda.synchronize("cuda:1")
encoder_hidden_states, hidden_states = block(
hidden_states=hidden_states,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_hidden_states_mask=encoder_hidden_states_mask,
temb=temb_c1,
image_rotary_emb=image_rotary_emb_c1,
joint_attention_kwargs=self.attention_kwargs,
)
# 后26层处理
temb_c2 = temb.to("cuda:2", non_blocking=True)
image_rotary_emb_c2 = tuple(item.to("cuda:2", non_blocking=True) for item in image_rotary_emb)
torch.cuda.synchronize("cuda:2")
for i, block in enumerate(self.transformer.transformer_blocks[30:], start=30):
hidden_states = hidden_states.to("cuda:2", non_blocking=True)
encoder_hidden_states = encoder_hidden_states.to("cuda:2", non_blocking=True)
encoder_hidden_states_mask = encoder_hidden_states_mask.to("cuda:2", non_blocking=True)
torch.cuda.synchronize("cuda:2")
encoder_hidden_states, hidden_states = block(
hidden_states=hidden_states,
encoder_hidden_states=encoder_hidden_states,
encoder_hidden_states_mask=encoder_hidden_states_mask,
temb=temb_c2,
image_rotary_emb=image_rotary_emb_c2,
joint_attention_kwargs=self.attention_kwargs,
)
# 最终处理
hidden_states = hidden_states.to("cuda:0", non_blocking=True)
torch.cuda.synchronize("cuda:0")
hidden_states = self.transformer.norm_out(hidden_states, temb)
neg_noise_pred = self.transformer.proj_out(hidden_states)
comb_pred = neg_noise_pred + true_cfg_scale * (noise_pred - neg_noise_pred)
cond_norm = torch.norm(noise_pred, dim=-1, keepdim=True)
noise_norm = torch.norm(comb_pred, dim=-1, keepdim=True)
noise_pred = comb_pred * (cond_norm / noise_norm)
# compute the previous noisy sample x_t -> x_t-1
latents_dtype = latents.dtype
latents = self.scheduler.step(noise_pred, t, latents, return_dict=False)[0]
if latents.dtype != latents_dtype:
if torch.backends.mps.is_available():
# some platforms (eg. apple mps) misbehave due to a pytorch bug: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/99272
latents = latents.to(latents_dtype)
if callback_on_step_end is not None:
callback_kwargs = {}
for k in callback_on_step_end_tensor_inputs:
callback_kwargs[k] = locals()[k]
callback_outputs = callback_on_step_end(self, i, t, callback_kwargs)
latents = callback_outputs.pop("latents", latents)
prompt_embeds = callback_outputs.pop("prompt_embeds", prompt_embeds)
# call the callback, if provided
if i == len(timesteps) - 1 or ((i + 1) > num_warmup_steps and (i + 1) % self.scheduler.order == 0):
progress_bar.update()
if XLA_AVAILABLE:
xm.mark_step()
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
self._current_timestep = None
if output_type == "latent":
image = latents
else:
latents = self._unpack_latents(latents, height, width, self.vae_scale_factor)
latents = latents.to(self.vae.dtype)
latents_mean = (
torch.tensor(self.vae.config.latents_mean)
.view(1, self.vae.config.z_dim, 1, 1, 1)
.to(latents.device, latents.dtype)
)
latents_std = 1.0 / torch.tensor(self.vae.config.latents_std).view(1, self.vae.config.z_dim, 1, 1, 1).to(
latents.device, latents.dtype
)
latents = latents / latents_std + latents_mean
image = self.vae.decode(latents, return_dict=False)[0][:, :, 0]
image = self.image_processor.postprocess(image, output_type=output_type)
# Offload all models
self.maybe_free_model_hooks()
if not return_dict:
return (image,)
return QwenImagePipelineOutput(images=image)
# 确保类定义在__main__之前
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 模型初始化代码
model_name = "/root/sj-tmp/Qwen-Image"
if torch.cuda.is_available():
torch_dtype = torch.bfloat16
device = "cuda"
else:
torch_dtype = torch.float32
device = "cpu"
pipe = CustomQwenImagePipeline.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype=torch_dtype,
)
# 设备分配
pipe.text_encoder.to("cuda:0")
pipe.vae.to("cuda:0")
for i, block in enumerate(pipe.transformer.transformer_blocks):
if i < 30:
block.to("cuda:1")
else:
block.to("cuda:2")
for name, module in pipe.transformer.named_children():
if name != "transformer_blocks":
module.to("cuda:0")
# 定义宽高比选项
aspect_ratios = {
"1:1 (方形)": (1328, 1328),
"16:9 (横屏)": (1664, 928),
"9:16 (竖屏)": (928, 1664),
"4:3 (传统)": (1472, 1140),
"3:4 (肖像)": (1140, 1472)
}
# 图像生成函数
def generate_image(
prompt,
negative_prompt="",
aspect_ratio="16:9 (横屏)",
seed=42,
true_cfg_scale=4.0,
guidance_scale=3.5,
num_inference_steps=50
):
# 获取选中的分辨率
width, height = aspect_ratios[aspect_ratio]
# 设置随机种子
generator = torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(seed) if seed >= 0 else None
# 中文提示词增强
zh_magic = "超清,4K,电影级构图"
full_prompt = f"{prompt} {zh_magic}" if any('\u4e00' <= char <= '\u9fff' for char in prompt) else prompt
# 生成图像
with torch.no_grad():
image = pipe(
prompt=full_prompt,
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
width=width,
height=height,
num_inference_steps=num_inference_steps,
true_cfg_scale=true_cfg_scale,
guidance_scale=guidance_scale,
generator=generator
).images[0]
return image
# 创建Gradio界面
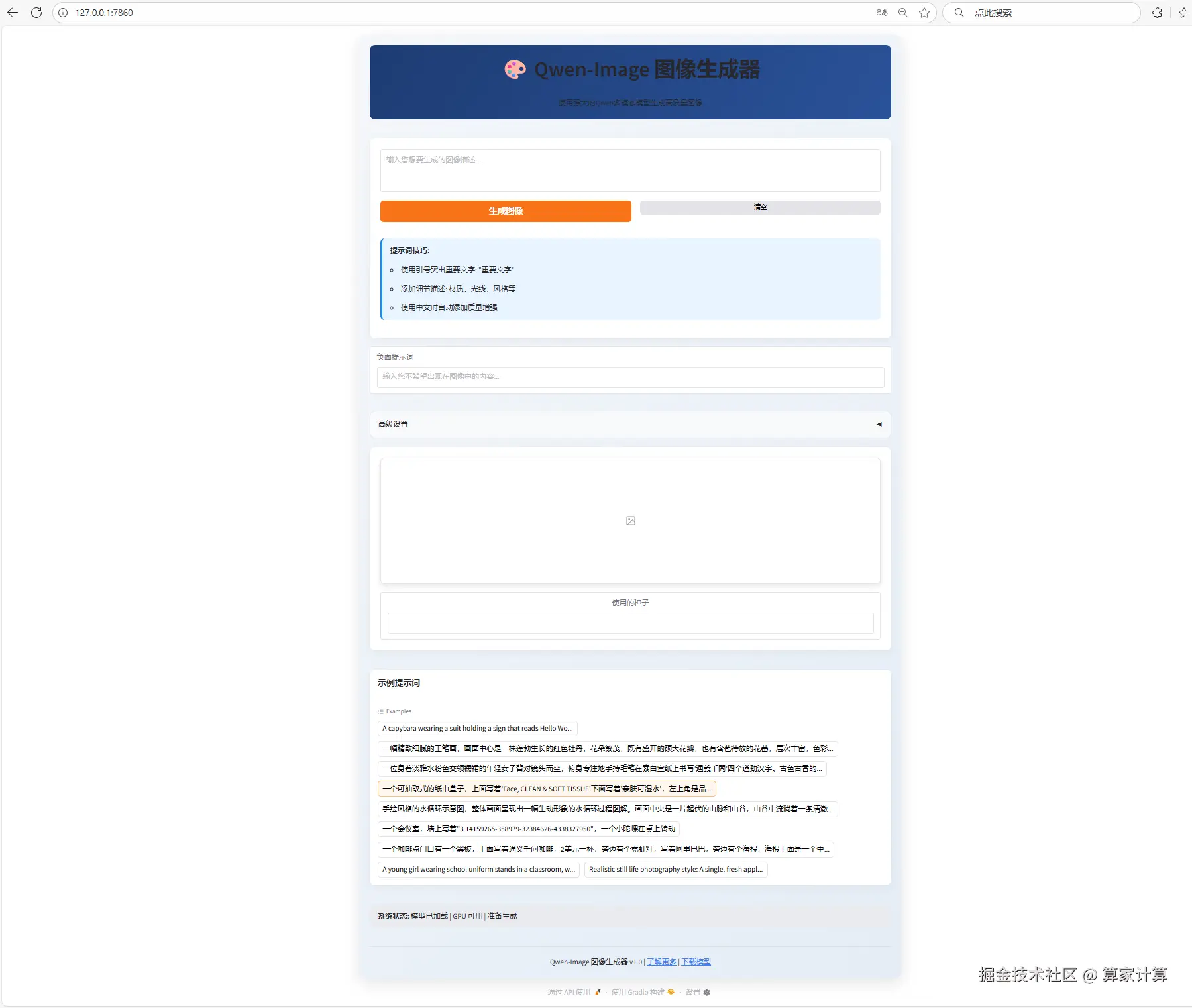
with gr.Blocks(title="Qwen-Image 图像生成器", theme=gr.themes.Soft()) as demo:
gr.Markdown("# 🎨 Qwen-Image 图像生成器")
gr.Markdown("使用强大的Qwen多模态模型生成高质量图像")
with gr.Row():
with gr.Column():
prompt = gr.Textbox(
label="提示词",
placeholder="描述你想要生成的图像内容...",
lines=3,
max_lines=5
)
negative_prompt = gr.Textbox(
label="负面提示词",
placeholder="描述你不希望在图像中出现的内容...",
lines=2
)
with gr.Row():
aspect_ratio = gr.Dropdown(
label="宽高比",
choices=list(aspect_ratios.keys()),
value="16:9 (横屏)"
)
seed = gr.Number(
label="随机种子",
value=42,
precision=0,
step=1
)
with gr.Accordion("高级设置", open=False):
true_cfg_scale = gr.Slider(
label="True CFG强度",
minimum=1.0,
maximum=10.0,
value=4.0,
step=0.5
)
guidance_scale = gr.Slider(
label="引导强度",
minimum=1.0,
maximum=10.0,
value=3.5,
step=0.1
)
num_inference_steps = gr.Slider(
label="迭代步数",
minimum=10,
maximum=100,
value=50,
step=5
)
generate_btn = gr.Button("生成图像", variant="primary")
with gr.Column():
output_image = gr.Image(
label="生成结果",
type="pil",
interactive=False,
height=500
)
# 示例提示词
examples = gr.Examples(
examples=[
["一个会议室,墙上写着'3.14159265-358979-32384626-4338327950',一个小陀螺在桌上转动", "", "16:9 (横屏)", 42],
["未来城市景观,霓虹灯光,赛博朋克风格,雨夜", "模糊,低质量", "16:9 (横屏)", 123],
["宁静的山水画,水墨风格,有仙鹤飞翔", "人物,现代建筑", "3:4 (肖像)", 456],
["奇幻森林,发光的蘑菇,精灵小屋,月光", "", "1:1 (方形)", 789]
],
inputs=[prompt, negative_prompt, aspect_ratio, seed],
label="示例提示"
)
# 绑定生成函数
generate_btn.click(
fn=generate_image,
inputs=[prompt, negative_prompt, aspect_ratio, seed, true_cfg_scale, guidance_scale, num_inference_steps],
outputs=output_image
)
# 启动Web服务 - 更新队列设置方式
#demo.queue(concurrency_count=1) # 将concurrency_count作为参数直接传递给queue()
demo.launch(
server_name="0.0.0.0",
server_port=7860,
share=False
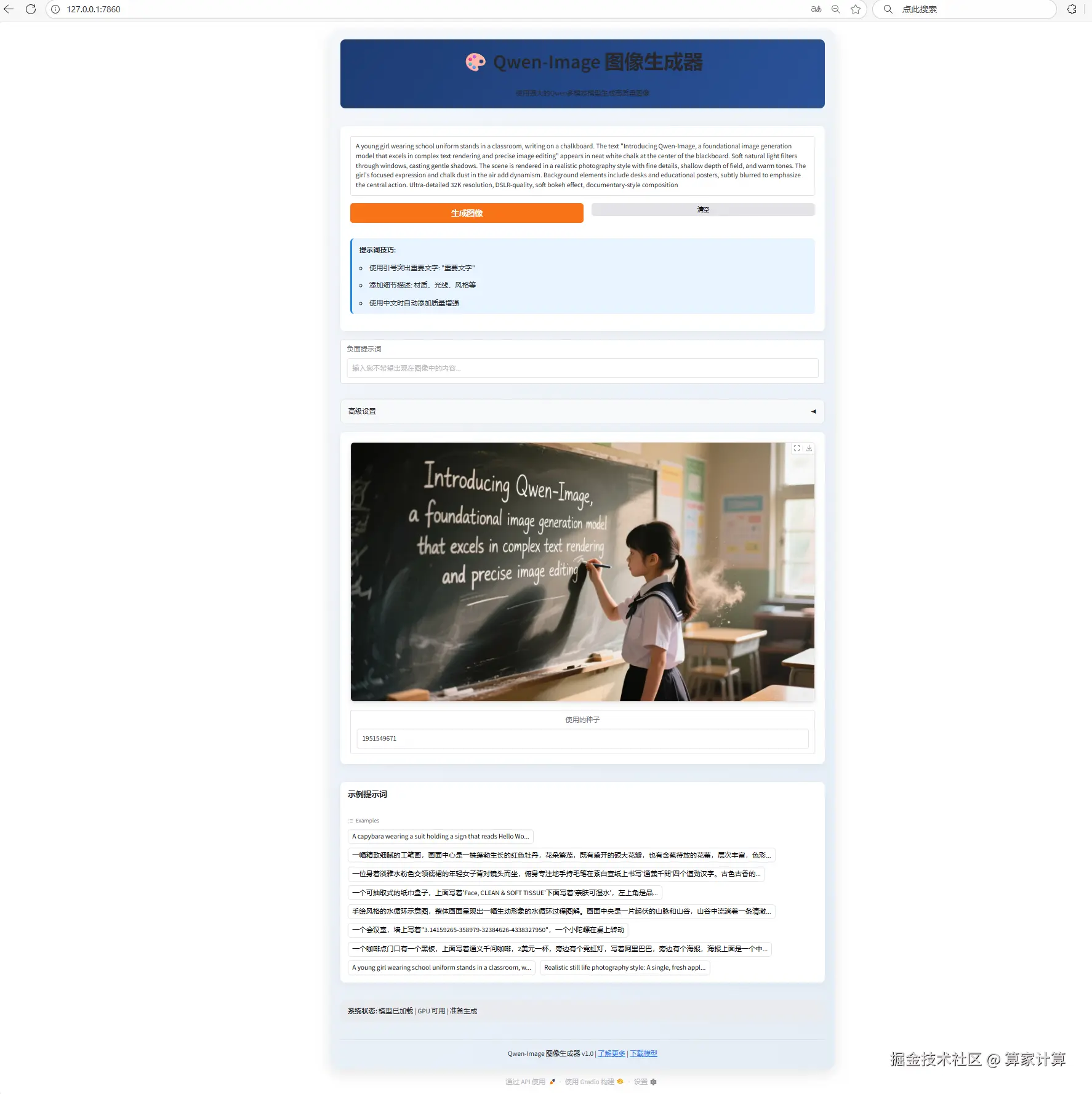
)运行app.py文件
python app.py
在浏览器中粘贴网址,如(http://127.0.0.1:7860/),便可进行web页面访问。
2.采用A100的显卡配置
若采用A100显卡,则可使用如下的demo.py文件运行模型。
python
import gradio as gr
import numpy as np
import random
import os
import json
import time
import threading
import queue
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor, as_completed
import torch.multiprocessing as mp
from multiprocessing import Process, Queue, Event
import atexit
import signal
mp.set_start_method('spawn', force=True)
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
import torch
# 使用本地模型路径
model_repo_id = "/root/sj-tmp/Qwen-Image"
MAX_SEED = np.iinfo(np.int32).max
MAX_IMAGE_SIZE = 1440
NUM_GPUS_TO_USE = int(os.environ.get("NUM_GPUS_TO_USE", torch.cuda.device_count()))
TASK_QUEUE_SIZE = int(os.environ.get("TASK_QUEUE_SIZE", 100))
TASK_TIMEOUT = int(os.environ.get("TASK_TIMEOUT", 300))
print(f"Config: Using {NUM_GPUS_TO_USE} GPUs, queue size {TASK_QUEUE_SIZE}, timeout {TASK_TIMEOUT} seconds")
class GPUWorker:
def __init__(self, gpu_id, model_repo_id, task_queue, result_queue, stop_event):
self.gpu_id = gpu_id
self.model_repo_id = model_repo_id
self.task_queue = task_queue
self.result_queue = result_queue
self.stop_event = stop_event
self.device = f"cuda:{gpu_id}"
self.pipe = None
def initialize_model(self):
"""Initialize the model on the specified GPU"""
try:
torch.cuda.set_device(self.gpu_id)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
torch_dtype = torch.bfloat16
else:
torch_dtype = torch.float32
# 使用本地模型路径,并确保只从本地加载
self.pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
self.model_repo_id,
torch_dtype=torch_dtype,
local_files_only=True # 确保只使用本地文件
)
self.pipe = self.pipe.to(self.device)
print(f"GPU {self.gpu_id} model initialized successfully")
return True
except Exception as e:
print(f"GPU {self.gpu_id} model initialization failed: {e}")
return False
def process_task(self, task):
"""Process a single task"""
try:
task_id = task['task_id']
prompt = task['prompt']
negative_prompt = task['negative_prompt']
seed = task['seed']
width = task['width']
height = task['height']
guidance_scale = task['guidance_scale']
num_inference_steps = task['num_inference_steps']
progress_callback = task['progress_callback']
def step_callback(pipe, i, t, callback_kwargs):
progress_callback(0.2 + i / num_inference_steps * 0.8, desc="GPU processing...")
return callback_kwargs
generator = torch.Generator(device=self.device).manual_seed(seed)
with torch.cuda.device(self.gpu_id):
image = self.pipe(
prompt=prompt,
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
true_cfg_scale=guidance_scale,
num_inference_steps=num_inference_steps,
width=width,
height=height,
generator=generator,
callback_on_step_end=step_callback
).images[0]
return {
'task_id': task_id,
'image': image,
'success': True,
'gpu_id': self.gpu_id
}
except Exception as e:
return {
'task_id': task_id,
'success': False,
'error': str(e),
'gpu_id': self.gpu_id
}
def run(self):
"""Worker main loop"""
if not self.initialize_model():
return
print(f"GPU {self.gpu_id} worker starting")
while not self.stop_event.is_set():
try:
# Get task from the task queue, set timeout to check stop event
task = self.task_queue.get(timeout=1)
if task is None: # Poison pill, exit signal
break
# Process the task
result = self.process_task(task)
# Put the result into the result queue
self.result_queue.put(result)
except queue.Empty:
continue
except Exception as e:
print(f"GPU {self.gpu_id} worker exception: {e}")
continue
print(f"GPU {self.gpu_id} worker stopping")
# Global GPU worker function for spawn mode
def gpu_worker_process(gpu_id, model_repo_id, task_queue, result_queue, stop_event):
worker = GPUWorker(gpu_id, model_repo_id, task_queue, result_queue, stop_event)
worker.run()
# Multi-GPU Manager Class
class MultiGPUManager:
def __init__(self, model_repo_id, num_gpus=None, task_queue_size=100):
self.model_repo_id = model_repo_id
self.num_gpus = num_gpus or torch.cuda.device_count()
self.task_queue = Queue(maxsize=task_queue_size)
self.result_queue = Queue()
self.stop_event = Event()
self.workers = []
self.worker_processes = []
self.task_counter = 0
self.pending_tasks = {}
print(f"Initializing Multi-GPU Manager with {self.num_gpus} GPUs, queue size {task_queue_size}")
def start_workers(self):
"""Start all GPU workers"""
for gpu_id in range(self.num_gpus):
# Use global function instead of instance method to ensure proper operation in spawn mode
process = Process(target=gpu_worker_process,
args=(gpu_id, self.model_repo_id, self.task_queue,
self.result_queue, self.stop_event))
process.start()
self.worker_processes.append(process)
# Start result processing thread
self.result_thread = threading.Thread(target=self._process_results)
self.result_thread.daemon = True
self.result_thread.start()
print(f"All {self.num_gpus} GPU workers have started")
def _process_results(self):
"""Background thread for processing results"""
while not self.stop_event.is_set():
try:
result = self.result_queue.get(timeout=1)
task_id = result['task_id']
if task_id in self.pending_tasks:
# Pass the result to the waiting task
self.pending_tasks[task_id]['result'] = result
self.pending_tasks[task_id]['event'].set()
except queue.Empty:
continue
except Exception as e:
print(f"Result processing thread exception: {e}")
continue
def submit_task(self, prompt, negative_prompt="", seed=42, width=1664, height=928,
guidance_scale=4, num_inference_steps=50, timeout=300):
"""Submit task and wait for result"""
return self.submit_task_with_progress(prompt, negative_prompt, seed, width, height,
guidance_scale, num_inference_steps, timeout, None)
def submit_task_with_progress(self, prompt, negative_prompt="", seed=42, width=1664, height=928,
guidance_scale=4, num_inference_steps=50, timeout=300, progress_callback=None):
"""Submit task and wait for result, with progress callback support"""
task_id = f"task_{self.task_counter}_{time.time()}"
self.task_counter += 1
task = {
'task_id': task_id,
'prompt': prompt,
'negative_prompt': negative_prompt,
'seed': seed,
'width': width,
'height': height,
'guidance_scale': guidance_scale,
'num_inference_steps': num_inference_steps,
'progress_callback': progress_callback
}
# Create waiting event
result_event = threading.Event()
self.pending_tasks[task_id] = {
'event': result_event,
'result': None,
'submitted_time': time.time()
}
try:
# Put task into queue
self.task_queue.put(task, timeout=10)
if progress_callback:
progress_callback(0.2, desc="Task submitted, waiting for GPU processing...")
# Wait for result, with progress update
start_time = time.time()
while not result_event.is_set():
if progress_callback:
elapsed = time.time() - start_time
# Estimate progress (between 40% and 80%)
estimated_progress = 0.2 + min(0.4, (elapsed / (timeout * 0.5)) * 0.4)
# progress_callback(estimated_progress, desc="GPU processing...")
if result_event.wait(timeout=2): # Check every 2 seconds
break
if time.time() - start_time > timeout:
# Timeout
del self.pending_tasks[task_id]
return {'success': False, 'error': 'Task timeout'}
if progress_callback:
progress_callback(0.8, desc="GPU processing complete...")
result = self.pending_tasks[task_id]['result']
del self.pending_tasks[task_id]
return result
except queue.Full:
del self.pending_tasks[task_id]
return {'success': False, 'error': 'Task queue is full'}
except Exception as e:
if task_id in self.pending_tasks:
del self.pending_tasks[task_id]
return {'success': False, 'error': str(e)}
def get_queue_status(self):
"""Get queue status"""
return {
'task_queue_size': self.task_queue.qsize(),
'result_queue_size': self.result_queue.qsize(),
'pending_tasks': len(self.pending_tasks),
'active_workers': len(self.worker_processes)
}
def stop(self):
"""Stop all workers"""
print("Stopping Multi-GPU Manager...")
self.stop_event.set()
# Send stop signal to each worker
for _ in range(self.num_gpus):
try:
self.task_queue.put(None, timeout=1)
except queue.Full:
pass
# Wait for all processes to end
for process in self.worker_processes:
process.join(timeout=5)
if process.is_alive():
process.terminate()
print("Multi-GPU Manager has stopped")
# Global Multi-GPU Manager instance
gpu_manager = None
def initialize_gpu_manager():
"""Initialize global GPU manager"""
global gpu_manager
if gpu_manager is None:
try:
# Ensure main process does not initialize CUDA
if torch.cuda.is_available():
print(f"Detected {torch.cuda.device_count()} GPUs")
gpu_manager = MultiGPUManager(
model_repo_id,
num_gpus=NUM_GPUS_TO_USE,
task_queue_size=TASK_QUEUE_SIZE
)
gpu_manager.start_workers()
print("GPU Manager initialized successfully")
return True
except Exception as e:
print(f"GPU Manager initialization failed: {e}")
gpu_manager = None
return False
# (1664, 928), (1472, 1140), (1328, 1328)
def get_image_size(aspect_ratio):
if aspect_ratio == "1:1":
return 1328, 1328
elif aspect_ratio == "16:9":
return 1664, 928
elif aspect_ratio == "9:16":
return 928, 1664
elif aspect_ratio == "4:3":
return 1472, 1140
elif aspect_ratio == "3:4":
return 1140, 1472
else:
return 1328, 1328
def infer(
prompt,
negative_prompt="",
seed=42,
randomize_seed=False,
aspect_ratio="16:9",
guidance_scale=5,
num_inference_steps=50,
progress=gr.Progress(track_tqdm=True),
request: gr.Request = None,
):
global gpu_manager
# Lazy load GPU manager
if gpu_manager is None:
progress(0.1, desc="Initializing GPU manager...")
initialize_gpu_manager()
# Return error if initialization fails
if gpu_manager is None:
print("GPU manager initialization failed, unable to process task")
from PIL import Image
error_image = Image.new('RGB', (512, 512), color='gray')
return error_image, seed
if randomize_seed:
seed = random.randint(0, MAX_SEED)
width, height = get_image_size(aspect_ratio)
# 直接使用原始 prompt,跳过 rewrite 步骤
progress(0.1, desc="Preparing prompt...")
print(f"Prompt: {prompt}")
# Submit task to queue
progress(0.3, desc="Submitting task to GPU queue...")
# Submit task using global GPU manager with progress tracking
result = gpu_manager.submit_task_with_progress(
prompt=prompt,
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
seed=seed,
width=width,
height=height,
guidance_scale=guidance_scale,
num_inference_steps=num_inference_steps,
timeout=TASK_TIMEOUT,
progress_callback=progress,
)
if result['success']:
progress(0.9, desc="Saving result...")
image = result['image']
gpu_id = result['gpu_id']
print(f"Task completed using GPU {gpu_id}")
progress(1.0, desc="Done!")
return image, seed
else:
print(f"Inference failed: {result['error']}")
# Return a blank image or error message
from PIL import Image
error_image = Image.new('RGB', (512, 512), color='red')
return error_image, seed
def get_system_status():
"""Get system status"""
if gpu_manager:
status = gpu_manager.get_queue_status()
return f"""
## System Status
- Active Workers: {status['active_workers']}
- Task Queue Size: {status['task_queue_size']}
- Result Queue Size: {status['result_queue_size']}
- Pending Tasks: {status['pending_tasks']}
- Total GPUs: {gpu_manager.num_gpus}
"""
else:
return "GPU manager not initialized"
examples = [
"A capybara wearing a suit holding a sign that reads Hello World",
"一幅精致细腻的工笔画,画面中心是一株蓬勃生长的红色牡丹,花朵繁茂,既有盛开的硕大花瓣,也有含苞待放的花蕾,层次丰富,色彩艳丽而不失典雅。牡丹枝叶舒展,叶片浓绿饱满,脉络清晰可见,与红花相映成趣。一只蓝紫色蝴蝶仿佛被画中花朵吸引,停驻在画面中央的一朵盛开牡丹上,流连忘返,蝶翼轻展,细节逼真,仿佛随时会随风飞舞。整幅画作笔触工整严谨,色彩浓郁鲜明,展现出中国传统工笔画的精妙与神韵,画面充满生机与灵动之感。",
"一位身着淡雅水粉色交领襦裙的年轻女子背对镜头而坐,俯身专注地手持毛笔在素白宣纸上书写"通義千問"四个遒劲汉字。古色古香的室内陈设典雅考究,案头错落摆放着青瓷茶盏与鎏金香炉,一缕熏香轻盈升腾;柔和光线洒落肩头,勾勒出她衣裙的柔美质感与专注神情,仿佛凝固了一段宁静温润的旧时光。",
" 一个可抽取式的纸巾盒子,上面写着'Face, CLEAN & SOFT TISSUE'下面写着'亲肤可湿水',左上角是品牌名'洁柔',整体是白色和浅黄色的色调",
"手绘风格的水循环示意图,整体画面呈现出一幅生动形象的水循环过程图解。画面中央是一片起伏的山脉和山谷,山谷中流淌着一条清澈的河流,河流最终汇入一片广阔的海洋。山体和陆地上绘制有绿色植被。画面下方为地下水层,用蓝色渐变色块表现,与地表水形成层次分明的空间关系。太阳位于画面右上角,促使地表水蒸发,用上升的曲线箭头表示蒸发过程。云朵漂浮在空中,由白色棉絮状绘制而成,部分云层厚重,表示水汽凝结成雨,用向下箭头连接表示降雨过程。雨水以蓝色线条和点状符号表示,从云中落下,补充河流与地下水。整幅图以卡通手绘风格呈现,线条柔和,色彩明亮,标注清晰。背景为浅黄色纸张质感,带有轻微的手绘纹理。",
'一个会议室,墙上写着"3.14159265-358979-32384626-4338327950",一个小陀螺在桌上转动',
'一个咖啡点门口有一个黑板,上面写着通义千问咖啡,2美元一杯,旁边有个霓虹灯,写着阿里巴巴,旁边有个海报,海报上面是一个中国美女,海报下方写着qwen newbee',
"""A young girl wearing school uniform stands in a classroom, writing on a chalkboard. The text "Introducing Qwen-Image, a foundational image generation model that excels in complex text rendering and precise image editing" appears in neat white chalk at the center of the blackboard. Soft natural light filters through windows, casting gentle shadows. The scene is rendered in a realistic photography style with fine details, shallow depth of field, and warm tones. The girl's focused expression and chalk dust in the air add dynamism. Background elements include desks and educational posters, subtly blurred to emphasize the central action. Ultra-detailed 32K resolution, DSLR-quality, soft bokeh effect, documentary-style composition""",
"Realistic still life photography style: A single, fresh apple resting on a clean, soft-textured surface. The apple is slightly off-center, softly backlit to highlight its natural gloss and subtle color gradients---deep crimson red blending into light golden hues. Fine details such as small blemishes, dew drops, and a few light highlights enhance its lifelike appearance. A shallow depth of field gently blurs the neutral background, drawing full attention to the apple. Hyper-detailed 8K resolution, studio lighting, photorealistic render, emphasizing texture and form."
]
css = """
#col-container {
margin: 0 auto;
max-width: 1024px;
}
"""
with gr.Blocks(css=css) as demo:
with gr.Column(elem_id="col-container"):
gr.Markdown('[](https://huggingface.co/Qwen/Qwen-Image )')
gr.Markdown(" # [Qwen-Image](https://huggingface.co/Qwen/Qwen-Image )")
gr.Markdown("[Learn more](https://huggingface.co/Qwen/Qwen-Image ) about the Qwen-Image series. Try on [Hugging Face API](https://huggingface.co/Qwen/Qwen-Image ), or [download model](https://huggingface.co/Qwen/Qwen-Image ) to run locally with ComfyUI or diffusers.")
gr.Markdown("**For better results when generating images with text, try enclosing the text you want in quotation marks like this: "text you want"**")
gr.Markdown("**如果想在生成图像时获得更好的文字效果,建议将你想要的文字用引号括起来,例如:"你想要的文字"。**")
with gr.Row():
prompt = gr.Text(
label="Prompt",
show_label=False,
placeholder="Enter your prompt",
container=False,
)
run_button = gr.Button("Run", scale=0, variant="primary")
result = gr.Image(label="Result", show_label=False)
with gr.Accordion("Advanced Settings", open=False):
negative_prompt = gr.Text(
label="Negative prompt",
max_lines=1,
placeholder="Enter a negative prompt",
visible=False,
)
seed = gr.Slider(
label="Seed",
minimum=0,
maximum=MAX_SEED,
step=1,
value=0,
)
randomize_seed = gr.Checkbox(label="Randomize seed", value=True)
with gr.Row():
aspect_ratio = gr.Radio(
label="Aspect ratio(width:height)",
choices=["1:1", "16:9", "9:16", "4:3", "3:4"],
value="16:9",
)
with gr.Row():
guidance_scale = gr.Slider(
label="Guidance scale",
minimum=0.0,
maximum=7.5,
step=0.1,
value=4.0,
)
num_inference_steps = gr.Slider(
label="Number of inference steps",
minimum=1,
maximum=50,
step=1,
value=50,
)
gr.Examples(examples=examples, inputs=[prompt], outputs=[result, seed], fn=infer, cache_examples=False, cache_mode="lazy")
gr.on(
triggers=[run_button.click, prompt.submit],
fn=infer,
inputs=[
prompt,
negative_prompt,
seed,
randomize_seed,
aspect_ratio,
guidance_scale,
num_inference_steps,
],
outputs=[result, seed],
concurrency_limit=NUM_GPUS_TO_USE
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
def cleanup():
if gpu_manager:
gpu_manager.stop()
# Register cleanup function
atexit.register(cleanup)
# Handle signals
def signal_handler(signum, frame):
print(f"Received signal {signum}, cleaning up resources...")
cleanup()
exit(0)
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, signal_handler)
signal.signal(signal.SIGTERM, signal_handler)
try:
demo.launch(server_name="0.0.0.0")
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("Received interrupt signal, cleaning up resources...")
cleanup()
except Exception as e:
print(f"Application exception: {e}")
cleanup()
raise
bash
#运行
python demo.py
在浏览器中粘贴网址,如(http://127.0.0.1:8080/),便可进行web页面访问。

四、效果展示
因硬件限制,没有A100,这里用3 * 4090的显卡配置进行展示。