一。进程处理多路IO请求
在没有多路复用IO之前,对于多路IO请求,一般只有阻塞与非阻塞IO两种方式
1.1 阻塞IO
需要结合多进程/多线程,每个进程/线程处理一路IO

缺点:客户端越多,需要创建的进程/线程越多,相对占用内存资源较多
1.2 非阻塞IO
单进程可以处理,但是需要不断检测客户端是否发出IO请求,需要不断占用cpu,消耗 cpu 资源

二.多路复用IO简介
- 本质上就是通过复用一个进程来处理多个IO请求
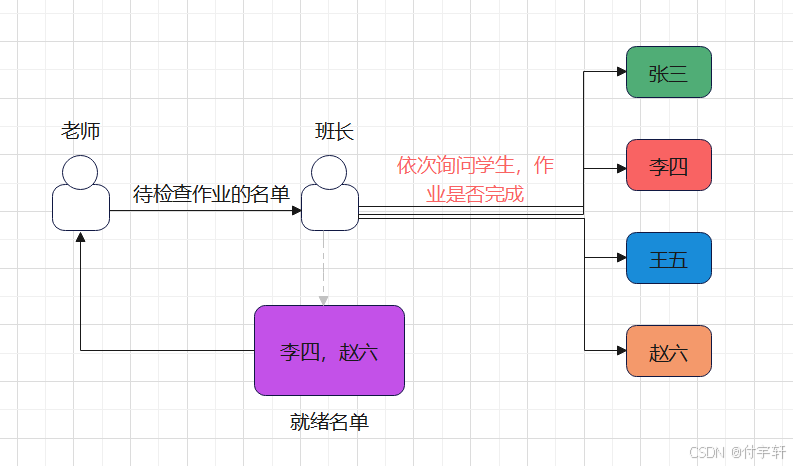
- 基本思想:由内核来监控多个文件描述符是否可以进行I/O操作,如果有就绪的文件描述符,将结果告知给用户进程,则用户进程在进行相应的I/O操作

类似于下图的老师检查学生作业

三.多路复用I/O方案
目前在Linux系统有三种多路复用I/O的方案
- select方案
- poll方案
- epoll方案
四.select 方案
4.1 设计思想
- 通过单进程创建一个文件描述符集合,将需要监控的文件描述符添加到这个集合中
- 由内核负责监控文件描述符是否可以进行读写,一旦可以读写,则通知相应的进程进行相应的I/O操作

4.2 实现方式
select多路复用I/O在实现时主要是以调用 select 函数来实现
cpp
select 函数
函数头文件
#include <sys/select.h>
函数原型
int select(int nfds, fd_set *readfds,fd_set*writefds,fd_set *exceptfds,struct timeval *timeout);
函数功能
监控一组文件描述符,阻塞当前进程,由内核检测相应的文件描述符是否就绪,一旦有文件描述符就绪,将就绪的文件描述符拷贝给进程,唤醒进程处理
函数参数
nfds:最大文件描述符加1
readfds:读文件描述符集合的指针
writefds:写文件描述符集合的指针
exceptfds:其他文件描述符集合的指针
timeout:超时时间结构体变量的指针
函数返回值
成功:返回已经就绪的文件描述符的个数。如果设置timeout,超时就会返回0
失败:-1,并设置errno操作文件描述符集合函数
cpp
void FD_CLR(int fd,fd_set *set)
将fd从文件描述符集合中删除
int FD_ISSET(int fd,fd_set *set)
判断fd是否在文件描述符集合中
void FD_SET(int fd,fd_set *set)
将文件描述符添加到文件描述符集合中
void FD_ZERO(fd_set *set)
将文件描述符集合清空
参数描述:
fd:文件描述符
set:文件描述符集合的指针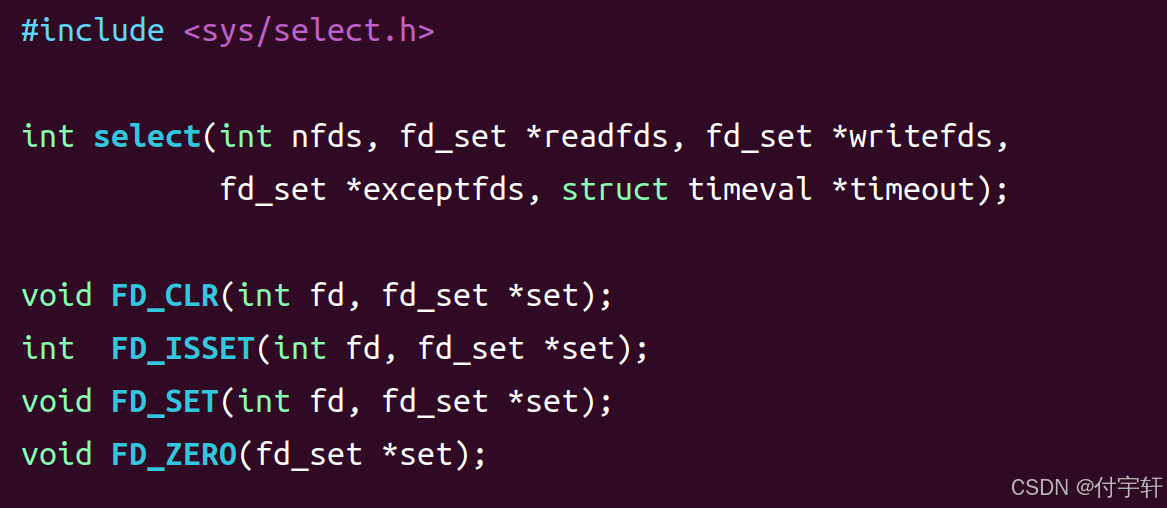
示例代码:使用select函数监控有名管道,如果有输入,则打印相应的信息
write.cpp
cpp
using namespace std;
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include <cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<deque>
#include<cstdio>
#include<ctime>
#include<deque>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/select.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define PATH "/home/linuxfu/pipo"
int main(){
int ret = access(PATH,F_OK);
if(ret == -1){
mkfifo(PATH,0644);
}
int fd = open(PATH,O_WRONLY);
if(fd == -1){
cout << "create failed" <<endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
char buf[128] = { 0 };
while(1){
memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf));
cout << "请输入你想要输入的字符串:";
fgets(buf,sizeof(buf) - 1,stdin);
buf[strlen(buf) - 1] = '\0';
ssize_t wtypes = write(fd,buf,size(buf));
if(wtypes == -1){
cout << "write failed" << endl;
close(fd);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}select.cpp
cpp
using namespace std;
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<deque>
#include<ctime>
#include<deque>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/select.h>
#define PATH "/home/linuxfu/pipo"
int main(){
int ret = access(PATH,F_OK);
if(ret == -1){
mkfifo(PATH,0644);
}
int fd = open(PATH,O_RDONLY);
if(fd == -1){
cout << "create failed" <<endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
fd_set rfds;
FD_ZERO(&rfds);
FD_SET(0,&rfds);
FD_SET(fd,&rfds);
struct timeval tv;
tv.tv_sec = 5;
tv.tv_usec = 0;
fd_set temp_rfds;//备份
struct timeval temp_tv;//备份
while(1){
temp_rfds = rfds;
temp_tv = tv;
int ret = select(fd + 1,&temp_rfds,NULL,NULL,&temp_tv);
if(ret == -1){
perror("ret");
}else if(ret == 0){
cout << "time out" << endl;
}else{
for(int i = 0;i < ret;i++){
if(FD_ISSET(0,&temp_rfds)){
string temp;
cin >> temp;
cout << temp << endl;
}
if(FD_ISSET(fd,&temp_rfds)){
char buf[128] = { 0 };
ssize_t rtype = read(fd,buf,size(buf));
if(rtype > 0){
printf("content:%s",buf);
}
}
}
}
}
}答案图片:

注意点:
- struct timeval结构体
cpp
struct timeval {
__kernel_old_time_t tv_sec; /* seconds *///秒数
__kernel_suseconds_t tv_usec; /* microseconds *///毫秒数
};2.select 函数理解

3.超时时间的说明
- 如果timeout之后,文件描述符集合中没有任何就绪的文件描述符,select函数就会返回0
- 超时之后,timeout会被select函数修改,表示超时时间已经使用完。如果想继续使用超时时间,需要备份之前的struct timeval
- 超时之后,表示没有就绪的文件描述符,此时文件描述符集合被赋值为空

因此,需要将之前的文件描述符集合进行备份。
4.3多路复用IO-select底层原理分析
文件描述符集合
cpp
typedef struct
{
/* XPG4.2 requires this member name. Otherwise avoid the name
from the global namespace. */
#ifdef __USE_XOPEN
__fd_mask fds_bits[__FD_SETSIZE / __NFDBITS];
# define __FDS_BITS(set) ((set)->fds_bits)
#else
__fd_mask __fds_bits[__FD_SETSIZE / __NFDBITS];
# define __FDS_BITS(set) ((set)->__fds_bits)
#endif
} fd_set;数组的类型为 long int 类型,在 64 位系统中 long int 的大小为 8 个字节
cpp
typedef long int __fd_mask;数组的大小为16 __FD_SETSIZE / __NFDBITS
cpp
#define __FD_SETSIZE 1024
#define __NFDBITS (8 * (int) sizeof (__fd_mask))文件描述符集合的数组最终在存储时,使用了位图的方式来记录相应的文件描述符,具体原理如下:
- 数组中没有直接存储文件描述符,而是使用某一位来表示该文件描述符是否需要监控
- 需要监控的文件描述符需要转成数组的某一个元素的某一位,然后将对应的位设置为1,例如当 fd = 60 的成员需要监控,则需要将数组的第0个成员的第 [60] bit 设置为1,当 fd = 64时,则需要将数组的第1个成员的第[0] bit 设置为1
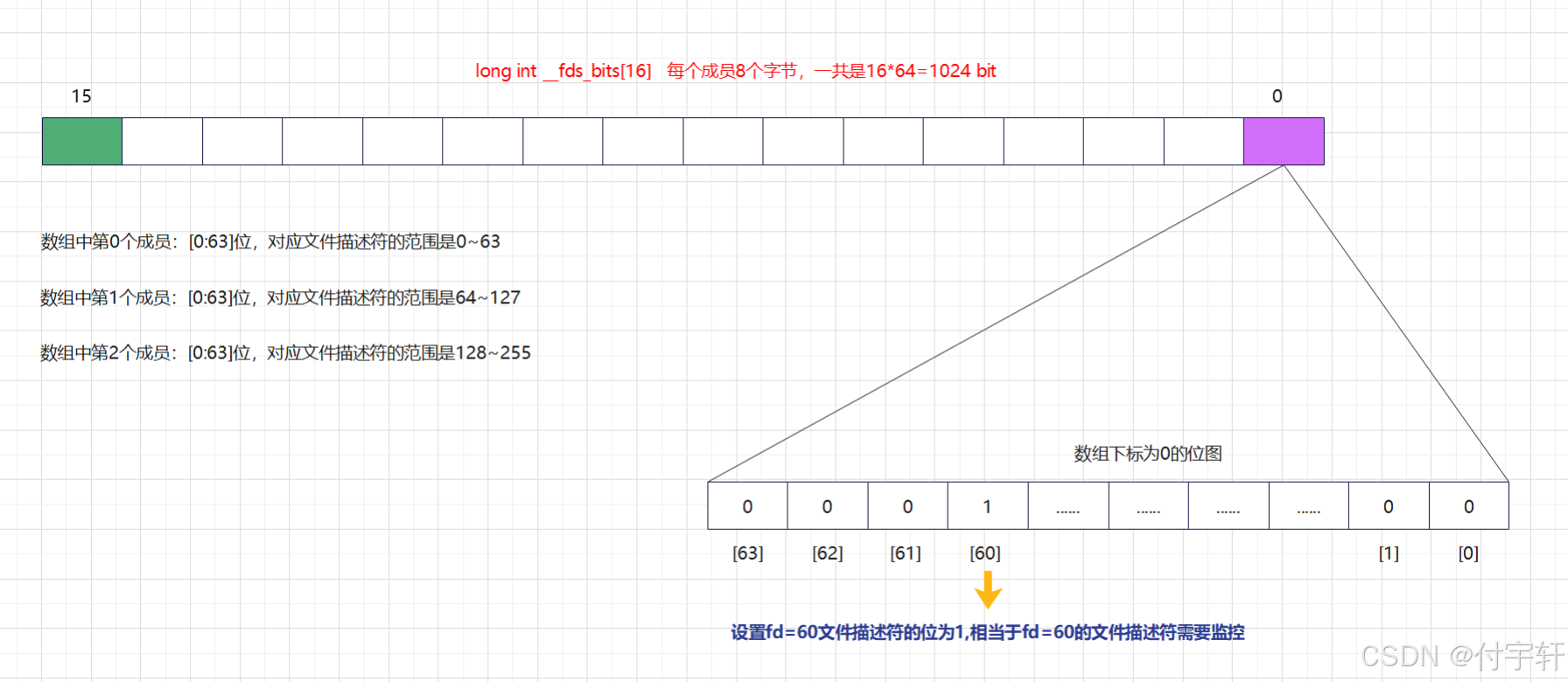
从上面的文件描述符集合内存管理可以分析出,select 最终只能存储1024个文件描述符
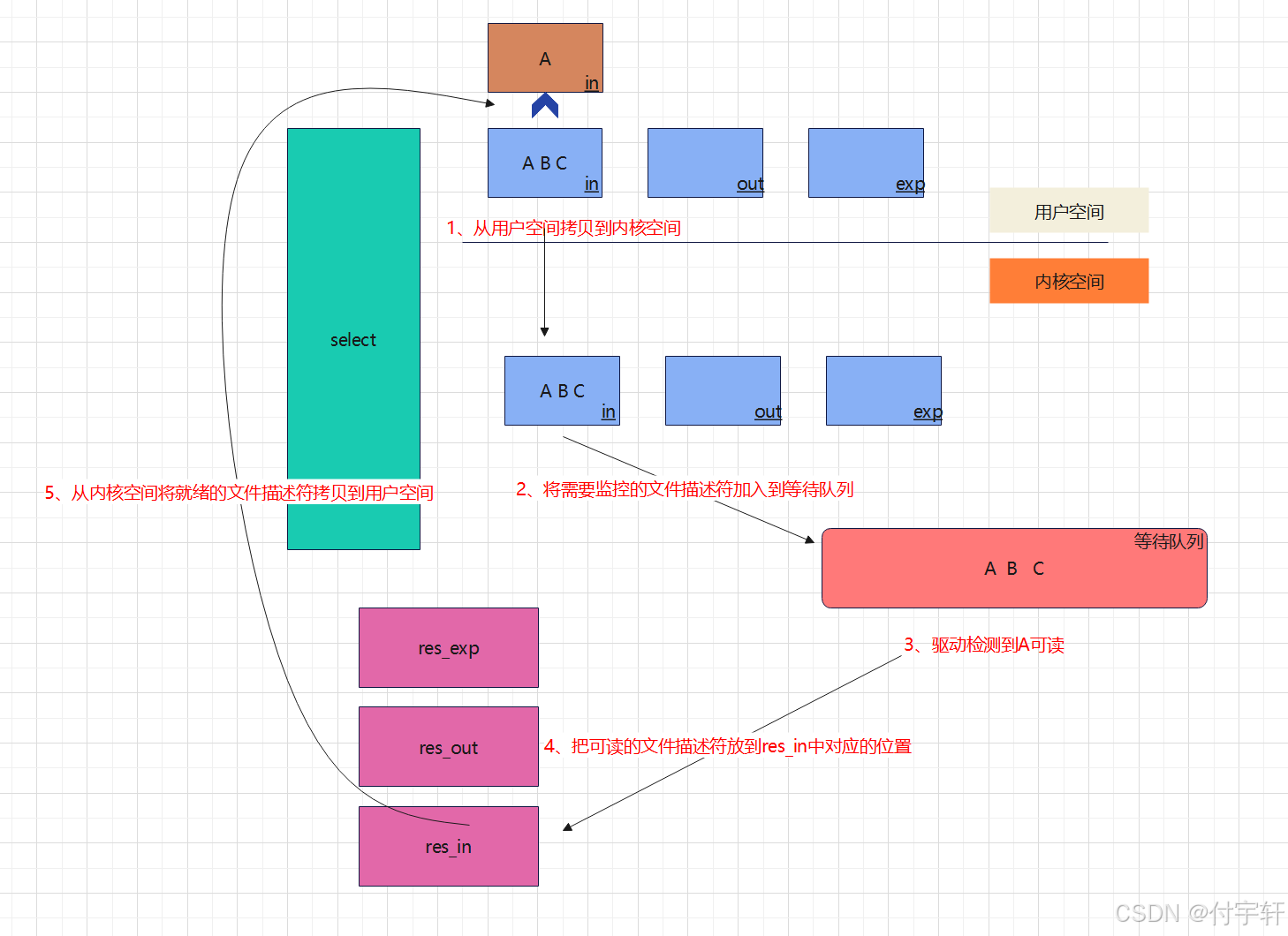
select 底层原理分析
cpp
一.在 select() 函数中一共需要使用三个文件描述符集合,分别是
1.in : 读文件描述符集合,主要包含 需要进行读的文件描述符的集合,反映在底层实际可以从设备中读取数据
2.out : 写文件描述符集合,主要包含 需要进行写的文件描述符的集合,反映在底层实际可以将数据写入到设备中
3.exp : 其他文件描述符集合,主要包含其他类型的操作的文件描述符集合
二.调用了select() 函数,内核做了如下事情:
1.从用户空间将集合的文件描述符拷贝到内核空间
2.循环遍历 fd_set 中所有的文件描述符,来检测是否有文件描述符可进行I/O操作
(1)如果有文件描述符可进行I/O操作,则设置返回的文件描述符集对应位1(res_in,res_out,res_exp),跳出循环,直接返回。最终会赋值给 in,out,exp 文件描述符集合
(2)如果没有文件描述符可进行I/O操作,则继续循环检测。如果设置 timeout ,则在超时后返回,此时select() 函数返回0
三.select() 函数减少了多进程/多线程的开销,但仍然有很多缺点:
1.每次调用select()函数都需要将fd集合拷贝到内核空间,这个开销在fd很多时就越大
2.每次都需要遍历所有的文件描述符集合,这个开销在fd很多时就越大
3.支持的文件描述符只有1024五.poll 方案
5.1 基本原理
多路复用poll的方式与select多路复用原理类似,但有很多地方不同,下面是具体的对比
-
在应用层是以结构体struct pollfd数组的形式来进行管理文件描述符,在内核中基于链表对数组进行扩展;select方式以集合的形式管理文件描述符且最大支持1024个文件描述
-

-
poll将请求与就绪事件通过结构体进行分开
-
select将请求与就绪文件描述符存储在同一个集合中,导致每次都需要进行重新赋值才能进行下一次的监控
-
在内核中仍然使用的是轮询的方式,与 select 相同,当文件描述符越来越多时,则会影响效率
5.2 poll 方案
poll多路复用实现主要调用 poll 函数
cpp
函数头文件
#include <poll.h>
函数原型
int poll(struct pollfd *fds, nfds_t nfds, int timeout);
函数功能
监控多个文件描述符的变化
函数参数
fds:sturct pollfd结构体指针
nfds:fds结构体的数量
timeout:超时时间,单位为ms
函数返回值
成功:大于0,返回就绪的文件描述符数量;=0,超时返回,没有文件描述符就绪
失败:-1,并设置errno参数相关说明
- struct pollfd 结构体说明
cpp
struct pollfd {
int fd; /* file descriptor */
short events; /* requested events */
short revents; /* returned events */
};- nfds_t 类型定义
cpp
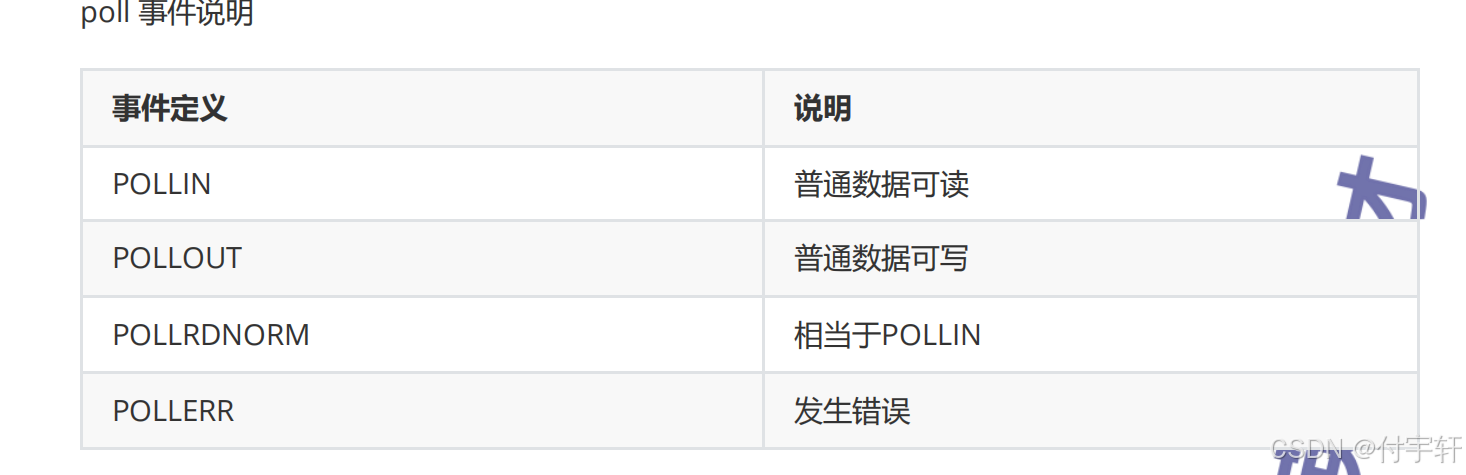
typedef unsigned long int nfds_t;poll 事件说明
示例代码:使用poll函数监控有名管道,如果有输入,则获取标准输入的内容并打印
write.cpp
cpp
using namespace std;
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include <cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<deque>
#include<cstdio>
#include<ctime>
#include<deque>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/select.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define PATH "/home/linuxfu/pipo"
int main(){
int ret = access(PATH,F_OK);
if(ret == -1){
mkfifo(PATH,0644);
}
int fd = open(PATH,O_WRONLY);
if(fd == -1){
cout << "create failed" <<endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
char buf[128] = { 0 };
while(1){
memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf));
cout << "请输入你想要输入的字符串:";
fgets(buf,sizeof(buf) - 1,stdin);
buf[strlen(buf) - 1] = '\0';
ssize_t wtypes = write(fd,buf,size(buf));
if(wtypes == -1){
cout << "write failed" << endl;
close(fd);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}poll.cpp
cpp
using namespace std;
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include <cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<deque>
#include<cstdio>
#include<ctime>
#include<deque>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <poll.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define PATH "/home/linuxfu/pipo"
int main(){
int ret = access(PATH,F_OK);
if(ret == -1){
mkfifo(PATH,0644);
}
int rfd = open(PATH,O_RDONLY);
if(rfd == -1){
cout << "create failed" <<endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
struct pollfd fds[2] = { 0 };
fds[0].fd = 0;
fds[0].events = POLLIN;
fds[1].fd = rfd;
fds[1].events = POLLIN;
while(1){
int ret = poll(fds,2,5000);
if(ret == -1){
perror("ret");
}else if(ret == 0){
cout << "time out" << endl;
}else{
for(int i = 0;i < 2;i++){
if(fds[0].revents == POLLIN){
char buf[128] = { 0 };
fgets(buf,sizeof(buf) - 1,stdin);
buf[strlen(buf) - 1] = '\0';
cout << "buf:"<< buf << endl;
}
if(fds[1].revents == POLLIN){
char buf[128] = { 0 };
ssize_t wtypes = read(rfd,buf,sizeof(buf));
if(wtypes > 0){
cout << "字符串" << buf << endl;
}
}
}
}
}
close(rfd);
return 0;
}
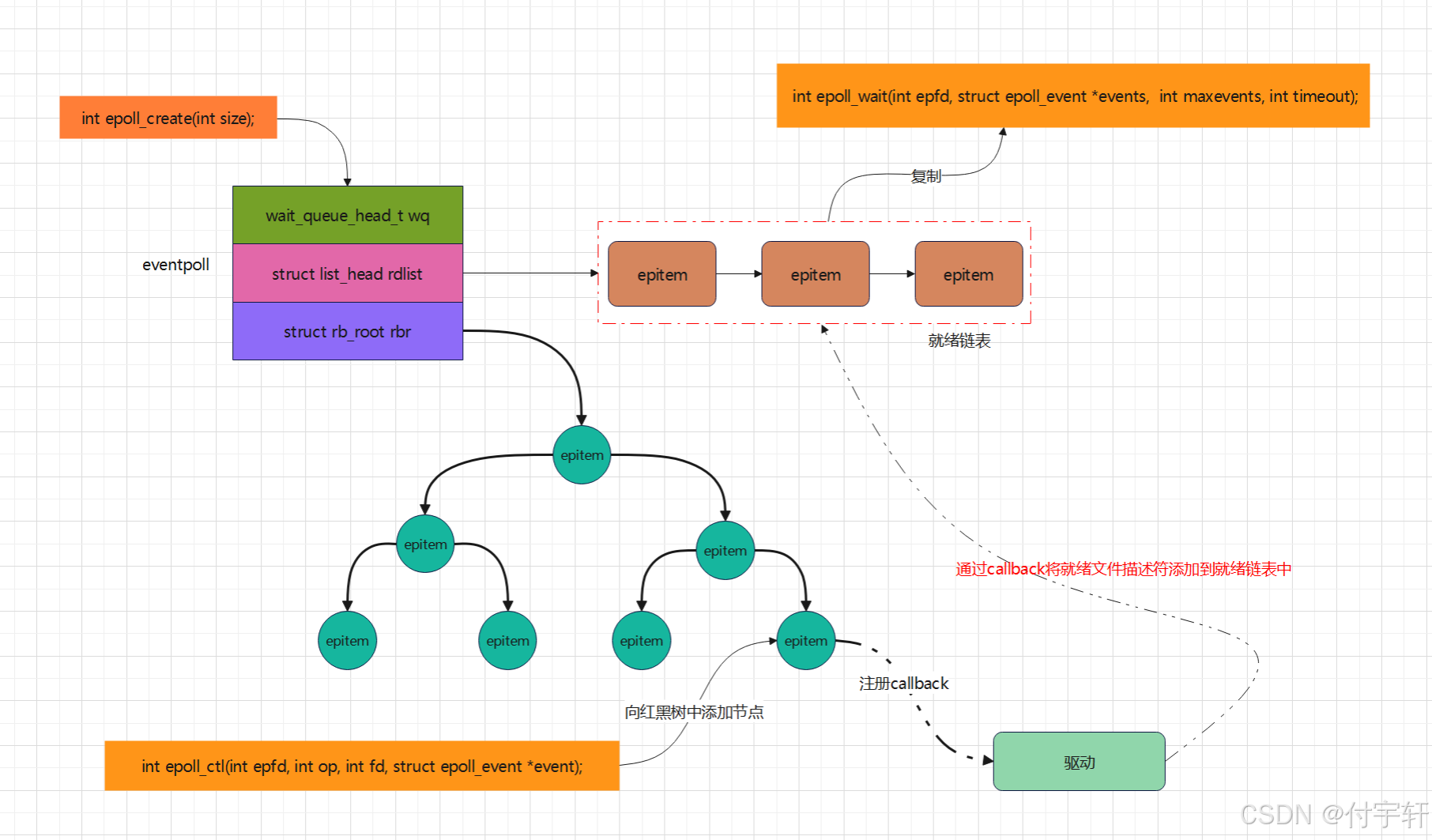
6.epoll 方案
6.1epoll 基本原理
epoll相对于select与poll有较大的不同,主要是针对前面两种多路复用 IO 接口的不足
select/poll的不足:
- select 方案使用数组存储文件描述符,最大支持1024个
- select 每次调用都需要将文件描述符集合拷贝到内核中,非常消耗资源
- poll 方案解决文件描述符存储数量限制问题,但其他问题没有得到解决
- select / poll 底层使用轮询的方式检测文件描述符是否就绪,文件描述符越多,则效率越低
**epoll优点:
(1) epoll底层使用红黑树,没有文件描述符数量的限制,并且可以动态增加与删除节点,不用重复拷贝
(2)epoll底层使用callback机制,没有采用遍历所有描述符的方式,效率较高**
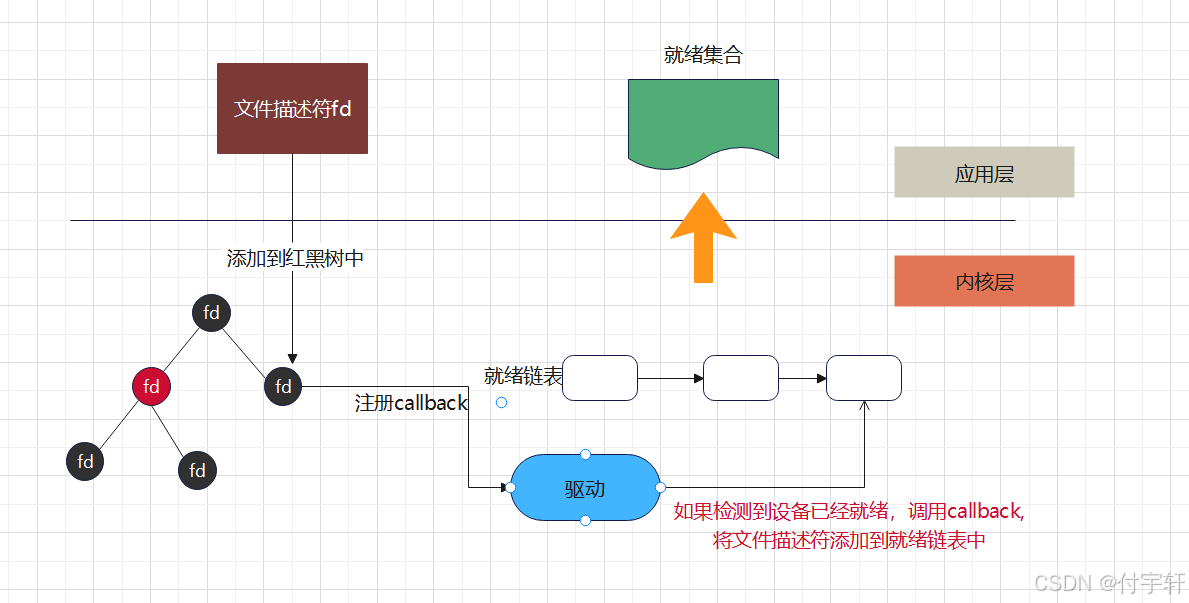
6.2 select/poll 方案图解
6.3 epoll 方案图解
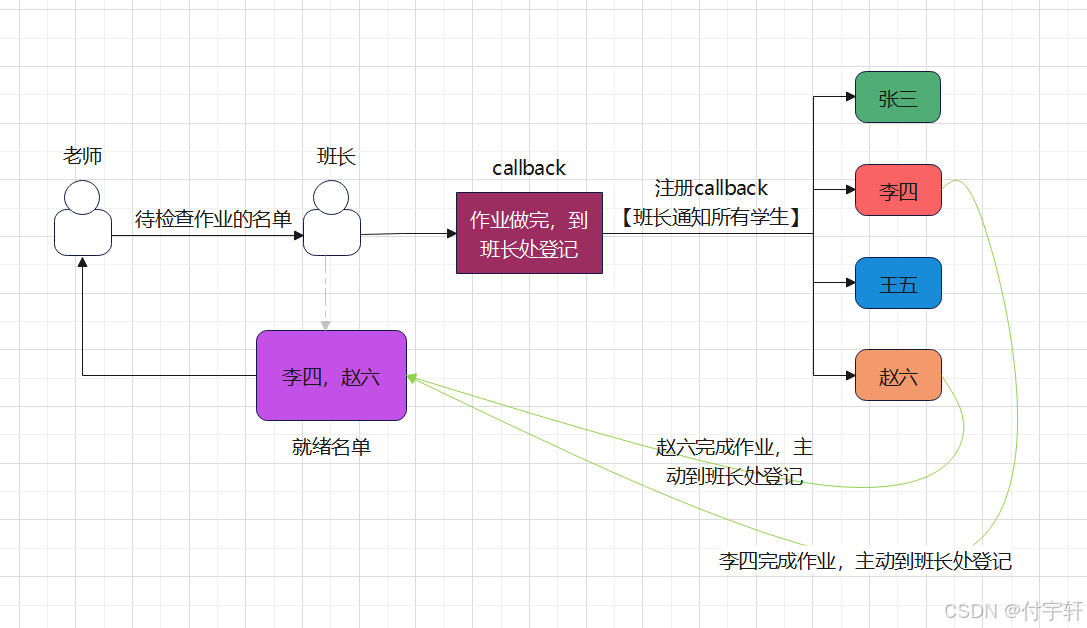
6.4epoll 创建
1.epoll创建需要调用epoll_create函数,用于创建epoll实例
cpp
函数头文件
#include <sys/epoll.h>
函数原型
int epoll_create(int size);
函数描述
epoll_create() creates a new epoll(7) instance. Since Linux 2.6.8, the size argument is ignored, but must be greater than zero;
函数功能
创建一个epoll实例,分配相关的数据结构空间
函数参数
size:需要填一个大于0的数,从Linux 2.6.8开始,size参数被忽略
函数返回值
成功:返回epoll文件描述符
失败:返回-1,并设置errno示例代码:创建一个epoll 实例
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
int main()
{
int epfd = epoll_create(1);
if(epfd == -1)
{
perror("epoll_create");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("epfd=%d\n",epfd);
return 0;
}- epoll 函数控制
epoll控制函数主要用于文件描述符集合的管理,包括增加、修改、删除等操作。
epoll_ctl函数详细信息如下
c
函数头文件
#include <sys/epoll.h>
函数原型
int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event);
函数参数
epfd:epoll 实例
op:epoll 操作命令字
EPOLL_CTL_ADD:在epoll实例中添加新的文件描述符(相当于向红黑树中添加节点),并将事件与fd关联
EPOLL_CTL_MOD:更改与目标文件描述符fd相关联的事件
EPOLL_CTL_DEL:从epoll实例中删除目标文件描述符fd ,事件参数被忽略
在系统中定义如下:
#define EPOLL_CTL_ADD 1 /* Add a file descriptor to the interface. */
#define EPOLL_CTL_DEL 2 /* Remove a file descriptor from the interface.
*/
#define EPOLL_CTL_MOD 3 /* Change file descriptor epoll_event structure.
*/
fd:操作的文件描述符
event:struct epoll_event结构体对象指针struct epoll_event 结构体定义如下:
c
ypedef union epoll_data {
void *ptr;
int fd;
uint32_t u32;
uint64_t u64;
} epoll_data_t;
struct epoll_event {
uint32_t events; /* Epoll events */
epoll_data_t data; /* User data variable */
};events : epoll事件,事件具体定义如下:
c
enum EPOLL_EVENTS
{
EPOLLIN = 0x001, // 读事件有效(非常常用)
#define EPOLLIN EPOLLIN
EPOLLPRI = 0x002,
#define EPOLLPRI EPOLLPRI
EPOLLOUT = 0x004, // 写事件有效(非常常用)
#define EPOLLOUT EPOLLOUT
EPOLLRDNORM = 0x040,
#define EPOLLRDNORM EPOLLRDNORM
EPOLLRDBAND = 0x080,
#define EPOLLRDBAND EPOLLRDBAND
EPOLLWRNORM = 0x100,
#define EPOLLWRNORM EPOLLWRNORM
EPOLLWRBAND = 0x200,
#define EPOLLWRBAND EPOLLWRBAND
EPOLLMSG = 0x400,
#define EPOLLMSG EPOLLMSG
EPOLLERR = 0x008,
#define EPOLLERR EPOLLERR
EPOLLHUP = 0x010,
#define EPOLLHUP EPOLLHUP
EPOLLRDHUP = 0x2000,
#define EPOLLRDHUP EPOLLRDHUP
EPOLLEXCLUSIVE = 1u << 28,
#define EPOLLEXCLUSIVE EPOLLEXCLUSIVE
EPOLLWAKEUP = 1u << 29,
#define EPOLLWAKEUP EPOLLWAKEUP
EPOLLONESHOT = 1u << 30,
#define EPOLLONESHOT EPOLLONESHOT
EPOLLET = 1u << 31 // 将EPOLL设为边缘触发(Edge Triggered)模式
#define EPOLLET EPOLLET
};epoll_data是一个共用体,主要使用 fd 成员用于存储文件描述符
epoll 等待事件发生(关联的文件描述符就绪),这里调epoll_wait 函数
epoll_wait 函数详细信息如下:
c
函数头文件
#include <sys/epoll.h>
函数原型
int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event *events, int maxevents, int timeout);
函数功能
等待文件描述符关联的事件发生
函数参数
epfd:epoll实例对象
events:存储就绪集合的数组的地址
maxevents:就绪集合的最大值
timeout:超时时间
函数返回值
成功:返回就绪的文件描述符数量,超时返回0
失败:返回-1,并设置errno6.5示例代码:
将有名管道描述符添加到epoll实例中,等待用户输入数据,如果没有则打印 timeout,否则获取用户输入并输出。
write.cpp
cpp
using namespace std;
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include <cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<deque>
#include<cstdio>
#include<ctime>
#include<deque>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/select.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define PATH "/home/linuxfu/pipo"
int main(){
int ret = access(PATH,F_OK);
if(ret == -1){
mkfifo(PATH,0644);
}
int fd = open(PATH,O_WRONLY);
if(fd == -1){
cout << "create failed" <<endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
char buf[128] = { 0 };
while(1){
memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf));
cout << "请输入你想要输入的字符串:";
fgets(buf,sizeof(buf) - 1,stdin);
buf[strlen(buf) - 1] = '\0';
ssize_t wtypes = write(fd,buf,size(buf));
if(wtypes == -1){
cout << "write failed" << endl;
close(fd);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}epoll.cpp
cpp
using namespace std;
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include <cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<deque>
#include<cstdio>
#include<ctime>
#include<deque>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define PATH "/home/linuxfu/pipo"
int main(){
int ret = access(PATH,F_OK);
if(ret == -1){
mkfifo(PATH,0644);
}
int rfd = open(PATH,O_RDONLY);
if(rfd == -1){
cout << "create failed" <<endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
int epfd = epoll_create(1);
if( epfd == -1){
perror("epfd");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
//将标准输入文件描述符添加到epoll中
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.events = EPOLLIN;
ev.data.fd = rfd;
int ret1 = epoll_ctl(epfd,EPOLL_CTL_ADD,rfd,&ev);
if(ret1 == -1){
perror("ret1");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
struct epoll_event ev1;
ev1.events = EPOLLIN;
ev1.data.fd = 0;
int ret2 = epoll_ctl(epfd,EPOLL_CTL_ADD,0,&ev1);
if(ret2 == -1){
perror("ret2");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
struct epoll_event events[2];
while(1){
int res = epoll_wait(epfd,events,2,4000);
if(res == -1){
perror("res");
}else if(res == 0){
printf("timeout\n");
}else if(res > 0){
for(int i = 0;i < res;i++){
if(events[i].data.fd == 0){
char buf[128] = { 0 };
fgets(buf,sizeof(buf)-1,stdin);
buf[strlen(buf) - 1] = '\0';
cout << "buf:" << buf << endl;
}
if(events[i].data.fd == rfd){
char buf[128] = { 0 };
ssize_t wtypes = read(rfd,buf,sizeof(buf));
if(wtypes > 0){
cout << "str:" << buf << endl;
}
}
}
}
}
close(rfd);
return 0;
}
6.6 epoll 底层结构