文章目录
-
- Ansible流程控制介绍
-
- [1. 条件判断](#1. 条件判断)
- [2. 循环](#2. 循环)
- [3. 循环控制](#3. 循环控制)
- [4. 错误处理](#4. 错误处理)
- [5. 包含和导入](#5. 包含和导入)
- [6. 块和异常处理](#6. 块和异常处理)
- [7. 角色的流程控制](#7. 角色的流程控制)
- *include_tasks、import_tasks_include之间的区别
- 条件语句再细说
- 循环语句再细说
- 实例-服务器安装基础环境优化
Ansible流程控制介绍
1. 条件判断
when
when用于根据条件决定是否执行任务。
yaml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Install package only on RedHat
package:
name: httpd
state: present
when: ansible_os_family == "RedHat"2. 循环
loop
loop用于遍历列表或集合。
yaml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Install multiple packages
package:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: present
loop:
- vim
- git
- curlwith_items
较老的循环方式,遍历列表。
yaml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Install packages using with_items
package:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: present
with_items:
- vim
- gitwith_dict
用于遍历字典。
yaml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Print dictionary items
debug:
msg: "Key: {{ item.key }}, Value: {{ item.value }}"
with_dict:
item1: value1
item2: value2with_sequence
生成序列并遍历。
yaml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Create files using with_sequence
file:
path: "/tmp/file{{ item }}"
state: touch
with_sequence: start=1 end=5with_fileglob
遍历匹配文件名的文件。
yaml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Read files from directory
debug:
msg: "Found file: {{ item }}"
with_fileglob:
- /tmp/*.txtwith_together
并行遍历多个列表。
yaml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Combine items from two lists
debug:
msg: "Item from list1: {{ item.0 }}, Item from list2: {{ item.1 }}"
with_together:
- ['a', 'b', 'c']
- [1, 2, 3]3. 循环控制
loop_control
提供更细粒度控制。
yaml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Custom loop variable
debug:
msg: "Current item: {{ custom_item }}"
loop:
- a
- b
loop_control:
loop_var: custom_item在Ansible中,loop_control是一个用于提供循环过程中更细粒度控制的选项。它允许你自定义循环变量名、设置循环的标签、限制循环的并行执行数量等。这使得在处理循环时可以更加灵活和精确。
下面是一个使用loop_control的示例,展示了如何自定义循环变量名:
yaml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Custom loop variable
debug:
msg: "Current item: {{ custom_item }}"
loop:
- a
- b
loop_control:
loop_var: custom_item在这个例子中,loop_control用于指定循环变量的名称。默认情况下,Ansible中的循环变量名为item,但通过loop_control,你可以将其更改为任何你想要的名称,比如这里的custom_item。这样,在循环体内部,就可以使用{``{ custom_item }}来引用当前迭代的元素。
这种自定义循环变量的功能在需要在循环内部引用多个循环变量或在复杂的剧本中提高代码的可读性时非常有用。通过loop_control,你可以更精确地控制循环的行为,使其更符合你的特定需求。
4. 错误处理
ignore_errors
在任务失败时继续执行后续任务。
yaml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Failing task
command: /bin/false
ignore_errors: yes
- name: This will run despite the previous failure
debug:
msg: "The previous task failed, but this still runs."failed_when
自定义任务失败的条件。
yaml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Custom failure condition
command: /bin/true
register: result
- name: Check the result
debug:
msg: "This task will fail if the command did not return 0."
failed_when: result.rc != 05. 包含和导入
include_tasks
动态包含任务文件。
yaml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Include tasks based on a condition
include_tasks: my_tasks.yml
when: ansible_os_family == "Debian"import_tasks
静态导入任务文件。
yaml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- import_tasks: my_imported_tasks.yml6. 块和异常处理
block
将一组任务组合在一起,便于管理和错误处理。
yaml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- block:
- name: Task 1
command: /bin/true
- name: Task 2
command: /bin/false
rescue:
- name: Handle failure
debug:
msg: "One of the tasks failed, handling the error."
# 当block中的任务错误时,会执行rescue中的任务7. 角色的流程控制
在角色中组织和控制任务执行。
yaml
# roles/myrole/tasks/main.yml
- name: Task in role
command: /bin/echo "This is a task in a role"
- include_tasks: another_tasks.yml这些示例展示了Ansible中的各种流程控制功能,帮助你在自动化任务和配置管理中实现更复杂的逻辑。
*include_tasks、import_tasks_include之间的区别
在Ansible中,
include_tasks、import_tasks和include指令都是用来组织和重用代码的,但它们在用法和上下文中有一些区别:
include_tasks:
动态包含任务文件 :
include_tasks可以根据条件动态地包含一个任务列表文件。使用场景 :当你需要基于某些条件(如操作系统、环境变量等)来决定是否执行一组任务时,可以使用
include_tasks。
-
示例:
yaml- hosts: all tasks: - name: Include tasks based on a condition include_tasks: my_tasks.yml when: ansible_os_family == "Debian"
import_tasks:
静态导入任务文件 :
import_tasks用于静态地导入一个任务列表文件,它不会根据条件来决定是否导入。使用场景 :当你需要在当前任务列表中静态地包含一组任务时,可以使用
import_tasks。示例:
```yaml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- import_tasks: my_imported_tasks.yml
```
include:
包含变量或文件 :
include用于包含变量文件或角色文件。使用场景 :当你需要在当前剧本中包含一个变量文件或角色文件时,可以使用
include。示例:
```yaml
- hosts: all
vars_files:
- vars.yml
```这些指令在Ansible中提供了灵活的代码组织和重用机制,使得剧本更加模块化和可维护。
include指令在Ansible中主要用于包含变量文件、任务文件、模板文件等,它的作用不仅限于任务列表,还包括其他资源类型。以下是include指令的一些额外说明:
变量文件:
include_vars:用于包含变量文件,这些变量可以在任务中使用。示例:
```yaml
- hosts: all
vars_files:
- vars.yml
```
任务文件:
虽然
include_tasks用于动态包含任务文件,但**include也可以用于静态包含任务文件**,这通常用于角色中。示例:
```yaml
- include: tasks/main.yml
```
模板文件:
include可以用于包含模板文件,这些文件可以用于生成配置文件等。示例:
```yaml
- name: Include a template file
include: my_template.j2
```
文件路径:
include指令支持相对路径和绝对路径。- 相对路径是相对于当前剧本文件的路径。
- 绝对路径是从文件系统的根目录开始的路径。
条件包含:
- 虽然
include本身不支持条件包含,但可以通过在包含的文件中使用条件语句来实现条件包含的效果。循环包含:
include指令可以与loop一起使用,实现循环包含文件。示例:
yaml- hosts: all tasks: - name: Include tasks from a list include: "{{ item }}" with_first_found: - "tasks/{{ ansible_os_family }}.yml" - "tasks/default.yml"错误处理:
- 如果
include指定的文件不存在,Ansible会报错。角色中的使用:
- 在Ansible角色中,
include指令通常用于包含任务文件、变量文件或模板文件。静态与动态:
include通常是静态的,意味着它在剧本解析时就确定了要包含的文件。- 与
include_tasks相比,include不提供动态包含的能力。与
import的区别:
import指令在Ansible的早期版本中用于包含任务,但现在推荐使用import_tasks。
include指令是Ansible剧本编写中非常灵活和强大的工具,可以有效地组织和管理代码。
条件语句再细说
使用when指令
且、或、非、是
且:and
或:or
非:!=
是:==

模糊条件
使用is match
yaml
...
yum:
name:
- xxx
- xxx
when: ansible_hostname is match 'web*'
...when指令的详细使用方法
在Ansible中,when指令用于条件判断,允许你根据特定条件决定是否执行某个任务。它可以根据变量的值、注册的结果或其他条件进行判断。
-
基本语法:
yaml- name: Task name command: your_command when: condition -
条件可以是:
- 变量比较:
when: variable_name == 'value' - 布尔值:
when: some_boolean_variable - 列表检查:
when: item in my_list - 注册变量结果:
when: result_variable is succeeded
- 变量比较:
以下是一个简单示例,展示如何使用when指令:
yaml
---
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Check if a file exists
stat:
path: /tmp/myfile.txt
register: file_stat
- name: Create a file if it does not exist
file:
path: /tmp/myfile.txt
state: touch
when: not file_stat.stat.exists
- name: Notify if the file was created
debug:
msg: "The file was created!"
when: file_stat.stat.exists == false上面是示例的解释:
stat模块 :检查/tmp/myfile.txt是否存在,并将结果注册到file_stat。- 创建文件任务 :仅在文件不存在时执行(
when: not file_stat.stat.exists)。 - 调试任务:如果文件被创建,输出一条消息。
变量比较
假设你有一个变量my_os,它存储了目标机器的操作系统类型。你只想在操作系统为Ubuntu时执行某个任务。
yaml
- name: Install package if OS is Ubuntu
apt: name=nginx state=present
when: my_os == 'Ubuntu'布尔值
如果你有一个布尔变量install_nginx,你想根据这个变量的值来决定是否安装Nginx。
yaml
- name: Install Nginx if the condition is true
command: apt-get install nginx
when: install_nginx列表检查
如果你有一个列表packages_to_install,并且你只想在列表中包含nginx时安装它。
yaml
- name: Install nginx if it is in the list
command: apt-get install nginx
when: 'nginx' in packages_to_install注册变量结果
假设你已经运行了一个任务来安装某些软件包,并且你将结果注册到了变量install_result中。只有当安装成功时,你才想执行下一个任务。
yaml
- name: Install some software
command: apt-get install some_software
register: install_result
- name: Run configuration script if software installed successfully
command: ./configure_software.sh
when: install_result is succeeded组合条件
你也可以组合多个条件来创建更复杂的逻辑。
yaml
- name: Install nginx only if it's not installed and the OS is Ubuntu
command: apt-get install nginx
when: nginx_not_installed and my_os == 'Ubuntu'在这个例子中,nginx_not_installed是一个布尔变量,表示Nginx是否已经安装。只有当Nginx未安装并且操作系统是Ubuntu时,才会执行安装Nginx的命令。
再探讨一下Ansible中的"列表检查"和"注册变量"的条件:
一、 列表检查(List Checking)
在Ansible中,你可以使用in关键字来检查一个值是否存在于一个列表中。这在你需要基于一组预定义的值来决定是否执行某个任务时非常有用。
例如,假设你有一个变量my_list,它是一个包含多个元素的列表,你想检查某个特定的值item是否在这个列表中:
yaml
- name: Check if item is in the list
command: echo "Item is in the list"
when: item in my_list在这个例子中,如果变量item的值存在于变量my_list中,那么echo "Item is in the list"命令将被执行。

二、 注册变量(Registered Variables)
在Ansible中,你可以使用register关键字来保存任务的输出,这样你就可以在后续的任务中引用这个输出。注册的变量通常用于条件判断,以决定是否执行后续的任务。
例如,你有一个任务,它执行一个命令并注册了其结果:
yaml
- name: Run a command and register the result
command: ls /nonexistent
register: command_result
ignore_errors: yes在这个例子中,ignore_errors: yes告诉Ansible即使命令失败也继续执行。register: command_result将命令的输出保存到变量command_result中。
然后,你可以使用when语句来检查这个注册变量的状态,并决定是否执行后续的任务:
yaml
- name: Check if the command was successful
command: echo "Command was successful"
when: command_result is succeeded在这个例子中,如果ls /nonexistent命令成功执行(即使它实际上没有找到任何文件,因为我们使用了ignore_errors: yes),那么echo "Command was successful"命令将被执行。
注册变量可以包含多种信息,包括命令的退出状态、标准输出和标准错误输出等。你可以根据这些信息来构建复杂的条件判断。例如,你可以检查命令是否失败:
yaml
- name: Check if the command failed
command: echo "Command failed"
when: command_result is failed在这个例子中,如果ls /nonexistent命令失败(这是预期的,因为/nonexistent目录不存在),那么echo "Command failed"命令将被执行。

更多的例子:
例 1:根据操作系统类型执行任务
yaml
---
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Install packages based on OS
package:
name:
- "{{ item }}"
state: present
loop:
- vim
- wget
when: ansible_os_family == 'Debian'解释:
这个任务会在Debian家族的操作系统(如Ubuntu)上安装vim和wget,只在when条件满足时执行。
例 2:根据变量值进行条件判断
yaml
---
- hosts: all
vars:
environment: production
tasks:
- name: Deploy application only in production
shell: deploy_script.sh
when: environment == 'production'解释:
此任务仅在environment变量等于production时执行,确保应用程序只在生产环境中部署。
例 3:根据注册变量的结果执行任务
yaml
---
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Check if a service is running
shell: systemctl is-active my_service
register: service_status
ignore_errors: yes
- name: Start the service if it is not running
service:
name: my_service
state: started
when: service_status.stdout != 'active'解释:
这个示例首先检查服务my_service是否正在运行。如果服务未运行(即service_status.stdout不是active),则会启动该服务。
例 4:使用多条件判断
yaml
---
- hosts: all
vars:
app_installed: true
app_version: '1.0.0'
tasks:
- name: Run upgrade if app is installed and version is less than 2.0.0
shell: upgrade_script.sh
when: app_installed == true and app_version | version_compare('2.0.0', '<')解释:
这个任务在应用程序已安装且版本低于2.0.0时执行升级脚本。使用version_compare函数进行版本比较。
循环语句再细说
如何使用
使用item变量结合with_items或loop指令
在Ansible中,
with_items和loop都是用来迭代列表或集合的指令,但它们有一些具体的区别和使用场景。以下是这两者的详细比较:一、 1. 基本概念
with_items:是Ansible的一个古老的循环结构,用于遍历列表。它的语法较为简单,但功能较为有限。
loop:是Ansible中更现代的循环语法,提供了更强大的功能和灵活性。它是with_items的推荐替代品。二、 2. 语法比较
with_items 示例
yaml
- name: Install packages using with_items
yum:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: present
with_items:
- vim
- wget
- curlloop 示例
yaml
- name: Install packages using loop
yum:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: present
loop:
- vim
- wget
- curl三、 3. 功能区别
- 可嵌套 :
loop支持嵌套循环,可以与其他循环指令结合使用,而with_items则不支持。
yaml
- name: Loop over a list of lists
debug:
msg: "{{ item }}"
loop:
- [1, 2, 3]
- [4, 5, 6]
loop_control:
subelements: 0
- 更好的变量支持 :
loop可以与其他的控制指令(如loop_control)结合使用,可以更灵活地控制迭代过程。四、 4. 性能和可读性
性能:
- 在某些情况下,
loop的性能可能会稍好,特别是在处理大型数据集时。可读性:
loop的语法更一致,易于理解,尤其是在复杂的场景下。推荐在新项目中使用loop。五、 5. 使用建议
- 推荐使用
loop:由于loop是Ansible的现代循环方式,功能更强大且灵活性更高,因此在新项目中应优先选择loop。with_items的使用 :对于一些简单的任务,可以继续使用with_items,但应注意其在未来可能会被弃用。六、 总结
尽管
with_items和loop都可以实现相似的功能,loop在灵活性、功能和可读性方面具有明显的优势。因此,建议在编写Ansible剧本时优先选择使用loop。
loop需在安装Ansible2X版本后才能使用
item变量有固定子元素?
在Ansible中,
item变量通常用于循环(如with_items或loop)来表示当前迭代的元素。具体来说,item可以用来访问循环中每个元素的子元素,特别是在处理字典或列表时。
- 列表中的字典:
yaml
- name: Example with list of dictionaries
debug:
msg: "Name is {{ item.name }}, Age is {{ item.age }}"
loop:
- { name: 'Alice', age: 30 }
- { name: 'Bob', age: 25 }在这个例子中,
item是每个字典,可以通过item.name和item.age访问它的子元素。
- 字典中的列表:
yaml
- name: Example with dictionary containing a list
debug:
msg: "Fruit is {{ item }} and Price is {{ prices[item] }}"
vars:
prices:
apple: 1.2
banana: 0.5
loop:
- apple
- banana这里,
item是循环中的水果名,使用prices[item]来获取对应价格。
item是动态的,具体内容取决于当前循环的上下文。- 可以在循环中使用
item的子元素访问来处理复杂数据结构,例如列表和字典的组合。- 结合
with_items或loop使用,可以使配置和任务更加灵活和可重复。
实例-服务器安装基础环境优化
需求
优化一台刚安装完的虚拟机:
- 改网卡信息
- 换新仓库
- 安装基础软件包(包括时间同步软件)
- 优化文件描述符
- *防火墙设置
部分实现
换指定新仓库
yaml
---
- name: the play1
hosts: all
become: no
tasks:
- name: task:备份原来的仓库
include: /path/to/task_backup_old_repos.yaml
- name: task:安装新仓库
include: /path/to/task_install_new_repos.yaml可使用get_url加其中的列表循环的方式安装新仓库:

当然也可以使用shell模块,里面使用wget命令




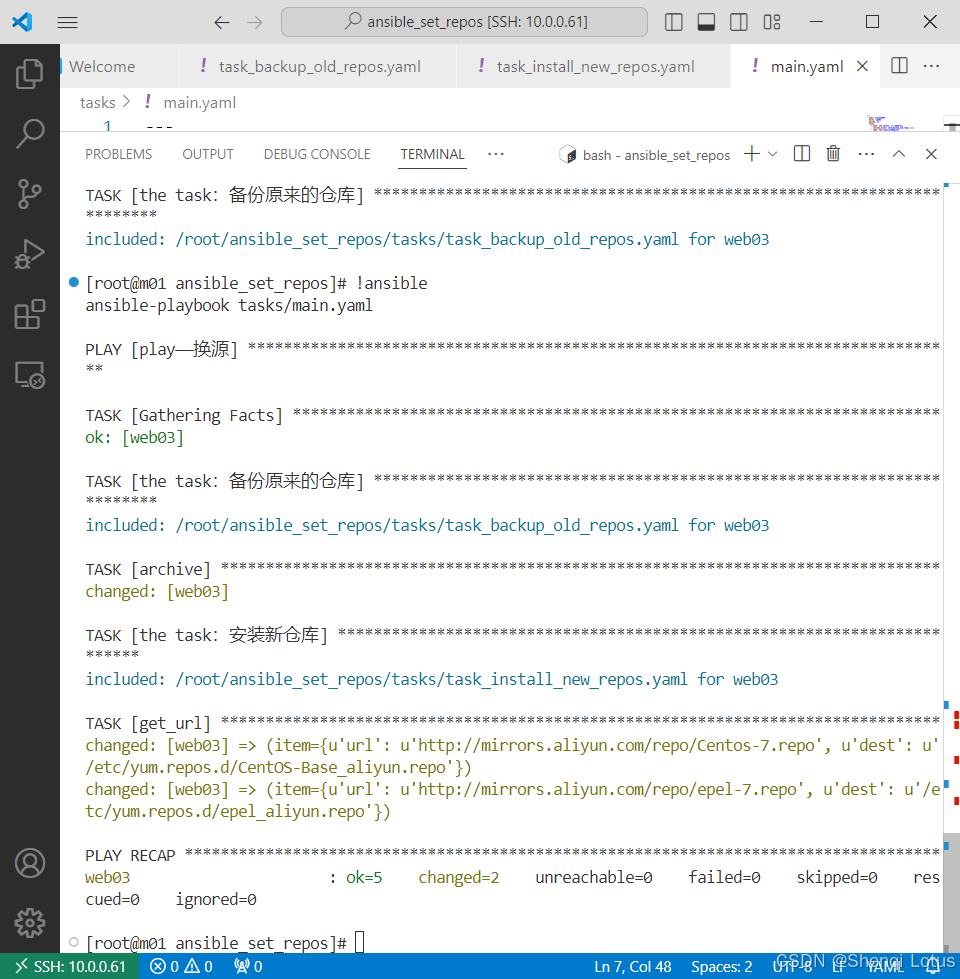
安装基础软件包
yaml
---
- name: the play1
hosts: all
tasks:
- name: 安装好些个基础软件包
yum:
name: {{item}}
state: present
loop:
- chrony
- aaa
- bbb
- ccc
- ddd
...