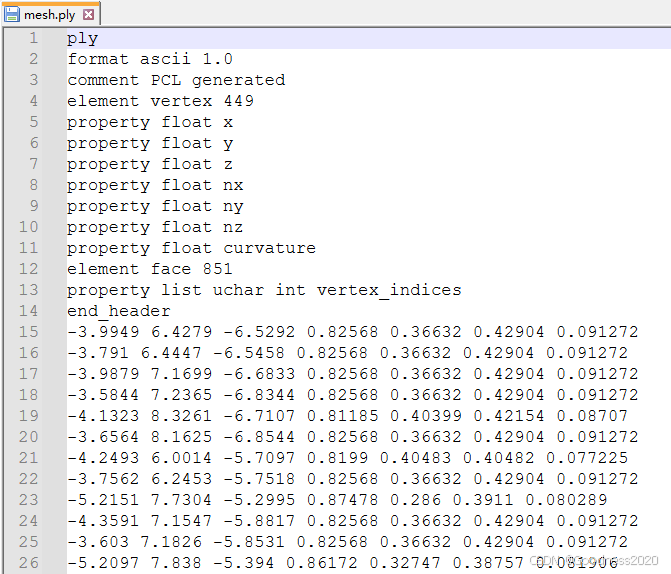
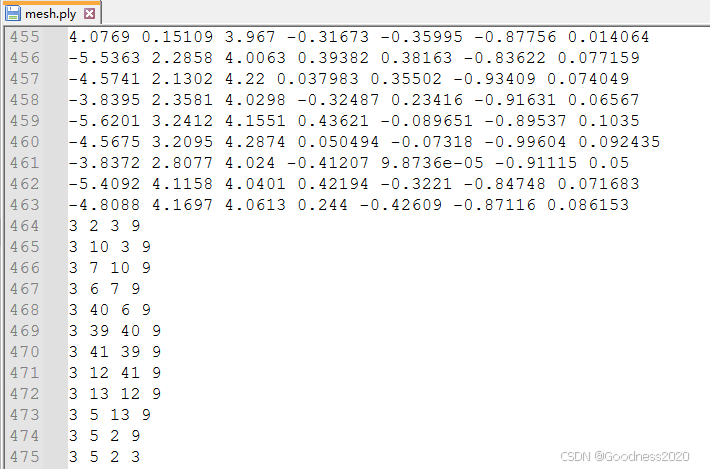
一、STL转化为PLY
利用PCL库中vtk_lib_io实现,#include <pcl/io/vtk_lib_io.h>,C++语言。
提供一个用于测试的数据:
通过网盘分享的文件:ply_stl
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1xnO5s2kiUf0Cs35XVyfTHA?pwd=xmax 提取码: xmax
cpp
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/io/vtk_lib_io.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace pcl;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// 读取STL文件
vtkSmartPointer<vtkSTLReader> reader4 = vtkSmartPointer<vtkSTLReader>::New();
reader4->SetFileName("mesh.stl");
reader4->Update();
// stl 格式 转出到 ply 格式
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> polydata = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData>::New();
polydata = reader4->GetOutput();
polydata->GetNumberOfPoints();
// 保存ply数据
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPLYWriter> plyWriter = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPLYWriter>::New();
plyWriter->SetFileName("stl2plyData.ply");
plyWriter->SetInputConnection(reader4->GetOutputPort());
plyWriter->SetFileTypeToASCII();
plyWriter->SetColorModeToOff();
plyWriter->Update();
plyWriter->Write();
// 从 ply 格式 转为 pcd 格式
PointCloud<PointXYZ>::Ptr cloudPcd(new PointCloud<PointXYZ>());
io::vtkPolyDataToPointCloud(polydata, *cloudPcd);
// 保存pcd数据
io::savePCDFileASCII("ply2PcdData.pcd", *cloudPcd);
visualization::PCLVisualizer vis("cloud visualization");
vis.getRenderWindow()->GlobalWarningDisplayOff();
vis.addCoordinateSystem(5.0);
vis.addPointCloud(cloudPcd);
while (!vis.wasStopped())
{
vis.spinOnce();
}
return 0;
}二、PLY转化为STL
利用python语言,需要安装numpy-stl安装包。
提供一个用于测试的数据:
通过网盘分享的文件:ply_stl
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1xnO5s2kiUf0Cs35XVyfTHA?pwd=xmax 提取码: xmax
python
import numpy as np
from stl import mesh
def read_ply(file_path):
with open(file_path, 'rb') as f:
header = f.readline()
while not header.startswith(b'element vertex'):
header = f.readline()
vertex_count = int(header.split()[-1])
print("vertex_count = ", vertex_count)
while not header.startswith(b'element face'):
header = f.readline()
face_count = int(header.split()[-1])
print("face_count = ", face_count)
while not header.startswith(b'end_header'):
header = f.readline()
# 读取顶点数据
vertices = []
for i in range(vertex_count):
header = f.readline()
header = header.split()[:3]
for j in range(len(header)):
vertices.append(float(header[j]))
vertices = np.array(vertices).reshape(-1, 3)
# 读取面数据
faces = []
for i in range(face_count):
header = f.readline()
header = header.split()[1:]
for j in range(len(header)):
faces.append(int(header[j]))
faces = np.array(faces).reshape(-1, 3)
return vertices, faces
def create_stl(vertices, faces, output_file):
cube = mesh.Mesh(np.zeros(faces.shape[0], dtype=mesh.Mesh.dtype))
for i, f in enumerate(faces):
for j in range(3):
cube.vectors[i][j] = vertices[f[j], :]
# save stl file
cube.save(output_file)
if __name__ == '__main__':
vertice, face = read_ply('mesh.ply')
print(vertice.shape)
print(face.shape)
create_stl(vertice, face, 'mesh.stl')ply数据格式展示