websocket server的优点
websocket server的好处:WebSocket 服务器能够实现实时的数据推送,服务器可以主动向客户端发送数据
1 不需要客户端不断轮询。
2 不需要实现httpserver跨域。
在需要修改协议的时候比较灵活,我们发送数据的时候比较方便,因为两边可以随时发送协议, 且做客户端的程序更为方便,websocket协议头部已经定义了包长,使用大部分库可以直接收数据,解决了粘包的问题,所以websocket协议是一个使用比较顺畅的协议
实现websocket server
先用boost 的协程顶一下,主要是需要将http协议升级到websocket, 因此在一个函数里面实现两种server的接收,http协议顺便就接收了,同时在客户端里面存储所有的链接对象,以下是主要实现的握手协议代码,以供参考
c
bool func_hand_shake(boost::asio::yield_context &yield)
{
DEFINE_EC
asio::streambuf content_;
size_t length = asio::async_read_until(v_socket, content_, "\r\n\r\n", yield[ec]);
ERROR_RETURN_FALSE
asio::streambuf::const_buffers_type bufs = content_.data();
std::string lines(asio::buffers_begin(bufs), asio::buffers_begin(bufs) + length);
//std::cout<<lines<<std::endl;
c_header_map hmap;
//std::string get;
int protocol = fetch_head_info(lines, hmap, v_app_stream);
if (protocol != GET)
return false;
cout << "GET:" << v_app_stream << endl; //like this--> live/1001 rtmp server must like this
auto iter = hmap.find("Upgrade");
if (iter == hmap.end())
{
//it is the http protocol ,not websocket
//func_hand_http(m, yield);
size_t ret = boost::asio::async_write(v_socket, boost::asio::buffer(FLV_HTTP_HEADERS,
FLV_HTTP_HEADERS_LEN), yield[ec]);
//ERROR_RETURN_FALSE
v_key = hash_add(v_app_stream.c_str(), HASH_PRIME_MIDDLE);
if (c_hubs::instance()->push(v_key, shared_from_this(), true) !=0)
{
//we can not find the stream
//return 404 error
if (ret == -1)
{
size_t len_ = sizeof(buffer404) - 1; //remove the '\0' one bytes
asio::async_write(v_socket, asio::buffer(buffer404, len_), yield[ec]);
//ERROR_RETURN_FALSE
//return false;
}
return false;
}
return true;
}
else
{
v_iswebsocket = true;
std::string response, key, encrypted_key;
//find the get
//std::string request;
size_t n = lines.find_first_of('\r');
//find the Sec-WebSocket-Key
size_t pos = lines.find("Sec-WebSocket-Key");
if (pos == lines.npos)
return false;
size_t end = lines.find("\r\n", pos);
key = lines.substr(pos + 19, end - pos - 19) + "258EAFA5-E914-47DA-95CA-C5AB0DC85B11";
//get the base64 encode string with sha1
#if 0
boost::uuids::detail::sha1 sha1;
sha1.process_bytes(key.c_str(), key.size());
unsigned int digest[5];
sha1.get_digest(digest);
#endif
#if 1
SHA1 sha;
unsigned int digest[5];
sha.Reset();
sha << key.c_str();
sha.Result(digest);
#endif
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
digest[i] = htonl(digest[i]);
}
encrypted_key = base64_encode(reinterpret_cast<const uint8_t*>(&digest[0]), 20);
//base64_encode(first, encrypted_key);
/*
The handshake from the server looks as follows :
HTTP / 1.1 101 Switching Protocols
Upgrade : websocket
Connection : Upgrade
Sec-WebSocket-Accept: s3pPLMBiTxaQ9kYGzzhZRbK + xOo =
Sec-WebSocket-Protocol: chat
*/
//set the response text
response.append("HTTP/1.1 101 WebSocket Protocol Handshake\r\n");
response.append("Upgrade: websocket\r\n");
response.append("Connection: Upgrade\r\n");
response.append("Sec-WebSocket-Accept: " + encrypted_key + "\r\n\r\n");
//response.append("Sec-WebSocket-Protocol: chat\r\n");
//response.append("Sec-WebSocket-Version: 13\r\n\r\n");
size_t ret = boost::asio::async_write(v_socket, boost::asio::buffer(response), yield[ec]);
//ERROR_RETURN_FALSE
//calculate the hash key
v_key = hash_add(v_app_stream.c_str(), HASH_PRIME_MIDDLE);
c_hubs::instance()->push(v_key, shared_from_this(),false);
}
return true;
}
rtmp协议
这个协议太过出名,实在没什么好说的
实现http协议
实现websocket协议的时候顺带实现,使用map数据结构存储
转发单线程,去除队列
1 数据共享
在发送数据的时候,rtmp 和 httpflv发送 以及 websocket发送使用同一缓存,这样有一个问题,即使我们使用共享的数据结构同时使用同一个内存,也不一定会共享申请内存时多余的头部,以下是数据结构
c
typedef struct s_memory
{
//head
uint8_t *v_data = NULL;
//v_data_h =>rtmp use it
uint8_t *v_data_h = NULL;
//real data
uint8_t *v_data_r = NULL;
//uint8_t *v_data = NULL;
size_t v_len;
uint32_t v_ts; // timestamp
en_flv_header v_av_type = en_flv_null;
void memory_create(uint32_t size, int header = 18)
{
//zero copy
//the last reserve 4 bytes for flv write 4 bytes tail for av data size
//the header 18 bytes for max rtmp use
v_data = new uint8_t[size + header +4];
v_len = size; //not include the header and tail
//we do not know the head where
//v_data_h = v_data;
v_data_r = v_data + header;
}
void memory_create(uint32_t size, int header, int tail)
{
v_data = new uint8_t[size + header + tail];
v_len = size; //not include the header and tail
v_data_h = v_data;
v_data_r = v_data + header;
}
~s_memory()
{
if (v_data != NULL)
delete[] v_data;
}
}s_memory;这边要做的就是在申请内存时多申请上头部和尾部,这样,使用的时候就可以在数据前面增加不同协议的数据头部。
所以是下面这句话
c
v_data = new uint8_t[size + header + tail];读者自行理解就好

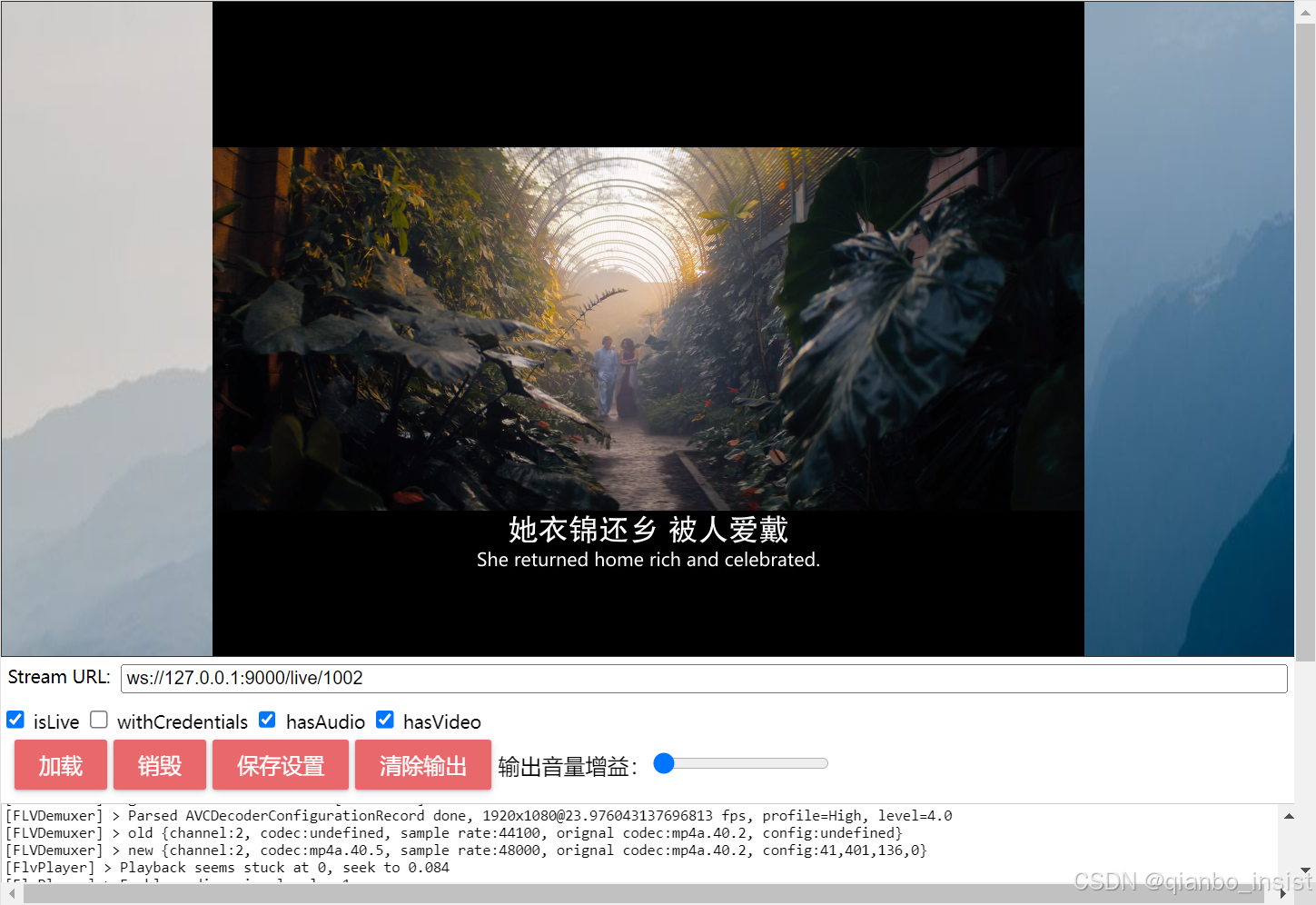
收到数据以后不进行任何的数据拷贝, 在缓冲数据前面加上数据头部,立刻发送出去,上图可以看到,rtmp协议和websocket flv 同时打开,vlc的rtmp协议稍稍会延后一点时间。两路内存占用如下图所示:
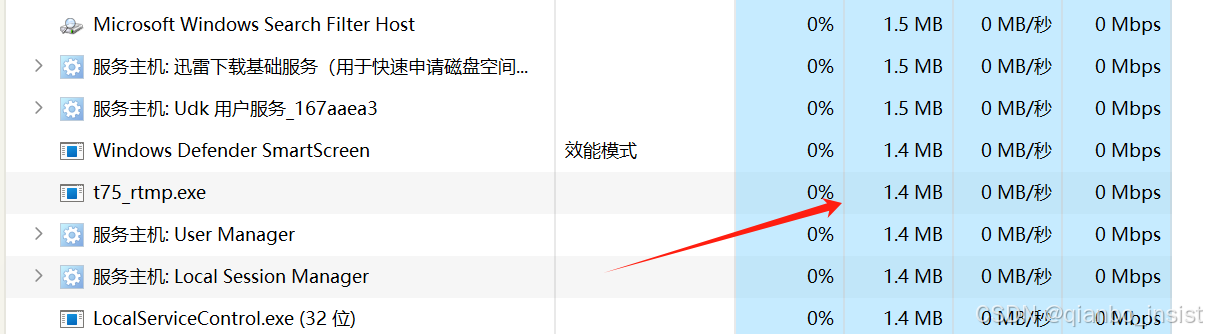
可以看到去除队列积压,内存占用比较小
多个线程需要修改头部的情况
如果使用多个线程,如何在各类协议之间共享数据呢,这是个问题,我们退而求其次,利用tcp 协议的特点,它是可以分开来发送批量数据,下图是使用websocket协议发送flv数据的示例,包括发送tag,taglen,data,datalen, 以及自身websocket发送的头部字节,分了三次发送,head和headlen 是实现websocket的头部而写。
c
/*
sock : need send socket
data : flv av data
datalen : flv av data len
*/
bool c_flvserver::func_set_head_send(tcp::socket &sock,
uint8_t* tag, int taglen, uint8_t *data, size_t datalen,
asio::yield_context &yield)
{
uint8_t buffer[10];
uint8_t *head = NULL;// buf;// 0x82;
int headlen = 0;
int totallen = taglen + datalen;
if (totallen <= 65535)
{
if (totallen < 126)
{
head = &buffer[0] +8;
//relen += 1;
*head = 0x82; //0x81:1000 0001 text code ; // 1000 0010 binary code
*(head + 1) = (uint8_t)totallen;
headlen = 2;
}
else //>=126 <65536
{
head = &buffer[0] +6;
*head = 0x82;
*(head + 1) = 126;
*(head + 2) = (uint8_t)((totallen >> 8) & 0xFF);
*(head + 3) = (uint8_t)(totallen & 0xFF);
headlen = 4;
}
}
else //>65535
{
head = &buffer[0];
*head = 0x82;
*(head + 1) = 127;
*(head + 2) = 0; //>>56
*(head + 3) = 0; //>>48
*(head + 4) = 0;// >>40
*(head + 5) = 0; // >> 32;
*(head + 6) = (uint8_t)(totallen >> 24);
*(head + 7) = (uint8_t)(totallen >> 16);
*(head + 8) = (uint8_t)(totallen >> 8);
*(head + 9) = (uint8_t)(totallen & 0xFF);
headlen = 10;
}
DEFINE_EC
asio::async_write(sock, asio::buffer(head, headlen), yield[ec]);
asio::async_write(sock, asio::buffer(tag, taglen), yield[ec]);
asio::async_write(sock, asio::buffer(data, datalen), yield[ec]);
//send the data
//flv_const_buffer bb(frame, framelen,tag,taglen, data, dlen);
//asio::async_write(sock, bb, yield[ec]);
return ec? false : true;
}这样在发送rtmp协议的时候,使用申请内存的多余头部空间,发送flv的时候 previous tag 长度四字节放在尾部,发送http协议的时候和flv类似,不需要发送websocket的头部字节,后面加上各类协议,比如rtsp 的tcp等等,也可以这样做,我们可以拷贝,但也可以不拷贝数据而进行零拷贝,零队列发送。
下面多打开几路观察内存
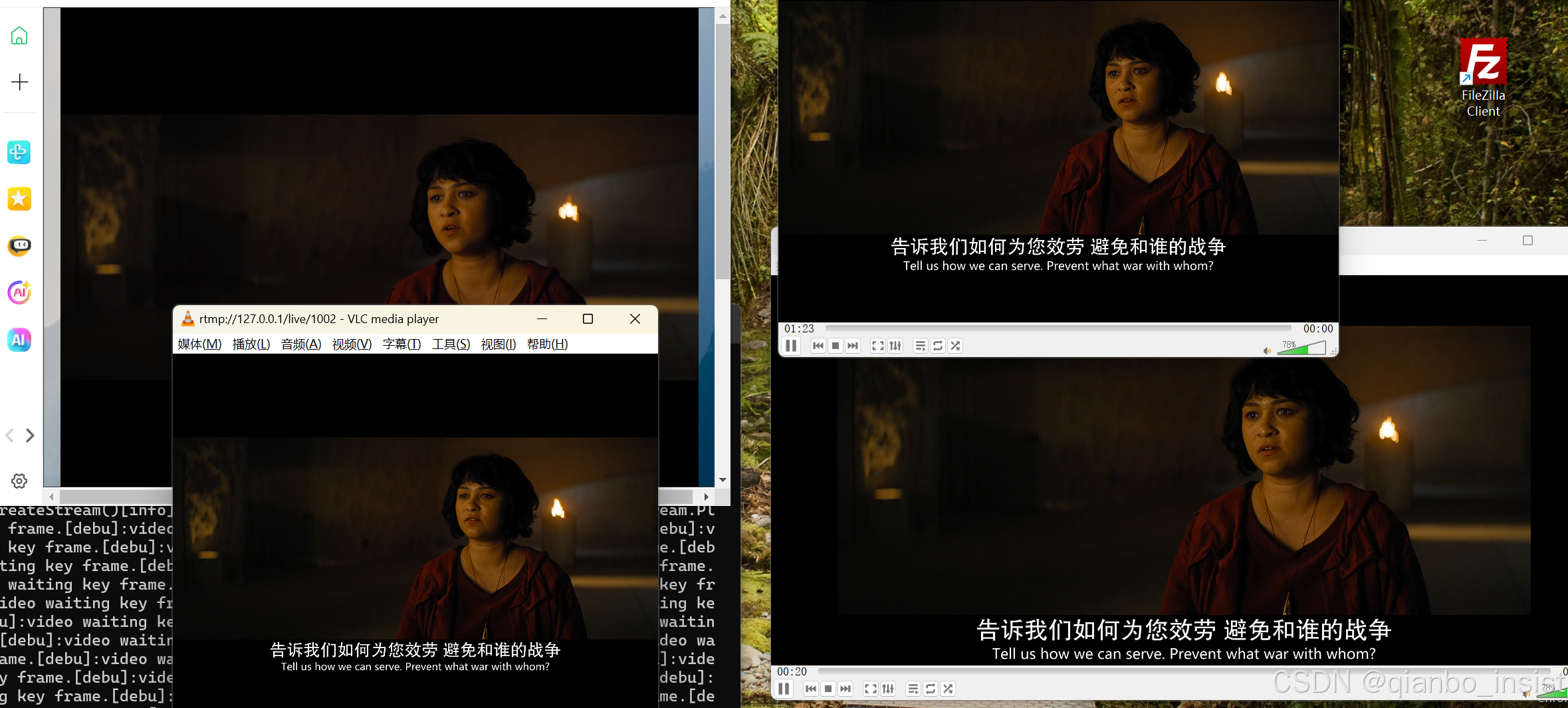
如下图所示:和刚才区别不大,小于10路内存都在1兆多以内

后面需要做的实现
实现更多的具体行业应用层服务和比较标准的协议输出, 将会做客户端发流,客户端收留,服务器对接,服务调用gpu等等,会比较谨慎。