标出输入、标准输出、错误输出
一、程序的基本三个IO流
一)文件描述符
任何程序在Linux系统中都有3个基本的文件描述符
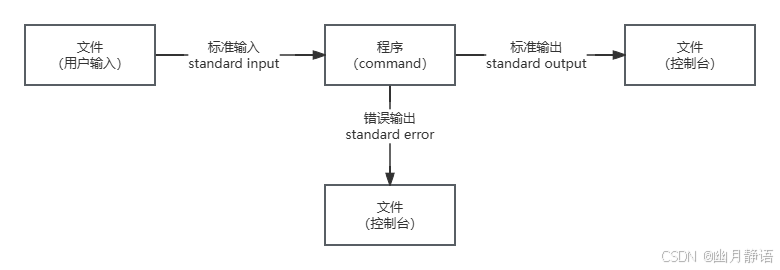
比如:
cd/proc/$$/fd
进入当前shell程序对于内核在文件系统的映射目录中:
sh
[root@localhost ~]# cd /proc/$$/fd
[root@localhost fd]# ll
total 0
lrwx------. 1 root root 64 Oct 14 07:22 0 -> /dev/pts/0
lrwx------. 1 root root 64 Oct 14 07:22 1 -> /dev/pts/0
lrwx------. 1 root root 64 Oct 14 07:22 2 -> /dev/pts/0
lrwx------. 1 root root 64 Oct 14 08:56 255 -> /dev/pts/0 文件描述符的意义:
0:标准输入(stdin):0代表:/dev/stdin文件的IO
1:标准输出(stdout):1代表:/dev/stdout文件的IO
2:错误输出(stderr):2代表:/dev/stderr文件的IO
程序已经写死,linux为我们准备了这些文件描述符,以及一些能够重定向这些文件描述符的操作方法,我们可以修改程序的默认输入/输出位置
二)重定向
重定向不是命令,是bash对关键字识别后应用文件描述符指向的操作
输出重定向
输入重定向来自文件
输入重定向来自字符串
基于文件描述符操作的重定向
二、输出重定向
重定向不是命令,是bash对关键字识别后应用文件描述符指向的操作
格式:
command [1-n] > file或文件操作符或设备
上面命令意思是:将一条命令执行结果(标准输出,或者错误输出,本来都要打印到屏幕上面的)重定向其它输出设备(文件,打开文件操作符,或打印机等等)1,2分别是标准输出,错误输出。
ls -l /:命令默认将执行结果输出到屏幕
ls -l / 1> ls.txt
1:代表的是ls命令的文件描述符,表示的是ls的标准输出
>:代表的输出重定向,这里重定向到后面的ls.txt文件中
文件描述符与重定向操作符之间不能出现空格,因为bash会用空白符切割字符串,有空格会认为1是一个文件
sh
# 创建ls.txt文件
[root@localhost ~]# touch ls.txt
# 将文件的标准输出,输入到ls.txt文件中
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l / 1> ls.txt
# 查看文件内容
[root@localhost ~]# cat ls.txt
total 28
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Apr 17 04:26 bin -> usr/bin
dr-xr-xr-x. 5 root root 4096 May 15 23:07 boot
drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 18 Jul 20 21:45 data
drwxr-xr-x. 20 root root 3240 Oct 14 07:20 dev
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 400 Jul 22 20:21 dump.rdb
drwxr-xr-x. 85 root root 8192 Oct 14 07:22 etc
drwxr-xr-x. 5 root root 39 Aug 20 04:24 home
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Apr 17 04:26 lib -> usr/lib
...... 再次执行ls -l /root 1> ls.txt命令,会发现文件ls.txt中只有/root的内容
因为:>操作符是覆盖重定向
sh
# 覆盖重定向
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l /root 1> ls.txt
# 查看文件内容
[root@localhost ~]# cat ls.txt
total 0
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Oct 14 09:21 ls.txt >>:是追加重定向操作符
这样就能追加内容
sh
# 追加重定向
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l /root 1>> ls.txt
# 查看文件内容
[root@localhost ~]# cat ls.txt
total 0
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Oct 14 09:22 ls.txt
total 4
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 54 Oct 14 09:22 ls.txt 注意:文件描述符在这种重定向到文件的操作中可以省略
sh
# 省略文件描述符
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l /root > ls.txt
# 省略文件描述符
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l /root >> ls.txt ls -l / /god命令让ls显示根目录/和/god目录的内容,但是我们的系统的/目录下没有god目录
输出的结果中包含可以显示内容的/的输出,和一个没有找到/god的报错输出
这个报错输出就是程序的错误输出
sh
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l / /god
ls: cannot access /god: No such file or directory
/:
total 24
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Apr 17 04:26 bin -> usr/bin
dr-xr-xr-x. 5 root root 4096 May 15 23:07 boot
drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 18 Jul 20 21:45 data
...... 如果想将错误输出重定向:
sh
# 创建lserr.txt
[root@localhost ~]# touch lserr.txt
# 将错误输出,输入到lserr.txt
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l / /god 2> lserr.txt
/:
total 24
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Apr 17 04:26 bin -> usr/bin
dr-xr-xr-x. 5 root root 4096 May 15 23:07 boot
drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 18 Jul 20 21:45 data
drwxr-xr-x. 20 root root 3240 Oct 14 07:20 dev
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 400 Jul 22 20:21 dump.rdb
drwxr-xr-x. 85 root root 8192 Oct 14 07:22 etc
......
# 查看保存内容
[root@localhost ~]# cat lserr.txt
ls: cannot access /god: No such file or directory 追加的方式:
sh
# 将保存内容,追加到lserr.txt
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l / /god 2>> lserr.txt
/:
total 24
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Apr 17 04:26 bin -> usr/bin
dr-xr-xr-x. 5 root root 4096 May 15 23:07 boot
drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 18 Jul 20 21:45 data
drwxr-xr-x. 20 root root 3240 Oct 14 07:20 dev
......
# 查看文件内容
[root@localhost ~]# cat lserr.txt
ls: cannot access /god: No such file or directory
ls: cannot access /god: No such file or directory 分别将输出重定向到不同的文件中
sh
# 将输出结果分别覆盖输入到文件中
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l / /god 1> ls.txt 2> lserr.txt
# 标准输出文件
[root@localhost ~]# cat ls.txt
/:
total 24
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Apr 17 04:26 bin -> usr/bin
dr-xr-xr-x. 5 root root 4096 May 15 23:07 boot
drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 18 Jul 20 21:45 data
......
# 错误输出文件
[root@localhost ~]# cat lserr.txt
ls: cannot access /god: No such file or directory 如果向重定向到同一个文件,这里会被覆盖,要用追加的方式:
sh
# 将输出结果分别追加输入到文件中
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l / /god 1>> ls.txt 2>> lserr.txt
# 标准输出文件
[root@localhost ~]# cat ls.txt
/:
total 24
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Apr 17 04:26 bin -> usr/bin
dr-xr-xr-x. 5 root root 4096 May 15 23:07 boot
drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 18 Jul 20 21:45 data
drwxr-xr-x. 20 root root 3240 Oct 14 07:20 dev
......
# 错误输出文件
[root@localhost ~]# cat lserr.txt
ls: cannot access /god: No such file or directory
ls: cannot access /god: No such file or directory
ls: cannot access /god: No such file or directory 也可以用文件描述符重定向到文件描述符
语法: 文件描述符>& 文件描述符
注意:>&前面必须有文件描述符,且不能有空格,后面的数字才能被认为是文件描述符
sh
# 创建lsall
[root@localhost ~]# touch lsall.txt
# 将所有输出结果,输入到lsall文件(方式1)
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l / /god > lsall.txt 2>&1
# 查看内容
[root@localhost ~]# cat lsall.txt
ls: cannot access /god: No such file or directory
/:
total 24
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Apr 17 04:26 bin -> usr/bin
dr-xr-xr-x. 5 root root 4096 May 15 23:07 boot
drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 18 Jul 20 21:45 data
......
# 将所有输出结果,输入到lsall文件(方式2)
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l / /god &> lsall.txt
# 查看内容,结果相同
[root@localhost ~]# cat lsall.txt
ls: cannot access /god: No such file or directory
/:
total 24
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Apr 17 04:26 bin -> usr/bin
dr-xr-xr-x. 5 root root 4096 May 15 23:07 boot
drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 18 Jul 20 21:45 data
......三、输入重定向
一)来自文件
read命令:
sh
# 获取键盘输入
[root@localhost ~]# read var01
abc
# 查看
[root@localhost ~]# echo $var01
abc read命令开启输入流,遇到换行符结束输入,将输入流的内容赋值给变量
sh
[root@localhost ~]# read var 0< /etc/profile
# 查看变量
[root@localhost ~]# echo $var
# /etc/profile 我们修改了read命令的输入源,使其来自文件,但是因为read命令的自身特征,读取第一行后遇到换行符,所以,只将第一行内容保存到变量var中
0<:0是标准输入的文件描述符,<是输入重定向操作符,后面要接文件
二)来自字符串
将字符串放入输入流
sh
# 输入hello world
[root@localhost ~]# read var03 <<< "hello world"
# 查看输出内容
[root@localhost ~]# echo $var03
hello world <<<:是输入重定向操作符,将命令的输入源重定向为操作符后面的字符串
sh
[root@localhost ~]# vi test.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo "----------"
cat <<EOF
hello world
hello linux
EOF
echo "---------"
[root@localhost ~]# bash test.sh
----------
hello world
hello linux
--------- <<:是重定向操作符,其后紧随的字符串为边界字符串,与结束的边界字符串组合,将其中的内容放入命令的标准输入中
如果将cat换成read,依然会受到换行符的影响
三)基于文件描述符操作的重定向
exec命令:
Replace the shell with the given command.
bash的内部命令
sh
[root@localhost ~]# exec ls -l /
total 24
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Apr 17 04:26 bin -> usr/bin
dr-xr-xr-x. 5 root root 4096 May 15 23:07 boot
......
Connection closing...Socket close.
Connection closed by foreign host.
Disconnected from remote host(192.168.100.160) at 21:52:39. 可以看到ls命令成功执行了,但是我们的xshell也断开了链接
因为exec调用内核系统调用将ls命令的指令替换当前bash的进程,指令接收后退出进程,所以我们的bash链接就中断了
这里我们可以调用exec命令,而不给出替换命令,只附加重定向操作符
这样我们就可以实现对当前bash开启文件描述符
这里我们可以调用exec命令,而不给出替换命令,只附加重定向操作符
这样我们就可以实现对当前bash开启文件描述符
sh
[root@localhost ~]# exec 8< /etc/profile
# 输入文件描述符8
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l /proc/$$/fd
total 0
lrwx------. 1 root root 64 Oct 14 09:53 0 -> /dev/pts/0
lrwx------. 1 root root 64 Oct 14 09:53 1 -> /dev/pts/0
lrwx------. 1 root root 64 Oct 14 09:53 2 -> /dev/pts/0
lrwx------. 1 root root 64 Oct 14 09:53 255 -> /dev/pts/0
lr-x------. 1 root root 64 Oct 14 09:53 8 -> /etc/profile 可以看到我们的bash多了一个输入文件描述符8指向文件/etc/profile
sh
# read输入内容
[root@localhost ~]# read var04 0<& 8
# 查看内容
[root@localhost ~]# echo $var04
# /etc/profile
# 用cat输入,查看内容
[root@localhost ~]# cat 0<& 8
# System wide environment and startup programs, for login setup
# Functions and aliases go in /etc/bashrc
...... 这里我们使用重定向操作符<&来复制输入文件描述符8给命令cat的标准输入0
类似的输出使用>&重定向操作符
sh
# 创建out.txt
[root@localhost ~]# touch out.txt
# 定义输入文件9
[root@localhost ~]# exec 9> out.txt
# 将输出结果输入到9(输入文件/root/out.txt)中
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l ./ >& 9
# 查看out文件
[root@localhost ~]# cat out.txt
total 16
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1132 Oct 14 09:38 lsall.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 100 Oct 14 09:35 lserr.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2164 Oct 14 09:35 ls.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Oct 14 10:00 out.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 86 Oct 14 09:49 test.sh
# 将错误信息输入到out中
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l /god 2>& 9
# 查看
[root@localhost ~]# cat out.txt
ls: cannot access /god: No such file or directory 这里再次强调重定向操作符前如果给出文件描述符,不能出现空格
sh
# 关闭文件描述符
[root@localhost ~]# exec 8<&-
[root@localhost ~]# exec 9<&- 以上是关闭文件描述符
sh
# 将输出信息,输入到out中
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l /god >& 9
# 输出错误,把9作为文件,在当前目录创建了9
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l /god &> 9
[root@localhost ~]# ll
total 24
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 49 Oct 14 10:06 9
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1132 Oct 14 09:38 lsall.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 100 Oct 14 09:35 lserr.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2164 Oct 14 09:35 ls.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 49 Oct 14 10:05 out.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 86 Oct 14 09:49 test.sh 以上两种都是特殊写法
>&操作符后面有两种情况:数值/字符串
数值:一定是一个有效的文件描述符
字符串:代表一个有效的文件
而&>操作符只能接文件
sh
# 允许允许的命令:
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l /god >& 9
ls: cannot access /god: No such file or directory 如果换成:ls-l /god &> 9,则不能将标准输出和错误输出到9的文件中
所以根据自己的情况,如果明确想文件输出推荐使用&>
四、重定向综合案例---一切皆文件
/dev/tcp/www.baidu.com/80将百度的地址端口映射为文件系统路径
开启文件描述符实际是对baidu的socket连接
sh
[root@localhost ~]# exec 12<> /dev/tcp/www.baidu.com/80 通过echo的标准输出,将http协议的请求头输出到12文件描述符,起始就是通过socket发送给baidu的服务器
sh
[root@localhost ~]# echo -e "GET / HTTP/1.0\n" >& 12 baidu服务器的返回可用通过12文件描述符读取到
sh
[root@localhost ~]# cat <& 12
HTTP/1.0 200 OK
Accept-Ranges: bytes
Cache-Control: no-cache
Content-Length: 9508
Content-Type: text/html
...... 注意,这个执行过程要快,时间长了,socket就超时断开连接了