原文: How to deploy Nest.js microservices using Kubernetes
The aim of the project is to use Nest.js to build a microservice project that communicate via gRPC and a gateway service to expose API, use RabbitMQ to handle message queues, and ELK for log management. Finally, Docker and Kubernetes will be used for building and deploying those services. To view the full example, please visit learn-backend on GitHub.
Code Structure
bash
.
├── apps
│ ├── gateway
│ │ ├── src
│ │ │ ├── gateway.module.ts
│ │ │ ├── gateway.controller.ts
│ │ │ └── main.ts
│ │ └── tsconfig.app.json
│ ├── product
│ │ ├── src
│ │ │ ├── main.ts
│ │ │ ├── product.module.ts
│ │ │ └── product.controller.ts
│ │ └── tsconfig.app.json
├── docker
│ ├── Dockerfile.gateway
│ └── Dockerfile.product
├── k8s
│ ├── gateway-deployment.yaml
│ └── product-deployment.yaml
├── proto
│ └── product.proto
├── types
│ └── proto
│ └── product.ts
├── tsconfig.build.json
├── tsconfig.json
├── nest-cli.json
├── package.json
├── pnpm-lock.yamlUsing Nest.js to create monorepo
First, follow the Workspaces guide to create a Nest.js monorepo project.
ts
nest new gateway
cd gateway
nest generate app productUsing gRPC for communication
A microservice is essentially an application that uses a different transport layer than HTTP. We can use gRPC, Thrift, or even just TCP as the transport layer. In this case, we will use gRPC. gRPC is a modern open source high performance Remote Procedure Call (RPC) framework that can run in any environment. It can efficiently connect services in and across data centers with pluggable support for load balancing, tracing, health checking and authentication. It is also applicable in last mile of distributed computing to connect devices, mobile applications and browsers to backend services. 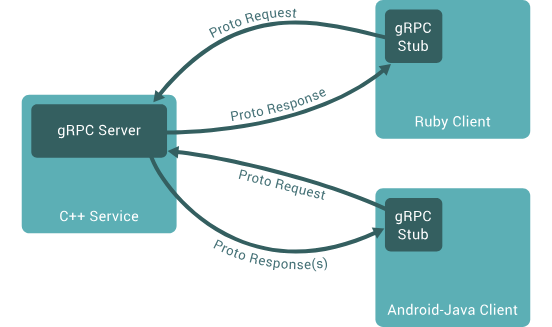
Protocol Buffers
Since microservice code can be written in various programming languages, we need a language-neutral, platform-neutral, and extensible mechanism for serializing structured data. By default, gRPC uses Protocol Buffers. The follows code defines protobuf to the product microservice.
proto
syntax = "proto3";
package product;
message Product {
string id = 1;
string name = 2;
string description = 3;
double unitPrice = 4;
int32 inventoryQuantity = 5;
string createdAt = 6;
string updatedAt = 7;
}
message CreateProductRequest {
string name = 1;
string description = 2;
double unitPrice = 3;
int32 inventoryQuantity = 4;
}
message CreateProductResponse { Product product = 1; }
message GetProductRequest { string id = 1; }
message GetProductResponse { Product product = 1; }
message UpdateProductRequest {
string id = 1;
string name = 2;
string description = 3;
double unitPrice = 4;
int32 inventoryQuantity = 5;
}
message UpdateProductResponse { Product product = 1; }
message DeleteProductRequest { string id = 1; }
message DeleteProductResponse { bool success = 1; }
service ProductService {
rpc CreateProduct(CreateProductRequest) returns (CreateProductResponse);
rpc GetProduct(GetProductRequest) returns (GetProductResponse);
rpc UpdateProduct(UpdateProductRequest) returns (UpdateProductResponse);
rpc DeleteProduct(DeleteProductRequest) returns (DeleteProductResponse);
}protoc
Since this is a TypeScript project, it is better to transform the protobuf definitions into TypeScript interfaces. We use ts-protoc to compile protobuf files to TypeScript interfaces. First, you need to install protoc on your computer. If you are using macOS, simply run:
bash
brew install protobufNext, add the follows command to the scripts section of your package.json:
bash
"proto-ts": "protoc --plugin=./node_modules/.bin/protoc-gen-ts_proto --ts_proto_out=./types ./proto/*.proto --ts_proto_opt=nestJs=true,addGrpcMetadata=true,addNestjsRestParameter=true,outputEncodeMethods=false,outputJsonMethods=false,outputClientImpl=false"This command not only generates TypeScript interfaces, but also generates controller interface for Nest.js.
ts
// Code generated by protoc-gen-ts_proto. DO NOT EDIT.
// versions:
// protoc-gen-ts_proto v2.2.5
// protoc v5.28.3
// source: proto/product.proto
/* eslint-disable */
import { Metadata } from '@grpc/grpc-js'
import { GrpcMethod, GrpcStreamMethod } from '@nestjs/microservices'
import { Observable } from 'rxjs'
export const protobufPackage = 'product'
export interface Product {
id: string
name: string
description: string
unitPrice: number
inventoryQuantity: number
createdAt: string
updatedAt: string
}
export interface CreateProductRequest {
name: string
description: string
unitPrice: number
inventoryQuantity: number
}
export interface CreateProductResponse {
product: Product | undefined
}
export interface GetProductRequest {
id: string
}
export interface GetProductResponse {
product: Product | undefined
}
export interface UpdateProductRequest {
id: string
name: string
description: string
unitPrice: number
inventoryQuantity: number
}
export interface UpdateProductResponse {
product: Product | undefined
}
export interface DeleteProductRequest {
id: string
}
export interface DeleteProductResponse {
success: boolean
}
export const PRODUCT_PACKAGE_NAME = 'product'
export interface ProductServiceClient {
createProduct(
request: CreateProductRequest,
metadata: Metadata,
...rest: any
): Observable<CreateProductResponse>
getProduct(
request: GetProductRequest,
metadata: Metadata,
...rest: any
): Observable<GetProductResponse>
updateProduct(
request: UpdateProductRequest,
metadata: Metadata,
...rest: any
): Observable<UpdateProductResponse>
deleteProduct(
request: DeleteProductRequest,
metadata: Metadata,
...rest: any
): Observable<DeleteProductResponse>
}
export interface ProductServiceController {
createProduct(
request: CreateProductRequest,
metadata: Metadata,
...rest: any
):
| Promise<CreateProductResponse>
| Observable<CreateProductResponse>
| CreateProductResponse
getProduct(
request: GetProductRequest,
metadata: Metadata,
...rest: any
):
| Promise<GetProductResponse>
| Observable<GetProductResponse>
| GetProductResponse
updateProduct(
request: UpdateProductRequest,
metadata: Metadata,
...rest: any
):
| Promise<UpdateProductResponse>
| Observable<UpdateProductResponse>
| UpdateProductResponse
deleteProduct(
request: DeleteProductRequest,
metadata: Metadata,
...rest: any
):
| Promise<DeleteProductResponse>
| Observable<DeleteProductResponse>
| DeleteProductResponse
}
export function ProductServiceControllerMethods() {
return function (constructor: Function) {
const grpcMethods: string[] = [
'createProduct',
'getProduct',
'updateProduct',
'deleteProduct'
]
for (const method of grpcMethods) {
const descriptor: any = Reflect.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(
constructor.prototype,
method
)
GrpcMethod('ProductService', method)(
constructor.prototype[method],
method,
descriptor
)
}
const grpcStreamMethods: string[] = []
for (const method of grpcStreamMethods) {
const descriptor: any = Reflect.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(
constructor.prototype,
method
)
GrpcStreamMethod('ProductService', method)(
constructor.prototype[method],
method,
descriptor
)
}
}
}
export const PRODUCT_SERVICE_NAME = 'ProductService'Starting RabbitMQ Docker Container
RabbitMQ is a reliable and mature messaging and streaming broker, which is easy to deploy on cloud environments, on-premises, and on your local machine. We use docker compose to start a simply container.
yaml
services:
rabbitmq:
image: rabbitmq:3-management
restart: always
container_name: rabbitmq
ports:
- 5672:5672
- 15672:15672
environment:
- RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER=root
- RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS=password
volumes:
- /var/lib/docker/volumes/rabbitmq:/var/lib/rabbitmqThen, visit http://localhost:15672/ to open the management platform. 
Starting ELK Docker Container
The ELK Stack is a powerful suite of open-source tools designed for searching, analyzing, and visualizing log data in real-time. It consists of three main components: Elasticsearch, a search and analytics engine; Logstash, a data processing pipeline that collects, parses, and stores logs; and Kibana, a visualization tool that allows users to explore and interact with data stored in Elasticsearch. Together, these tools provide a robust solution for managing and analyzing large volumes of log data from various sources, making it easier to monitor and troubleshoot applications and infrastructure. First, create logstash/pipeline/logstash.conf and add the configuration as follows:
bash
input {
beats {
port => 5000
}
}
filter {
# Add your filters here
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["elasticsearch:9200"]
index => "%{[@metadata][beat]}-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
stdout { codec => rubydebug }
}Then, run the follows docker-compose.yaml file via docker compose up -d:
yaml
services:
elasticsearch:
image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:8.16.0
container_name: elasticsearch
restart: 'always'
environment:
- discovery.type=single-node
- xpack.security.enabled=false
- bootstrap.memory_lock=true
- "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx512m"
ulimits:
memlock:
soft: -1
hard: -1
volumes:
- esdata:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data
ports:
- "9200:9200"
- "9300:9300"
networks:
- elk
logstash:
image: docker.elastic.co/logstash/logstash:8.16.0
container_name: logstash
restart: 'always'
volumes:
- ./logstash/pipeline:/usr/share/logstash/pipeline
ports:
- "5044:5044"
- "9600:9600"
networks:
- elk
depends_on:
- elasticsearch
kibana:
image: docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:8.16.0
container_name: kibana
restart: 'always'
environment:
- ELASTICSEARCH_URL=http://elasticsearch:9200
ports:
- "5601:5601"
networks:
- elk
depends_on:
- elasticsearch
networks:
elk:
driver: bridge
volumes:
esdata:
driver: localNest.js Microservice
Instantiating a microservice is as straightforward as setting up a normal HTTP service. Simply follow the Nest.js Microservices instructions. In this case, we also integrateELK and RabbitMQ.
apps/product/main.ts
There are two important points to note:
- If
product.protoimports other.protofiles, such ascommon.proto, you must also include thecommon.protofile. There are two ways to address this:
Option 1: Directly import common.proto into the protoPath:
bash
protoPath: [join(process.cwd(), 'proto/product.proto'), join(process.cwd(), 'proto/common.proto')],Option 2: Load the entire proto directory.
bash
loader: {
includeDirs: [process.cwd(), 'proto']
}- Configure the service to listen on
0.0.0.0:10087instead oflocalhost:10087. This is because each Kubernetes Pod operates within its own network namespace, andlocalhostjust refers to the Pod's loopback address. Other Pods cannot communicate with it usinglocalhost.
ts
import { ecsFormat } from '@elastic/ecs-winston-format'
import { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core'
import { MicroserviceOptions, Transport } from '@nestjs/microservices'
import { WinstonModule } from 'nest-winston'
import { join } from 'path'
import * as winston from 'winston'
import { ElasticsearchTransport } from 'winston-elasticsearch'
import { ProductModule } from './product.module'
// Using winston and ELK instead of the official logger
export const logger = WinstonModule.createLogger({
instance: winston.createLogger({
level: 'info',
format: ecsFormat(),
transports: [
new ElasticsearchTransport({
level: 'info',
indexPrefix: 'learn-backend-logging', // Remember this line and we'll use it to config Kibana Data View
indexSuffixPattern: 'YYYY-MM-DD',
clientOpts: {
node: 'http://0.0.0.0:9200',
maxRetries: 5,
requestTimeout: 10000,
sniffOnStart: false,
tls: { rejectUnauthorized: false }
}
})
]
})
})
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.createMicroservice<MicroserviceOptions>(
ProductModule,
{
transport: Transport.GRPC,
options: {
package: 'product',
protoPath: join(process.cwd(), 'proto/product.proto'),
url: '0.0.0.0:10087'
},
logger
}
)
await app.listen()
}
bootstrap()apps/product/product.module.ts
ts
import { ConfigModule } from '@app/config'
import { RabbitMQModule } from '@golevelup/nestjs-rabbitmq'
import { Logger, Module } from '@nestjs/common'
import { ProductController } from './product.controller'
import { ProductService } from './product.service'
@Module({
imports: [
ConfigModule,
RabbitMQModule.forRoot(RabbitMQModule, {
exchanges: [{ name: 'MQ_SERVICE', type: 'topic' }],
uri: 'amqp://root:password@0.0.0.0:5672',
connectionInitOptions: { wait: false },
deserializer: (message: Buffer) => {
return message
},
serializer: (msg: unknown) => {
const encodedMessage = JSON.stringify(msg)
return Buffer.from(encodedMessage)
}
})
],
controllers: [ProductController],
providers: [ProductService, Logger]
})
export class ProductModule {}apps/product/product.controller.ts
After running the pnpm run proto-ts command, you will generate the ProductServiceController interface. You can implement it and create the template code as follows:
ts
import { AmqpConnection, RabbitSubscribe } from '@golevelup/nestjs-rabbitmq'
import { Controller, Logger } from '@nestjs/common'
import { GrpcMethod } from '@nestjs/microservices'
import { Observable } from 'rxjs'
import {
CreateProductRequest,
CreateProductResponse,
DeleteProductRequest,
DeleteProductResponse,
GetProductRequest,
GetProductResponse,
ProductServiceController,
UpdateProductRequest,
UpdateProductResponse
} from 'types/proto/product'
@Controller()
export class ProductController implements ProductServiceController {
constructor(private readonly logger: Logger, private readonly amqpConnection: AmqpConnection,) {}
@GrpcMethod('ProductService', 'CreateProduct')
createProduct(
request: CreateProductRequest
): Promise<CreateProductResponse> | CreateProductResponse {
throw new Error('Method not implemented.')
}
@GrpcMethod('ProductService', 'GetProduct')
getProduct(
request: GetProductRequest
):
| Promise<GetProductResponse>
| Observable<GetProductResponse>
| GetProductResponse {
// record log to elasticsearch
this.logger.log('call getProduct rpc')
// publish rabbitmq message
this.amqpConnection.publish(
'MQ_SERVICE',
'get_product_by_id',
request
)
return {}
}
updateProduct(
request: UpdateProductRequest
):
| Promise<UpdateProductResponse>
| Observable<UpdateProductResponse>
| UpdateProductResponse {
throw new Error('Method not implemented.')
}
deleteProduct(
request: DeleteProductRequest
):
| Promise<DeleteProductResponse>
| Observable<DeleteProductResponse>
| DeleteProductResponse {
throw new Error('Method not implemented.')
}
@RabbitSubscribe({
exchange: 'MQ_SERVICE',
routingKey: 'get_product_by_id'
})
public async subscribe(content: Buffer, msg: unknown) {
const message = JSON.parse(content.toString())
console.log(message, msg)
}
}Nest.js Gateway
The Gateway service is simply a HTTP service, we want to use it call Product microservice service and expose the APIs.
apps/gateway/main.ts
ts
import { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core'
import { GatewayModule } from './gateway.module'
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(GatewayModule)
await app.listen(10086)
}
bootstrap()apps/gateway/gateway.module.ts
To call the Product microservice, you need to register it at first. Kubernetes uses an internal DNS name system for service discovery. We will name the Product microservice service product-service at the follows chapter. In production, you can reach the Product microservice using product-service:10087, while in development, you just use 0.0.0.0:10087.
ts
import { ConfigModule } from '@app/config'
import { Logger, Module } from '@nestjs/common'
import { ClientsModule, Transport } from '@nestjs/microservices'
import { join } from 'path'
import { GatewayController } from './gateway.controller'
@Module({
imports: [
ClientsModule.register([
{
name: 'ORDER_SERVICE',
transport: Transport.GRPC,
options: {
url:
process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
? 'product-service:10087' // For Kubernetes production environment
: '0.0.0.0:10087', // For local development environment
package: 'product',
protoPath: join(process.cwd(), 'proto/product.proto'),
loader: {
includeDirs: [process.cwd(), 'proto']
}
}
}
]),
],
providers: [GatewayController]
})
export class GatewayModule {}apps/gateway/gateway.controller.ts
ts
import { Metadata } from '@grpc/grpc-js'
import {
Controller,
Get,
Inject,
Logger,
OnModuleInit,
Param
} from '@nestjs/common'
import { ClientGrpc } from '@nestjs/microservices'
import { Observable } from 'rxjs'
import {
GetProductResponse,
ProductServiceController
} from 'types/proto/product'
@Controller()
export class GatewayController implements OnModuleInit {
private productService: ProductServiceController
constructor(@Inject('PRODUCT_SERVICE') private productClient: ClientGrpc) {}
onModuleInit() {
this.productService =
this.productClient.getService<ProductServiceController>('ProductService')
}
@Get(':id')
getProduct(
@Param('id') id: string
):
| Promise<GetProductResponse>
| Observable<GetProductResponse>
| GetProductResponse {
const metadata = new Metadata()
return this.productService.getProduct(
{
id
},
metadata
)
}
}Dockerfile
With the code phrase completed, we are now writing Dockerfiles for the Gateway service and the Product service.
docker/Dockerfile.gateway
yaml
FROM node:20-alpine AS builder
WORKDIR /app
COPY package.json pnpm-lock.yaml ./
RUN npm install -g pnpm
RUN pnpm install
COPY . .
RUN pnpm build gateway
FROM node:20-alpine AS runner
WORKDIR /app
COPY --from=builder /app/dist/apps/gateway ./dist
COPY --from=builder /app/node_modules ./node_modules
COPY package.json .
COPY proto ./proto
ENV NODE_ENV=production
EXPOSE 10086
CMD ["node", "dist/main"]docker/Dockerfile.product
yaml
FROM node:20-alpine AS builder
WORKDIR /app
COPY package.json pnpm-lock.yaml ./
RUN npm install -g pnpm
RUN pnpm install
COPY . .
RUN pnpm build product
FROM node:20-alpine AS runner
WORKDIR /app
COPY --from=builder /app/dist/apps/product ./dist
COPY --from=builder /app/node_modules ./node_modules
COPY package.json .
COPY proto ./proto
ENV NODE_ENV=production
EXPOSE 10087
CMD ["node", "dist/main"]Finally, run the follows commands in the root path:
bash
docker build -t commerce/gateway-service:0.0.1 -f docker/Dockerfile.gateway .
docker build -t commerce/product-service:0.0.1 -f docker/Dockerfile.product .
Set up Kubernetes Dashboard
Firstly, install helm on your computer. If you are using macOS, simply run:
bash
brew install helmThen, install Kubernetes Dashboard package:
bash
# Add kubernetes-dashboard repository
helm repo add kubernetes-dashboard https://kubernetes.github.io/dashboard/
# Deploy a Helm Release named "kubernetes-dashboard" using the kubernetes-dashboard chart
helm upgrade --install kubernetes-dashboard kubernetes-dashboard/kubernetes-dashboard --create-namespace --namespace kubernetes-dashboard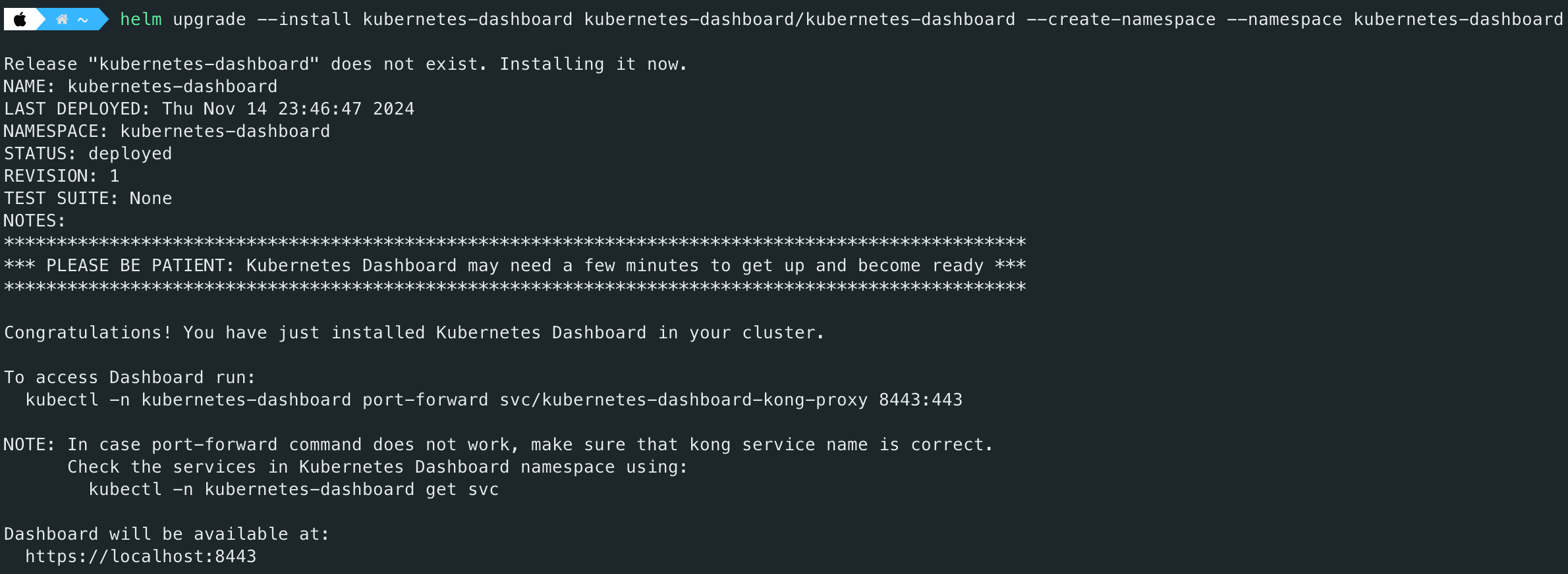 Once Kubernetes Dashboard is installed, you can verify it using the follows command:
Once Kubernetes Dashboard is installed, you can verify it using the follows command:
bash
kubectl get svc -n kubernetes-dashboard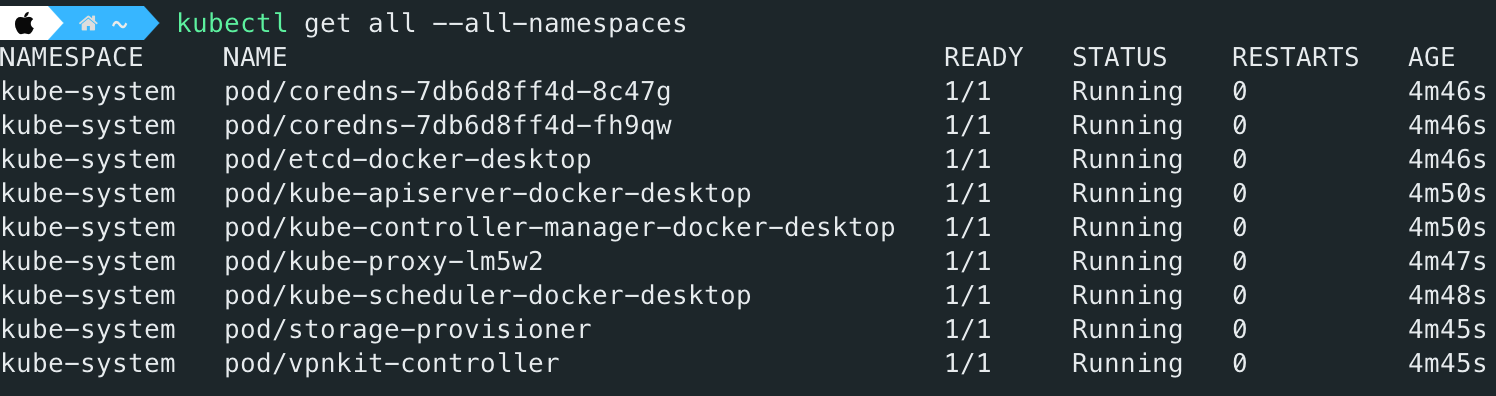
Creating Account and Token
Follow the instruction. First, create a Kubernetes manifest file to create a service account. For example:
bash
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: admin-user
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: admin-user
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: admin-user
namespace: kube-systemNext, apply the above configuration to the Kubernetes cluster.
bash
kubectl create -f k8s-dashboard-account.yamlNext, generate a token using the follows command:
bash
kubectl -n kube-system create token admin-userStarting Kubernetes Dashboard Server
bash
kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard port-forward svc/kubernetes-dashboard-kong-proxy 8443:443Finally, fill out your token on the field. 
Kubernetes Deployment
k8s/gateway-deployment.yaml
yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: gateway-deployment
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: gateway
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: gateway
spec:
containers:
- name: gateway
image: commerce/gateway-service:0.0.1
ports:
- containerPort: 10086
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: gateway-service
spec:
selector:
app: gateway
ports:
- port: 10086
targetPort: 10086
type: LoadBalancerk8s/product-deployment.yaml
yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: product-deployment
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: product
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: product
spec:
containers:
- name: product
image: commerce/product-service:0.0.1
ports:
- containerPort: 10087
env:
- name: NODE_ENV
value: production
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: product-service
spec:
selector:
app: product
ports:
- port: 10087
targetPort: 10087
type: ClusterIPFinally, run kubectl apply -f k8s/ to deploy your services. 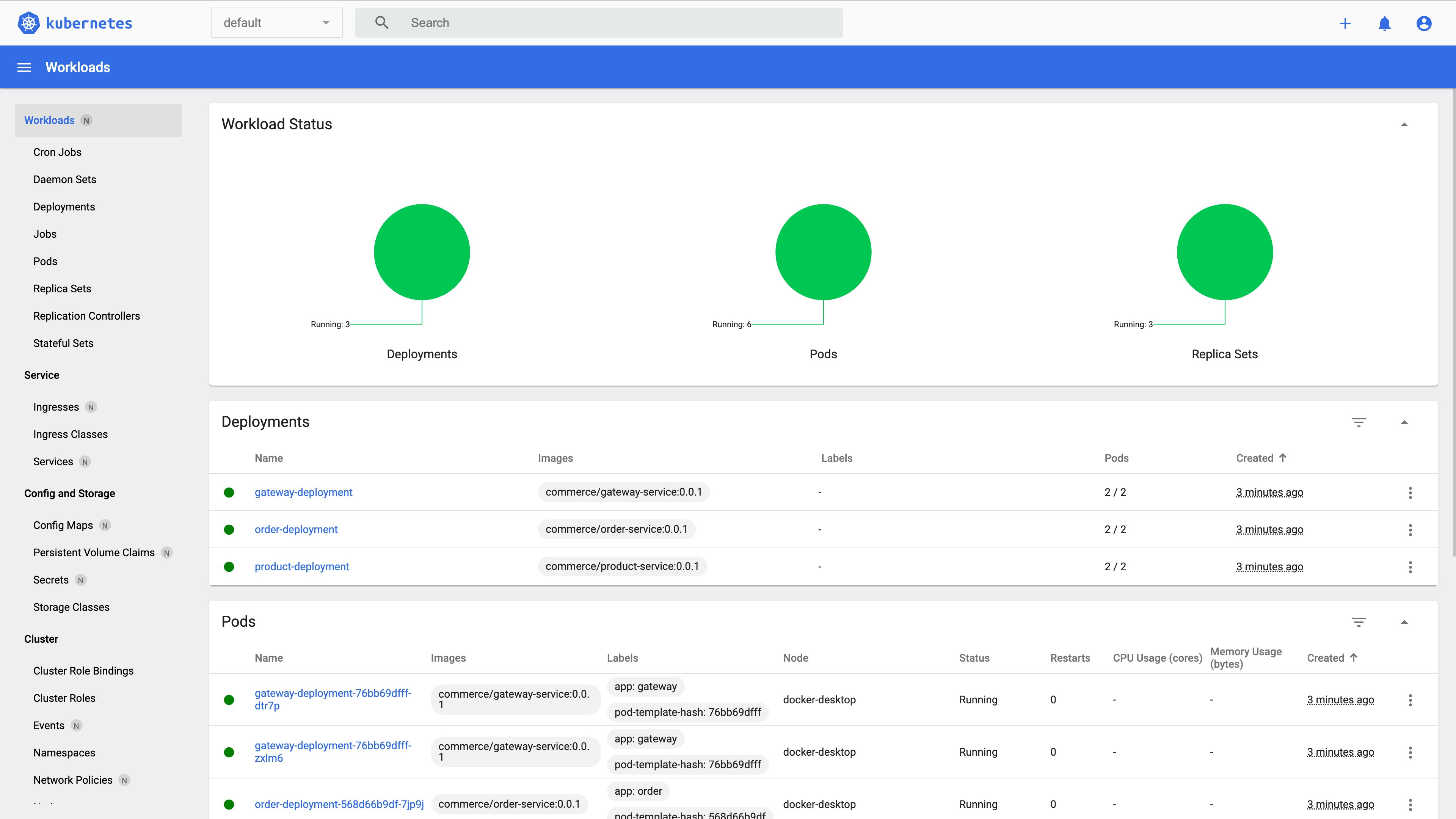
Kibana Configuration
Submit some logs in advance to let ElasticSearch generate index , visit https://localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v to check whether your index successfully added. 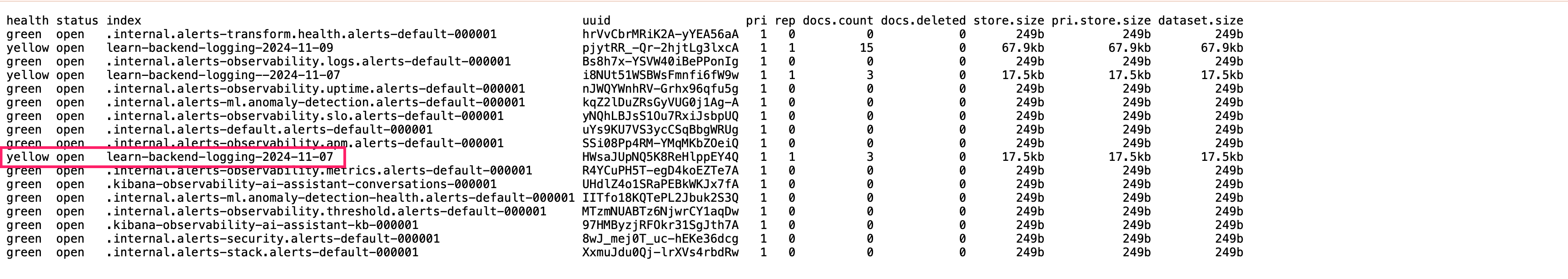 Visit http://localhost:5601/app/management/kibana/dataViews to create data view, the
Visit http://localhost:5601/app/management/kibana/dataViews to create data view, the index pattern matches the indexPrefix you configured. 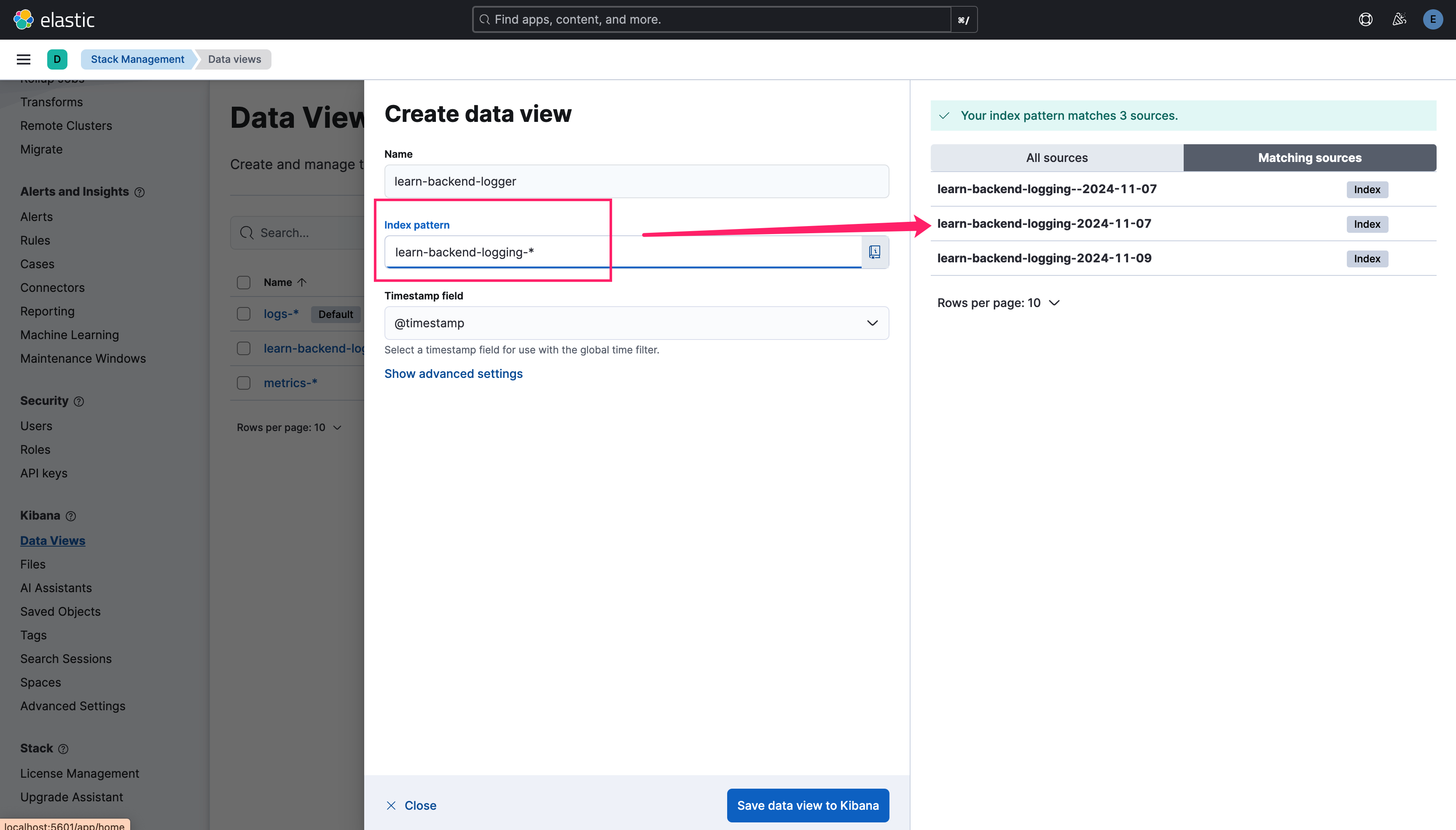 Finally visit http://localhost:5601/app/discover and select your data view, and the logs will be displayed on the right panel.
Finally visit http://localhost:5601/app/discover and select your data view, and the logs will be displayed on the right panel. 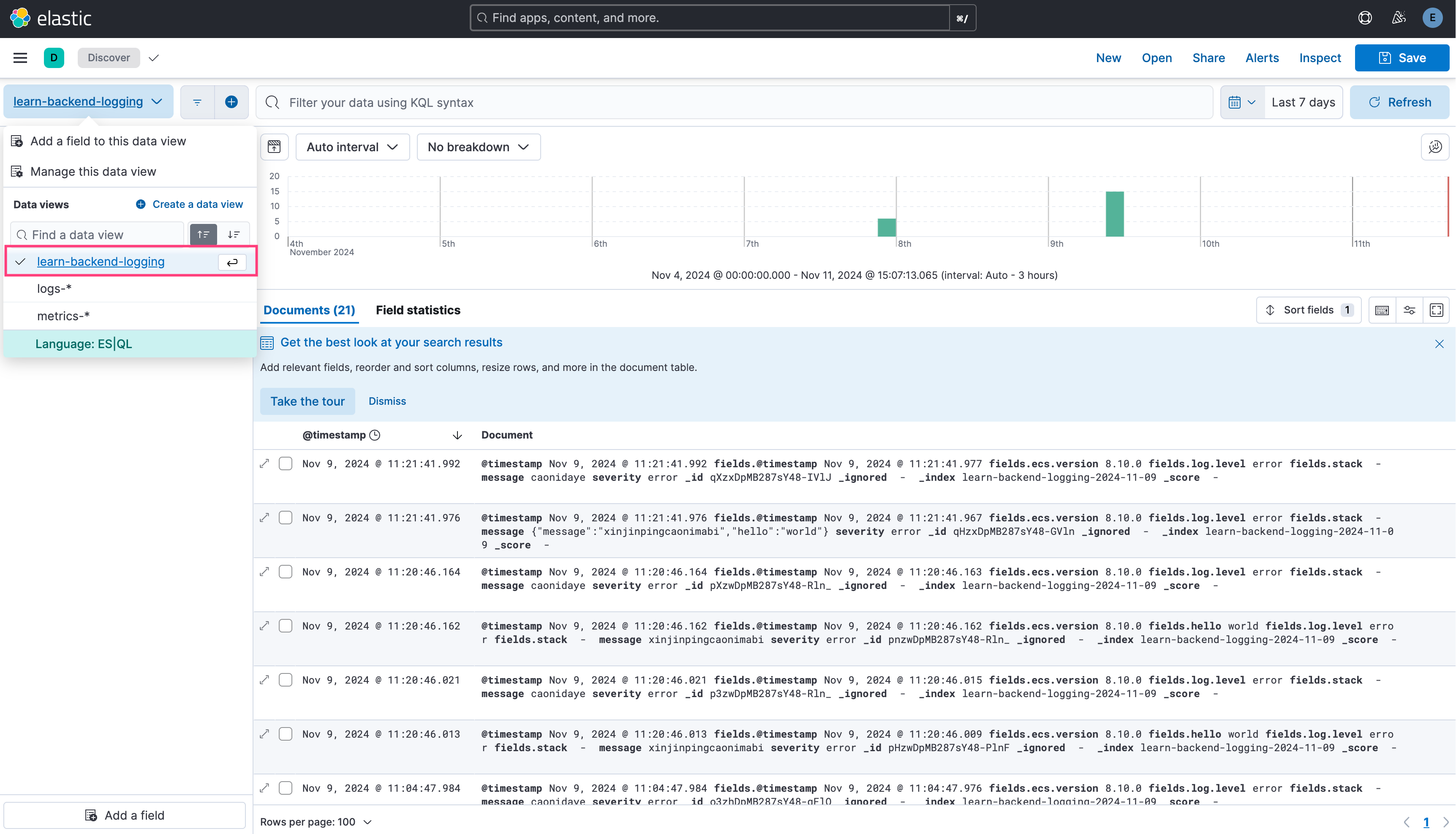
Summary
This is an MVP version of a Nest.js microservices project, covering the basics of coding, building, and deploying. However, there's still a long way to go. Challenges such as security, high availability, and performance optimization remain to be addressed. If you have ideas or suggestions, feel free to reach out to me @YanceyOfficial on X or comment this article directly. Your input is always welcome as we work towards making this project more robust and production-ready.