1. 网站服务程序
1970 年,作为互联网前身的 ARPANET(阿帕网)已初具雏形,并开始向非军用部门开放,许多大学和商业机构开始陆续接入。虽然彼时阿帕网的规模(只有 4 台主机联网运行)还不如现在的局域网成熟,但是它依然为网络技术的进步打下了扎实的基础。
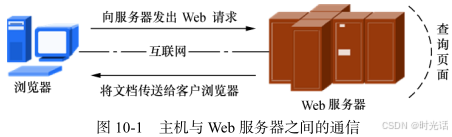
想必大多数人都是通过访问网站而开始接触互联网的吧。我们平时访问的网站服务就是Web 网络服务,一般是指允许用户通过浏览器访问互联网中各种资源的服务。如图所示,Web 网络服务是一种被动访问的服务程序,即只有接收到互联网中其他主机发出的请求后才会响应,最终用于提供服务程序的 Web 服务器会通过 HTTP(超文本传输协议)或 HTTPS(安全超文本传输协议)把请求的内容传送给用户。
目前能够提供 Web 网络服务的程序有 IIS、Nginx 和 Apache 等。其中,IIS(Internet
Information Service,互联网信息服务)是 Windows 系统中默认的 Web 服务程序,这是一款图形化的网站管理工具,不仅可以提供 Web 网站服务,还可以提供 FTP、NMTP、SMTP 等服务。但是,IIS 只能在 Windows 系统中使用,暂时不在我们的学习范围之内。
2004 年 10 月 4 日,为俄罗斯知名门户站点而开发的 Web 服务程序 Nginx 横空出世。Nginx程序作为一款轻量级的网站服务软件,因其稳定性和丰富的功能而快速占领服务器市场,但Nginx 最被认可的还是其系统资源消耗低且并发能力强的特性,因此得到了国内诸如新浪、网易、腾讯等门户网站的青睐。
Apache 程序是目前拥有很高市场占有率的 Web 服务程序之一,其跨平台和安全性广泛被认可且拥有快速、可靠、简单的 API 扩展。Apache 它的名字取自美国印第安人的土著语,寓意为"拥有高超的作战策略和无穷的耐性"。Apache服务程序可以运行在 Linux 系统、UNIX 系统甚至是 Windows 系统中,它支持基于 IP、域名及端口号的虚拟主机功能,支持多种认证方式,集成有代理服务器模块、安全 Socket 层(SSL),能够实时监视服务状态与定制日志消息,并支持各类丰富的模块。
注:Apache 程序是 RHEL 5、6、7、8 系统中默认的 Web 服务程序,其相关知识点一直也是 RHCSA 和 RHCE 认证考试的重点内容。
我们再来回忆一下软件仓库的配置过程。
第一步:把系统镜像挂载到/media/cdrom 目录。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# mkdir -p /media/cdrom
[root@linuxprobe~]# mount /dev/cdrom /media/cdrom
mount: /media/cdrom: WARNING: device write-protected, mounted read-only. 第二步:使用 Vim 文本编辑器创建软件仓库的配置文件。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/rhel8.repo
[BaseOS]
name=BaseOS
baseurl=file:///media/cdrom/BaseOS
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
[AppStream]
name=AppStream
baseurl=file:///media/cdrom/AppStream
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0 第三步:动手安装 Apache 服务程序。注意,在使用 dnf 命令进行安装时,跟在命令后面的 Apache 服务的软件包名称为 httpd。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# dnf install httpd
Updating Subscription Management repositories.
Unable to read consumer identity
This system is not registered to Red Hat Subscription Management. You can use
subscription-manager to register.
AppStream 3.1 MB/s | 3.2 kB 00:00
BaseOS 2.7 MB/s | 2.7 kB 00:00
Dependencies resolved.
===============================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
===============================================================================
Installing:
httpd x86_64 2.4.37-10.module+el8+2764+7127e69e AppStream 1.4 M
Installing dependencies:
apr x86_64 1.6.3-9.el8 AppStream 125 k
apr-util x86_64 1.6.1-6.el8 AppStream 105 k
httpd-filesystem noarch 2.4.37-10.module+el8+7127e69e AppStream 34 k
httpd-tools x86_64 2.4.37-10.module+el8+7127e69e AppStream 101 k
mod_http2 x86_64 1.11.3-1.module+el8+605475b7 AppStream 156 k
redhat-logos-httpd noarch 80.7-1.el8 BaseOS 25 k
Installing weak dependencies:
apr-util-bdb x86_64 1.6.1-6.el8 AppStream 25 k
apr-util-openssl x86_64 1.6.1-6.el8 AppStream 27 k
Enabling module streams:
httpd 2.4
Transaction Summary
===============================================================================
Install 9 Packages
Total size: 2.0 M
Installed size: 5.4 M
Is this ok [y/N]: y
Downloading Packages:
Running transaction check
Transaction check succeeded.
Running transaction test
Transaction test succeeded.
..................省略部分输出信息..................
Complete! 第四步:启用 httpd 服务程序并将其加入到开机启动项中,使其能够随系统开机而运行,从而持续为用户提供 Web 服务。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# systemctl start httpd
[root@linuxprobe~]# systemctl enable httpd
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/httpd.service→
/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service. 大家在浏览器(这里以 Firefox 浏览器为例)的地址栏中输入 http://127.0.0.1 并按回车键,就可以看到用于提供 Web 服务的默认页面了,如图所示。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# firefox 
2. 配置服务文件参数
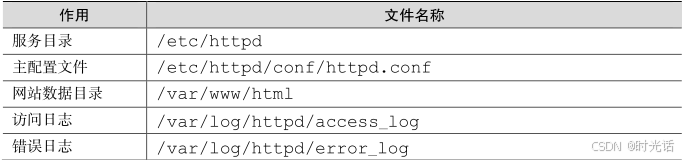
需要提醒大家的是,前文介绍的 httpd 服务程序的安装和运行,仅仅是 httpd 服务程序的一些皮毛,我们依然有很长的道路要走。在 Linux 系统中配置服务,其实就是修改服务的配置文件。因此,还需要知道这些配置文件的所在位置以及用途。httpd 服务程序的主要配置文件及存放位置如表所示。
主配置文件中保存的是最重要的服务参数,一般会被保存到/etc 目录中以软件名称命名的一个文件夹之中,名字为"服务名称.conf",例如这里的"/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf"。大家在熟悉以后就能记住了。
在这个配置文件中,所有以井号(#)开始的行都是注释行,其目的是对 httpd 服务程序的功能或某一行参数进行介绍,我们不需要逐行研究这些内容。 在 httpd 服务程序的主配置文件中,存在 3 种类型的信息:注释行信息、全局配置、区域配置,如图所示。

全局配置参数就是一种全局性的配置参数,可作用于所有的子站点,既保证了子站点的正常访问,也有效降低了频繁写入重复参数的工作量。区域配置参数则是单独针对每个独立的子站点进行设置的。在 httpd 服务程序主配置文件中,最为常用的参数如表所示。
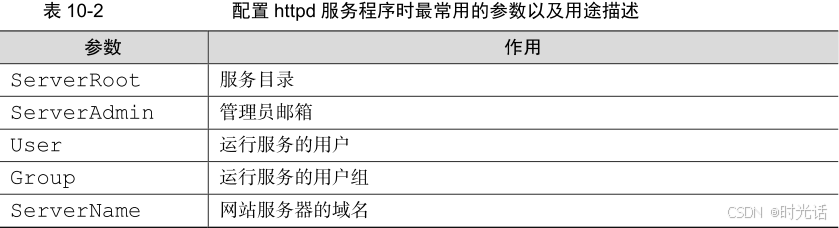
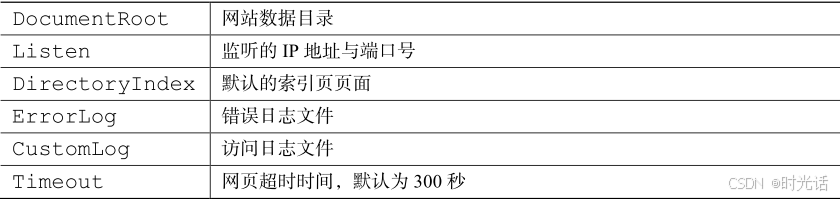
从表中可知,DocumentRoot 参数用于定义网站数据的保存路径,其参数的默认值是/var/www/html(即把网站数据存放到这个目录中);而当前网站普遍的首页面名称是index.html,因此可以向/var/www/html/index.html 文件中写入一段内容,替换掉 httpd 服务程序的默认首页面。该操作会立即生效。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# echo "Welcome To LinuxProbe.Com" > /var/www/html/index.html
[root@linuxprobe~]# firefox 在执行上述操作之后,再在 Firefox 浏览器中刷新 httpd 服务程序,可以看到该程序的首页面内容已经发生了改变,如图所示。
在默认情况下,网站数据保存在/var/www/html 目录中,如果想把保存网站数据的目录修改为/home/wwwroot 目录,该怎么操作?
**第一步:**建立网站数据的保存目录,并创建首页文件。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# mkdir /home/wwwroot
[root@linuxprobe~]# echo "The New Web Directory" > /home/wwwroot/index.html **第二步:**打开 httpd 服务程序的主配置文件,将约第 122 行用于定义网站数据保存路径的参数 DocumentRoot 修改为/home/wwwroot,同时还需要将约第 127 行与第 134 行用于定义目录权限的参数 Directory 后面的路径也修改为/home/wwwroot。配置文件修改完毕后即可保存并退出。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
..................省略部分输出信息..................
117 #
118 # DocumentRoot: The directory out of which you will serve your
119 # documents. all requests are taken from this directory, but
120 # symbolic links and aliases may be used to point to other locations.
121 #
122 DocumentRoot "/home/wwwroot"
123
124 #
125 # Relax access to content within /var/www.
126 #
127 <Directory "/home/wwwroot">
128 AllowOverride None
129 # Allow open access:
130 Require all granted
131 </Directory>
132
133 # Further relax access to the default document root:
134 <Directory "/home/wwwroot">
..................省略部分输出信息.................. **第三步:**重新启动 httpd 服务程序并验证效果,浏览器刷新页面后的内容如图所示。怎么提示权限不足了?
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# systemctl restart httpd
[root@linuxprobe~]# firefox 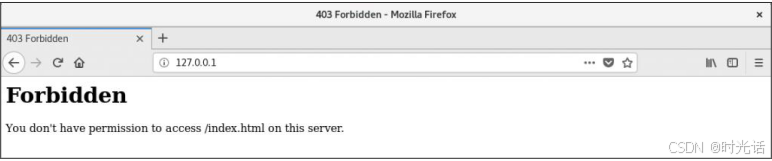
3. SELinux 安全子系统
SELinux(Security-Enhanced Linux)是美国国家安全局在 Linux 开源社区的帮助下开发的一个强制访问控制(MAC,Mandatory Access Control)的安全子系统。Linux 系统使用 SELinux技术的目的是为了让各个服务进程都受到约束,使其仅获取到本应获取的资源。
例如,您在自己的电脑上下载了一个美图软件,正全神贯注地使用它给照片进行美颜的时候,它却在后台默默监听着浏览器中输入的密码信息,而这显然不应该是它应做的事情(哪怕是访问电脑中的图片资源,都情有可原)。SELinux 安全子系统就是为了杜绝此类情况而设计的,它能够从多方面监控违法行为:对服务程序的功能进行限制(SELinux 域限制可以确保服务程序做不了出格的事情);对文件资源的访问进行限制(SELinux 安全上下文确保文件资源只能被其所属的服务程序进行访问)。
注:如果一般权限和防火墙是"门窗"的话,那么 SELinux 便是在门窗外面安装的"防护栏",可以让系统内部更加安全。
SELinux 服务比较复杂,配置难度也很大,加之很多运维人员对这项技术理解不深,从而导致很多服务器在部署好 Linux系统后直接将 SELinux 禁用了。这绝对不是明智的选择。
SELinux 服务有 3 种配置模式,具体如下。
➢ enforcing :强制启用安全策略模式,将拦截服务的不合法请求。
➢ permissive :遇到服务越权访问时,只发出警告而不强制拦截。
➢ disabled :对于越权的行为不警告也不拦截。
本书中所有的实验都是在强制启用安全策略模式下进行的,虽然在禁用 SELinux 服务后确实能够减少报错几率,但这在生产环境中相当不推荐。建议大家检查一下自己的系统,查看 SELinux 服务主配置文件中定义的默认状态。如果是 permissive 或 disabled,建议赶紧修改为 enforcing。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# vim /etc/selinux/config
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
SELINUX=enforcing
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these three values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are protected.
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted SELinux 服务的主配置文件中,定义的是 SELinux 的默认运行状态,可以将其理解为系统重启后的状态,因此它不会在更改后立即生效。可以使用 getenforce 命令获得当前 SELinux服务的运行模式:
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# getenforce
Enforcing 为了确认上图forbidden的结果是因为 SELinux 而导致的,可以用 setenforce [0|1]命令修改SELinux 当前的运行模式(0 为禁用,1 为启用)。注意,这种修改只是临时的,在系统重启
后就会失效:
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# setenforce 0
[root@linuxprobe~]# getenforce
Permissive 再次刷新网页,就会看到正常的网页内容了,如图所示。可见,问题是出在了 SELinux服务上。
bash
[root@linuxprobe wwwroot]# firefox 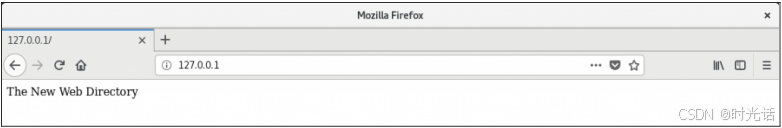
现在,我们来总结一下前面的操作中到底是哪里出了问题?
httpd 服务程序的功能是允许用户访问网站内容,因此 SELinux 肯定会默认放行用户对网站的请求操作。但是,我们将网站数据的默认保存目录修改为/home/wwwroot,这就产生问题了。在前面小节中讲到,/home 目录是用来存放普通用户的家目录数据的,而现在,httpd 提供的网站服务却要去获取普通用户家目录中的数据,这显然违反了 SELinux 的监管原则。
现在,把 SELinux 服务恢复到强制启用安全策略模式,然后分别查看原始网站数据的保存目录与当前网站数据的保存目录是否拥有不同的 SELinux 安全上下文值。
在 ls 命令中,-Z 参数用于查看文件的安全上下文值,-d 参数代表对象是个文件夹。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# setenforce 1
[root@linuxprobe~]# ls -Zd /var/www/html
drwxr-xr-x. root root system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0 /var/www/htm
l
[root@linuxprobe~]# ls -Zd /home/wwwroot
drwxrwxrwx. root root unconfined_u:object_r:home_root_t:s0 /home/wwwroot 在文件上设置的 SELinux 安全上下文是由用户段、角色段以及类型段等多个信息项共同组成的。其中,用户段 system_u 代表系统进程的身份,角色段 object_r 代表文件目录的角色,类型段 httpd_sys_content_t 代表网站服务的系统文件。
针对当前这种情况,我们只需要使用 semanage 命令,将当前网站目录/home/wwwroot 的SELinux 安全上下文修改为跟原始网站目录的一样就行了。
semanage 命令
semanage 命令用于管理 SELinux 的策略,英文全称为"SELinux manage"。
语法格式:semanage [参数] [文件]
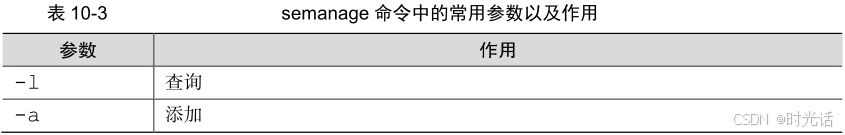
SELinux 服务极大地提升了 Linux 系统的安全性,将用户权限牢牢地锁在笼子里。semanage 命令不仅能够像传统的 chcon 命令那样设置文件、目录的策略,还能够管理网络端口、消息接口。使用 semanage 命令时,经常用到的几个参数及其作用如表所示。

例如,向新的网站数据目录中新添加一条 SELinux 安全上下文,让这个目录以及里面的所有文件能够被 httpd 服务程序访问到:
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/wwwroot
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/wwwroot/* 注意,在执行上述设置之后,还无法立即访问网站,还需要使用 restorecon 命令将设置好的 SELinux 安全上下文立即生效。在使用 restorecon 命令时,可以加上-Rv 参数对指定的目录进行递归操作,以及显示 SELinux 安全上下文的修改过程。最后,再次刷新页面,就可以正常看到网页内容了,结果如图所示。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# restorecon -Rv /home/wwwroot/
Relabeled /home/wwwroot from unconfined_u:object_r:user_home_dir_t:s0 to
unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /home/wwwroot/index.html from unconfined_u:object_r:user_home_t:s0 to
unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
[root@linuxprobe~]# firefox 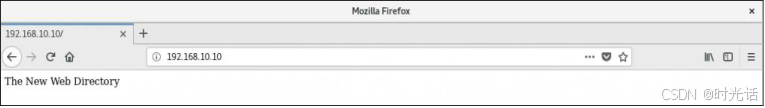
4. 个人用户主页功能
如果想在系统中为每位用户建立一个独立的网站,通常的方法是基于虚拟网站主机功能来部署多个网站。但这个工作会让管理员苦不堪言(尤其是用户数量很庞大时),而且在用户自行管理网站时,还会碰到各种权限限制,需要为此做很多额外的工作。其实,httpd 服务程序提供的个人用户主页功能完全可以胜任这个工作。该功能可以让系统内所有的用户在自己的家目录中管理个人的网站,而且访问起来也非常容易。
第一步: 在 httpd 服务程序中,默认没有开启个人用户主页功能。为此,我们需要编辑下面的配置文件,然后在第 17 行的 UserDir disabled 参数前面加上井号(#),表示让 httpd 服务程序开启个人用户主页功能;同时再把第 24 行的 UserDir public_html 参数前面的井号(#)去掉(UserDir 参数表示网站数据在用户家目录中的保存目录名称,即 public_html 目录)。最后,在修改完毕后记得保存。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/userdir.conf
1 #
2 # UserDir: The name of the directory that is appended onto a user's home
3 # directory if a~user request is received.
4 #
5 # The path to the end user account 'public_html' directory must be
6 # accessible to the webserver userid. This usually means that~userid
7 # must have permissions of 711, ~userid/public_html must have permissions
8 # of 755, and documents contained therein must be world-readable.
9 # Otherwise, the client will only receive a "403 Forbidden" message.
10 #
11 <IfModule mod_userdir.c>
12 #
13 # UserDir is disabled by default since it can confirm the presence
14 # of a username on the system (depending on home directory
15 # permissions).
16 #
17 # UserDir disabled
18
19 #
20 # To enable requests to /~user/ to serve the user's public_html
21 # directory, remove the "UserDir disabled" line above, and uncomment
22 # the following line instead:
23 #
24 UserDir public_html
25 </IfModule>
26
27 #
28 # Control access to UserDir directories. The following is an example
29 # for a site where these directories are restricted to read-only.
30 #
31 <Directory "/home/*/public_html">
32 AllowOverride FileInfo AuthConfig Limit Indexes
33 Options MultiViews Indexes SymLinksIfOwnerMatch IncludesNoExec
34 Require method GET POST OPTIONS
35 </Directory> **第二步:**在用户家目录中建立用于保存网站数据的目录及首页面文件。另外,还需要把家目录的权限修改为 755,保证其他人也有权限读取里面的内容。
bash
[root@linuxprobe home]# su - linuxprobe
[linuxprobe@linuxprobe~]$ mkdir public_html
[linuxprobe@linuxprobe~]$ echo "This is linuxprobe's website" > public_html/index.html
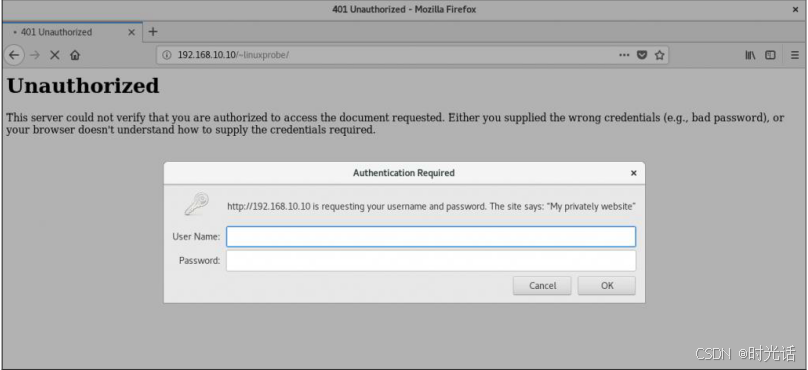
[linuxprobe@linuxprobe~]$ chmod -R 755 /home/linuxprobe **第三步:**重新启动 httpd 服务程序,在浏览器的地址栏中输入网址,其格式为"网址/~用户名"(其中的波浪号是必需的,而且网址、波浪号、用户名之间没有空格)。从理论上来讲,现在就可以看到用户的个人网站了。出乎意料的是,系统显示报错页面,如图所示。这一定还是 SELinux 惹的祸。
bash
[linuxprobe@linuxprobe~]$ exit
logout
[root@linuxprobe~]# systemctl restart httpd
[root@linuxprobe~]# firefox
第四步: 思考这次报错的原因是什么。httpd 服务程序在提供个人用户主页功能时,该用户的网站数据目录本身就应该是存放到与这位用户对应的家目录中的,所以应该不需要修改家目录的 SELinux 安全上下文。但是,前文还讲到了 SELinux 域的概念。SELinux 域确保服务程序不能执行违规的操作,只能本本分分地为用户提供服务。httpd 服务中突然开启的这项个人用户主页功能到底有没有被 SELinux 域默认允许呢?
接下来使用 getsebool 命令查询并过滤出所有与 HTTP 协议相关的安全策略。其中,off为禁止状态,on 为允许状态。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# getsebool -a | grep http
httpd_anon_write --> off
httpd_builtin_scripting --> on
httpd_can_check_spam --> off
httpd_can_connect_ftp --> off
httpd_can_connect_ldap --> off
httpd_can_connect_mythtv --> off
httpd_can_connect_zabbix --> off
httpd_can_network_connect --> off
httpd_can_network_connect_cobbler --> off
httpd_can_network_connect_db --> off
httpd_can_network_memcache --> off
httpd_can_network_relay --> off
httpd_can_sendmail --> off
httpd_dbus_avahi --> off
httpd_dbus_sssd --> off
httpd_dontaudit_search_dirs --> off
httpd_enable_cgi --> on
httpd_enable_ftp_server --> off
httpd_enable_homedirs --> off
httpd_execmem --> off
httpd_graceful_shutdown --> off
httpd_manage_ipa --> off
httpd_mod_auth_ntlm_winbind --> off
httpd_mod_auth_pam --> off
httpd_read_user_content --> off
httpd_run_ipa --> off
httpd_run_preupgrade --> off
httpd_run_stickshift --> off
httpd_serve_cobbler_files --> off
httpd_setrlimit --> off
httpd_ssi_exec --> off
httpd_sys_script_anon_write --> off
httpd_tmp_exec --> off
httpd_tty_comm --> off
httpd_unified --> off
httpd_use_cifs --> off
httpd_use_fusefs --> off
httpd_use_gpg --> off
httpd_use_nfs --> off
httpd_use_openstack --> off
httpd_use_sasl --> off
httpd_verify_dns --> off
mysql_connect_http --> off
named_tcp_bind_http_port --> off
prosody_bind_http_port --> off 面对如此多的 SELinux 域安全策略规则,实在没有必要逐个理解它们,我们只要能通过名字大致猜测出相关的策略用途就足够了。比如,想要开启 httpd 服务的个人用户主页功能,那么用到的 SELinux 域安全策略应该是 httpd_enable_homedirs 吧?大致确定后就可以用setsebool 命令来修改 SELinux 策略中各条规则的布尔值了。大家一定要记得在 setsebool 命令后面加上-P 参数,让修改后的 SELinux 策略规则永久生效且立即生效。随后刷新网页,其效果如图所示。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# setsebool -P httpd_enable_homedirs=on
[root@linuxprobe~]# firefox 
有时,网站的拥有者并不希望直接将网页内容显示出来,而只想让通过身份验证的用户看到里面的内容,这时就可以在网站中添加密码功能了。
第一步: 先使用 htpasswd 命令生成密码数据库。-c 参数表示第一次生成;后面再分别添加密码数据库的存放文件,以及验证要用到的用户名称(该用户不必是系统中已有的本地账户)
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# htpasswd -c /etc/httpd/passwd linuxprobe
New password: 此处输入用于网页验证的密码
Re-type new password: 再输入一遍进行确认
Adding password for user linuxprobe 第二步:继续编辑个人用户主页功能的配置文件。把第 31~37 行的参数信息修改成下列内容,其中以井号(#)开头的内容为添加的注释信息,可将其忽略。随后保存并退出配置文件,重启 httpd 服务程序即可生效。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/userdir.conf
..................省略部分输出信息..................
27 #
28 # Control access to UserDir directories. The following is an example
29 # for a site where these directories are restricted to read-only.
30 #
31 <Directory "/home/*/public_html">
32 AllowOverride all
#刚刚生成出的密码验证文件保存路径
33 authuserfile "/etc/httpd/passwd"
#当用户访问网站时的提示信息
34 authname "My privately website"
#验证方式为密码模式
35 authtype basic
#访问网站时需要验证的用户名称
36 require user linuxprobe
37 </Directory>
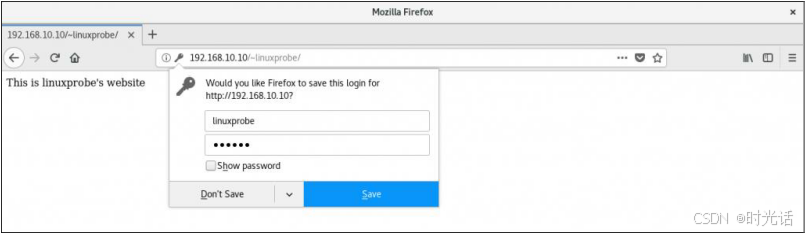
[root@linuxprobe~]# systemctl restart httpd 此后,当用户再想访问某个用户的个人网站时,就必须输入账户和密码才能正常访问了。另外,验证时使用的账户和密码是用 htpasswd 命令生成的专门用于网站登录的账户和密码,而不是系统中的账户和密码,请不要搞错了。登录界面如图所示。
5. 虚拟主机功能
如果每台运行 Linux 系统的服务器上只能运行一个网站,那么人气低、流量小的草根站长就要被迫承担高昂的服务器租赁费用了,这显然也会造成硬件资源的浪费。在虚拟专用服务器(Virtual Private Server,VPS)与云计算技术诞生以前,IDC 服务供应商为了能够更充分地利用服务器资源,同时也为了降低购买门槛,纷纷启用了虚拟主机功能。
利用虚拟主机功能,可以把一台处于运行状态的物理服务器分割成多个"虚拟的服务器"。但是,该技术无法实现目前云主机技术的硬件资源隔离,而只能让这些虚拟的服务器共同使用物理服务器的硬件资源,供应商只能限制硬盘的使用空间大小。出于各种考虑的因素(主要是价格低廉),目前依然有很多企业或个人站长在使用虚拟主机的形式来部署网站。
Apache 的虚拟主机功能是服务器基于用户请求的不同 IP 地址、主机域名或端口号,提供多个网站同时为外部提供访问服务的技术。如图所示,用户请求的资源不同,最终获取到的网页内容也各不相同。如果大家之前没有做过网站,可能不太理解其中的原理,等一会儿搭建出实验环境并看到实验效果之后,一定就能明白了。
再次提醒大家,在做每个实验之前请先将虚拟机还原到最初始的状态,以免多个实验之间相互产生冲突。
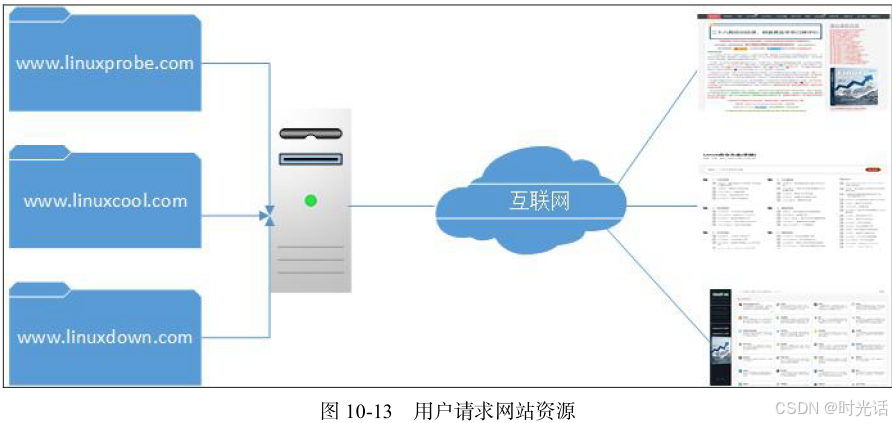
5.1 基于 IP 地址
如果一台服务器有多个 IP 地址,而且每个 IP 地址与服务器上部署的每个网站一一对应,这样当用户请求访问不同的 IP 地址时,会访问到不同网站的页面资源。而且,每个网站都有一个独立的 IP 地址,这对搜索引擎优化也大有裨益。因此以这种方式提供虚拟网站主机功能不仅最常见,而且也受到了网站站长的欢迎(尤其是草根站长)。
通过前面的学习,我们知道了配置网站的两种方法,大家在实验中和工作中可随意选择。就当前的实验来讲,需要配置的 IP 地址如图所示。
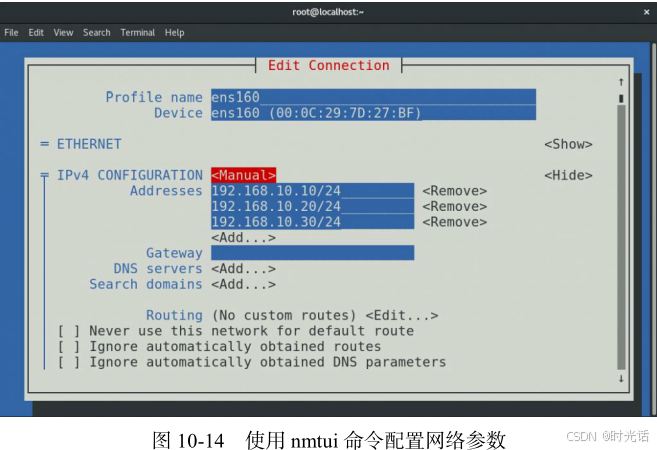
在配置完毕并重启网络服务之后,记得检查网络的连通性,确保 3 个 IP 地址均可正常访问,如图 所示(这很重要,一定要测试好,然后再进行下一步)。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# nmcli connection up ens160
Connection successfully activated (D-Bus active path: /org/freedesktop/
NetworkManager/ActiveConnection/6) 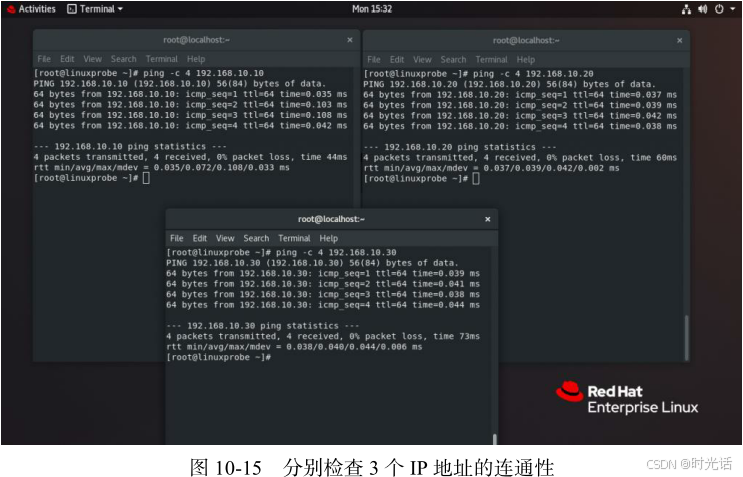
第一步::分别在/home/wwwroot 中创建用于保存不同网站数据的 3 个目录,并向其中分别写入网站的首页文件。每个首页文件中应有明确区分不同网站内容的信息,方便稍后能更直观地检查效果。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# mkdir -p /home/wwwroot/10
[root@linuxprobe~]# mkdir -p /home/wwwroot/20
[root@linuxprobe~]# mkdir -p /home/wwwroot/30
[root@linuxprobe~]# echo "IP:192.168.10.10" > /home/wwwroot/10/index.html
[root@linuxprobe~]# echo "IP:192.168.10.20" > /home/wwwroot/20/index.html
[root@linuxprobe~]# echo "IP:192.168.10.30" > /home/wwwroot/30/index.html 第二步:从 httpd 服务的配置文件中大约第 132 行处开始,分别追加写入 3 个基于 IP 地址的虚拟主机网站参数,然后保存并退出。记得需要重启 httpd 服务,这些配置才生效。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
..................省略部分输出信息..................
132 <VirtualHost 192.168.10.10>
133 DocumentRoot /home/wwwroot/10
134 ServerName www.linuxprobe.com
135 <Directory /home/wwwroot/10>
136 AllowOverride None
137 Require all granted
138 </Directory>
139 </VirtualHost>
140 <VirtualHost 192.168.10.20>
141 DocumentRoot /home/wwwroot/20
142 ServerName www.linuxcool.com
143 <Directory /home/wwwroot/20>
144 AllowOverride None
145 Require all granted
146 </Directory>
147 </VirtualHost>
148 <VirtualHost 192.168.10.30>
149 DocumentRoot /home/wwwroot/30
150 ServerName www.linuxdown.com
151 <Directory /home/wwwroot/30>
152 AllowOverride None
153 Require all granted
154 </Directory>
155 </VirtualHost>
..................省略部分输出信息..................
[root@linuxprobe~]# systemctl restart httpd 第三步::此时访问网站,则会看到 httpd 服务程序的默认首页面中显示"权限不足"。大家现在应该立刻就反应过来---这是 SELinux 在捣鬼。由于当前的/home/wwwroot 目录及里面的网站数据目录的 SELinux 安全上下文与网站服务不吻合,因此 httpd 服务程序无法获取到这些网站数据目录。我们需要手动把新的网站数据目录的 SELinux 安全上下文设置正确(见前文的实验),并使用 restorecon 命令让新设置的 SELinux 安全上下文立即生效,这样就可以立即看到网站的访问效果了,如图所示。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/wwwroot
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/wwwroot/10
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/wwwroot/10/*
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/wwwroot/20
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/wwwroot/20/*
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/wwwroot/30
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/wwwroot/30/*
[root@linuxprobe~]# restorecon -Rv /home/wwwroot
Relabeled /home/wwwroot from unconfined_u:object_r:user_home_dir_t:s0 to
unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /home/wwwroot/10 from unconfined_u:object_r:user_home_t:s0 to unconfined_
u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /home/wwwroot/10/index.html from unconfined_u:object_r:user_home_t:s0
to unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /home/wwwroot/20 from unconfined_u:object_r:user_home_t:s0 to unconfined_
u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /home/wwwroot/20/index.html from unconfined_u:object_r:user_home_t:s0
to unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /home/wwwroot/30 from unconfined_u:object_r:user_home_t:s0 to
unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /home/wwwroot/30/index.html from unconfined_u:object_r:user_home_t:
s0 to unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
[root@linuxprobe~]# firefox 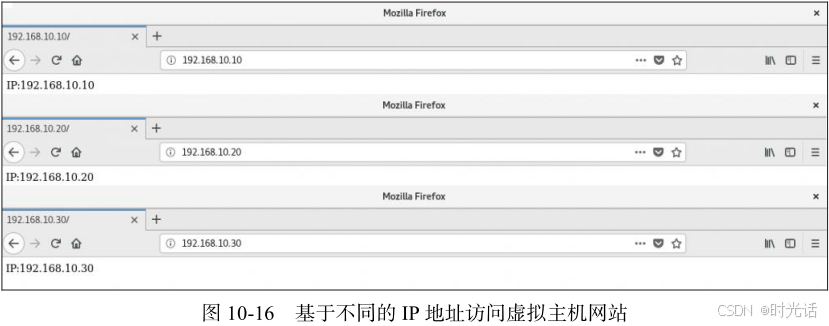
5.2 基于主机域名
当服务器无法为每个网站都分配一个独立 IP 地址的时候,可以尝试让 Apache 自动识别用户请求的域名,从而根据不同的域名请求来传输不同的内容。在这种情况下的配置更加简单,只需要保证位于生产环境中的服务器上有一个可用的 IP 地址(这里以 192.168.10.10 为例)就可以了。由于当前还没有介绍如何配置 DNS 解析服务,因此需要手动定义 IP 地址与域名之间的对应关系。/etc/hosts 是 Linux 系统中用于强制把某个主机域名解析到指定 IP 地址的配置文件。简单来说,只要这个文件配置正确,即使网络参数中没有 DNS 信息也依然能够将域名解析为某个 IP 地址。
**第一步:**手动定义 IP 地址与域名之间对应关系的配置文件,保存并退出后会立即生效。可以通过分别 ping 这些域名来验证域名是否已经成功解析为 IP 地址。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# vim /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.10.10 www.linuxprobe.com www.linuxcool.com www.linuxd
own.com
[root@linuxprobe~]# ping -c 4 www.linuxprobe.com
PING www.linuxprobe.com (192.168.10.10) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from www.linuxprobe.com (192.168.10.10): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.070 ms
64 bytes from www.linuxprobe.com (192.168.10.10): icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.077 ms
64 bytes from www.linuxprobe.com (192.168.10.10): icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.061 ms
64 bytes from www.linuxprobe.com (192.168.10.10): icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.069 ms
--- www.linuxprobe.com ping statistics ---
4 packets transmitted, 4 received, 0% packet loss, time 2999ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.061/0.069/0.077/0.008 ms
[root@linuxprobe~]# **第二步:**分别在/home/wwwroot 中创建用于保存不同网站数据的 3 个目录,并向其中分别写入网站的首页文件。每个首页文件中应有明确区分不同网站内容的信息,方便稍后能更直观地检查效果。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# mkdir -p /home/wwwroot/linuxprobe
[root@linuxprobe~]# mkdir -p /home/wwwroot/linuxcool
[root@linuxprobe~]# mkdir -p /home/wwwroot/linuxdown
[root@linuxprobe~]# echo "www.linuxprobe.com" > /home/wwwroot/linuxprobe/index.html
[root@linuxprobe~]# echo "www.linuxcool.com" > /home/wwwroot/linuxcool/index.html
[root@linuxprobe~]# echo "www.linuxdown.com" > /home/wwwroot/linuxdown/index.html 第三步: 从 httpd 服务的配置文件中大约第 132 行处开始,分别追加写入 3 个基于主机名的虚拟主机网站参数,然后保存并退出。记得需要重启 httpd 服务,这些配置才生效。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
..................省略部分输出信息..................
132 <VirtualHost 192.168.10.10>
133 Documentroot /home/wwwroot/linuxprobe
134 ServerName www.linuxprobe.com
135 <Directory /home/wwwroot/linuxprobe>
136 AllowOverride None
137 Require all granted
138 </Directory>
139 </VirtualHost>
140 <VirtualHost 192.168.10.10>
141 Documentroot /home/wwwroot/linuxcool
142 ServerName www.linuxcool.com
143 <Directory /home/wwwroot/linuxcool>
144 AllowOverride None
145 Require all granted
146 </Directory>
147 </VirtualHost>
148 <VirtualHost 192.168.10.10>
149 Documentroot /home/wwwroot/linuxdown
150 ServerName www.linuxdown.com
151 <Directory /home/wwwroot/linuxdown>
152 AllowOverride None
153 Require all granted
154 </Directory>
155 </VirtualHost>
..................省略部分输出信息..................
[root@linuxprobe~]# systemctl restart httpd **第四步:**因为当前的网站数据目录还是在/home/wwwroot 目录中,因此还是必须要正确设置网站数据目录文件的 SELinux 安全上下文,使其与网站服务功能相吻合。最后记得用restorecon 命令让新配置的 SELinux 安全上下文立即生效,这样就可以立即访问到虚拟主机网站了,效果如图 所示。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/wwwroot
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/wwwroot/linuxprobe
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/wwwroot/linuxprobe/*
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/wwwroot/linuxcool
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/wwwroot/linuxcool/*
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/wwwroot/linuxdown
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/wwwroot/linuxdown/*
[root@linuxprobe~]# restorecon -Rv /home/wwwroot
Relabeled /home/wwwroot from unconfined_u:object_r:user_home_dir_t:s0 to unconfined_
u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /home/wwwroot/linuxprobe from unconfined_u:object_r:user_home_t:s0 to
unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /home/wwwroot/linuxprobe/index.html from unconfined_u:object_r:user_
home_t:s0 to unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /home/wwwroot/linuxcool from unconfined_u:object_r:user_home_t:s0 to
unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /home/wwwroot/linuxcool/index.html from unconfined_u:object_r:user_home_
t:s0 to unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /home/wwwroot/linuxdown from unconfined_u:object_r:user_home_t:s0 to
unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /home/wwwroot/linuxdown/index.html from unconfined_u:object_r:user_
home_t:s0 to unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
[root@linuxprobe~]# firefox 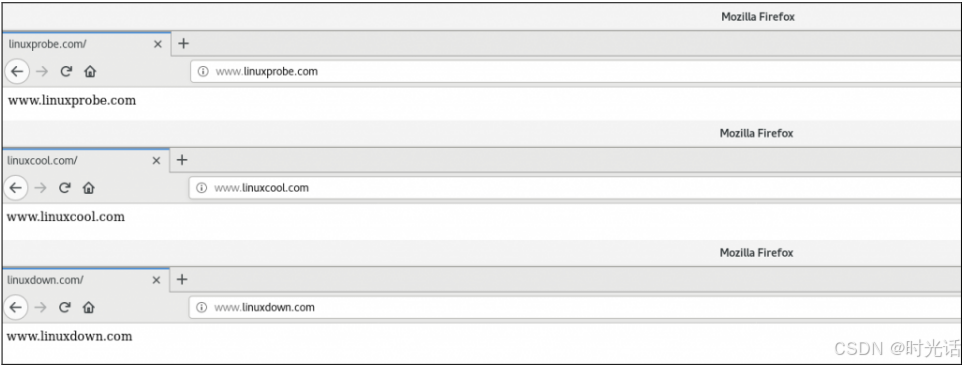
5.3 基于端口号
基于端口号的虚拟主机功能可以让用户通过指定的端口号来访问服务器上的网站资源。在使用 Apache 配置虚拟网站主机功能时,基于端口号的配置方式是最复杂的。因此我们不仅要考虑 httpd 服务程序的配置因素,还需要考虑到 SELinux 服务对新开设端口的监控。一般来说,使用 80、443、8080 等端口号来提供网站访问服务是比较合理的,如果使用其他端口号则会受到 SELinux 服务的限制。
在接下来的实验中,我们不但要考虑到目录上应用的 SELinux 安全上下文的限制,还需要考虑 SELinux 域对 httpd 服务程序的管控。
**第一步:**分别在/home/wwwroot 中创建用于保存不同网站数据的 3 个目录,并向其中分别写入网站的首页文件。每个首页文件中应有明确区分不同网站内容的信息,方便稍后能更直观地检查效果。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# mkdir -p /home/wwwroot/6111
[root@linuxprobe~]# mkdir -p /home/wwwroot/6222
[root@linuxprobe~]# mkdir -p /home/wwwroot/6333
[root@linuxprobe~]# echo "port:6111" > /home/wwwroot/6111/index.html
[root@linuxprobe~]# echo "port:6222" > /home/wwwroot/6222/index.html
[root@linuxprobe~]# echo "port:6333" > /home/wwwroot/6333/index.html **第二步:**在 httpd 服务配置文件的第 46 行~48 行分别添加用于监听 6111、6222 和 6333端口的参数。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
..................省略部分输出信息..................
37 # Listen: Allows you to bind Apache to specific IP addresses and/or
38 # ports, instead of the default. See also the
39 # directive.
40 #
41 # Change this to Listen on specific IP addresses as shown below to
42 # prevent Apache from glomming onto all bound IP addresses.
43 #
44 #Listen 12.34.56.78:80
45 Listen 80
46 Listen 6111
47 Listen 6222
48 Listen 6333
..................省略部分输出信息.................. **第三步:**从 httpd 服务的配置文件中大约第 134 行处开始,分别追加写入 3 个基于端口号的虚拟主机网站参数,然后保存并退出。记得需要重启 httpd 服务,这些配置才生效。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
..................省略部分输出信息..................
134 <VirtualHost 192.168.10.10:6111>
135 DocumentRoot /home/wwwroot/6111
136 ServerName www.linuxprobe.com
137 <Directory /home/wwwroot/6111>
138 AllowOverride None
139 Require all granted
140 </Directory>
141 </VirtualHost>
142 <VirtualHost 192.168.10.10:6222>
143 DocumentRoot /home/wwwroot/6222
144 ServerName www.linuxcool.com
145 <Directory /home/wwwroot/6222>
146 AllowOverride None
147 Require all granted
148 </Directory>
149 </VirtualHost>
150 <VirtualHost 192.168.10.10:6333>
151 DocumentRoot /home/wwwroot/6333
152 ServerName www.linuxdown.com
153 <Directory /home/wwwroot/6333>
154 AllowOverride None
155 Require all granted
156 </Directory>
157 </VirtualHost>
..................省略部分输出信息.................. **第四步:**因为我们把网站数据目录存放在/home/wwwroot 目录中,因此还是必须要正确设置网站数据目录文件的 SELinux 安全上下文,使其与网站服务功能相吻合。最后记得用restorecon 命令让新配置的 SELinux 安全上下文立即生效。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/wwwroot
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/wwwroot/6111
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/wwwroot/6111/*
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/wwwroot/6222
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/wwwroot/6222/*
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/wwwroot/6333
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t /home/wwwroot/6333/*
[root@linuxprobe~]# restorecon -Rv /home/wwwroot/
Relabeled /home/wwwroot from unconfined_u:object_r:user_home_dir_t:s0 to
unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /home/wwwroot/6111 from unconfined_u:object_r:user_home_t:s0 to
unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /home/wwwroot/6111/index.html from unconfined_u:object_r:user_home_t:
s0 to unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /home/wwwroot/6222 from unconfined_u:object_r:user_home_t:s0 to
unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /home/wwwroot/6222/index.html from unconfined_u:object_r:user_home_t:
s0 to unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /home/wwwroot/6333 from unconfined_u:object_r:user_home_t:s0 to
unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
Relabeled /home/wwwroot/6333/index.html from unconfined_u:object_r:user_home_t:
s0 to unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
[root@linuxprobe~]# systemctl restart httpd
Job for httpd.service failed because the control process exited with error code.
See "systemctl status httpd.service" and "journalctl -xe" for details. 在妥当配置 httpd 服务程序和 SELinux 安全上下文并重启 httpd 服务后,竟然出现报错信息。这是因为 SELinux 服务检测到 6111、6222 和 6333 端口原本不属于 Apache 服务应该需要的资源,但现在却以 httpd 服务程序的名义监听使用了,所以 SELinux 会拒绝使用Apache 服务使用这 3 个端口。可以使用 semanage 命令查询并过滤出所有与 HTTP 协议相关且SELinux 服务允许的端口列表。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage port -l | grep http
http_cache_port_t tcp 8080, 8118, 8123, 10001-10010
http_cache_port_t udp 3130
http_port_t tcp 80, 81, 443, 488, 8008, 8009, 8443
, 9000
pegasus_http_port_t tcp 5988
pegasus_https_port_t tcp 5989 第五步:SELinux 允许的与 HTTP 协议相关的端口号中默认没有包含 6111、6222 和 6333,因此需要将这 3 个端口号手动添加进去。该操作会立即生效,而且在系统重启过后依然有效。设置好后再重启 httpd 服务程序,然后就可以看到网页内容了,结果如图所示。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage port -a -t http_port_t -p tcp 6111
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage port -a -t http_port_t -p tcp 6222
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage port -a -t http_port_t -p tcp 6333
[root@linuxprobe~]# semanage port -l | grep http
http_cache_port_t tcp 8080, 8118, 8123, 10001-10010
http_cache_port_t udp 3130
http_port_t tcp 6333, 6222, 6111, 80, 81, 443, 488, 8
008,
8009, 8443, 9000
pegasus_http_port_t tcp 5988
pegasus_https_port_t tcp 5989
[root@linuxprobe~]# systemctl restart httpd
[root@linuxprobe~]# firefox 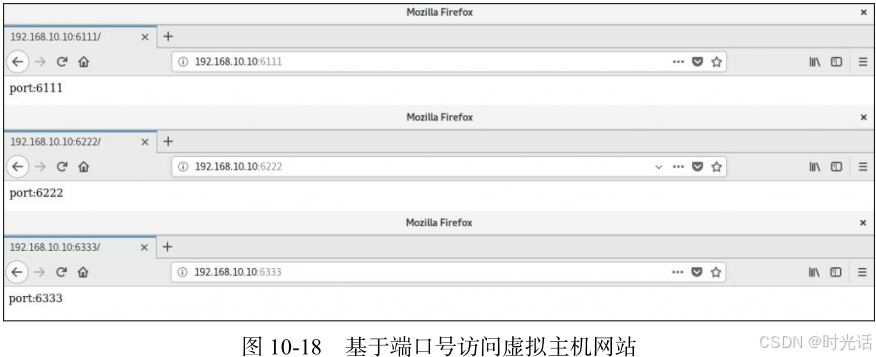
6. Apache 的访问控制
Apache 可以基于源主机名、源 IP 地址或源主机上的浏览器特征等信息对网站上的资源进行访问控制。它通过 Allow 指令允许某个主机访问服务器上的网站资源,通过 Deny 指令实现禁止访问。在允许或禁止访问网站资源时,还会用到 Order 指令,这个指令用来定义 Allow或 Deny 指令起作用的顺序,其匹配原则是按照顺序进行匹配,若匹配成功则执行后面的默认指令。比如"Order Allow, Deny"表示先将源主机与允许规则进行匹配,若匹配成功则允许访问请求,反之则拒绝访问请求。
第一步:先在服务器上的网站数据目录中新建一个子目录,并在这个子目录中创建一个包含 Successful 单词的首页文件。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# mkdir /var/www/html/server
[root@linuxprobe~]# echo "Successful" > /var/www/html/server/index.html 第二步:打开 httpd 服务的配置文件,在第 161 行后面添加下述规则来限制源主机的访问。这段规则的含义是允许使用 Firefox 浏览器的主机访问服务器上的首页文件,除此之外的所有请求都将被拒绝。使用 Firefox 浏览器的访问效果如图 10-19 所示,使用其他浏览器的访问效果如图 10-20 所示。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
..................省略部分输出信息..................
161 <Directory "/var/www/html/server">
162 SetEnvIf User-Agent "Firefox" ff=1
163 Order allow,deny
164 Allow from env=ff
165 </Directory>
..................省略部分输出信息..................
[root@linuxprobe~]# systemctl restart httpd
[root@linuxprobe~]# firefox 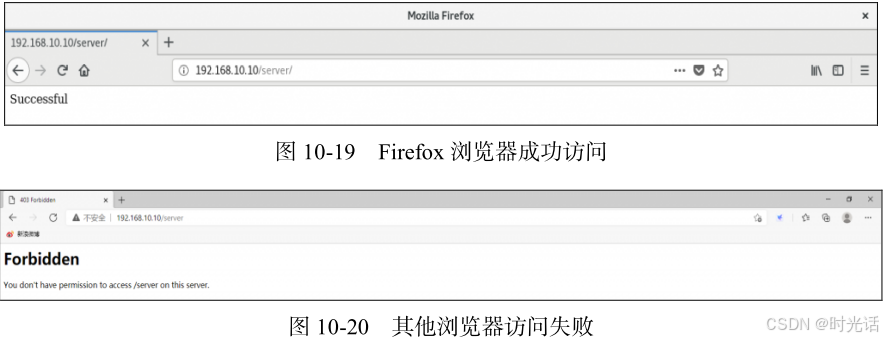
除了匹配源主机的浏览器特征之外,还可以通过匹配源主机的 IP 地址进行访问控制。例如,我们只允许 IP 地址为 192.168.10.20 的主机访问网站资源,那么就可以在 httpd 服务配置文件的第 161 行后面添加下述规则。这样在重启 httpd 服务程序后再用本机(即服务器,其 IP 地址为 192.168.10.10)来访问网站的首页面时就会提示访问被拒绝了,如图所示。
bash
[root@linuxprobe~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
..................省略部分输出信息..................
161 <Directory "/var/www/html/server">
162 Order allow,deny
163 Allow from 192.168.10.20
164 </Directory>
..................省略部分输出信息..................
[root@linuxprobe~]# systemctl restart httpd
[root@linuxprobe~]# firefox