NIO群聊系统demo示例
基本框架:
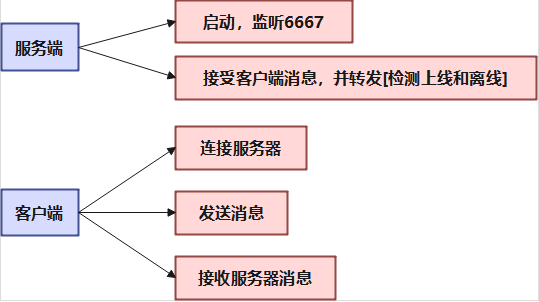
一、服务端
服务端代码
java
package nio.groupchat;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class MyServer {
//定义属性
private Selector selector;
//做监听的
private ServerSocketChannel listenChannel;
public static final int Port = 6667;
//构造器
//初始化
public MyServer(){
try{
//得到选择器
selector = Selector.open();
//
listenChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//bind port
listenChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(Port));
//set 非阻塞
listenChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//将listener注册到selector
listenChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void listen(){
try {
//循环
while(true){
int count = selector.select(2000);
if(count>0){//event come
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
//取出selectorkey
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
//listened accept
if(key.isAcceptable()){
SocketChannel socketChannel = listenChannel.accept();
//将该sc注册到select上面
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
System.out.println(socketChannel.getRemoteAddress()+"上线");
}
if(key.isReadable()){//channel is readable
//del reading
readData(key);
}
//delete current key
iterator.remove();
}
}else {
System.out.println("waiting......");
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
}
}
//读取客户端消息
private void readData(SelectionKey key){
//取到关联的channel
SocketChannel socketChannel = null;
try {
socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
//创建buffer
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int count = socketChannel.read(buffer);
if(count>0){//得到数据
String msg = new String(buffer.array());
//输出
System.out.println("from client:"+msg);
//向其他客户端转发消息
sendInfoToOtherClients(msg,socketChannel);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
try {
System.out.println(socketChannel.getRemoteAddress()+"离线了");
//取消注册
key.cancel();
//关闭通道
socketChannel.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
} finally {
}
}
//转发消息给其他的通道
private void sendInfoToOtherClients(String msg,SocketChannel self) throws IOException {
//遍历所有注册到seleector上的socketchannel 排除self
for (SelectionKey key : selector.keys()) {
Channel target = key.channel();
//排除自己
if(target instanceof SocketChannel && target != self){
SocketChannel dest = (SocketChannel) target;
ByteBuffer wrap = ByteBuffer.wrap(msg.getBytes());
//将数据写入通道
dest.write(wrap);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个服务器
MyServer myServer = new MyServer();
myServer.listen();
}
}服务端流程分析
- 初始化 MyServer 类 :
- 在构造器中,创建了一个
Selector和一个ServerSocketChannel。 Selector是 NIO 的核心,用于管理多个Channel(如SocketChannel)的 I/O 操作。ServerSocketChannel被设置为非阻塞模式,并绑定到端口6667,以便监听客户端的连接请求。ServerSocketChannel被注册到Selector,并且监听的事件类型是OP_ACCEPT,即等待客户端连接。
- 在构造器中,创建了一个
- 监听客户端连接 :
- 在
listen()方法中,使用selector.select(2000)阻塞式地等待最多 2000 毫秒,直到有客户端的连接请求或数据读取请求到达。 - 如果有事件发生,调用
iterator()方法遍历selectedKeys中的所有SelectionKey,处理不同类型的事件。
- 在
- 处理客户端连接(
OP_ACCEPT) :- 当
SelectionKey的事件类型为OP_ACCEPT时,表示有新的客户端连接到达。服务器通过ServerSocketChannel.accept()接受连接,返回一个新的SocketChannel,用于与该客户端进行通信。 - 将新连接的
SocketChannel设置为非阻塞模式,并注册到selector,监听OP_READ事件,表示该通道可以读取数据。
- 当
- 读取客户端数据(
OP_READ) :- 当
SelectionKey的事件类型为OP_READ时,表示该通道有数据可以读取。调用readData(key)方法读取客户端发送过来的数据。 - 在
readData方法中,首先获取到与该SelectionKey关联的SocketChannel。然后通过socketChannel.read()方法读取数据,并将数据存入一个ByteBuffer中。 - 读取到的数据转为字符串后,打印出消息内容,并将该消息通过
sendInfoToOtherClients()方法转发给其他客户端。
- 当
- 消息转发 :
sendInfoToOtherClients()方法遍历所有注册到Selector上的SocketChannel(排除当前通道self),将接收到的消息发送到所有其他客户端。- 每个目标客户端的
SocketChannel被包装成ByteBuffer,然后通过write()方法发送数据。
- 客户端断开连接的处理 :
- 如果在
readData中读取数据时发生异常(如客户端断开连接),则会捕获IOException异常,表明客户端已经离线。 - 服务器通过
key.cancel()取消该SelectionKey的注册,关闭与客户端的SocketChannel连接。
- 如果在
代码流程概述
- 初始化 :服务器启动时,初始化
Selector和ServerSocketChannel,并绑定到指定端口6667。 - 客户端连接 :服务器通过
ServerSocketChannel接受来自客户端的连接请求,并为每个连接创建一个SocketChannel。 - 事件轮询:服务器进入循环,阻塞式地等待客户端事件(如连接请求或数据读取),并处理每个事件。
- 数据读取与转发:当有客户端发送消息时,服务器读取消息,并将消息转发给其他客户端。
- 断开连接处理:当客户端断开连接时,服务器关闭该客户端的连接。
二、客户端
客户端代码
java
package nio.groupchat;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Set;
public class MyClient {
//定义相关的属性
public static final String Host = "127.0.0.1";
public static int Port = 6667;
private Selector selector;
private SocketChannel socketChannel;
private String username;
//构造器
public MyClient() throws IOException {
//初始化
selector = Selector.open();
//连接服务器
socketChannel = socketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress(Host,Port));
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
username = socketChannel.getLocalAddress().toString().substring(1);
System.out.println(username+" is ok");
}
public void sendInfo(String info){
info = username + "说:" +info;
try {
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(info.getBytes()));
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
}
}
public void readInfo(){
try {
int readChannels = selector.select(2000);
if(readChannels>0){//有可用的通道
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
if(key.isReadable()){
//得到相关的通道
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
//得到一个buffer
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//读取
sc.read(buffer);
//把缓冲区的数据转成字符串
String msg = new String(buffer.array());
System.out.println(msg.trim());
}
}
iterator.remove();
}else {
//System.out.println("没有可用的通道");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//启动客户端
MyClient myClient = new MyClient();
//启动一个线程,每隔三秒读取数据
new Thread(){
@Override
public void run(){
while (true){
myClient.readInfo();
try {
Thread.currentThread().sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}.start();
//发送数据
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (scanner.hasNext()){
String s = scanner.nextLine();
myClient.sendInfo(s);
}
}
}客户端代码流程分析
1. 类和属性定义
Host和Port:客户端连接的服务器的 IP 地址和端口,Host设置为"127.0.0.1"(本地地址),Port设置为6667。selector:Selector用于管理客户端的 I/O 事件。socketChannel:SocketChannel用于与服务器建立连接并进行数据交换。username:客户端的用户名,由客户端的本地地址(即SocketChannel的地址)截取得出,用于标识客户端。
2. 构造器:MyClient()
Selector.open():创建一个新的Selector实例,用于管理多个通道。SocketChannel.open():打开一个SocketChannel实例,连接到服务器的指定Host和Port。socketChannel.configureBlocking(false):设置SocketChannel为非阻塞模式,这意味着 I/O 操作不会阻塞程序的执行。socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ):将SocketChannel注册到Selector上,并监听OP_READ事件,表示该通道有数据可读时会触发事件。username:通过客户端本地地址获取用户名,用于标识当前客户端。
3. sendInfo(String info) 方法
info = username + "说:" + info:将发送的信息格式化成"username 说:message"。socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(info.getBytes())):将格式化后的消息写入到SocketChannel中,发送给服务器。- 如果发生
IOException,抛出运行时异常。
4. readInfo() 方法
-
selector.select(2000):调用select()方法阻塞最多 2000 毫秒,等待可用的事件(如数据可读)。如果没有事件发生,继续等待。 -
if(readChannels > 0):如果有可读通道(即readChannels > 0),则开始处理。 -
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator():遍历所有的已就绪的SelectionKey。 -
if(key.isReadable()):如果
SelectionKey是可读的,表示
SocketChannel中有数据可读。
- 获取与该
SelectionKey关联的SocketChannel。 - 创建一个
ByteBuffer来存储读取的数据。 - 调用
socketChannel.read(buffer)从通道中读取数据。 - 将读取的字节数据转换为字符串并输出。
- 获取与该
5. 主方法:main(String[] args)
-
MyClient myClient = new MyClient():创建客户端实例并初始化连接。 -
启动一个线程
:启动一个新线程,每 3 秒钟读取一次服务器返回的消息。
myClient.readInfo():每次调用readInfo()从服务器获取并打印消息。Thread.sleep(3000):每 3 秒读取一次数据。
-
从命令行输入消息并发送
:
- 使用
Scanner获取用户的输入,用户输入的每一行消息会通过sendInfo()发送到服务器。
- 使用
代码流程概述
- 初始化客户端 :
- 客户端连接到服务器(
127.0.0.1:6667)。 - 设置
SocketChannel为非阻塞模式,注册到Selector上监听OP_READ事件。
- 客户端连接到服务器(
- 发送消息 :
- 用户输入消息后,客户端通过
SocketChannel.write()将消息发送到服务器。
- 用户输入消息后,客户端通过
- 读取消息 :
- 客户端通过一个独立线程每 3 秒轮询
Selector,检查是否有可读的通道。 - 当有数据可读时,从
SocketChannel读取数据并输出到控制台。
- 客户端通过一个独立线程每 3 秒轮询
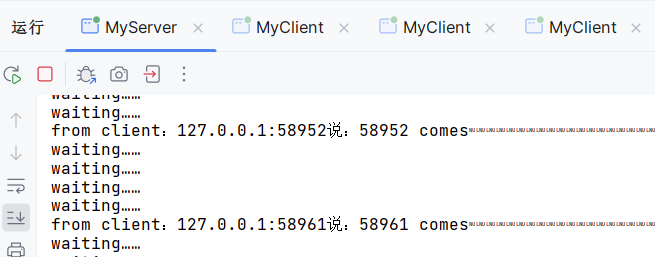
三、效果演示
客户端
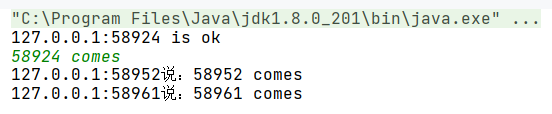
服务端