本专栏内容为:前端专栏 记录学习前端,分为若干个子专栏,html js css vue等
💓博主csdn个人主页:小小unicorn⏩专栏分类:css专栏
🚚代码仓库:小小unicorn的代码仓库🚚
🌹🌹🌹关注我带你学习编程知识
目录
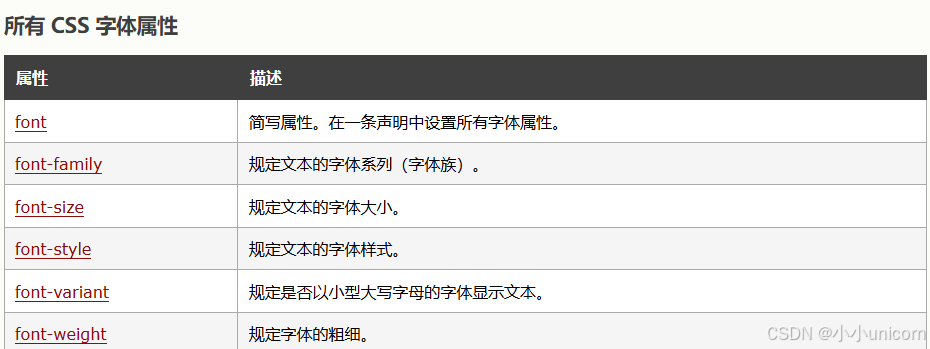
字体
为您的网站选择正确的字体很重要!
字体选择很重要
选择正确的字体会对网站的用户体验产生巨大影响。
正确的字体可以为您的品牌创造强有力的形象。
使用易于阅读的字体很重要。字体为您的文本增加了价值。为字体选择正确的颜色和文本大小也很重要。
通用字体族
在 CSS 中,有五个通用字体族:
- 衬线字体(Serif)- 在每个字母的边缘都有一个小的笔触。它们营造出一种形式感和优雅感。
- 无衬线字体(Sans-serif)- 字体线条简洁(没有小笔画)。它们营造出现代而简约的外观。
- 等宽字体(Monospace)- 这里所有字母都有相同的固定宽度。它们创造出机械式的外观。
- 草书字体(Cursive)- 模仿了人类的笔迹。
- 幻想字体(Fantasy)- 是装饰性/俏皮的字体。
所有不同的字体名称都属于这五个通用字体系列之一。
Serif 和 Sans-serif 字体之间的区别

提示:在计算机屏幕上,无衬线字体被认为比衬线字体更易于阅读。
一些字体的例子:

CSS font-family 属性
在 CSS 中,我们使用 font-family 属性规定文本的字体。
font-family 属性应包含多个字体名称作为"后备"系统,以确保浏览器/操作系统之间的最大兼容性。请以您需要的字体开始,并以通用系列结束(如果没有其他可用字体,则让浏览器选择通用系列中的相似字体)。字体名称应以逗号分隔。
注释:如果字体名称不止一个单词,则必须用引号引起来,例如:"Times New Roman"。
实例:
为三个段落规定不同的字体:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.p1 {
font-family: "Times New Roman", Times, serif;
}
.p2 {
font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
}
.p3 {
font-family: "Lucida Console", "Courier New", monospace;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>CSS font-family</h1>
<p>这是一个段落,以 Times New Roman 字体显示:</p>
<p class="p1">This is a paragraph, shown in the Times New Roman font.</p>
<p>这是一个段落,以 Arial 字体显示:</p>
<p class="p2">This is a paragraph, shown in the Arial font.</p>
<p>这是一个段落,以 Lucida Console 字体显示:</p>
<p class="p3">This is a paragraph, shown in the Lucida Console font.</p>
</body>
</html>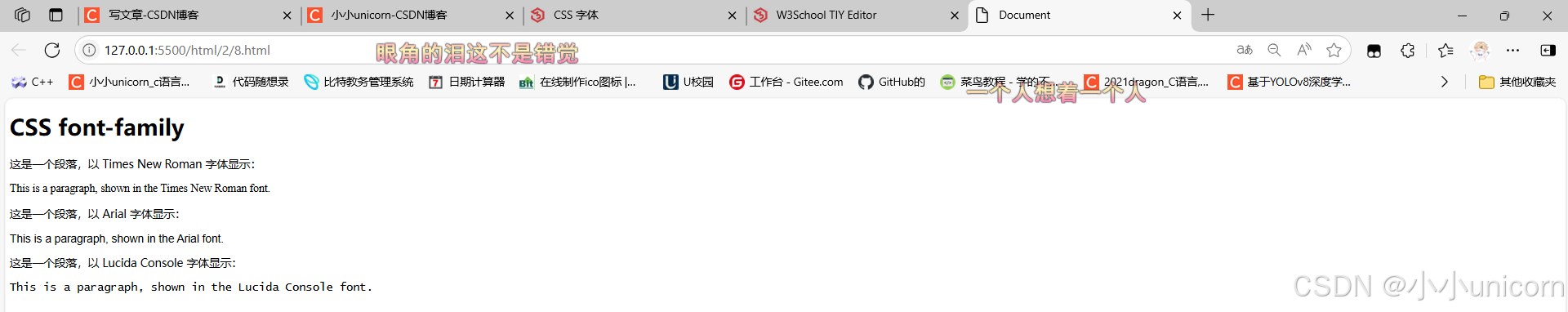
字体样式
font-style 属性主要用于指定斜体文本。
此属性可设置三个值:
normal- 文字正常显示italic- 文本以斜体显示oblique- 文本为"倾斜"(倾斜与斜体非常相似,但支持较少)
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.p1 {
font-family: "Times New Roman", Times, serif;
}
.p2 {
font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
}
.p3 {
font-family: "Lucida Console", "Courier New", monospace;
}
/* 正常显示 */
p.normal{
font-style: normal;
}
/* 斜体显示 */
p.italic{
font-style: italic;
}
/* 倾斜显示 */
p.oblique{
font-style: oblique;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>CSS font-family</h1>
<p>这是一个段落,以 Times New Roman 字体显示:</p>
<p class="p1">This is a paragraph, shown in the Times New Roman font.</p>
<p>这是一个段落,以 Arial 字体显示:</p>
<p class="p2">This is a paragraph, shown in the Arial font.</p>
<p>这是一个段落,以 Lucida Console 字体显示:</p>
<p class="p3">This is a paragraph, shown in the Lucida Console font.</p>
<p class="normal">This is a paragraph in normal style.</p>
<p class="italic">This is a paragraph in italic style.</p>
<p class="oblique">This is a paragraph in oblique style.</p>
</body>
</html>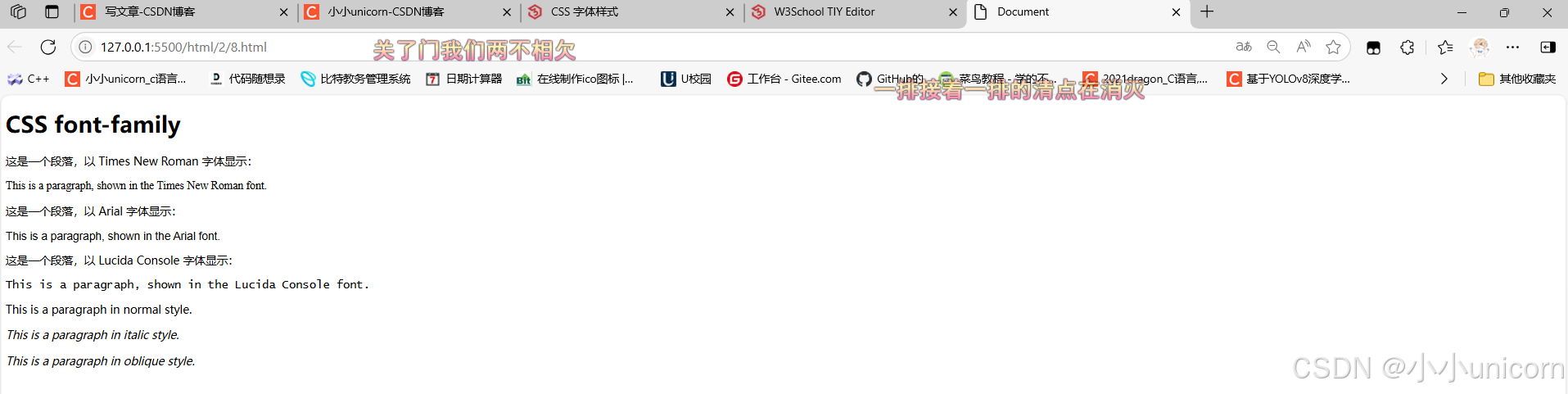
字体粗细
font-weight 属性指定字体的粗细:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.p1 {
font-family: "Times New Roman", Times, serif;
}
.p2 {
font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
}
.p3 {
font-family: "Lucida Console", "Courier New", monospace;
}
/* 正常显示 */
p.normal{
font-style: normal;
}
/* 斜体显示 */
p.italic{
font-style: italic;
}
/* 倾斜显示 */
p.oblique{
font-style: oblique;
}
/* 正常 */
p.normal {
font-weight: normal;
}
细
p.light {
font-weight: lighter;
}
粗
p.thick {
font-weight: bold;
}
p.thicker {
font-weight: 900;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>CSS font-family</h1>
<p>这是一个段落,以 Times New Roman 字体显示:</p>
<p class="p1">This is a paragraph, shown in the Times New Roman font.</p>
<p>这是一个段落,以 Arial 字体显示:</p>
<p class="p2">This is a paragraph, shown in the Arial font.</p>
<p>这是一个段落,以 Lucida Console 字体显示:</p>
<p class="p3">This is a paragraph, shown in the Lucida Console font.</p>
<p class="normal">This is a paragraph in normal style.</p>
<p class="italic">This is a paragraph in italic style.</p>
<p class="oblique">This is a paragraph in oblique style.</p>
<p class="normal">This is a paragraph.</p>
<p class="light">This is a paragraph.</p>
<p class="thick">This is a paragraph.</p>
<p class="thicker">This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>

字体变体
font-variant 属性指定是否以 small-caps 字体(小型大写字母)显示文本。
在 small-caps 字体中,所有小写字母都将转换为大写字母。但是,转换后的大写字母的字体大小小于文本中原始大写字母的字体大小。
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.p1 {
font-family: "Times New Roman", Times, serif;
}
.p2 {
font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
}
.p3 {
font-family: "Lucida Console", "Courier New", monospace;
}
/* 正常显示 */
p.normal{
font-style: normal;
}
/* 斜体显示 */
p.italic{
font-style: italic;
}
/* 倾斜显示 */
p.oblique{
font-style: oblique;
}
/* 正常 */
p.normal {
font-weight: normal;
}
p.light {
font-weight: lighter;
}
p.thick {
font-weight: bold;
}
p.thicker {
font-weight: 900;
}
p.normal1 {
font-variant: normal;
}
p.small1 {
font-variant: small-caps;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>CSS font-family</h1>
<p>这是一个段落,以 Times New Roman 字体显示:</p>
<p class="p1">This is a paragraph, shown in the Times New Roman font.</p>
<p>这是一个段落,以 Arial 字体显示:</p>
<p class="p2">This is a paragraph, shown in the Arial font.</p>
<p>这是一个段落,以 Lucida Console 字体显示:</p>
<p class="p3">This is a paragraph, shown in the Lucida Console font.</p>
<p class="normal">This is a paragraph in normal style.</p>
<p class="italic">This is a paragraph in italic style.</p>
<p class="oblique">This is a paragraph in oblique style.</p>
<p class="normal">This is a paragraph.</p>
<p class="light">This is a paragraph.</p>
<p class="thick">This is a paragraph.</p>
<p class="thicker">This is a paragraph.</p>
<p class="normal1">My name is Bill Gates.</p>
<p class="small1">My name is Bill Gates.</p>
</body>
</html>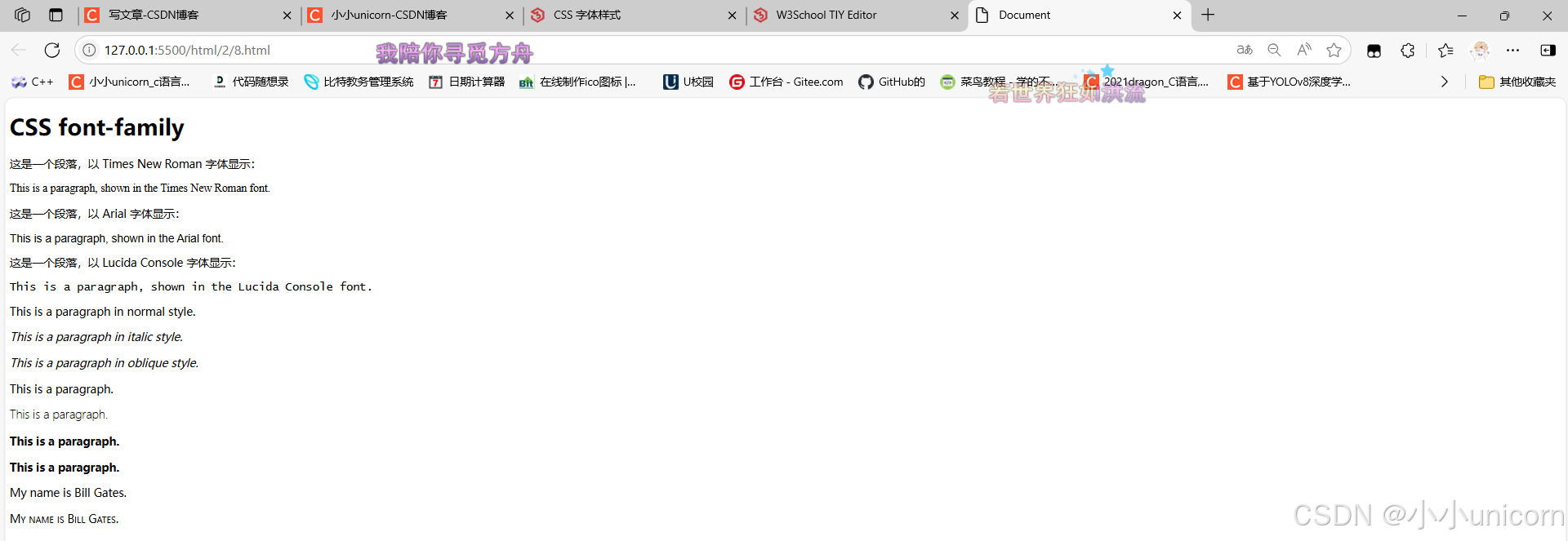
字体大小
font-size 属性设置文本的大小。
在网页设计中,能够管理文本大小很重要。但是,不应使用调整字体大小来使段落看起来像标题,或是使标题看起来像段落。
请始终使用正确的 HTML 标签,例如<h1> - <h6>用于标题,而 <p> 仅用于段落。
font-size 值可以是绝对或相对大小。
绝对尺寸:
- 将文本设置为指定大小
- 不允许用户在所有浏览器中更改文本大小(可访问性不佳)
- 当输出的物理尺寸已知时,绝对尺寸很有用
相对尺寸:
- 设置相对于周围元素的大小
- 允许用户在浏览器中更改文本大小
注释:如果您没有指定字体大小,则普通文本(如段落)的默认大小为 16px(16px = 1em)。
以像素设置字体大小
使用像素设置文本大小可以完全控制文本大小:
示例:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
h1 {
font-size: 40px;
}
h2 {
font-size: 30px;
}
p {
font-size: 14px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>这是标题 1</h1>
<h2>这是标题 2</h2>
<p>这是一个段落。</p>
<p>这是另一个段落。</p>
</body>
</html>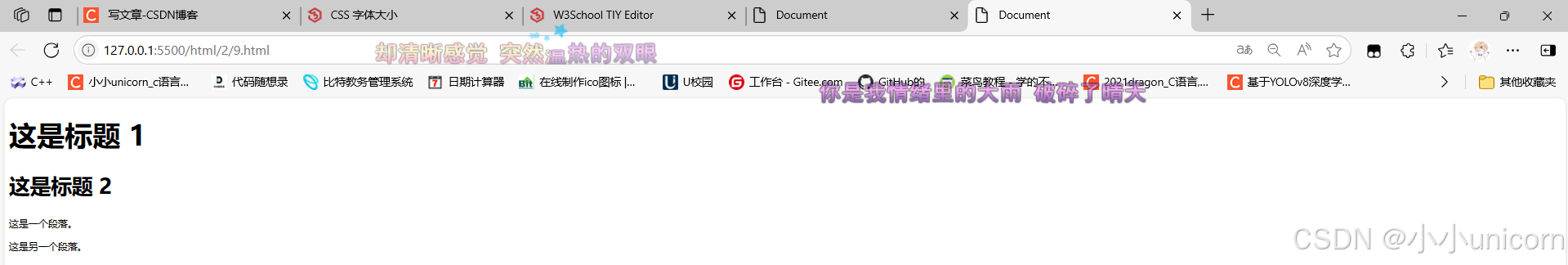
提示:如果您使用了像素,则仍然可以使用缩放工具来调整整个页面的大小。
用 em 设置字体大小
为了允许用户调整文本大小(在浏览器菜单中),许多开发人员使用 em 而不是像素。
W3C 建议使用 em 尺寸单位。
1em 等于当前字体大小。浏览器中的默认文本大小为 16px。因此,默认大小 1em 为 16px。
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
/* h1 { */
/* font-size: 40px;
}
h2 {
font-size: 30px;
}
p {
font-size: 14px;
} */
h1 {
font-size: 2.5em; /* 40px/16=2.5em */
}
h2 {
font-size: 1.875em; /* 30px/16=1.875em */
}
p {
font-size: 0.875em; /* 14px/16=0.875em */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>这是标题 1</h1>
<h2>这是标题 2</h2>
<p>这是一个段落。</p>
<p>这是另一个段落。</p>
<h1>这是标题 1</h1>
<h2>这是标题 2</h2>
<p>这是一个段落。</p>
<p>用 em 设置字体大小允许所有主要浏览器调整文本大小。不幸的是,旧版本的 IE 仍然存在问题。在调整文本大小时,会变得比原来更大或更小。</p>
</body>
</html>在上例中,em 单位的文本大小与上一个例子中的像素大小相同。但是,若使用 em 尺寸,则可以在所有浏览器中调整文本大小。
不幸的是,旧版本的Internet Explorer仍然存在问题。放大文本时它比应该大的尺寸更大,缩小文本时会更小。

使用百分比和 Em 的组合
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
font-size: 100%;
}
h1 {
font-size: 2.5em;
}
h2 {
font-size: 1.875em;
}
p {
font-size: 0.875em;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>这是标题 1</h1>
<h2>这是标题 2</h2>
<p>这是一个段落。</p>
<p>以 % 和 em 中设置字体大小会在所有主要浏览器中显示相同的大小,并允许所有浏览器调整文本大小!</p>
</body>
</html>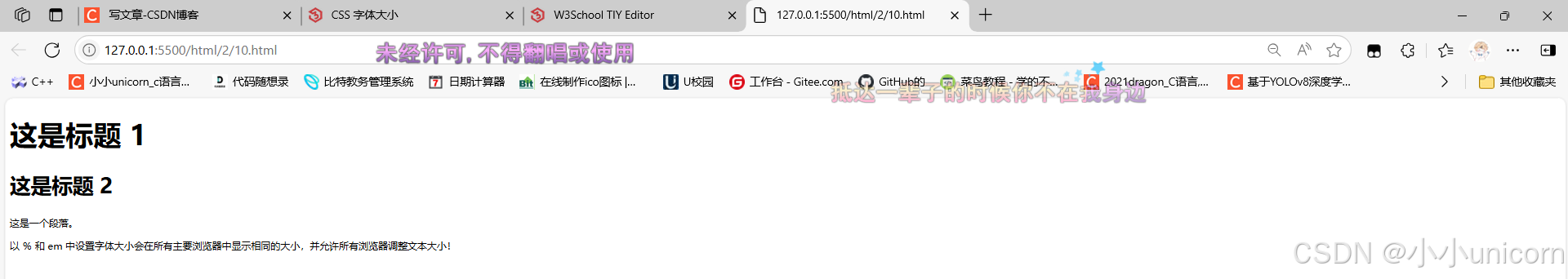
我们的代码目前运行良好!它在所有浏览器中显示相同的文本大小,并允许所有浏览器缩放或调整文本大小!
响应式字体大小
可以使用 vw 单位设置文本大小,它的意思是"视口宽度"("viewport width")。
这样,文本大小将遵循浏览器窗口的大小,请调整浏览器窗口的大小,以查看字体大小如何缩放:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 style="font-size:10vw;">响应式文本</h1>
<p style="font-size:5vw;">请调整浏览器窗口的大小,以查看文本大小如何缩放。</p>
<p style="font-size:5vw;">调整文本大小时,请使用 "vw" 单位。 10vw 将尺寸设置为视口宽度的 10%。</p>
<p>视口是浏览器窗口的大小。 1vw = 视口宽度的 1%。如果视口为 50 厘米宽,则 1vw 为 0.5 厘米。</p>
</body>
</html>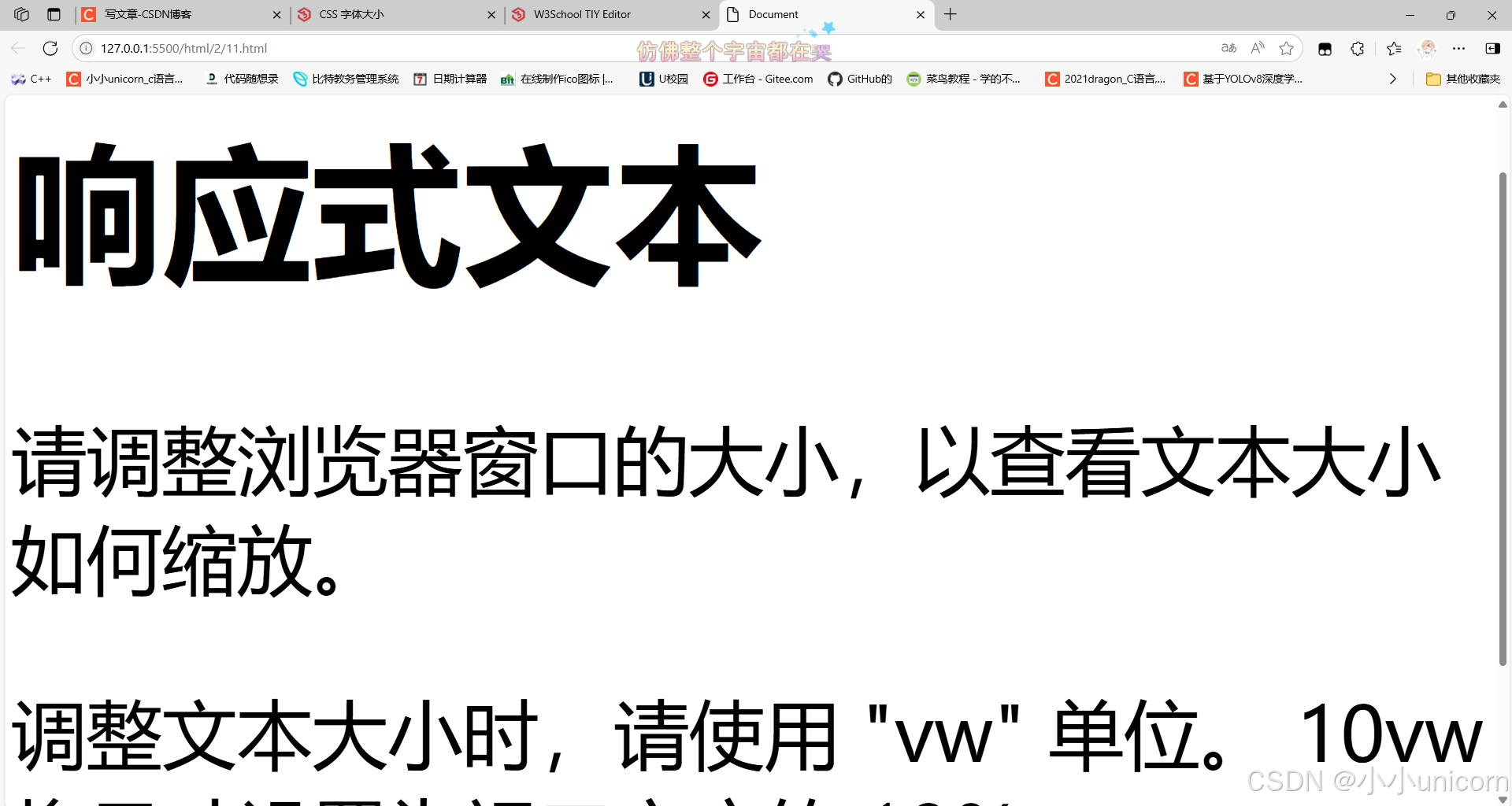
视口(Viewport)是浏览器窗口的大小。1vw= 视口宽度的 1%。如果视口为 50 厘米宽,则 1vw 为 0.5 厘米。
谷歌字体
如果您不想使用 HTML 中的任何标准字体,则可以使用Google Fonts API向页面添加数百种其他字体。
只需添加一个样式表链接并引用您选择的字体系列:
示例:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Sofia">
<style>
body {
font-family: "Sofia";
font-size: 22px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 style="font-size:0.5vw;">响应式文本</h1>
<p style="font-size:5vw;">请调整浏览器窗口的大小,以查看文本大小如何缩放。</p>
<p style="font-size:5vw;">调整文本大小时,请使用 "vw" 单位。 10vw 将尺寸设置为视口宽度的 10%。</p>
<p>视口是浏览器窗口的大小。 1vw = 视口宽度的 1%。如果视口为 50 厘米宽,则 1vw 为 0.5 厘米。</p>
<h1>Sofia Font</h1>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit.</p>
</body>
</html>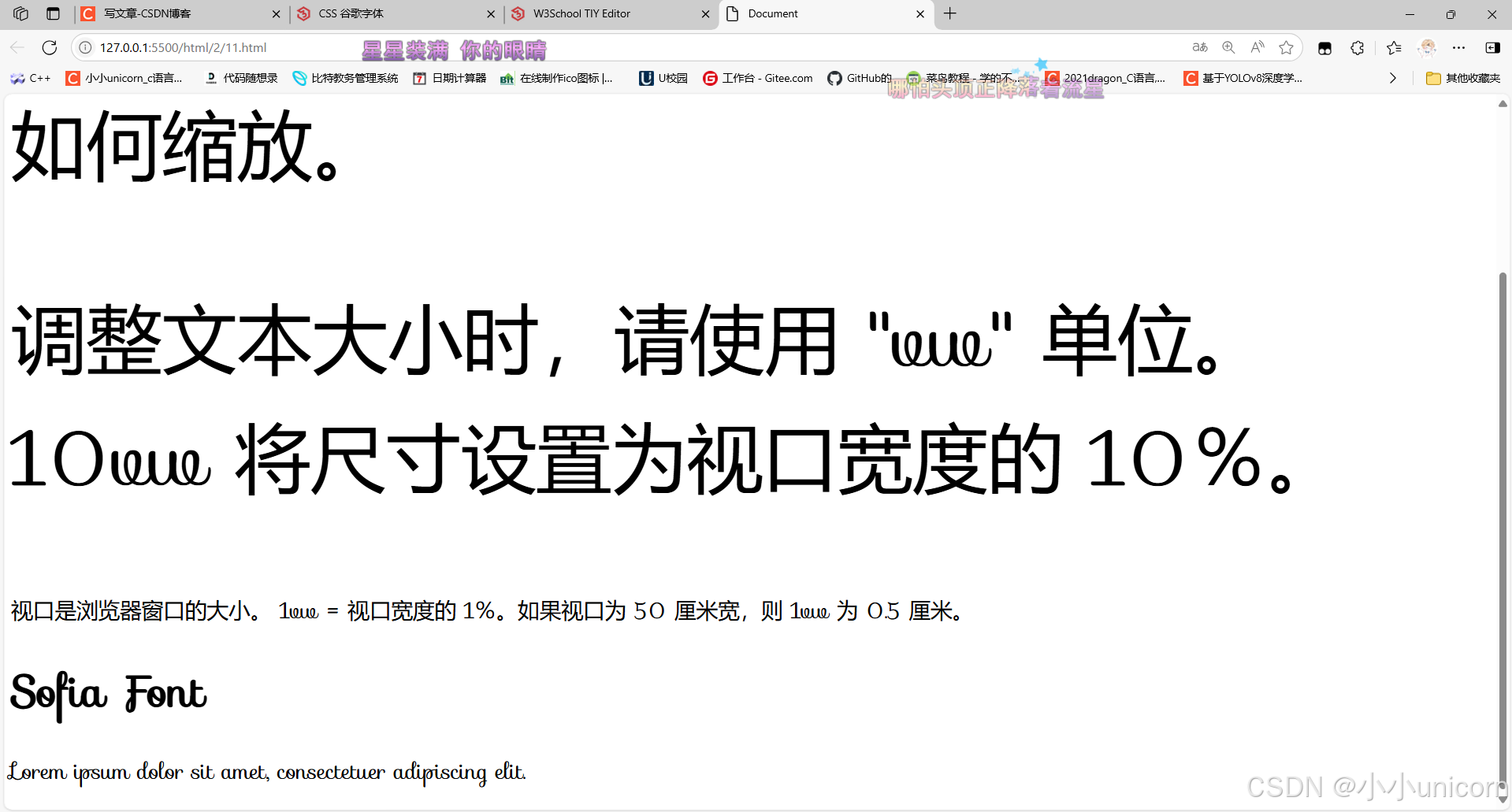
简写字体属性
字体属性
为了缩短代码,也可以在一个属性中指定所有单个字体属性。
font 属性是以下属性的简写属性:
使用简写声明设置一些字体属性:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Sofia">
<style>
/* body {
font-family: "Sofia";
font-size: 22px;
} */
p.a {
font: 20px Arial, sans-serif;
}
p.b {
font: italic bold 12px/30px Georgia, serif;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- <h1 style="font-size:0.5vw;">响应式文本</h1>
<p style="font-size:5vw;">请调整浏览器窗口的大小,以查看文本大小如何缩放。</p>
<p style="font-size:5vw;">调整文本大小时,请使用 "vw" 单位。 10vw 将尺寸设置为视口宽度的 10%。</p>
<p>视口是浏览器窗口的大小。 1vw = 视口宽度的 1%。如果视口为 50 厘米宽,则 1vw 为 0.5 厘米。</p>
<h1>Sofia Font</h1>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit.</p> -->
<h1>字体属性</h1>
<p class="a">这是一个段落 字体大小设置为20px, 字体为: Arial.</p>
<p class="b">这是一个段落. 字体设置为斜体并且粗, 大小为12px, 高度为30px, 字体为:Georgia.</p>
</body>
</html>
注意:font-size 和 font-family 的值是必需的。如果缺少其他值之一,则会使用其默认值。