1 前言
相较于 C# 中的协程(详见 → 【Unity3D】协同程序),Kotlin 中协程更灵活,难度更大。
协程是一种并发设计模式,用于简化异步编程,它允许以顺序化的方式表达异步操作,避免回调地狱等问题。使用协程,可以将异步操作的代码像同步代码一样写,而无需显式地管理线程。
在 Kotlin 中,协程由 kotlinx.coroutines 库提供支持。它使用 suspend 修饰符来标记挂起函数(即可暂停执行并稍后恢复执行的函数),这使得编写异步代码更加直观和简单。
协程和线程具有以下异同点。
1)并发模型
- 线程:线程是操作系统提供的执行单位,一个进程可以拥有多个线程,线程之间相对独立,数据共享需要通过特殊手段(如锁)保证安全。
- 协程:协程是一种用户态的轻量级线程,由开发者控制其运行与暂停,可以在同一线程上并发执行,通过挂起和恢复的方式,实现非阻塞的并发。
2)资源消耗
- 线程:每个线程都需要分配一定的内存和系统资源,线程切换时会有一定的开销。
- 协程:协程是用户级的,由协程调度器(Coroutine Dispatcher)调度,通常会复用较少的系统资源,因此更轻量级。
3)编程模型
- 线程:多线程编程通常以共享状态和锁为基础,编写并发代码较为复杂。
- 协程:协程提供了一种结构化并发编程的方式,通过挂起函数的调用实现代码的暂停和恢复,使得异步编程更易于理解和维护。
4)错误处理
- 线程:多线程编程中,错误处理相对困难,需要开发者手动处理异常和线程间的通信。
- 协程:协程提供了更加简单和一致的错误处理方式,通过结构化的异常处理机制,可以轻松处理协程中的异常。
5)性能
- 线程:创建和管理线程可能会带来较大的开销,尤其是在大量线程同时运行时,线程切换的开销也会比较高。
- 协程:协程由于是轻量级的用户级线程,资源消耗较少,因此在大规模并发场景下可能表现更优。
总的来说,协程相比于传统的线程模型,更加灵活、轻量级,并且提供了更加简单和结构化的并发编程方式,使得异步编程更加容易和优雅。
2 协程相关类图

3 协程源码
3.1 协程作用域源码(CoroutinueScope)
协程的作用域定义了协程的作用域范围,当该作用域被销毁时,其中的协程也会被取消。协程的作用阈主要有 CoroutineScope、MainScope、GlobalScope、lifecycleScope 、viewModelScope,主要区别如下。
- CoroutineScope:CoroutineScope 是通用的协程作用域,用于定义协程的作用域范围,当该作用域被销毁时,其中的协程也会被取消。
- MainScope:MainScope 是 Kotlin 中提供的特定于 Android 的协程作用域,用于在 Android 主线程上启动协程,通常在 Android 的 Activity 或 Fragment 中使用 MainScope,以确保在主线程上运行协程,并在相关生命周期结束时取消协程。
- GlobalScope:GlobalScope 是 Kotlin 中提供的一个全局协程作用域,它是一个顶层对象,用户可以在任何地方使用 GlobalScope 启动协程,但不推荐在 Android 中使用它,因为它的生命周期很长,并且不受管理,可能导致内存泄漏等问题。
- lifecycleScope:lifecycleScope 是 Android Jetpack 中的 Lifecycle 模块提供的一个扩展属性,它的生命周期与相关的组件(如 Activity 或 Fragment)的生命周期绑定,从而避免内存泄漏等问题。
- viewModelScope:viewModelScope 是 Android Jetpack 中 Lifecycle 模块提供的一个扩展属性,它的生命周期与 ViewModel 的生命周期绑定,从而避免内存泄漏等问题。
3.1.1 CoroutineScope
Kotlin
public fun CoroutineScope(context: CoroutineContext): CoroutineScope =
ContextScope(if (context[Job] != null) context else context + Job()) 说明:CoroutineScope 是通用的协程作用域,用于定义协程的作用域范围,当该作用域被销毁时,其中的协程也会被取消。
3.1.2 MainScope
Kotlin
public fun MainScope(): CoroutineScope = ContextScope(SupervisorJob() + Dispatchers.Main) 说明:MainScope 是 Kotlin 中提供的特定于 Android 的协程作用域,用于在 Android 主线程上启动协程,通常在 Android 的 Activity 或 Fragment 中使用 MainScope,以确保在主线程上运行协程,并在相关生命周期结束时取消协程。
3.1.3 GlobalScope
Kotlin
public object GlobalScope : CoroutineScope 说明:GlobalScope 是 Kotlin 中提供的一个全局协程作用域,它是一个顶层对象,用户可以在任何地方使用 GlobalScope 启动协程,但不推荐在 Android 中使用它,因为它的生命周期很长,并且不受管理,可能导致内存泄漏等问题。GlobalScope 是一个单例,其作用域的生命周期跟随应用程序的生命周期,中间不能取消(cancel)。
3.1.4 lifecycleScope
Kotlin
public val LifecycleOwner.lifecycleScope: LifecycleCoroutineScope
get() = lifecycle.coroutineScope
// -----------------------------------------------------------
public val Lifecycle.coroutineScope: LifecycleCoroutineScope
get() {
while (true) {
val existing = mInternalScopeRef.get() as LifecycleCoroutineScopeImpl?
if (existing != null) {
return existing
}
val newScope = LifecycleCoroutineScopeImpl(this,
SupervisorJob() + Dispatchers.Main.immediate
)
if (mInternalScopeRef.compareAndSet(null, newScope)) {
newScope.register()
return newScope
}
}
}
// -----------------------------------------------------------
internal class LifecycleCoroutineScopeImpl(
override val lifecycle: Lifecycle,
override val coroutineContext: CoroutineContext
) : LifecycleCoroutineScope(), LifecycleEventObserver
// -----------------------------------------------------------
public abstract class LifecycleCoroutineScope internal constructor() : CoroutineScope 说明:lifecycleScope 是 Android Jetpack 中的 Lifecycle 模块提供的一个扩展属性,它的生命周期与相关的组件(如 Activity 或 Fragment)的生命周期绑定,从而避免内存泄漏等问题。
使用 lifecycleScope 时,需要在 build.gradle 中引入以下依赖。
Kotlin
implementation "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-runtime-ktx:2.5.1" 并导入包名。
Kotlin
import androidx.lifecycle.lifecycleScope AppCompatActivity、FragmentActivity 与 LifecycleOwner 存在以下继承关系。因此可以在 AppCompatActivity 和 FragmentActivity 中直接访问 lifecycleScope。
java
AppCompatActivity → FragmentActivity → ComponentActivity → LifecycleOwner3.1.5 viewModelScope
Kotlin
public val ViewModel.viewModelScope: CoroutineScope
get() {
val scope: CoroutineScope? = this.getTag(JOB_KEY)
if (scope != null) {
return scope
}
return setTagIfAbsent(JOB_KEY,
CloseableCoroutineScope(SupervisorJob() + Dispatchers.Main.immediate)
)
}
// --------------------------------------------------------------------------
internal class CloseableCoroutineScope(context: CoroutineContext) : Closeable, CoroutineScope {
override val coroutineContext: CoroutineContext = context
override fun close() {
coroutineContext.cancel()
}
} 说明:viewModelScope 是 Android Jetpack 中 Lifecycle 模块提供的一个扩展属性,它的生命周期与 ViewModel 的生命周期绑定,从而避免内存泄漏等问题。
使用 viewModelScope 时,需要在 build.gradle 中引入以下依赖。
Kotlin
implementation 'androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-viewmodel-ktx:2.5.1' 并导入包名。
Kotlin
import androidx.lifecycle.viewModelScope3.2 协程调度器源码(Dispatchers)
Kotlin
public actual object Dispatchers {
// 线程池, 适合执行CPU密集型任务(大量占用量CPU的任务)
public actual val Default: CoroutineDispatcher = DefaultScheduler
// Android中是UI线程, Swing中是invokerLater线程
public actual val Main: MainCoroutineDispatcher get() = MainDispatcherLoader.dispatcher
// 在当前线程上执行
public actual val Unconfined: CoroutineDispatcher = kotlinx.coroutines.Unconfined
// 线程池, 适合执行磁盘读写、网络IO、数据库操作等任务
public val IO: CoroutineDispatcher = DefaultIoScheduler
// ...
}3.3 协程启动方式源码
协程的启动方式主要有 launch、async、runBlocking、withContext,它们的区别如下。
- launch:launch 用于启动一个新的协程,并返回一个 Job 对象,该对象代表了这个新协程;启动的协程在后台运行,不会阻塞当前线程的执行,并且不会返回协程的执行结果。
- async:async 用于启动一个新的协程,并返回一个 Deferred 对象,它是 Job 的子类,可以通过 await 函数获取协程的执行结果;启动的协程在后台运行,不会阻塞当前线程的执行。
- runBlocking:runBlocking 是一个顶层函数,用于启动一个新的协程并阻塞当前线程,直到协程执行完成; runBlocking 本质上是为了在顶层(如 main 函数)使用协程,以及在测试中使用协程;在生产代码中不推荐使用 runBlocking,因为它会阻塞当前线程,可能导致性能问题。
- withContext:withContext 用于切换协程的上下文,它会创建一个新的协程并在指定的上下文中执行,它会挂起原来的协程,待新协程执行结束后才恢复执行。
3.3.1 launch
Kotlin
public fun CoroutineScope.launch(
context: CoroutineContext = EmptyCoroutineContext,
start: CoroutineStart = CoroutineStart.DEFAULT,
block: suspend CoroutineScope.() -> Unit
): Job {
val newContext = newCoroutineContext(context)
val coroutine = if (start.isLazy)
LazyStandaloneCoroutine(newContext, block) else
StandaloneCoroutine(newContext, active = true)
coroutine.start(start, coroutine, block)
return coroutine
} 说明:launch 用于启动一个新的协程,并返回一个 Job 对象,该对象代表了这个新协程;启动的协程在后台运行,不会阻塞当前线程的执行,并且不会返回协程的执行结果。
3.3.2 async
Kotlin
public fun <T> CoroutineScope.async(
context: CoroutineContext = EmptyCoroutineContext,
start: CoroutineStart = CoroutineStart.DEFAULT,
block: suspend CoroutineScope.() -> T
): Deferred<T> {
val newContext = newCoroutineContext(context)
val coroutine = if (start.isLazy)
LazyDeferredCoroutine(newContext, block) else
DeferredCoroutine<T>(newContext, active = true)
coroutine.start(start, coroutine, block)
return coroutine
} 说明:async 用于启动一个新的协程,并返回一个 Deferred 对象,它是 Job 的子类,可以通过 await 函数获取协程的执行结果;启动的协程在后台运行,不会阻塞当前线程的执行。
3.3.3 runBlocking
runBlocking 官方介绍见 → runBlocking。
Kotlin
public actual fun <T> runBlocking(context: CoroutineContext, block: suspend CoroutineScope.() -> T): T {
...
val currentThread = Thread.currentThread()
val contextInterceptor = context[ContinuationInterceptor]
val eventLoop: EventLoop?
val newContext: CoroutineContext
if (contextInterceptor == null) {
// 如果没有指定调度器(dispatcher), 则创建或使用私有事件循环(eventLoop)
eventLoop = ThreadLocalEventLoop.eventLoop
newContext = GlobalScope.newCoroutineContext(context + eventLoop)
} else {
eventLoop = (contextInterceptor as? EventLoop)?.takeIf { it.shouldBeProcessedFromContext() }
?: ThreadLocalEventLoop.currentOrNull()
newContext = GlobalScope.newCoroutineContext(context)
}
val coroutine = BlockingCoroutine<T>(newContext, currentThread, eventLoop)
coroutine.start(CoroutineStart.DEFAULT, coroutine, block)
return coroutine.joinBlocking()
} 说明:runBlocking 是一个顶层函数,用于启动一个新的协程并阻塞当前线程,直到协程执行完成; runBlocking 本质上是为了在顶层(如 main 函数)使用协程,以及在测试中使用协程;在生产代码中不推荐使用 runBlocking,因为它会阻塞当前线程,可能导致性能问题。
3.3.4 withContext
Kotlin
public suspend fun <T> withContext(
context: CoroutineContext,
block: suspend CoroutineScope.() -> T
): T {
// ...
return suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn sc@ { uCont ->
val oldContext = uCont.context
val newContext = oldContext.newCoroutineContext(context)
newContext.ensureActive()
if (newContext === oldContext) {
val coroutine = ScopeCoroutine(newContext, uCont)
return@sc coroutine.startUndispatchedOrReturn(coroutine, block)
}
if (newContext[ContinuationInterceptor] == oldContext[ContinuationInterceptor]) {
val coroutine = UndispatchedCoroutine(newContext, uCont)
withCoroutineContext(newContext, null) {
return@sc coroutine.startUndispatchedOrReturn(coroutine, block)
}
}
val coroutine = DispatchedCoroutine(newContext, uCont)
block.startCoroutineCancellable(coroutine, coroutine)
coroutine.getResult()
}
} 说明:withContext 用于切换协程的上下文,它会创建一个新的协程并在指定的上下文中执行,它会挂起原来的协程,待新协程执行结束后才恢复执行。
3.4 协程启动模式源码(CoroutineStart)
Kotlin
public enum class CoroutineStart {
// 立即执行协程体
DEFAULT,
// 只有在需要的情况下运行, 需要调用job.start()函数才启动协程
LAZY,
// 立即执行协程体, 但在开始运行前无法取消
ATOMIC,
// 立即在当前线程执行协程体, 直到第一个suspend函数调用(启动较快)
UNDISPATCHED;
// ...
}4 协程应用
4.1 协程作用域应用
4.1.1 CoroutineScope
Kotlin
fun main() {
println("main-start")
CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default).launch {
for (i in 1..2) {
println("CoroutineScope-A-$i")
delay(100)
}
}
CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.IO).launch {
for (i in 1..2) {
println("CoroutineScope-B-$i")
delay(100)
}
}
println("main-end")
Thread.sleep(1000) // 阻塞当前线程, 避免程序过早结束, 协程提前取消
} 打印如下。
Kotlin
main-start
main-end
CoroutineScope-A-1
CoroutineScope-B-1
CoroutineScope-A-2
CoroutineScope-B-2 说明:结果表明 main、CoroutineScope-A、CoroutineScope-B 并行。
4.1.2 MainScope
Kotlin
fun main() {
println("main-start")
MainScope().launch(Dispatchers.Default) {
test("MainScope-A")
}
MainScope().launch(Dispatchers.IO) {
test("MainScope-B")
}
println("main-end")
Thread.sleep(1000) // 阻塞当前线程, 避免程序过早结束, 协程提前取消
}
suspend fun test(tag: String) {
for (i in 1..2) {
println("$tag-$i")
delay(100)
}
} 打印如下。
Kotlin
main-start
main-end
MainScope-B-1
MainScope-A-1
MainScope-A-2
MainScope-B-2 说明:结果表明 main、MainScope-A、MainScope-B 并行。
4.1.3 GlobalScope
Kotlin
fun main() {
println("main-start")
GlobalScope.launch(Dispatchers.Default, CoroutineStart.DEFAULT) {
test("GlobalScope-A")
test("GlobalScope-B")
}
println("main-end")
Thread.sleep(1000) // 阻塞当前线程, 避免程序过早结束, 协程提前取消
}
suspend fun test(tag: String) {
for (i in 1..2) {
println("$tag-$i")
delay(100)
}
} 打印如下。
Kotlin
main-start
main-end
GlobalScope-A-1
GlobalScope-A-2
GlobalScope-B-1
GlobalScope-B-2 说明:结果表明 main 与 GlobalScope 并行。
4.1.4 lifecycleScope
Kotlin
import android.os.Bundle
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import androidx.lifecycle.lifecycleScope
import kotlinx.coroutines.launch
class MyActivity: AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
lifecycleScope.launch {
println("lifecycleScope")
}
}
} 说明:使用 lifecycleScope 时,需要在 build.gradle 中引入以下依赖。
Kotlin
implementation "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-runtime-ktx:2.5.1"4.1.5 viewModelScope
Kotlin
import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModel
import androidx.lifecycle.viewModelScope
import kotlinx.coroutines.launch
class MyViewModel: ViewModel() {
init {
viewModelScope.launch {
println("viewModelScope")
}
}
} 说明:使用 viewModelScope 时,需要在 build.gradle 中引入以下依赖。
Kotlin
implementation 'androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-viewmodel-ktx:2.5.1'4.1.6 子协程
Kotlin
fun main() {
println("main-start")
CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default).launch {
test("CoroutineScope-A")
launch(Dispatchers.Default) { // 也可以通过async启动子协程
test("CoroutineScope-B")
}
launch(Dispatchers.Default) { // 也可以通过async启动子协程
test("CoroutineScope-C")
}
}
println("main-end")
Thread.sleep(1000) // 阻塞当前线程, 避免程序过早结束, 协程提前取消
}
suspend fun test(tag: String) {
for (i in 1..2) {
println("$tag-$i")
delay(100)
}
} 打印如下。
Kotlin
main-start
main-end
CoroutineScope-A-1
CoroutineScope-A-2
CoroutineScope-B-1
CoroutineScope-C-1
CoroutineScope-B-2
CoroutineScope-C-2 说明:结果表明 main 与 CoroutineScope-A 并行,CoroutineScope-A 运行结束后,又启动了 GlobalScope-B、CoroutineScope-C 两个子协程,它们又并行。
4.2 协程启动方式应用
4.2.1 launch
Kotlin
fun main() {
println("main-start")
MainScope().launch(Dispatchers.Default, CoroutineStart.DEFAULT) {
test("MainScope")
}
println("main-end")
Thread.sleep(1000) // 阻塞当前线程, 避免程序过早结束, 协程提前取消
}
suspend fun test(tag: String) {
for (i in 1..2) {
println("$tag-$i")
delay(100)
}
} 打印如下。
Kotlin
main-start
main-end
MainScope-1
MainScope-24.2.2 async
Kotlin
fun main() {
println("main-start")
MainScope().launch(Dispatchers.Default) {
var deferred = async { // 启动子协程
test("MainScope")
"async return value"
}
println("MainScope-xxx")
var res = deferred.await() // 获取子协程的返回值, 此处会挂起当前协程, 直到子协程执行完成
println(res)
}
println("main-end")
Thread.sleep(1000) // 阻塞当前线程, 避免程序过早结束, 协程提前取消
}
suspend fun test(tag: String) {
for (i in 1..2) {
println("$tag-$i")
delay(100)
}
} 打印如下。
Kotlin
main-start
main-end
MainScope-xxx
MainScope-1
MainScope-2
async return value 说明:结果表明 deferred.await() 会挂起当前协程(MainScope),直到子协程(async)执行完成。
4.2.3 runBlocking
Kotlin
fun main() {
println("main-start")
runBlocking {
var deferred = async { // 启动子协程
test("runBlocking")
"async return value"
}
launch { // 启动子协程
var res = deferred.await() // 获取子协程的返回值, 此处会挂起当前协程, 直到子协程执行完成
println(res)
}
println("runBlocking-xxx")
}
println("main-end")
Thread.sleep(1000) // 阻塞当前线程, 避免程序过早结束, 协程提前取消
}
suspend fun test(tag: String) {
for (i in 1..2) {
println("$tag-$i")
delay(100)
}
} 打印如下。
Kotlin
main-start
runBlocking-xxx
runBlocking-1
runBlocking-2
async return value
main-end 说明:结果表明 runBlocking 启动了一个新的协程(runBlocking),并阻塞了当前线程(main),直到协程执行完成;deferred.await() 会挂起当前子协程(async),直到子协程(launch)执行完成。
4.2.4 withContext
1)不使用 withContext 返回值
Kotlin
@OptIn(ExperimentalStdlibApi::class)
fun main() {
println("main-start")
runBlocking(Dispatchers.IO) {
println("context1=${coroutineContext[CoroutineDispatcher]}")
withContext(Dispatchers.Default) { // 启动子协程, 并挂起当前协程
println("context2=${coroutineContext[CoroutineDispatcher]}")
test("withContext")
}
println("runBlocking-xxx")
}
println("main-end")
Thread.sleep(1000) // 阻塞当前线程, 避免程序过早结束, 协程提前取消
}
suspend fun test(tag: String) {
for (i in 1..2) {
println("$tag-$i")
delay(100)
}
} 打印如下。
Kotlin
main-start
context1=Dispatchers.IO
context2=Dispatchers.Default
withContext-1
withContext-2
runBlocking-xxx
main-end 说明:结果表明 withContext 创建了子协程,并挂起了 runBlocking 协程,直到 withContext 协程执行完毕才恢复执行。
2)使用 withContext 返回值
Kotlin
@OptIn(ExperimentalStdlibApi::class)
fun main() {
println("main-start")
runBlocking(Dispatchers.IO) {
println("context1=${coroutineContext[CoroutineDispatcher]}")
var res = withContext(Dispatchers.Default) { // 启动子协程, 并挂起当前协程
println("context2=${coroutineContext[CoroutineDispatcher]}")
"withContext return value"
}
println("res=$res")
}
println("main-end")
Thread.sleep(1000) // 阻塞当前线程, 避免程序过早结束, 协程提前取消
} 打印如下。
Kotlin
main-start
context1=Dispatchers.IO
context2=Dispatchers.Default
res=withContext return value
main-end4.3 Job 应用
Job 状态流程转换如下。(图片来自 Job.kt 源码)
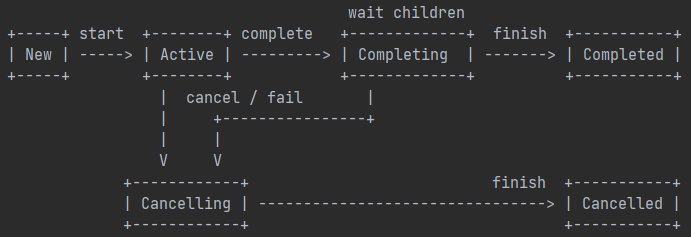
4.3.1 start
Kotlin
fun main() {
println("main-start")
var job = MainScope().launch(Dispatchers.Default, CoroutineStart.LAZY) {
test("MainScope")
}
job.start() // 注释该行, job不会执行, test中日志将不会打印
println("main-end")
Thread.sleep(1000) // 阻塞当前线程, 避免程序过早结束, 协程提前取消
}
suspend fun test(tag: String) {
for (i in 1..2) {
println("$tag-$i")
delay(100)
}
} 打印如下。
Kotlin
main-start
main-end
MainScope-1
MainScope-2 说明:注释掉 job.start(),job 不会执行,test 中日志将不会打印。
4.3.2 cancel
Kotlin
fun main() {
println("main-start")
var job = CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default).launch {
test("CoroutineScope")
}
job.cancel()
println("main-end")
Thread.sleep(1000) // 阻塞当前线程, 避免程序过早结束, 协程提前取消
}
suspend fun test(tag: String) {
for (i in 1..2) {
println("$tag-$i")
delay(100)
}
} 打印如下。
Kotlin
main-start
main-end
CoroutineScope-1 说明:CoroutineScope-2 未打印出来,因为协程执行到一半被取消了。
4.3.3 join
Kotlin
fun main() {
println("main-start")
var job = CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default).launch {
test("CoroutineScope")
}
MainScope().launch(Dispatchers.Default) {
println("MainScope-xxx")
job.join() // 挂起当前协程, 直到job执行完成
test("MainScope")
}
println("main-end")
Thread.sleep(1000) // 阻塞当前线程, 避免程序过早结束, 协程提前取消
}
suspend fun test(tag: String) {
for (i in 1..2) {
println("$tag-$i")
delay(100)
}
} 打印如下。
Kotlin
main-start
main-end
MainScope-xxx
CoroutineScope-1
CoroutineScope-2
MainScope-1
MainScope-2 说明:结果表明 job.join() 挂起了 MainScope 协程,直到 CoroutineScope 协程执行完毕才恢复执行。
4.4 异常处理应用
4.4.1 try-catch 处理异常
Kotlin
fun main() {
println("main-start")
CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.IO).launch {
try {
var a = 1 / 0
} catch (e: Exception) {
println(e)
}
}
println("main-end")
Thread.sleep(1000) // 阻塞当前线程, 避免程序过早结束, 协程提前取消
} 打印如下。
Kotlin
main-start
main-end
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero4.4.2 CoroutineExceptionHandler 处理异常
Kotlin
@OptIn(ExperimentalStdlibApi::class)
fun main() {
println("main-start")
var exceptionHandler = CoroutineExceptionHandler { context, throwable ->
println("context=${context[CoroutineDispatcher]}, message=${throwable}")
}
CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.IO + exceptionHandler).launch {
var a = 1 / 0
}
println("main-end")
Thread.sleep(1000) // 阻塞当前线程, 避免程序过早结束, 协程提前取消
} 打印如下。
Kotlin
main-start
main-end
context=Dispatchers.IO, message=java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero5 协程并发安全
5.1 不安全的并发访问
Kotlin
fun main() {
var count = 0
CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default).launch {
var jobList = List(1000) { // 创建1000个子协程
CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default).launch {
count++
}
}
jobList.joinAll() // 挂起当前协程, 直到所有子协程执行完成
println(count) // 期望打印1000, 但每次运行结果不一样, 如:990、981、995等
}
Thread.sleep(1000) // 阻塞当前线程, 避免程序过早结束, 协程提前取消
}5.2 安全的并发访问
安全的并发访问工具主要有 Atomic、Mutex、Semaphore、Channel。
- Atomic:原子操作,主要接口:getAndIncrement、getAndDecrement、getAndAdd、getAndAccumulate、incrementAndGet、decrementAndGet、addAndGet、accumulateAndGet 等。
- Mutex:轻量级锁,主要接口:withLock 等。
- Semaphore:轻量级信号量,主要接口:withPermit 等。
- Channel:并发安全的消息通道,主要接口:send、receive。
5.2.1 Atomic
使用 Java 提供的原子操作类型数据,如:AtomicBoolean、AtomicInteger、AtomicLong、AtomicIntegerArray、AtomicLongArray、AtomicReference、AtomicReferenceArray,可以解决一些并发安全访问的问题。
Kotlin
fun main() {
var count = AtomicInteger()
CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default).launch {
var jobList = List(1000) { // 创建1000个子协程
CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default).launch {
count.getAndIncrement()
}
}
jobList.joinAll() // 挂起当前协程, 直到所有子协程执行完成
println(count.get()) // 打印: 1000
}
Thread.sleep(1000) // 阻塞当前线程, 避免程序过早结束, 协程提前取消
}5.2.2 Mutex
Mutex 是轻量级锁,它的 lock 和 unlock 从语义上与线程锁比较类似,之所以轻量是因为它在获取不到锁时不会阻塞线程,而是挂起等待锁的释放。
Kotlin
fun main() {
var count = 0
var mutex = Mutex()
CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default).launch {
var jobList = List(1000) { // 创建1000个子协程
CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default).launch {
mutex.withLock {
count++
}
}
}
jobList.joinAll() // 挂起当前协程, 直到所有子协程执行完成
println(count) // 打印: 1000
}
Thread.sleep(1000) // 阻塞当前线程, 避免程序过早结束, 协程提前取消
}5.2.3 Semaphore
Semaphore 是轻量级信号量,信号可以有多个,协程在获取到信号后即可执行并发操作。
Kotlin
fun main() {
var count = 0
var semaphore = Semaphore(1) // 创建一个信号量, 里面只有一个信号
CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default).launch {
var jobList = List(1000) { // 创建1000个子协程
CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default).launch {
semaphore.withPermit {
count++
}
}
}
jobList.joinAll() // 挂起当前协程, 直到所有子协程执行完成
println(count) // 打印: 1000
}
Thread.sleep(1000) // 阻塞当前线程, 避免程序过早结束, 协程提前取消
} 说明:Semaphore 的入参表示信号个数,当 Semaphore 的参数为 1 时, 效果等价与 Mutex。
6 加载网络图片案例
build.gradle 中需要引入以下依赖。
XML
dependencies {
implementation 'com.github.bumptech.glide:glide:4.12.0'
implementation "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-runtime-ktx:2.5.1"
...
} AndroidManifest.xml 中需要配置以下权限。
XML
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" /> MainActivity.kt
Kotlin
package com.zhyan8.kotlinStudy
import android.os.Bundle
import android.view.View
import android.widget.Button
import android.widget.ImageView
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import androidx.lifecycle.lifecycleScope
import com.bumptech.glide.Glide
import kotlinx.coroutines.Dispatchers
import kotlinx.coroutines.launch
import kotlinx.coroutines.withContext
class MainActivity: AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var imageView: ImageView
private lateinit var button: Button
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
imageView = findViewById(R.id.imageView)
button = findViewById(R.id.btn_back)
button.setOnClickListener{
lifecycleScope.launch(Dispatchers.IO) {
loadImageFromUrl("https://images.cnblogs.com/cnblogs_com/blogs/787006/galleries/2393602/o_240421081243_g0001.jpg")
}
}
}
private suspend fun loadImageFromUrl(url: String) {
val bitmap = Glide.with(this@MainActivity)
.asBitmap()
.load(url)
.submit()
.get()
withContext(Dispatchers.Main) {
imageView.visibility = View.VISIBLE
button.visibility = View.GONE
imageView.setImageBitmap(bitmap)
}
}
} activity_main.xml
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:gravity="center">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:scaleType="centerCrop"
android:visibility="gone" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_back"
android:layout_width="250dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="加载图片"
android:textSize="40sp"/>
</LinearLayout> 运行效果如下。

声明:本文转自【Kotlin】协程。