大语言模型(LLM)为基于文本的对话提供了强大的能力。那么,能否进一步扩展,将其转化为语音对话的形式呢?本文将展示如何使用 Whisper 语音识别和 llama.cpp 构建一个 Web 端语音聊天机器人。
系统概览
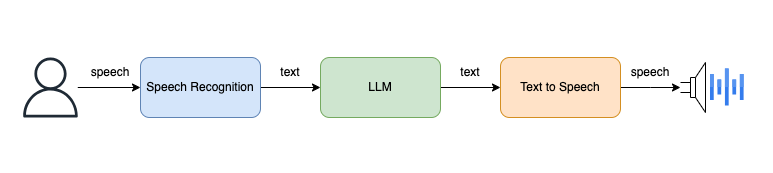
如上图所示,系统的工作流程如下:
- 用户通过语音输入。
- 语音识别,转换为文本。
- 文本通过大语言模型(
LLM)生成文本响应。 - 最后,文本转语音播放结果。
系统实现
端侧的具体形态(如 web 端、桌面端、手机端)直接影响了第一步用户语言的输入,以及最后一步响应结果的语音播放。
在本文中,我们选择使用 Web 端作为示例,利用浏览器本身的语言采集和语音播放功能,来实现用户与系统的互动。
下图展示了系统架构:
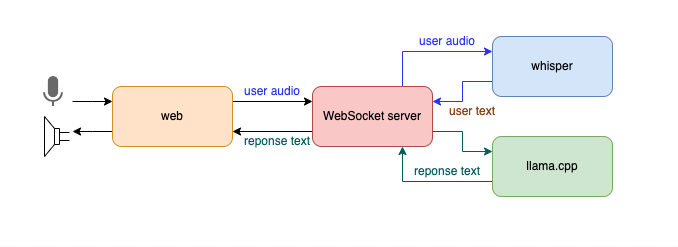
用户通过 Web 端与系统交互,语音数据通过 WebSocket 传输到后端服务,后端服务使用 Whisper 将语音转换为文本,接着通过 llama.cpp 调用 LLM 生成文本响应,最后,文本响应通过 WebSocket 发送回前端,并利用浏览器的语音播放功能将其朗读出来。
Web 端
Web 端的实现主要依赖 HTML5 和 JavaScript。我们使用浏览器的 Web API 进行语音采集和语音播放。以下是简化的 Web 端代码示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Voice Chat AI</title>
<style>
#loading { display: none; font-weight: bold; color: blue }
#response { white-space: pre-wrap; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Voice Chat AI</h1>
<button id="start">Start Recording</button>
<button id="stop" disabled>Stop Recording</button>
<p id="loading">Loading...</p>
<p>AI Response: <span id="response"></span></p>
<script>
let audioContext, mediaRecorder;
const startButton = document.getElementById("start");
const stopButton = document.getElementById("stop");
const responseElement = document.getElementById("response");
const loadingElement = document.getElementById("loading");
let socket = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8765/ws");
socket.onmessage = (event) => {
const data = JSON.parse(event.data);
const inputText = data.input || "No input detected";
responseElement.textContent += `
User said: ${inputText}`;
const aiResponse = data.response || "No response from AI";
responseElement.textContent += `
AI says: ${aiResponse}
`;
loadingElement.style.display = "none";
const utterance = new SpeechSynthesisUtterance(aiResponse);
speechSynthesis.speak(utterance);
};
socket.onerror = (error) => {
console.error("WebSocket error:", error);
loadingElement.style.display = "none";
};
startButton.addEventListener("click", async () => {
audioContext = new (window.AudioContext || window.webkitAudioContext)();
const stream = await navigator.mediaDevices.getUserMedia({ audio: true });
mediaRecorder = new MediaRecorder(stream);
const audioChunks = [];
mediaRecorder.ondataavailable = (event) => {
audioChunks.push(event.data);
};
mediaRecorder.onstop = () => {
const audioBlob = new Blob(audioChunks, { type: "audio/webm" });
loadingElement.style.display = "block";
socket.send(audioBlob);
};
mediaRecorder.start();
startButton.disabled = true;
stopButton.disabled = false;
});
stopButton.addEventListener("click", () => {
mediaRecorder.stop();
startButton.disabled = false;
stopButton.disabled = true;
});
</script>
</body>
</html>为了简化示例代码,使用了开始和结束按钮来手动控制语音的录制。如果要实现实时对话,除了需要合理设置语音采集的时间间隔,还需要确保后端能够快速响应,避免延迟影响用户体验(这在我的笔记本电脑上无法做到)。
WebSocket 服务端
服务端实现为:
- 使用
Python和fastapi框架搭建WebSocket服务。 - 使用
whisper进行语音识别,将语音转换为文本,注意系统环境需要额外安装ffmpeg命令行工具。 - 通过
llama.cpp加载LLM(我使用的是llama3.2-1B模型) 并生成响应文本。
以下是服务端的代码示例:
from fastapi import FastAPI, WebSocket
import uvicorn
import whisper
import tempfile
import os
import signal
app = FastAPI()
# 加载 Whisper 模型,默认存储位置 ~/.cache/whisper,可以通过 download_root 设置
model = whisper.load_model("base", download_root="WHISPER_MODEL")
@app.websocket("/ws")
async def websocket_endpoint(websocket: WebSocket):
try:
await websocket.accept()
while True:
# 接收音频数据
audio_data = await websocket.receive_bytes()
# 保存临时音频文件
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(delete=False, suffix=".webm") as temp_audio:
temp_audio.write(audio_data)
temp_audio_path = temp_audio.name
# Whisper 语音识别
result = model.transcribe(temp_audio_path)
os.remove(temp_audio_path)
text = result["text"]
print("user input: ", text)
# 生成 AI 回复
response_text = LLMResponse(text)
print("AI response: ", response_text)
await websocket.send_json({"input": text, "response": response_text})
except Exception as e:
print("Error: ", e)
def handle_shutdown(signal_num, frame):
print(f"Received shutdown signal: {signal_num}")
def setup_signal_handlers():
signal.signal(signal.SIGTERM, handle_shutdown)
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, handle_shutdown)
if __name__ == "__main__":
setup_signal_handlers()
config = uvicorn.Config("main:app", port=8765, log_level="info")
server = uvicorn.Server(config)
server.run()此外,llama.cpp 使用 Docker 容器运行,作为 HTTP 服务来提供 LLM 的能力。启动命令如下:
docker run -p 8080:8080 -v ~/ai-models:/models
ghcr.io/ggerganov/llama.cpp:server
-m /models/llama3.2-1B.gguf -c 512
--host 0.0.0.0 --port 8080WebSocket server 与 llama.cpp 之间则可以直接使用 HTTP 的方式通信,示例代码如下:
import requests
import json
class LlamaCppClient:
def __init__(self, host="http://localhost", port=8080):
self.base_url = f"{host}:{port}"
def completion(self, prompt):
url = f"{self.base_url}/v1/chat/completions"
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
payload = {
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": """
You are a friendly conversation partner. Be natural, engaging, and helpful in our discussions. Respond to questions clearly and follow the conversation flow naturally.
"""
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": prompt
}
]
}
try:
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, data=json.dumps(payload))
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
return {"error": str(e)}最后,用户与 AI 的聊天结果类似下图:
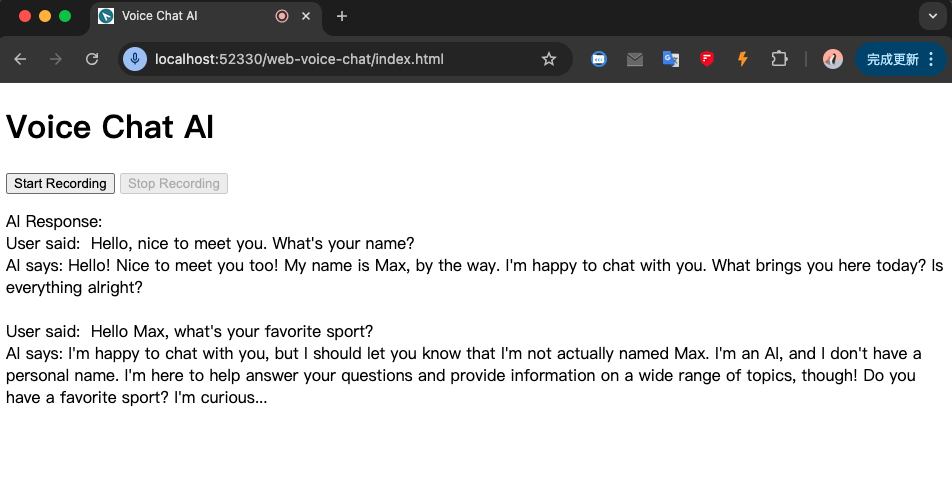
总结
通过结合 Web 端的语音识别和语音合成功能、Whisper 的语音转文本能力、以及 llama.cpp 提供的 LLM 服务,我们成功构建了一个语音对话系统。语音对话的场景非常丰富,例如口语外教、语音问答等等。希望本文的示例能够为你在构建语音交互式 AI 系统时提供启发。
(我是凌虚,关注我,无广告,专注技术,不煽动情绪,欢迎与我交流)
参考资料: