Linux从0到1------线程自定义封装
1. Thread.hpp
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <functional>
template<class T>
using func_t = std::function<void(T)>;
template<class T>
class Thread
{
public:
Thread(func_t<T> func, const std::string &threadname, T data)
:_tid(0), _threadname(threadname), _isrunning(false), _func(func), _data(data)
{}
static void *ThreadRoutine(void* args) // 静态成员方法,没有this指针
{
Thread *ts = static_cast<Thread *>(args);
ts->_func(ts->_data);
return nullptr;
}
bool Start()
{
int n = pthread_create(&_tid, nullptr, ThreadRoutine, this);
if(n == 0)
{
_isrunning = true;
return true;
}
else return false;
}
bool Join()
{
if(!_isrunning) return false;
int n = pthread_join(_tid, nullptr);
if(n == 0)
{
_isrunning = false;
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool IsRunning()
{
return _isrunning;
}
~Thread()
{}
private:
pthread_t _tid; // 库级别线程id
std::string _threadname; // 线程名
bool _isrunning; // 运行状态
func_t<T> _func; // 线程执行的回调方法
T _data;
};- 需要格外注意一点,
ThreadRoutine必须写成静态成员函数,因为普通成员函数会默认携带this指针,这样就会有两个参数,一个this,一个void* args。而pthread_create函数只接受只有一个参数void* args的函数。 - 将
ThreadRoutine写成静态成员函数后,它将无法通过隐含的this指针访问到成员变量_func。为了解决这个问题,可以将this指针显示的传给pthread_create函数的void* args参数,这样ThreadRoutine就拿到了this指针,之后再做一些变换就可以访问到_func了。
2. main.cc
- 作文测试文件,测试封装的效果:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string>
#include "Thread.hpp"
std::string GetThreadName()
{
static int number = 1; // 声明周期随进程,且只在当前作用域有效
char name[64];
snprintf(name, sizeof(name), "Thread-%d", number++);
return name;
}
void Print(int num)
{
while(num--)
{
std::cout << "hello world" << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
Thread<int> t(Print, GetThreadName(), 5);
std::cout << "is thread running?" << t.IsRunning() << std::endl;
t.Start();
std::cout << "is thread running?" << t.IsRunning() << std::endl;
t.Join();
std::cout << "Join done" << std::endl;
return 0;
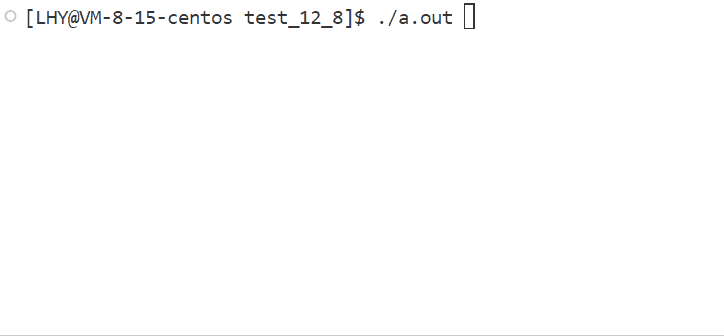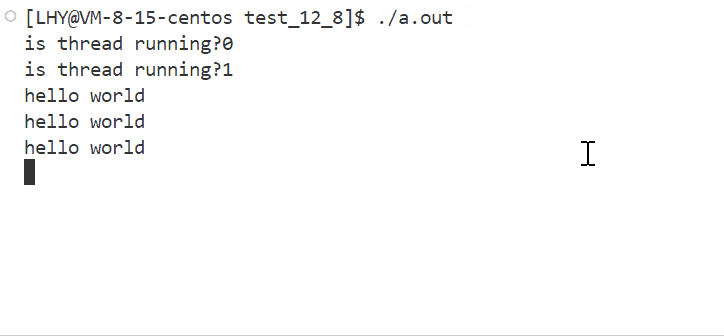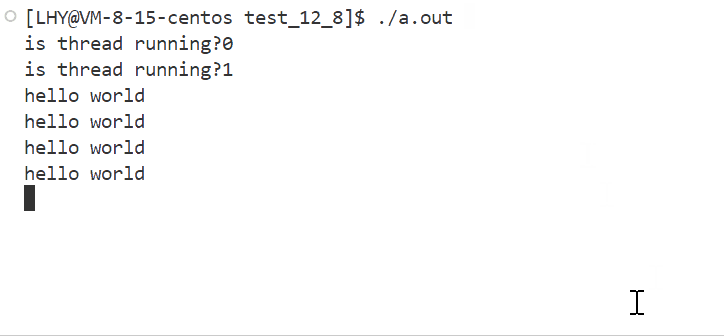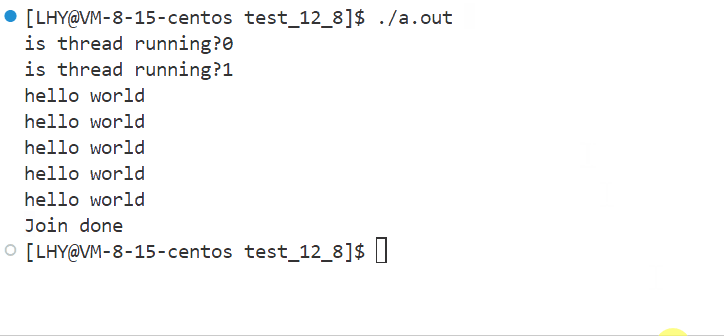
}- 运行结果: