数据驱动
数据的改变从而驱动自动化测试用例的执行,最终引起测试结果的改变。简单说就是参数化的应用。
测试驱动在自动化测试中的应用场景:
- 测试步骤的数据驱动;
- 测试数据的数据驱动;
- 配置的数据驱动;
1、pytest结合数据驱动-yaml
实现读yaml文件,先创建env.yml文件配置测试数据
工程目录结构:
-
data目录:存放yaml文件
dev: 127.0.0.1
#dev: 127.0.0.2
#prod: 127.0.0.3 -
testcase目录:存放测试用例文件
import pytest
import yaml
class TestYaml:
@pytest.mark.parametrize("env", yaml.safe_load(open("./env.yml")))
def test_yaml(self, env):
if "test" in env:
print("这是测试环境")print(env)
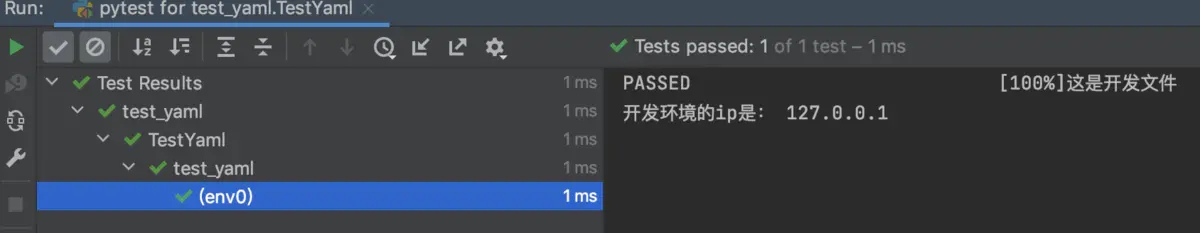
print("测试环境的ip是:", env["test"])
elif "dev" in env:
print("这是开发文件")
print("开发环境的ip是:", env["dev"])print(env)
结果示例:
2、pytest结合数据驱动-excel
常用的读取方式有:xlrd、xlwings、pandas、openpyxl
以读excel文件,实现A+B=C并断言为例~
工程目录结构:
data目录:存放excel数据文件
-
func目录:存放被测函数文件
def my_add(x, y):
result = x + y
return result -
testcase目录:存放测试用例文件
import openpyxl
import pytest
from test_pytest.read_excel.func.operation import my_add
def test_get_excel():
"""
解析excel数据
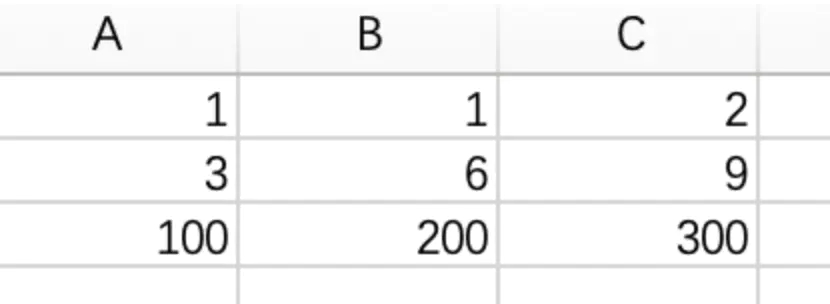
:return: [[1,1,2],[3,6,9],[100,200,300]]
"""
book = openpyxl.load_workbook('../data/param.xlsx')
sheet = book.active
cells = sheet["A1":"C3"]
print(cells)
values = []
for row in sheet:
data = []
for cell in row:
data.append(cell.value)
values.append(data)
print(values)
return values
class TestWithExcel:
@pytest.mark.parametrize('x,y,expected', test_get_excel())
def test_add(self, x, y, expected):
assert my_add(int(x), int(y)) == int(expected)
3、pyetst结合数据驱动-csv
csv:逗号文件,以逗号分隔的string文件
读取csv数据:
- 内置函数open()
- 内置模块csv
- 方法:csv.reader(iterable)
- 参数:iterable,文件或列表对象
- 返回:迭代器,遍历迭代器,每次会返回一行数据
以读csv文件,实现A+B=C并断言为例~
工程目录结构:
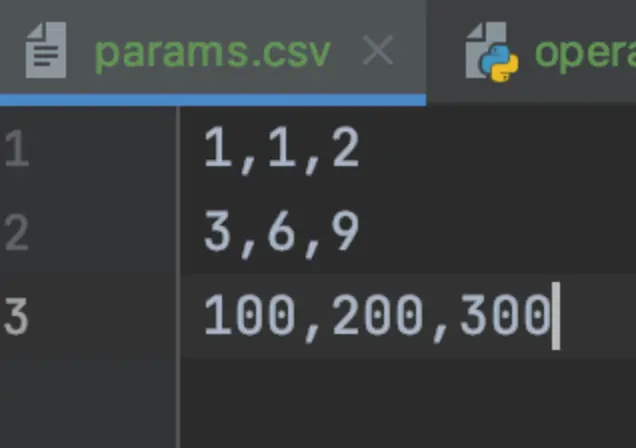
data目录:存放csv数据文件
-
func目录:存放被测函数文件
def my_add(x, y):
result = x + y
return result -
testcase目录:存放测试用例文件
import csv
import pytest
from test_pytest.read_csv.func.operation import my_add
def test_get_csv():
"""
解析csv文件
:return:
"""
with open('../data/params.csv') as file:
raw = csv.reader(file)
data = []
for line in raw:
data.append(line)
print(data)
return data
class TestWithCsv:
@pytest.mark.parametrize('x,y,expected', test_get_csv())
def test_add(self, x, y, expected):
assert my_add(int(x), int(y)) == int(expected)
4、pytest结合数据驱动-json
json:js对象,是一种轻量级的数据交换格式。
json结构:
- 对象{"key":value}
- 数组[value1,value2...]
查看json文件:
- 1.pycharm
- 2.txt记事本
读取json文件:
- 内置函数open()
- 内置库json
- 方法 json.loads() json.dumps()
以读json文件,实现A+B=C并断言为例~
工程目录结构:
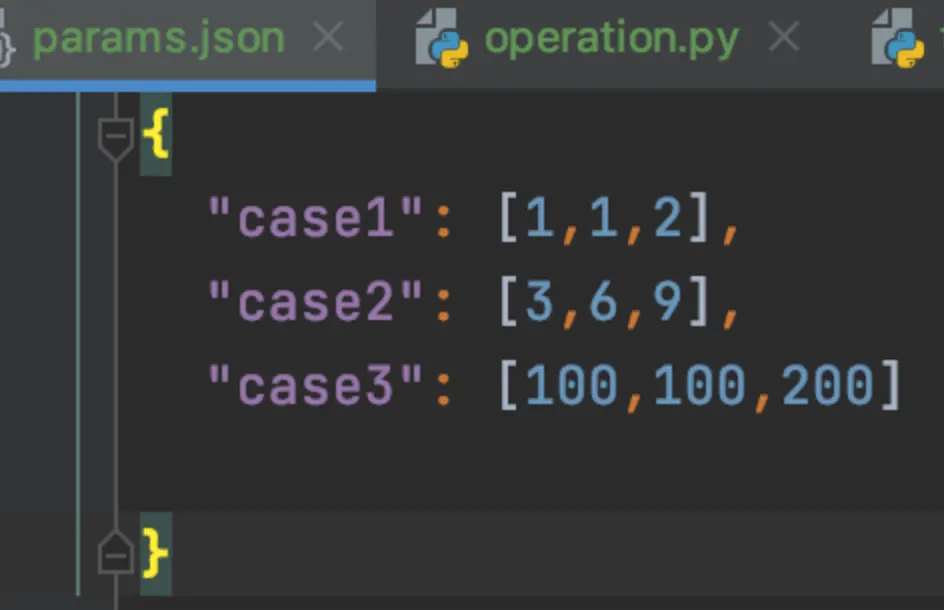
data目录:存放json数据文件
-
func目录:存放被测函数文件
def my_add(x, y):
result = x + y
return result -
testcase目录:存放测试用例文件
import json
import pytest
from test_pytest.read_json.func.operation import my_add
def test_get_json():
"""
解析json数据
:return: [[1,1,2],[3,6,9],[100,200,300]]
"""
with open('../data/params.json', 'r') as file:
data = json.loads(file.read())
print(list(data.values()))
return list(data.values())
class TestWithJson:
@pytest.mark.parametrize('x,y,expected', test_get_json())
def test_add(self, x, y, expected):
assert my_add(int(x), int(y)) == int(expected)