要求:
1)严禁上网抄袭、互相抄袭和各种形式的抄袭(如代码抄袭,运行截图一图多用),一旦发现单次作业按零分处理!
2)课程报告正文内容基本格式为:宋体,小五号,1.5 倍行距。
3)作业报告请务必保持排版的整洁规范,排版混乱者将直接判为不及格。
4)为避免办公软件兼容性导致的显示差异问题,要求在提交课程报告 WORD 文件的同
时提交相应的 PDF 版本。
一、实验目的
-
掌握通过反射动态加载类、创建实例、访问和修改对象的私有字段、调用对象的方法等操作。
-
掌握如何通过反射获取注解的操作。
-
掌握反射与设计模式的使用。
- 实验内容
|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| public class Student { private String name; private int age; public Student() { this.name = "Unknown"; this.age = 0; } public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void displayInfo() { System.out.println("Name: " + name + ", Age: " + age); } private void privateMethod() { System.out.println("Private method called"); } } |
-
使用反射对类进行相关的操作。创建一个简单类 Student包含私有字段 name 和 age。包含一个无参构造方法和一个带参构造方法。包含公共方法 getName()、getAge() 和 displayInfo()。包含一个私有方法 privateMethod()。
-
使用反射机制动态加载 Student 类。
-
使用反射机制创建 Student 类的实例。
-
使用反射机制访问和修改 Student 类的私有字段。
-
使用反射机制调用 Student 类的公共方法和私有方法。
代码:
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class ReflectionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 动态加载Student类
Class<?> studentClass = Class.forName("Student");
// 使用无参构造函数创建Student实例
Student student1 = (Student) studentClass.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
// 使用带参构造函数创建Student实例
Constructor<?> constructor = studentClass.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, int.class);
Student student2 = (Student) constructor.newInstance("晓晓", 25);
// 访问和修改私有字段
Field nameField = studentClass.getDeclaredField("name");
nameField.setAccessible(true);
nameField.set(student2, "晓晓");
Field ageField = studentClass.getDeclaredField("age");
ageField.setAccessible(true);
ageField.setInt(student2, 20);
// 调用公共方法
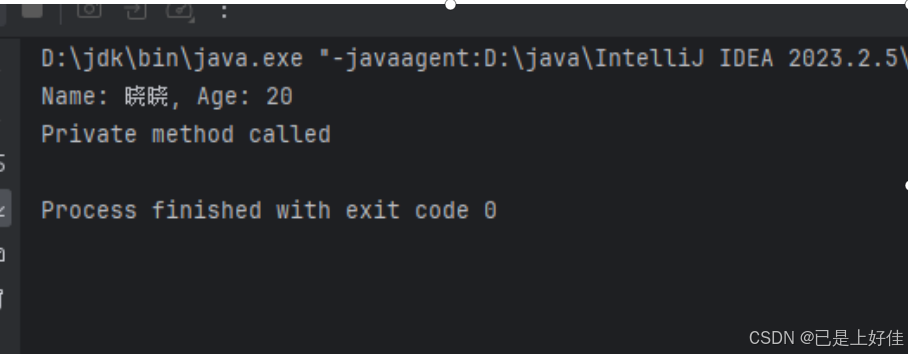
Method displayInfoMethod = studentClass.getMethod("displayInfo");
displayInfoMethod.invoke(student2);
// 调用私有方法
Method privateMethod = studentClass.getDeclaredMethod("privateMethod");
privateMethod.setAccessible(true);
privateMethod.invoke(student2);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行截图:
- 有如下场景:项目的持久化层需要使用到的数据库有Redis、MySql、MongoDB。
要求:
- 定义一个DataService接口,接口提供add()、delete()、update()、find()四个接口,对应各种数据库的增删改查操作。
- 分别实现RedisDataService、MySqlDataService、MongoDBDataService。
- 通过反射机制,实现动态工厂模式
- 从配置文件中读取需要使用的数据库名称,如redis对应"RedisDataService"、MySql对应"MySqlDataService"、MongoDB对应"MySqlDataService"
- 实例化配置文件中所配置的数据库服务对象
其中项目的数据库至少需要选择一种,可选择多种;
配置文件格式如下,则代表项目需要两种类型的数据库,需要创建两个实例。
|--------------------------------------------------|
| MySql:MySqlDataService MongoDB: MySqlDataService |
代码:
public interface DataService {
void add();
void delete();
void update();
void find();
}
public class RedisDataService implements DataService {
public void add() { System.out.println("Adding via Redis"); }
public void delete() { System.out.println("Deleting via Redis"); }
public void update() { System.out.println("Updating via Redis"); }
public void find() { System.out.println("Finding via Redis"); }
}
public class MySqlDataService implements DataService {
public void add() { System.out.println("Adding via MySQL"); }
public void delete() { System.out.println("Deleting via MySQL"); }
public void update() { System.out.println("Updating via MySQL"); }
public void find() { System.out.println("Finding via MySQL"); }
}
public class MongoDBDataService implements DataService {
public void add() { System.out.println("Adding via MongoDB"); }
public void delete() { System.out.println("Deleting via MongoDB"); }
public void update() { System.out.println("Updating via MongoDB"); }
public void find() { System.out.println("Finding via MongoDB"); }
}
import java.util.Properties;
public class DataServiceFactory {
public static DataService getDataService(String serviceName) {
try {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(serviceName);
return (DataService) clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
}
MySql=MySqlDataService
MongoDB=MongoDBDataService
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Application {
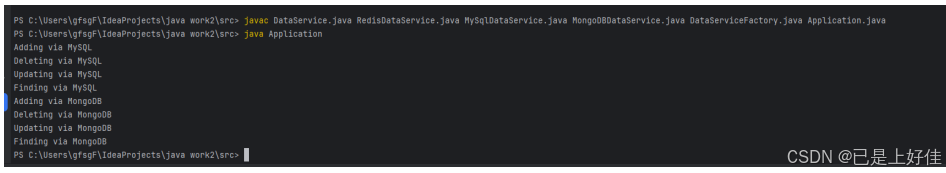
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("config.properties"));
for (String key : properties.stringPropertyNames()) {
String className = properties.getProperty(key);
DataService service = DataServiceFactory.getDataService(className);
if (service != null) {
service.add();
service.delete();
service.update();
service.find();
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行截图:
- 通过反射和注解,自动生成接口文档。
|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| public class UserController { public static class UserDTO { @ApiModelProperty("用户id") Integer userId; @ApiModelProperty("用户名称") String name ; } public static class UserVO { @ApiModelProperty("用户id") Integer userId; @ApiModelProperty("用户名称") String name; @ApiModelProperty("手机号") String phone; } @PostMapping("/get_user") public UserVO conf(UserDTO dto) { return new UserVO(); } } @Target(ElementType.FIELD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface ApiModelProperty { // 字段的注释 public String value() default ""; } |
要求:
- 实现自定义注解ApiModelProperty,用于字段描述。
- 实现自定义注解PostMapping,用于注明请求方法。
- UserDTO代表请求参数,UserVO对应响应参数。
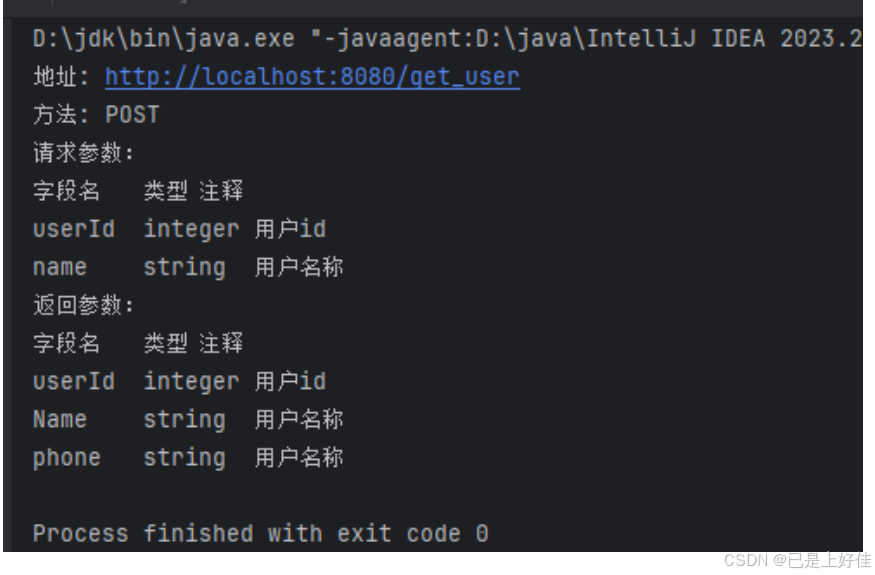
- 使用反射机制获取注解信息,并生成一个接口文档,格式如下:
|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| 地址: http://localhost:8080/get_user 方法: post 请求参数: 字段名 类型 注释 userId integer 用户id name string 用户名称 返回参数: 字段名 类型 注释 userId integer 用户id Name string 用户名称 phone string 用户名称 |
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ApiModelProperty {
String value() default "";
}
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface PostMapping {
String value() default "";
}
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class ApiDocumentationGenerator {
public static void generateDocumentation(Class<?> controllerClass) {
Method[] methods = controllerClass.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(PostMapping.class)) {
PostMapping postMapping = method.getAnnotation(PostMapping.class);
System.out.println("地址: http://localhost:8080" + postMapping.value());
System.out.println("方法: post");
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if (parameterTypes.length > 0) {
System.out.println("请求参数:");
System.out.println(" 字段名 类型 注释");
printFields(parameterTypes[0]);
}
Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
System.out.println("返回参数:");
System.out.println(" 字段名 类型 注释");
printFields(returnType);
}
}
}
private static void printFields(Class<?> clazz) {
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
ApiModelProperty apiModelProperty = field.getAnnotation(ApiModelProperty.class);
if (apiModelProperty != null) {
System.out.println(" " + field.getName() + " " + field.getType().getSimpleName().toLowerCase() + " " + apiModelProperty.value());
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
generateDocumentation(UserController.class);
}
}
三、思考题
- 反射机制实现动态代理的原理是什么?
++++反射机制实现动态代理的原理是在运行时创建代理类和对象,通过代理对象拦截对真实对象方法的调用,并允许在调用前后执行特定操作。这是通过 `java.lang.reflect.Proxy` 类和 `InvocationHandler` 接口实现的。++++
- 简述简单工厂设计模式与动态工厂设计模式的区别?
++++简单工厂设计模式是创建型模式,通过一个工厂类来创建不同类型的对象,客户端与具体产品解耦。动态工厂设计模式是简单工厂的扩展,它使用一个工厂方法来创建对象,允许在运行时动态决定创建何种产品。简单工厂在添加新产品时需要修改工厂类,而动态工厂通过继承或接口实现避免了这一点。++++