目录
一、整数替换

递归法+记忆化搜索法,解题代码:
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
// 递归+记忆化搜索法
unordered_map<long long, long long> hash;
int integerReplacement(int n)
{
return dfs(n);
}
int dfs(long long n)
{
if(hash.count(n))
return hash[n];
if(n == 1)
{
hash[n] = 0;
return 0;
}
if(n % 2 == 0) // 偶数
{
hash[n] = 1+dfs(n/2);
return hash[n];
}
else // 奇数
{
hash[n] = 1+min(dfs(n-1), dfs(n+1));
return hash[n];
}
}
};
贪心策略:
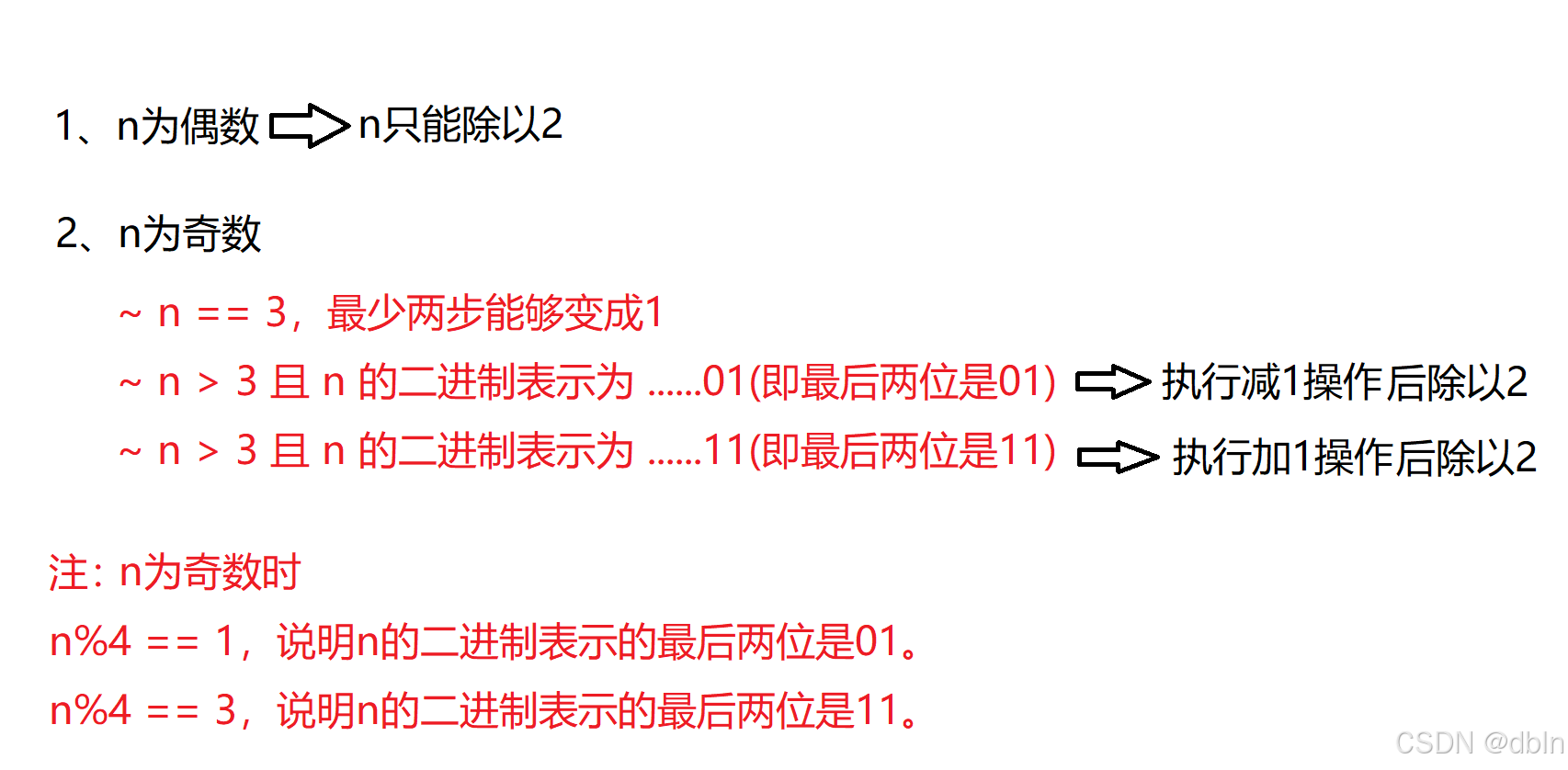
首先,我们需要明确一些前置知识:
1、偶数的二进制表示的最后一位是0。
2、奇数的二进制表示的最后一位是1。
3、/2操作,对于数的二进制表示来说就是右移一位。
贪心法解题代码:
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
int integerReplacement(int n)
{
// 贪心算法
int count = 0;
while(n != 1)
{
if(n % 2 == 0)
{
count++;
n /= 2;
}
else
{
if(n == 3)
{
count += 2;
n = 1;
}
else if(n % 4 == 1) // ......01(位表示)
{
count += 2;
n = (n-1) / 2;
}
else // ......11(位表示)
{
count += 2;
n = n / 2 + 1;
}
}
}
return count;
}
};
二、俄罗斯套娃信封问题

动态规划法,解题代码:
首先,对数组进行排序。
dp[i]:表示以 i 位置信封为结尾的套娃信封序列中,最长的套娃信封序列的长度。
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
int maxEnvelopes(vector<vector<int>>& e)
{
// 动态规划算法
int m = e.size();
sort(e.begin(), e.end());
vector<int> dp(m, 1);
int ret = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < m; i++)
{
int a = e[i][0], b = e[i][1];
for(int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
int x = e[j][0], y = e[j][1];
if(x < a && y < b)
dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j]+1);
ret = max(ret, dp[i]);
}
}
return ret;
}
};
贪心策略:
首先,对数组进行排序,但是要重写一下排序规则:如果两个区间的左端点不相等,按照左端点从小到大进行排序,如果两个区间的左端点相等,按照左端点从大到小进行排序。
然后根据之前的题目:最长递增子序列的贪心方法进行解题。
解题代码:
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
int maxEnvelopes(vector<vector<int>>& e)
{
sort(e.begin(), e.end(), [&](const vector<int>& v1, const vector<int>& v2)
{
if(v1[0] != v2[0])
return v1[0] < v2[0];
else
return v1[1] > v2[1];
});
vector<int> ret;
ret.push_back(e[0][1]);
int m = e.size();
for(int i = 1; i < m; i++)
{
int n = e[i][1];
if(ret.back() < n)
ret.push_back(n);
else
{
int left = 0, right = ret.size()-1;
while(left < right)
{
int mid = left + (right-left) / 2;
if(ret[mid] < n)
left = mid+1;
else
right = mid;
}
ret[left] = n;
}
}
return ret.size();
}
};
三、可被三整除的最大和

贪心策略:

解题代码:
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
int maxSumDivThree(vector<int>& nums)
{
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int sum = 0;
int x1 = INF, x2 = INF, y1 = INF, y2 = INF;
for(auto x:nums)
{
sum += x;
if(x%3 == 1)
{
if(x < x1)
x2 = x1, x1 = x;
else if(x < x2)
x2 = x;
}
else if(x%3 == 2)
{
if(x < y1)
y2 = y1, y1 = x;
else if(x < y2)
y2 = x;
}
}
if(sum%3 == 0)
return sum;
else if(sum%3 == 1)
return max(sum-x1, sum-y1-y2);
else
return max(sum-x1-x2, sum-y1);
}
};
四、距离相等的条形码

贪心策略:
进行模拟,每次将同一类元素全部处理,即如果元素1出现的次数最多,那么就将所有的元素1放置好,再去放置其他元素。
先将出现次数最多的元素,从第一个位置开始,进行放置, 然后隔一个位置放置。然后依次将其他元素放置到空位置。

解题代码:
cpp
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> rearrangeBarcodes(vector<int>& b) {
unordered_map<int, int> hash;
int maxval = 0, maxcount = 0;
// 统计出现次数最多的元素及其次数
for(auto& x : b)
{
hash[x]++;
if(maxcount < hash[x])
maxcount = hash[x], maxval = x;
}
int m = b.size();
vector<int> ret(m);
int index = 0;
//先放置出现次数最多的元素
for(int i = 0; i < maxcount; i++)
{
ret[index] = maxval;
index += 2;
}
hash.erase(maxval);
for(auto& [a, b] : hash)
{
for(int i = 0; i < b; i++)
{
if(index >= m)
index = 1;
ret[index] = a;
index += 2;
}
}
return ret;
}
};
五、重构字符串

贪心策略:
字符的放置方法和题目四:距离相等的条形码,是一样的。
但是,设字符串s大小为n,如果s中出现次数最多的字符的次数大于(n+1)/ 2,那么无论怎样放置,都无法得到想要的结果。
解题代码:
cpp
class Solution {
public:
string reorganizeString(string s) {
int n = s.size();
unordered_map<char, int> hash;
int maxcount = 0;
char maxval;
for(auto& x:s)
{
hash[x]++;
if(hash[x] > maxcount)
maxcount = hash[x], maxval = x;
}
if(maxcount > (n+1)/2)
return "";
string ret(n, ' ');
int index = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < maxcount; i++)
{
ret[index] = maxval;
index += 2;
}
hash.erase(maxval);
for(auto& [a, b]:hash)
{
for(int i = 0; i < b; i++)
{
if(index >= n)
index = 1;
ret[index] = a;
index += 2;
}
}
return ret;
}
};