今天,这篇文章带你将深入理解Spring Boot中30+常用注解,通过代码示例和关系图,帮助你彻底掌握Spring核心注解的使用场景和内在联系。
一、启动类与核心注解
1.1 @SpringBootApplication
组合注解:
@SpringBootApplication**=@Configuration+@EnableAutoConfiguration+****@ComponentScan**
java
@SpringBootApplication
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args);
}
}三个核心功能:
@Configuration:声明配置类
@EnableAutoConfiguration:启用自动配置
@ComponentScan:组件扫描(默认扫描启动类所在包及其子包)
二、配置与Bean管理
2.1 @Configuration
声明配置类,内部包含多个@Bean方法
java
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
return new HikariDataSource();
}
}2.2 @Bean vs @Component
|------|----------|------------|
| 特性 | @Bean | @Component |
| 声明位置 | 配置类方法 | 类级别 |
| 控制粒度 | 第三方库类 | 自己编写的类 |
| 依赖注入 | 方法参数自动注入 | 字段/构造器 |
2.3 @Scope Bean作用域
java
@Bean
@Scope("prototype")
public Service prototypeService() {
return new Service();
}三、依赖注入(DI)
3.1 @Autowired
自动注入的三种方式:
java
// 构造器注入(推荐)
@Autowired
public MyController(MyService service) {
this.service = service;
}
// Setter注入
@Autowired
public void setService(MyService service) {
this.service = service;
}
// 字段注入(不推荐)
@Autowired
private MyService service;3.2 @Qualifier
解决多个同类型Bean的冲突
java
@Autowired
@Qualifier("mainService")
private Service service;3.3 @Primary
设置首选Bean
java
@Bean
@Primary
public Service primaryService() {
return new PrimaryService();
}四、组件扫描与分层架构
4.1 分层注解

java
@Service
public class UserService {
// 业务逻辑
}
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/users")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
}五、Web开发注解
5.1 请求映射
java
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public User getUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
return userService.findById(id);
}
@PostMapping
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
public User createUser(@RequestBody User user) {
return userService.save(user);
}5.2 参数绑定
java
@GetMapping
public List<User> searchUsers(
@RequestParam(defaultValue = "1") int page,
@RequestParam(required = false) String name) {
// 分页查询逻辑
}六、条件装配注解
6.1 @ConditionalOnProperty
java
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(
prefix = "feature",
name = "new-payment",
havingValue = "true")
public PaymentService newPaymentService() {
return new NewPaymentService();
}6.2 其他条件注解
@ConditionalOnClass:类路径存在指定类时生效
@ConditionalOnMissingBean:容器中不存在指定Bean时生效
七、AOP编程
7.1 切面配置
java
@Aspect
@Component
public class LoggingAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
private void serviceLayer() {}
@Around("serviceLayer()")
public Object logMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
// 记录方法执行时间
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
long duration = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
System.out.println(joinPoint.getSignature() + " executed in " + duration + "ms");
return result;
}
}八、配置属性绑定
8.1 @ConfigurationProperties
java
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "app")
public class AppConfig {
private String name;
private int version;
private List<String> servers = new ArrayList<>();
// getters/setters
}application.yml配置:
XML
app:
name: MyApplication
version: 2
servers:
- server1
- server2九、Bean 的生命周期
Spring Boot 中的 Bean 生命周期是理解 Spring 容器管理 Bean 的关键。Bean 的生命周期大致可以分为以下几个阶段:
实例化(Instantiation):Spring 容器通过调用无参构造方法创建 Bean 实例。
属性赋值(Population):Spring 容器通过反射将配置文件或注解中定义的属性值注入到 Bean 中。
初始化前处理(Pre-initialization):
BeanNameAware:如果 Bean 实现了 BeanNameAware 接口,Spring 会调用其 setBeanName 方法,将 Bean 的名称传递给 Bean。
BeanFactoryAware:如果 Bean 实现了 BeanFactoryAware 接口,Spring 会调用其 setBeanFactory 方法,将 BeanFactory 传递给 Bean。
BeanPostProcessor:Spring 会调用 BeanPostProcessor 的 postProcessBeforeInitialization 方法,对 Bean 进行前置处理。
初始化(Initialization):
InitializingBean:如果 Bean 实现了 InitializingBean 接口,Spring 会调用其 afterPropertiesSet 方法进行初始化。
@PostConstruct:如果 Bean 中有方法使用了 @PostConstruct 注解,Spring 会调用该方法进行初始化。
使用(Usage):Bean 已经初始化完成,可以被应用程序使用。
销毁前处理(Pre-destruction):
DisposableBean:如果 Bean 实现了 DisposableBean 接口,Spring 会调用其 destroy 方法进行销毁前的清理工作。
@PreDestroy:如果 Bean 中有方法使用了 @PreDestroy 注解,Spring 会调用该方法进行销毁前的清理工作。
销毁(Destruction):Spring 容器关闭时,销毁 Bean。
java
@Component
public class MyBean implements BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
private String name;
public MyBean() {
System.out.println("1. 实例化 Bean");
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("2. 设置 Bean 名称");
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("3. 设置 BeanFactory");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("4. 初始化 Bean");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("6. 销毁 Bean");
}
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("5. @PostConstruct 注解的初始化方法");
}
@PreDestroy
public void preDestroy() {
System.out.println("7. @PreDestroy 注解的销毁前方法");
}
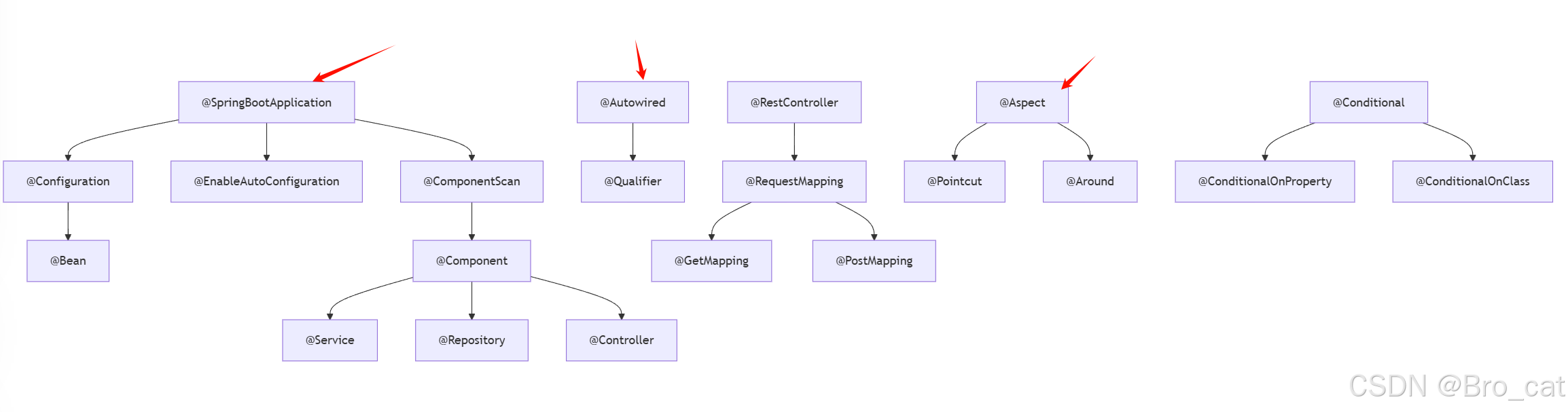
}十、注解关系图谱
总结
Spring Boot 中的注解和 Bean 生命周期是开发中非常重要的概念。通过合理使用各种注解,可以大大简化开发过程,提高开发效率。同时,理解 Bean 的生命周期有助于更好地管理 Bean 的创建、初始化和销毁过程,确保应用程序的稳定性和可靠性。