写在前面
最简单的一集
实验室分为两个部分。在A部分中,实现一个缓存模拟器。在B部分中,编写一个矩阵针对高速缓存性能优化的转置功能。
感觉是比较经典的问题,之前在体系结构的课程中接触过,终于能通过lab实操一下了。
实验目录的 traces 子目录包含参考跟踪文件的集合,将用于评估A部分中编写的缓存模拟器的正确性。跟踪文件是由 Linux 称为valgrind 的程序产生的。
先安装valgrind:
apt install valgrind比如 我们用valgrind 捕获 ls -l 的内存访问
valgrind --log-fd=1 --tool=lackey -v --trace-mem=yes ls -l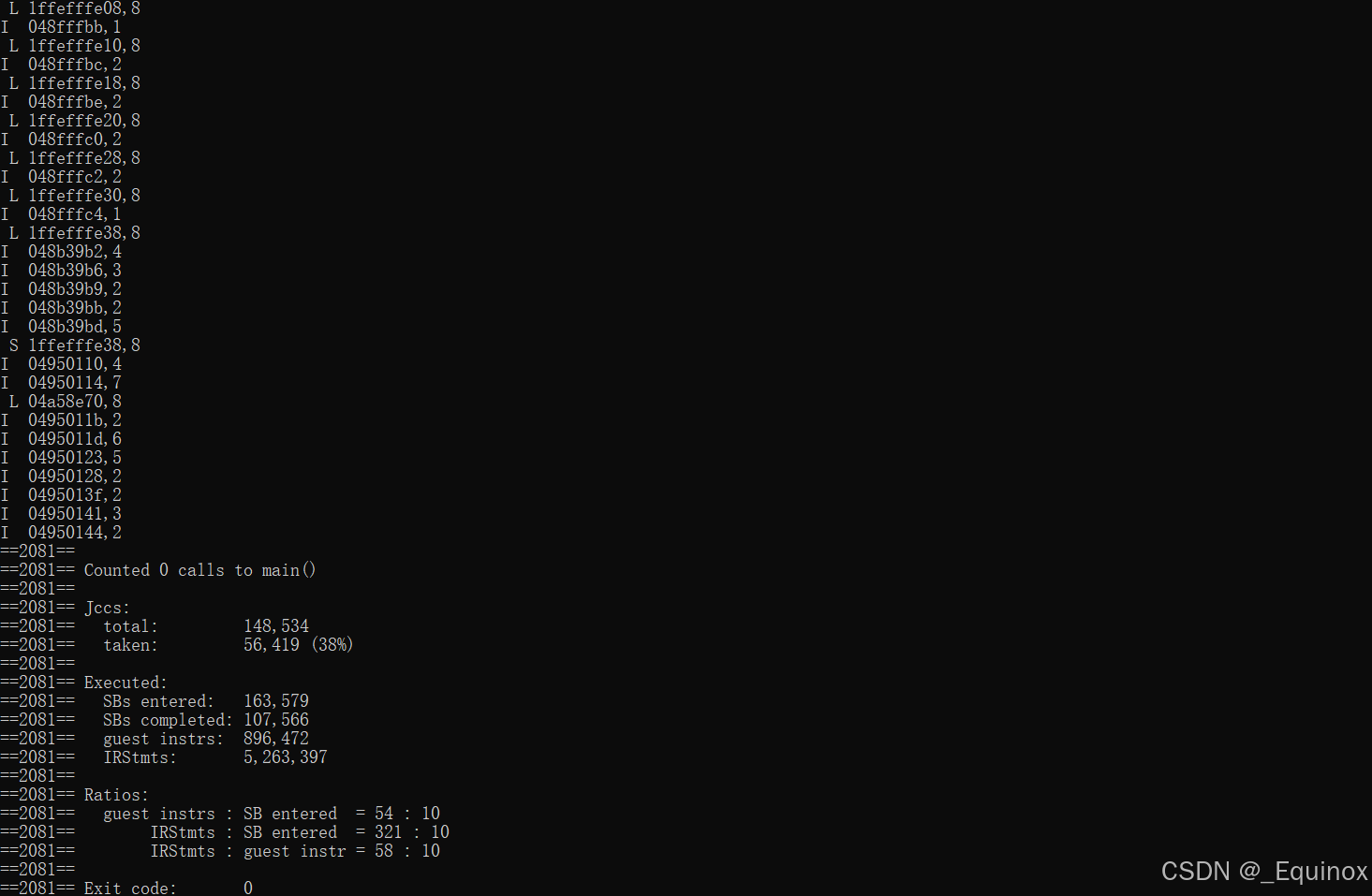
操作-地址-大小 三元组格式
- I 表示指令读取
- L 表示数据读取
- S 表示数据存储
- M 表示数据修改
PartA:Writing a Cache Simulator
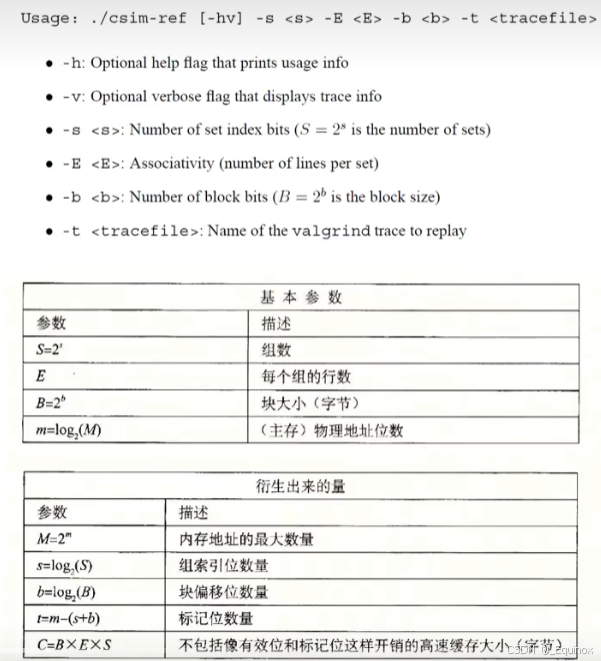
在A部分中,需要在 csim.c 中编写一个缓存模拟器该模拟器将 valgrind 内存跟踪作为输入,模拟此跟踪上的高速缓存存储器的命中/未命中行为,并输出命中,不命中和驱逐的总数目。
需要考虑的问题
1、处理输入参数。
2、模拟缓存行为。
3、考虑LRU(最近最少使用)算法。
下面的程序参考了知乎 林夕丶 的做法
这个实验的pdf 提示通过 getopt() 来解析命令行参数,具体用法问大模型或者查阅文档即可。
需要用到的全局变量、数据结构以及函数:
s, E, b:缓存参数,分别表示组索引位数(S = 2^s)、每组行数(E)和块偏移位数(B = 2^b)。T:全局时间戳,用于LRU(最近最少使用)替换策略。(LRU其实可以O(1)维护,但是C语言没有哈希表,所以暴力了)cache:二维数组,表示缓存结构,每个组包含多个行(lineNode)。result[3]:统计命中、未命中和替换次数。lineNode:表示缓存行,包含标签(tag)和时间戳(t)。时间戳用于LRU策略。init():初始化缓存结构。findCache():处理内存访问,判断是否命中、未命中或替换。opt():解析命令行参数,配置缓存参数并打开轨迹文件。setResult():更新统计结果和缓存行状态。
c++
/*===========头文件===============*/
#include "cachelab.h"
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <getopt.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
/*===========头文件===============*/
void usage(void) { exit(1); } // 打印帮助信息可以不实现
int verbose = 0, s, E, b, S, B; // cache的参数,由命令行输入,opt函数解析
int T = 0; //时间戳,第一个访存指令的时刻为1,之后每次数据访存都累加1
typedef __uint64_t u64;
typedef unsigned int uint;
// 行的定义
typedef struct lineNode {
int t; // 时刻
u64 tag; // 标记位
} * groupNode; // 组
enum Category { HIT, MISS, EVICTION }; // 命中 / 缺失 / 驱逐
uint result[3]; // 统计命中、未命中和替换次数
const char *categoryString[3] = {"hit ", "miss ", "eviction "};
groupNode *cache; // cache 就是若干组
void init(); // 初始化cache
FILE *opt(int argc, char **argv); // 解析命令行选项
void findCache(u64 tag, int group_pos, char *result); // 查询主函数的逻辑:
- 解析命令行参数
- 初始化cache
- 接收操作并处理
- pdf要求我们最后打印 命中次数 缺失次数 驱逐次数
c++
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
FILE *tracefile = opt(argc, argv); // 从命令行获取 S E B
init(); // 根据输入参数初始化cache
// 接下来处理每一条指令
char oper[2];
u64 address;
int size; //访问的地址和字节数
while (fscanf(tracefile, "%s %lx,%d\n", oper, &address, &size) == 3) {
if (oper[0] == 'I') continue; // 忽略I
int group_pos = (address >> b) & ~(~0u << s); // 从 第 b位开始取,取s位
u64 address_tag = address >> (b + s); // b + s之后的位都是
char resultV[20]; // 为了 -v 设置的string显示
memset(resultV, 0, sizeof resultV);
++T;
findCache(address_tag, group_pos, resultV);
if (oper[0] == 'M') findCache(address_tag, group_pos, resultV); // M需要两次
if (verbose) fprintf(stdout, "%s %lx,%d %s\n", oper, address, size, resultV);
}
printSummary(result[0], result[1], result[2]);
return 0;
}核心函数逻辑:
opt
就是利用 getopt 库函数,解析命令行参数
c
FILE *opt(int argc, char **argv)
{
FILE *tracefile;
/* Parse the command line 这里c用int是为了保证兼容性,因为有的系统char是unsigned的*/
for (int c; (c = getopt(argc, argv, "hvsEbt")) != EOF;) {
switch (c) {
case 'h': /* print help message */
usage();
break;
case 'v': /* emit additional diagnostic info */
verbose = 1;
break;
case 't': /* 文件 */
tracefile = fopen(argv[optind], "r");
if (tracefile == NULL) usage();
break;
case 's': // 组数的位
s = atoi(argv[optind]);
if (s <= 0) usage();
S = 1 << s;
break;
case 'E': // 每一组的行数
E = atoi(argv[optind]);
if (E <= 0) usage();
break;
case 'b':
b = atoi(argv[optind]);
if (b <= 0) usage();
B = 1 << b;
break;
}
}
return tracefile;
}findCache
模拟 cache访问,维护LRU逻辑
c
void findCache(u64 tag, int group_pos, char *resultV)
{
groupNode group = cache[group_pos];
int min_t_pos = 0, empty_line = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < E; ++i) {
struct lineNode line = group[i];
if (!line.t)
empty_line = i; // 有空行
else {
if (line.tag == tag) { // 命中,设置hit
setResult(group, HIT, tag, i, resultV);
return;
}
if (group[min_t_pos].t > line.t)
min_t_pos = i; // 取最小的时刻值,也就是最近最少访问的了
}
}
setResult(group, MISS, tag, empty_line, resultV);
if (empty_line == -1) //要读或者写但是没有一个 空行 说明得发生eviction
setResult(group, EVICTION, tag, min_t_pos, resultV);
}剩下的都很简单
完整代码:
c
/*===========头文件===============*/
#include "cachelab.h"
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <getopt.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
/*===========头文件===============*/
void usage(void) { exit(1); } // 打印帮助信息可以不实现
int verbose = 0, s, E, b, S, B; // cache的参数,由命令行输入,opt函数解析
int T = 0; //时间戳,第一个访存指令的时刻为1,之后每次数据访存都累加1
typedef __uint64_t u64;
typedef unsigned int uint;
// 行的定义
typedef struct lineNode {
int t; // 时刻
u64 tag; // 标记位
} * groupNode; // 组
enum Category { HIT, MISS, EVICTION }; // 命中 / 缺失 / 驱逐
uint result[3]; // 统计命中、未命中和替换次数
const char *categoryString[3] = {"hit ", "miss ", "eviction "};
groupNode *cache; // cache 就是若干组
void init(); // 初始化cache
FILE *opt(int argc, char **argv); // 解析命令行选项
void findCache(u64 tag, int group_pos, char *result); // 查询
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
FILE *tracefile = opt(argc, argv); // 从命令行获取 S E B
init(); // 根据输入参数初始化cache
// 接下来处理每一条指令
char oper[2];
u64 address;
int size; //访问的地址和字节数
while (fscanf(tracefile, "%s %lx,%d\n", oper, &address, &size) == 3) {
if (oper[0] == 'I') continue; // 忽略I
int group_pos = (address >> b) & ~(~0u << s); // 从 第 b位开始取,取s位
u64 address_tag = address >> (b + s); // b + s之后的位都是
char resultV[20]; // 为了 -v 设置的string显示
memset(resultV, 0, sizeof resultV);
++T;
findCache(address_tag, group_pos, resultV);
if (oper[0] == 'M') findCache(address_tag, group_pos, resultV); // M需要两次
if (verbose) fprintf(stdout, "%s %lx,%d %s\n", oper, address, size, resultV);
}
printSummary(result[0], result[1], result[2]);
return 0;
}
// 初始化整个cache
void init()
{
cache = (groupNode *)malloc(sizeof(groupNode) * S);
for (int i = 0; i < S; ++i) {
cache[i] = (struct lineNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct lineNode) * E);
for (int j = 0; j < E; ++j) cache[i][j].t = 0;
}
}
// category是缓存的种类,resultV是main传下来的,为了verbose的输出
void setResult(groupNode group, enum Category category, int tag, int pos, char *resultV)
{
++result[category];
group[pos].tag = tag;
group[pos].t = T;
if (verbose) strcat(resultV, categoryString[category]);
}
// 遍历这个组的所有行,然后看一下是否命中,最后再进行相应的操作即可
void findCache(u64 tag, int group_pos, char *resultV)
{
groupNode group = cache[group_pos];
int min_t_pos = 0, empty_line = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < E; ++i) {
struct lineNode line = group[i];
if (!line.t)
empty_line = i; // 有空行
else {
if (line.tag == tag) { // 命中,设置hit
setResult(group, HIT, tag, i, resultV);
return;
}
if (group[min_t_pos].t > line.t)
min_t_pos = i; // 取最小的时刻值,也就是最近最少访问的了
}
}
setResult(group, MISS, tag, empty_line, resultV);
if (empty_line == -1) //要读或者写但是没有一个 空行 说明得发生eviction
setResult(group, EVICTION, tag, min_t_pos, resultV);
}
FILE *opt(int argc, char **argv)
{
FILE *tracefile;
/* Parse the command line 这里c用int是为了保证兼容性,因为有的系统char是unsigned的*/
for (int c; (c = getopt(argc, argv, "hvsEbt")) != EOF;) {
switch (c) {
case 'h': /* print help message */
usage();
break;
case 'v': /* emit additional diagnostic info */
verbose = 1;
break;
case 't': /* 文件 */
tracefile = fopen(argv[optind], "r");
if (tracefile == NULL) usage();
break;
case 's': // 组数的位
s = atoi(argv[optind]);
if (s <= 0) usage();
S = 1 << s;
break;
case 'E': // 每一组的行数
E = atoi(argv[optind]);
if (E <= 0) usage();
break;
case 'b':
b = atoi(argv[optind]);
if (b <= 0) usage();
B = 1 << b;
break;
}
}
// printf("-%d 4 -%d 1 -%d 4 -t \n", s, E, b);
return tracefile;
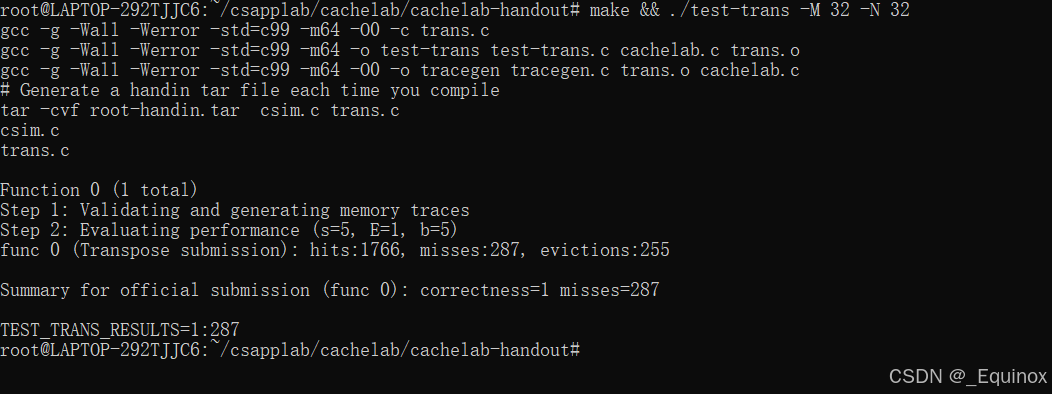
}执行结果:
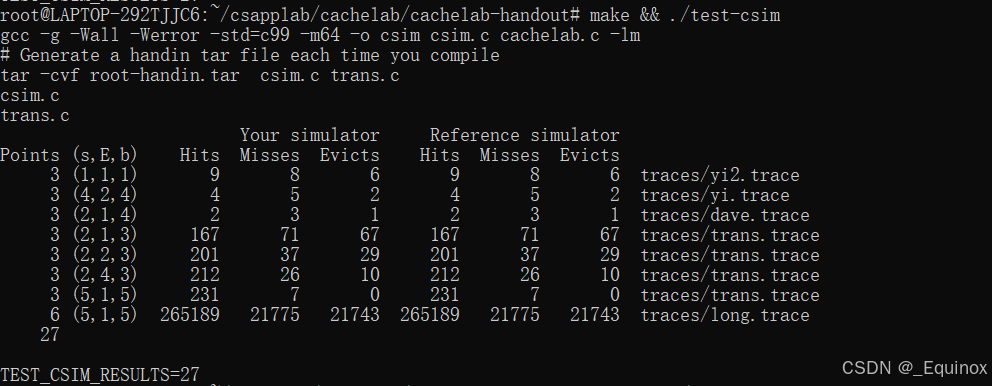
Part B: Optimizing Matrix Transpose
这个part指向性非常明确,我们优化矩阵转置的操作,令其缓存友好。
一共要实现三个转置函数:32×32,64×64,61×67
32×32
考虑分块转置,因为 一个 cache 块的大小为 32字节,即 8个int,我们 8 * 8 分块进行矩阵转置。
组号分布非常的舒服:
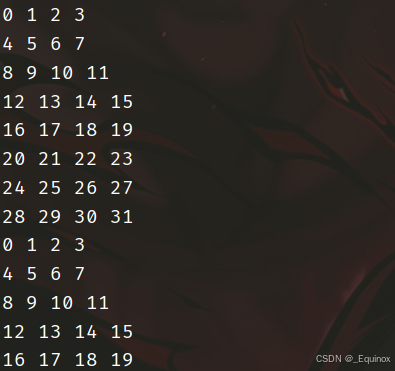
注意先把 A 的 每块一行取出来放到临时变量,如果直接赋值,那么会 load 然后 store 两次访存,造成块驱逐。
c++
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 32; i += 8) {
for (j = 0; j < 32; j += 8) {
for (int cnt = 0; cnt < 8; ++cnt, ++i) {
int temp1 = A[i][j];
int temp2 = A[i][j + 1];
int temp3 = A[i][j + 2];
int temp4 = A[i][j + 3];
int temp5 = A[i][j + 4];
int temp6 = A[i][j + 5];
int temp7 = A[i][j + 6];
int temp8 = A[i][j + 7];
B[j][i] = temp1;
B[j + 1][i] = temp2;
B[j + 2][i] = temp3;
B[j + 3][i] = temp4;
B[j + 4][i] = temp5;
B[j + 5][i] = temp6;
B[j + 6][i] = temp7;
B[j + 7][i] = temp8;
}
i -= 8;
}
}
64×64
直接用 8 * 8 分块转置,会1:4699
注意到 64 * 64 的组号分布
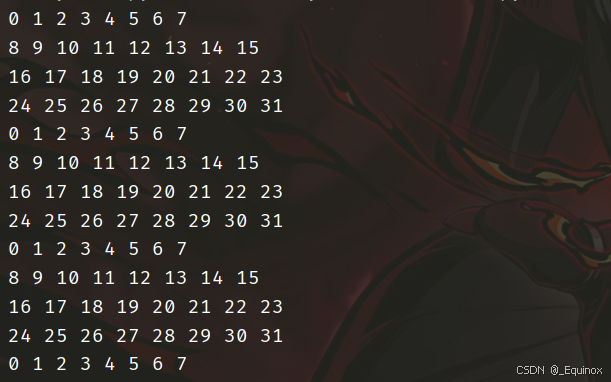
竖着循环周期是4,所以我们 8 * 8分块,往下填的时候,每4个就把上面四个驱逐,导致命中率极低。
那么我们不妨 改成4 * 4 的分块转置,然后就能通过了。
c
void transpose_64(int M, int N, int A[N][M], int B[M][N])
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 64; i += 4) {
for (j = 0; j < 64; j += 4) {
for (int cnt = 0; cnt < 4; ++cnt, ++i) {
int temp1 = A[i][j];
int temp2 = A[i][j + 1];
int temp3 = A[i][j + 2];
int temp4 = A[i][j + 3];
B[j][i] = temp1;
B[j + 1][i] = temp2;
B[j + 2][i] = temp3;
B[j + 3][i] = temp4;
}
i -= 4;
}
}
}
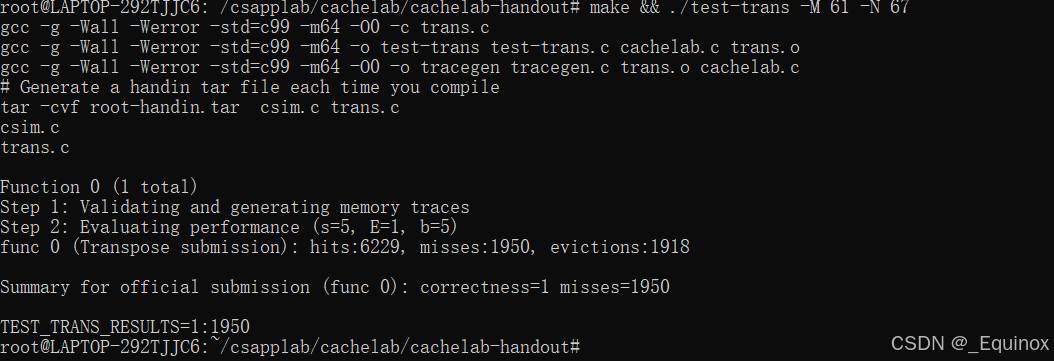
61 × 67
组号分布:
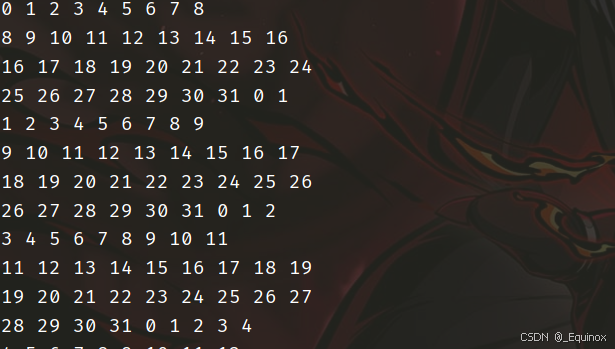
因为 61 和 67 俩数都是质数,导致组号分布很难被卡,我们想要直接计算比较好的分块大小很难,所以直接暴力枚举,测试出来17最优
c
void transpose_61(int M, int N, int A[N][M], int B[M][N])
{
int i, j;
const int BLOCK = 17;
for (i = 0; i < N; i += BLOCK) {
for (j = 0; j < M; j += BLOCK) {
for (int x = i; x < N && x < i + BLOCK; ++x)
for (int y = j; y < M && y < j + BLOCK; ++y) B[y][x] = A[x][y];
}
}
}
完整代码:
c
/*
* trans.c - Matrix transpose B = A^T
*
* Each transpose function must have a prototype of the form:
* void trans(int M, int N, int A[N][M], int B[M][N]);
*
* A transpose function is evaluated by counting the number of misses
* on a 1KB direct mapped cache with a block size of 32 bytes.
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include "cachelab.h"
int is_transpose(int M, int N, int A[N][M], int B[M][N]);
/*
* transpose_submit - This is the solution transpose function that you
* will be graded on for Part B of the assignment. Do not change
* the description string "Transpose submission", as the driver
* searches for that string to identify the transpose function to
* be graded.
*/
// cache参数: 32个组,每组一块,block=32字节
char transpose_submit_desc[] = "Transpose submission";
void transpose_32(int M, int N, int A[N][M], int B[M][N]);
void transpose_64(int M, int N, int A[N][M], int B[M][N]);
void transpose_61(int M, int N, int A[N][M], int B[M][N]);
void transpose_submit(int M, int N, int A[N][M], int B[M][N])
{
switch (M) {
case 32:
transpose_32(M, N, A, B);
break;
case 64:
transpose_64(M, N, A, B);
break;
case 61:
transpose_61(M, N, A, B);
break;
}
}
void transpose_32(int M, int N, int A[N][M], int B[M][N])
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 32; i += 8) {
for (j = 0; j < 32; j += 8) {
for (int cnt = 0; cnt < 8; ++cnt, ++i) {
int temp1 = A[i][j];
int temp2 = A[i][j + 1];
int temp3 = A[i][j + 2];
int temp4 = A[i][j + 3];
int temp5 = A[i][j + 4];
int temp6 = A[i][j + 5];
int temp7 = A[i][j + 6];
int temp8 = A[i][j + 7];
B[j][i] = temp1;
B[j + 1][i] = temp2;
B[j + 2][i] = temp3;
B[j + 3][i] = temp4;
B[j + 4][i] = temp5;
B[j + 5][i] = temp6;
B[j + 6][i] = temp7;
B[j + 7][i] = temp8;
}
i -= 8;
}
}
}
void transpose_64(int M, int N, int A[N][M], int B[M][N])
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 64; i += 4) {
for (j = 0; j < 64; j += 4) {
for (int cnt = 0; cnt < 4; ++cnt, ++i) {
int temp1 = A[i][j];
int temp2 = A[i][j + 1];
int temp3 = A[i][j + 2];
int temp4 = A[i][j + 3];
B[j][i] = temp1;
B[j + 1][i] = temp2;
B[j + 2][i] = temp3;
B[j + 3][i] = temp4;
}
i -= 4;
}
}
}
void transpose_61(int M, int N, int A[N][M], int B[M][N])
{
int i, j;
const int BLOCK = 17;
for (i = 0; i < N; i += BLOCK) {
for (j = 0; j < M; j += BLOCK) {
for (int x = i; x < N && x < i + BLOCK; ++x)
for (int y = j; y < M && y < j + BLOCK; ++y) B[y][x] = A[x][y];
}
}
}
/*
* You can define additional transpose functions below. We've defined
* a simple one below to help you get started.
*/
/*
* trans - A simple baseline transpose function, not optimized for the cache.
*/
char trans_desc[] = "Simple row-wise scan transpose";
void trans(int M, int N, int A[N][M], int B[M][N])
{
int i, j, tmp;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < M; j++) {
tmp = A[i][j];
B[j][i] = tmp;
}
}
}
/*
* registerFunctions - This function registers your transpose
* functions with the driver. At runtime, the driver will
* evaluate each of the registered functions and summarize their
* performance. This is a handy way to experiment with different
* transpose strategies.
*/
void registerFunctions()
{
/* Register your solution function */
registerTransFunction(transpose_submit, transpose_submit_desc);
/* Register any additional transpose functions */
// registerTransFunction(transpose_submit3, trans_desc);
}
/*
* is_transpose - This helper function checks if B is the transpose of
* A. You can check the correctness of your transpose by calling
* it before returning from the transpose function.
*/
int is_transpose(int M, int N, int A[N][M], int B[M][N])
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < M; ++j) {
if (A[i][j] != B[j][i]) {
return 0;
}
}
}
return 1;
}