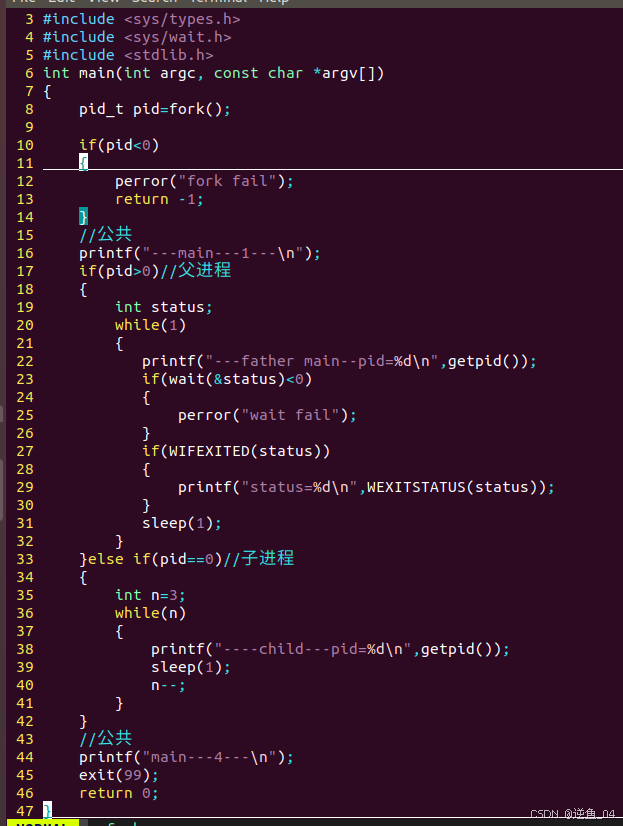
1.waitpid
pid_t waitpid(pid_t pid, int *wstatus, int options);
The value of pid can be:
< -1 meaning wait for any child process whose process group ID is equal to the absolute value of pid.
eg:
pid = -100
进程组 id = |-100| = 100
-1 meaning wait for any child process.
eg:
pid = -1
等待所有子进程 ---当前进程的所有进程
0 meaning wait for any child process whose process group ID is equal to that of the calling process.
eg:
等待 进程组id = PPID 的进程组中的所有子进程
> 0 meaning wait for the child whose process ID is equal to the value of pid.
eg:
pid = 100
等待 pid 为100的子进程状态改变
options:
WNOHANG 以非阻塞的方式 回收子进程 ---1. 如果是非阻塞 ,在没有子进程状态改变时,此时返回0
- 必须配合循环使用 (轮询)


2.exit
exit
_exit
void exit(int status);
功能:
造成进程正常结束
参数:
status //表示退出时带出的状态值
status & 0377 //
exit退出时处理流程:
1.调用 atexit 注册的相关函数
2.刷新所有的stdio的流
#include <unistd.h>
void _exit(int status);
#include <stdlib.h>
void _Exit(int status);
立即结束进程


3.【1】进程和线程的对比
进程(重量级的进程): 更多侧重于 成为 资源分配的单位 ---- 资源分配的基本单位
线程(轻量级的进程): 更侧重于 成为一个 执行单位 ---- 调度执行的最小单位
线程组成:
线程id //long -- 8字节
程序计数器 (program counter) //寄存器 --- 8字节
其它寄存器 // 51 * 8 字节 = 408字节
栈 //8M
【2】进程的组成:
text|data|bss|堆栈| + pcb
线程 --- 主要侧重 去 执行任务 (资源更多的是共享了进程资源)
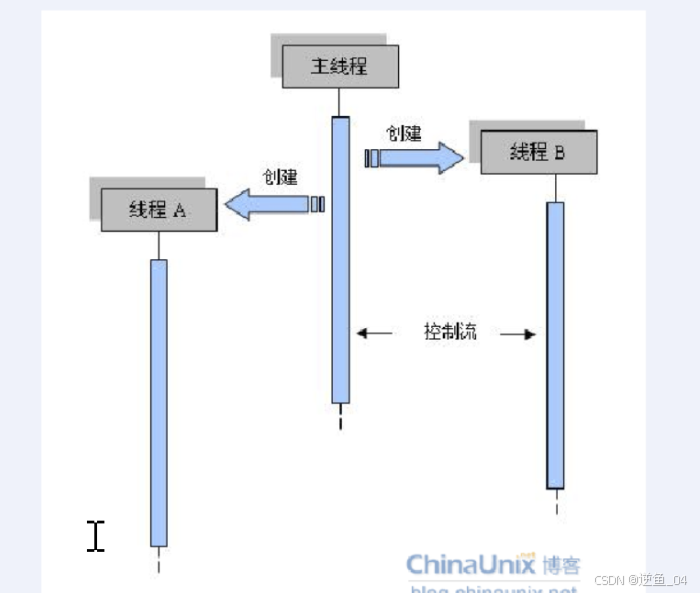
【3】线程 和 进程之间的关系:
1.线程是依附于进程的
2.进程不存在,相关的线程也不复存在
3.一个进程中,可以创建多个线程
4.进一步提高了并发程度
4.线程的创建
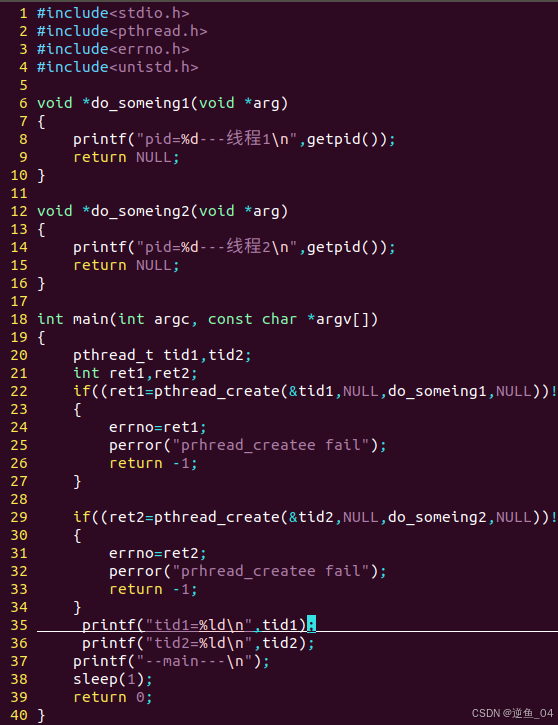
pthread_create //线程创建
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr,
void *(*start_routine) (void *), void *arg);
功能:
创建一个新的线程
参数:
@thread --- 线程id
@attr --- 线程属性 //默认属性 NULL --可结合性
//可分离属性
@start_routine ---线程执行函数//线程回调函数 --- 提现线程任务执行的部分
@arg ---这是传给 start_routine 函数的参数
void * do_something(void *arg) //线程执行函数
{
}
返回值:
成功 0
失败 返回错误码
创建出来的线程 --- 次线程 子线程
原先main函数对应执行流 --- 主线程
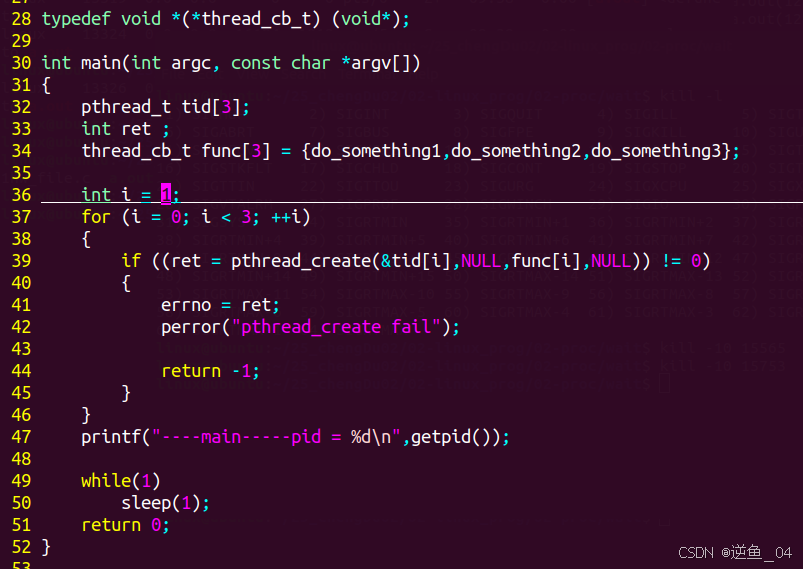
【1】利用函数指针的数组创建多线程
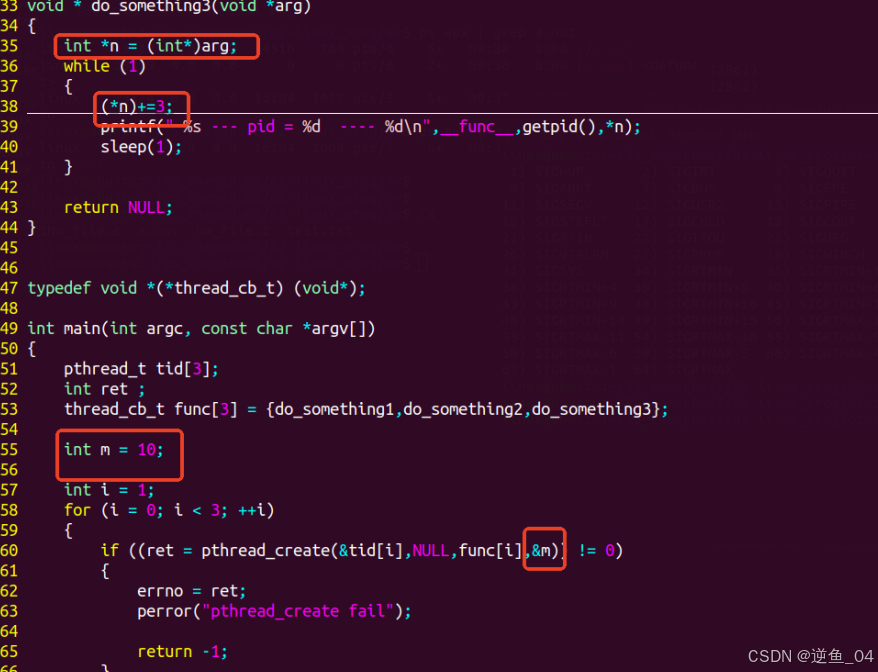
【2】通过传入地址可使多线程修改同一个值(需要传入数值的通用地址并进行强制转换),如果传入值就不可以
The new thread terminates in one of the following ways:
* It calls pthread_exit(3),
specifying an exit status value that is available to another thread
in the same process that calls pthread_join(3).
* It returns from start_routine().
This is equivalent to calling pthread_exit(3) with the value supplied in the return statement.
* It is canceled (see pthread_cancel(3)).
* Any of the threads in the process calls exit(3), or the main thread performs a return from main().
This causes the termination of all threads in the process.
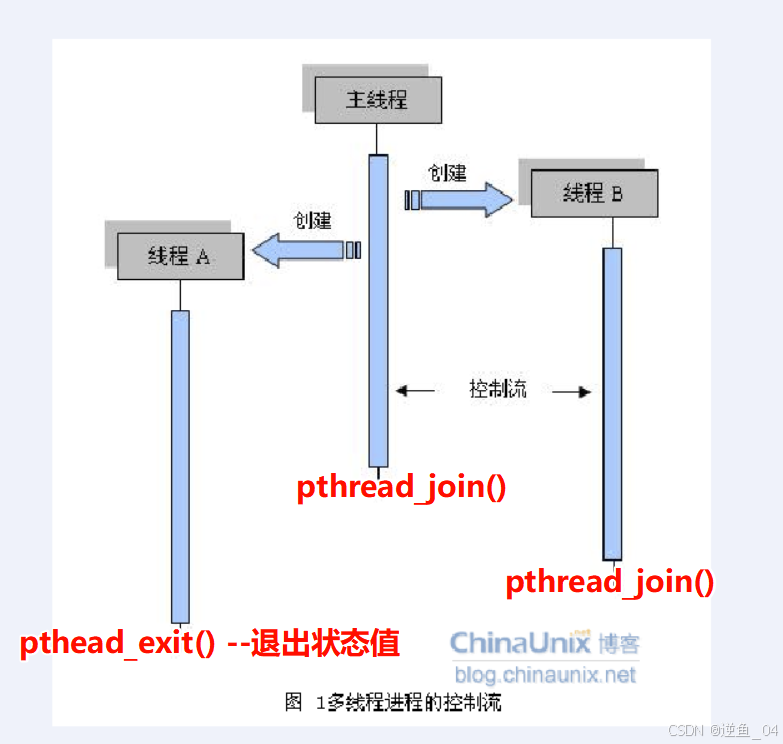
pthread_exit
void pthread_exit(void *retval);
功能:
结束线程
参数:
retval --- 带出的值的 地址
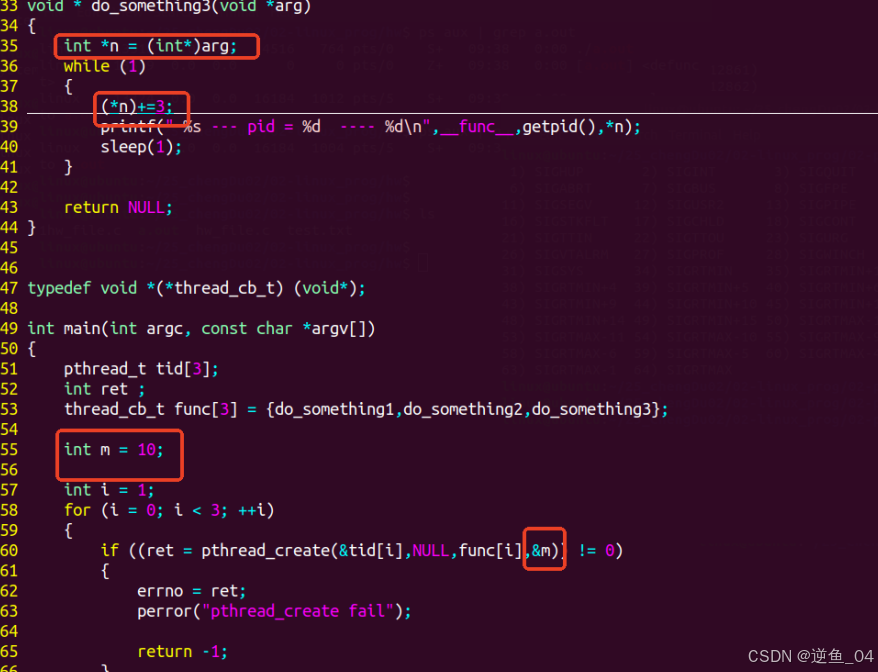
通过传入地址可使多线程修改同一个值(需要传入数值的通用地址并进行强制转换),如果传入值就不可以
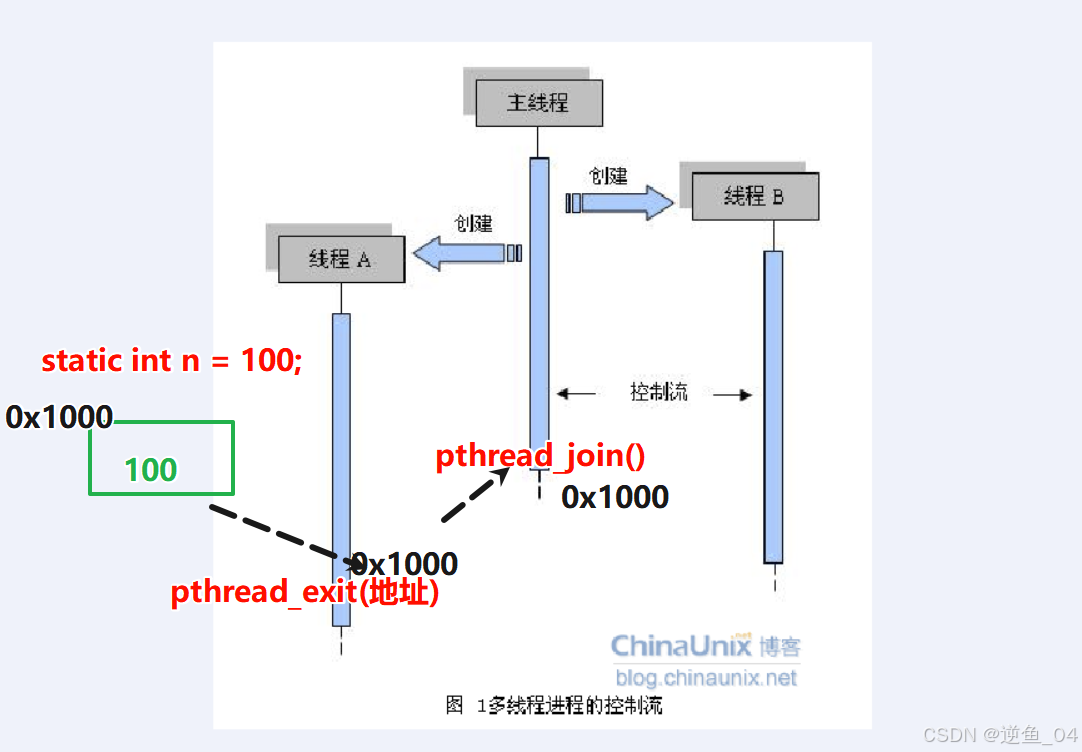
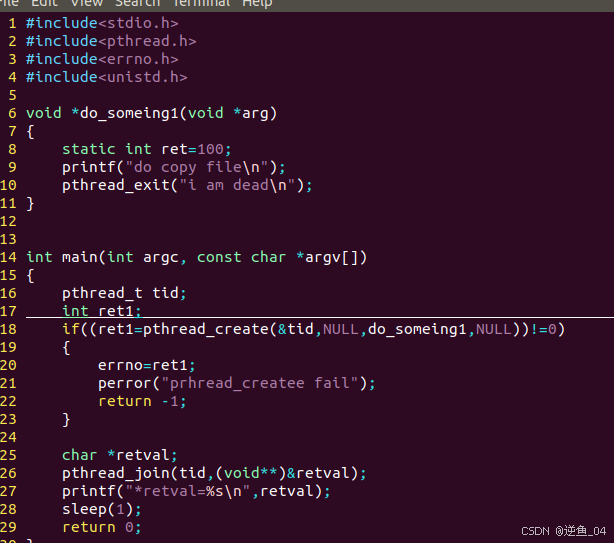
传入字符串地址直接可以打印字符串