混淆矩阵
|--------|--------|--------|
| | 真实值=正例 | 真实值=负例 |
| 预测值=正例 | TP | FP |
| 预测值=负例 | FN | TN |
(根据阈值预测)
P精确度计算:TP/(TP+FP)
R召回率计算:TP/(TP+FN)
AP
综合考虑P R
根据不同的阈值计算出不同的PR组合, 画出PR曲线,计算曲线下面积即为PR
(所有点插值法计算,简单来讲就是近似计算小矩形面积和)
python
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def calculate_precision_recall(confusion_matrices):
#计算P R
recall = []
precision = []
for tp, fp, fn in confusion_matrices:
if tp + fp == 0:
p = 0.0
else:
p = tp / (tp + fp)
if tp + fn == 0:
r = 0.0
else:
r = tp / (tp + fn)
precision.append(p)
recall.append(r)
return recall, precision
def calculate_ap_all_points(recall, precision):
#所有点插值法计算面积
recall = np.concatenate(([0.], recall, [1.]))
precision = np.concatenate(([0.], precision, [0.]))
for i in range(precision.size - 1, 0, -1):
precision[i - 1] = np.maximum(precision[i - 1], precision[i])
ap = np.sum(np.diff(recall) * precision[1:])
return ap
# 示例 (每个元素为 [TP, FP, FN])
confusion_matrices = [
[10, 0, 0],
[8, 1, 2],
[6, 2, 4],
[5, 3, 5],
[4, 4, 6],
[3, 7, 7],
]
# 计算精确率和召回率
recall, precision = calculate_precision_recall(confusion_matrices)
# 计算AP
ap = calculate_ap_all_points(recall, precision)
print(f"平均精度 (AP): {ap}")
plt.plot(recall, precision, marker='o')
plt.xlabel('Recall')
plt.ylabel('Precision')
plt.title('Precision-Recall Curve (AP = {:.3f})'.format(ap))
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()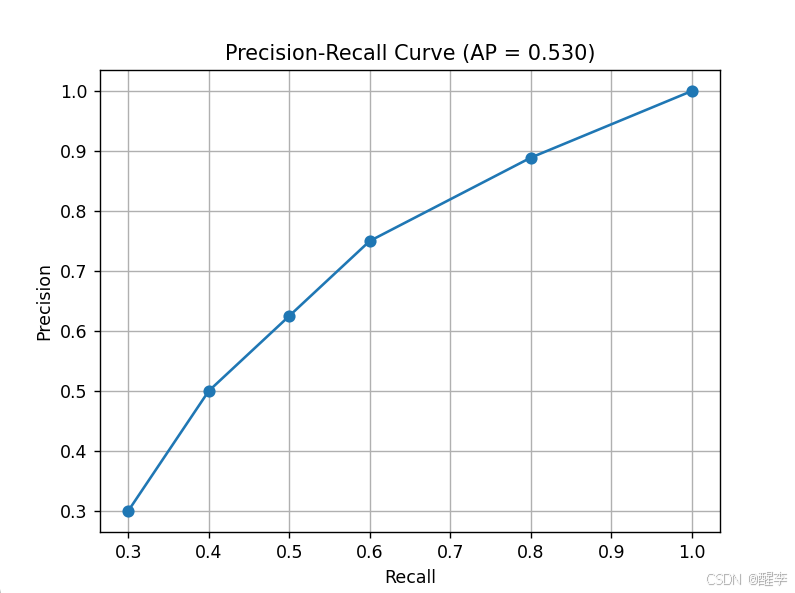
AR
平均召回率
主要是考虑漏检,专注于R
python
import numpy as np
def calculate_ar(true_positives, false_negatives, max_detections):
recall_values = []
for tp, fn in zip(true_positives, false_negatives):
if tp + fn == 0:
recall = 0.0
else:
recall = tp / (tp + fn)
recall_values.append(recall)
# 假设我们只考虑前 max_detections 个召回率值
if len(recall_values) > max_detections:
recall_values = recall_values[:max_detections]
if not recall_values:
return 0.0
ar = np.mean(recall_values)
return ar
# 示例数据
true_positives = [10, 8, 6, 5, 4, 3] # TP
false_negatives = [0, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7] # FP
max_detections = 5 # 最大检测次数
# 计算AR
ar = calculate_ar(true_positives, false_negatives, max_detections)
print(f"平均召回率 (AR): {ar}")
#计算maxDets 为10时候的AR
max_detections_2 = 10
ar_2 = calculate_ar(true_positives, false_negatives, max_detections_2)
print(f"平均召回率 (AR)maxDets为10 : {ar_2}")平均精度(Average Precision,AP)以及AP50、AP75、APs、APm、APl、Box AP、Mask AP等不同阈值和细分类别的评估指标说明-CSDN博客