watch的作用是监听数据的变化,当数据发生变化时,执行一个回调函数,它的实现依赖于 Vue 的响应式系统(reactive和ref)
案例
通过以下案例来理解,首先引入reactive、effect、watch三个函数,声明obj响应式数据,接着执行watch函数,第一个参数为监听数据,第二个参数为监听回调,最后两秒后修改obj的name值
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<script src="../../dist/vue.global.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script>
const { reactive, effect, watch } = Vue
// 1. reactive 构建响应性数据
const obj = reactive({
name: 'jc'
})
// 2. 执行了 watch 函数
watch(obj, (value, oldValue) => {
console.log('watch 触发了')
console.log(value)
})
// 3. 两秒后触发 setter 行为
setTimeout(() => {
obj.name = 'cc'
}, 2000)
</script>
</body>
</html>doWatch方法
watch函数定义在packages/runtime-core/src/apiWatch.ts文件下:
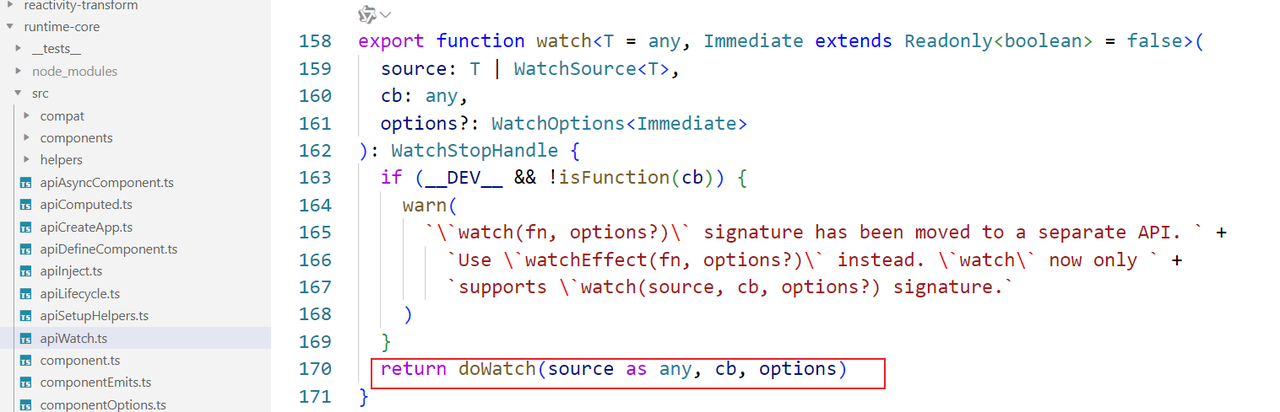
该函数实际执行的是doWatch方法,它会根据传入的参数( source 和 cb )生成一个监听器
1)根据 source 的类型生成 getter
getter是一个函数,用于获取监听数据的值,根据source的类型:
reactive类型,直接返回sourceref类型,返回source.value- 如果
source是一个函数,getter会执行这个函数
2)定义 job 函数
job是watch的核心逻辑,它会在数据变化时执行,它的主要任务是:
- 获取新的值
newValue - 检查新值和旧值是否不同
- 如果不同,执行回调函数
cb
3)调度器 scheduler
scheduler决定了job的执行时机,Vue 提供了三种调度方式:
-
sync:同步执行 -
post:在渲染后执行 -
pre:在渲染前执行(默认)function doWatch(
source: WatchSource | WatchSource[] | WatchEffect | object,
cb: WatchCallback | null,
{ immediate, deep, flush, onTrack, onTrigger }: WatchOptions = EMPTY_OBJ
): WatchStopHandle {
// 省略const instance = currentInstance let getter: () => any let forceTrigger = false let isMultiSource = false if (isRef(source)) { // 是否 ref 类型 getter = () => source.value forceTrigger = isShallow(source) } else if (isReactive(source)) { // 是否 reactive 类型 getter = () => source deep = true // 主动开启 深度监听 } else if (isArray(source)) { isMultiSource = true forceTrigger = source.some(s => isReactive(s) || isShallow(s)) getter = () => source.map(s => { if (isRef(s)) { return s.value } else if (isReactive(s)) { return traverse(s) } else if (isFunction(s)) { return callWithErrorHandling(s, instance, ErrorCodes.WATCH_GETTER) } else { __DEV__ && warnInvalidSource(s) } }) } else if (isFunction(source)) { if (cb) { // getter with cb getter = () => callWithErrorHandling(source, instance, ErrorCodes.WATCH_GETTER) } else { // no cb -> simple effect getter = () => { if (instance && instance.isUnmounted) { return } if (cleanup) { cleanup() } return callWithAsyncErrorHandling( source, instance, ErrorCodes.WATCH_CALLBACK, [onCleanup] ) } } } else { getter = NOOP __DEV__ && warnInvalidSource(source) } // 省略 if (cb && deep) { const baseGetter = getter // getter 为 () => source getter = () => traverse(baseGetter()) } // 省略 // 定义 oldValue isMultiSource 是否有多个源 [value1, value2] 需要监听 let oldValue = isMultiSource ? [] : INITIAL_WATCHER_VALUE // job 核心逻辑 const job: SchedulerJob = () => { if (!effect.active) { return } if (cb) { // watch(source, cb) const newValue = effect.run() if ( deep || forceTrigger || (isMultiSource ? (newValue as any[]).some((v, i) => hasChanged(v, (oldValue as any[])[i]) ) : hasChanged(newValue, oldValue)) || (__COMPAT__ && isArray(newValue) && isCompatEnabled(DeprecationTypes.WATCH_ARRAY, instance)) ) { // cleanup before running cb again if (cleanup) { cleanup() } callWithAsyncErrorHandling(cb, instance, ErrorCodes.WATCH_CALLBACK, [ newValue, // pass undefined as the old value when it's changed for the first time oldValue === INITIAL_WATCHER_VALUE ? undefined : oldValue, onCleanup ]) oldValue = newValue } } else { // watchEffect effect.run() } } // important: mark the job as a watcher callback so that scheduler knows // it is allowed to self-trigger (#1727) job.allowRecurse = !!cb let scheduler: EffectScheduler if (flush === 'sync') { scheduler = job as any // the scheduler function gets called directly } else if (flush === 'post') { scheduler = () => queuePostRenderEffect(job, instance && instance.suspense) } else { // default: 'pre' scheduler = () => queuePreFlushCb(job) // 调度器赋值 也是核心逻辑 } const effect = new ReactiveEffect(getter, scheduler) if (__DEV__) { effect.onTrack = onTrack effect.onTrigger = onTrigger } // initial run if (cb) { if (immediate) { // 默认自动执行 watch 一次 job() // job 触发意味着 watch 被立即执行一次 } else { oldValue = effect.run() // 等于执行 fn 函数 即 () => traverse(baseGetter()) 即 () => source 即 传入的监听数据 } } else if (flush === 'post') { queuePostRenderEffect( effect.run.bind(effect), instance && instance.suspense ) } else { effect.run() } return () => { effect.stop() // 监听停止 if (instance && instance.scope) { remove(instance.scope.effects!, effect) } }}
根据传入source监听数据类型不同走不同逻辑,当前source为reactive类型,所以getter直接赋值为() => source,另外还可以看到类型为reactive时,默认开启深度监听 deep = true
由于存在cb监听回调和deep,所以baseGetter等于getter ,即() => source, getter赋值为() => traverse(baseGetter())
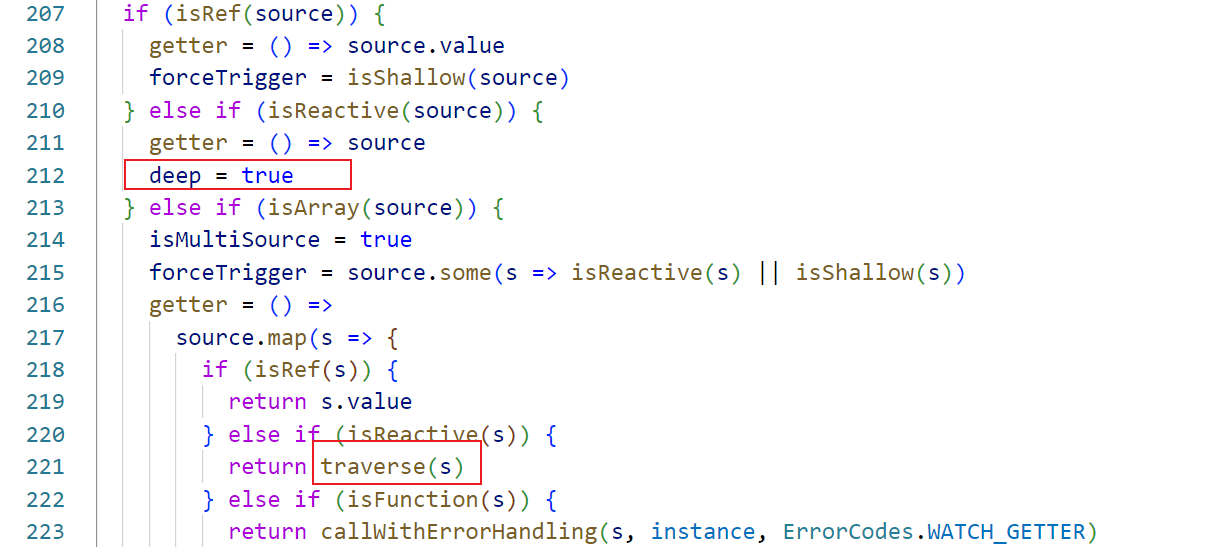
之后又定义了oldValue值,默认为空对象,也是回调函数中的oldValue。接着定义了一个 job 函数,这是 watch 的核心逻辑,后面再分析
然后又创建了一个调度器scheduler ,在computed中提到过,在依赖触发时,会执行该方法。此时scheduler被赋值为() => queuePreFlushCb(job),将job函数传入到queuePreFlushCb方法中,该逻辑之后来分析

接着又创建了一个ReactiveEffect实例,将赋值后的getter和scheduler传入
由于存在cb回调函数,根据判断配置中immediate存在时,就执行job方法,我们可以理解为job的触发watch被立即执行一次 。否则执行effect.run即执行fn方法
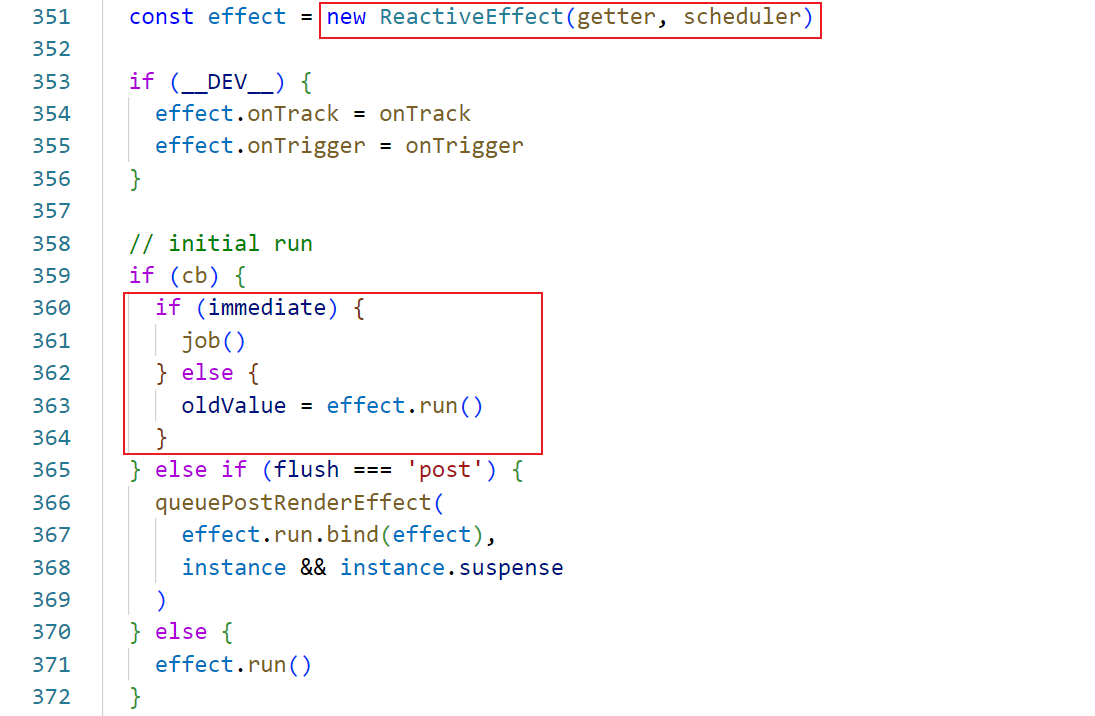
当前fn为getter即() => traverse(baseGetter()),就是执行() => source,结果为传入的监听对象source :
此时watch函数执行完毕,两秒后触发obj的setter行为,依赖触发trigger执行,当前effects为:
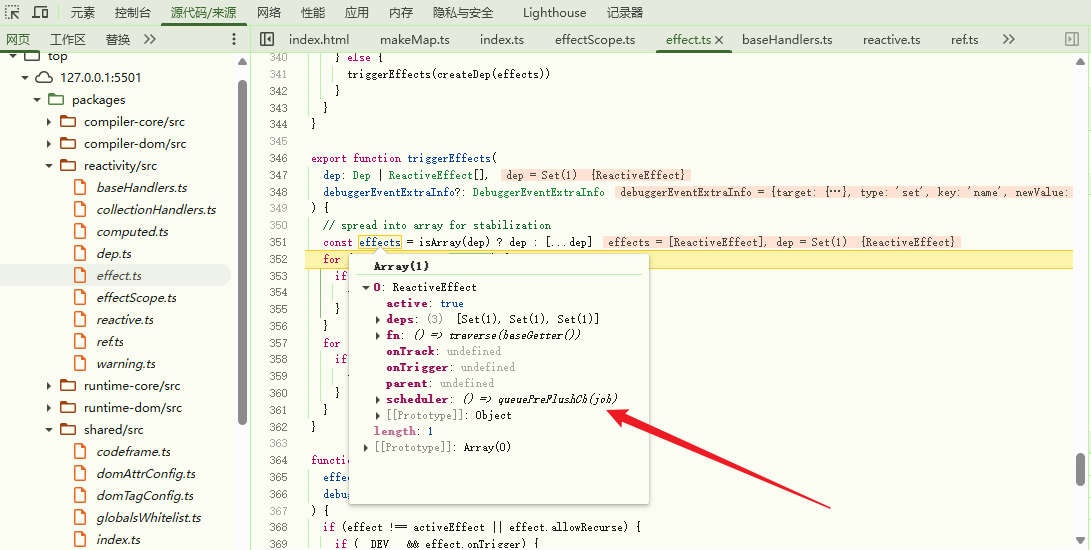
之后再遍历执行每个 effect ,此时存在 scheduler 调度器 ,执行scheduler方法。当前scheduler为之前赋值的() => queuePreFlushCb(job),再来看下queuePreFlushCb方法,该方法定义在packages/runtime-core/src/scheduler.ts文件中:
export function queuePreFlushCb(cb: SchedulerJob) {
queueCb(cb, activePreFlushCbs, pendingPreFlushCbs, preFlushIndex)
}queueCb方法
实际执行的是queueCb方法:
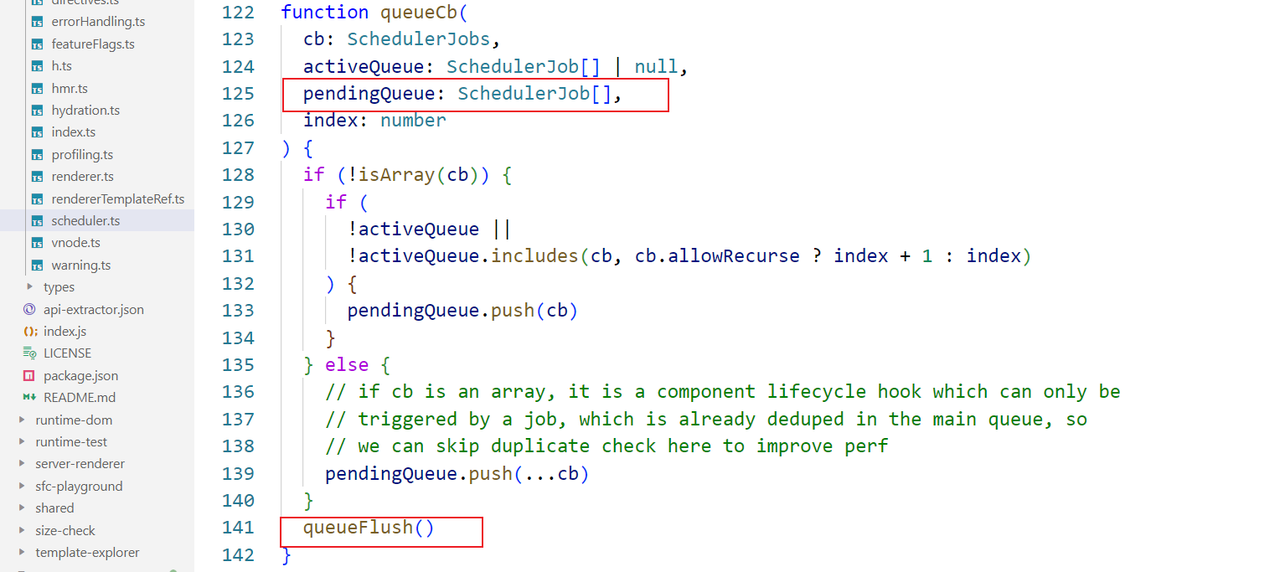
该方法定义了一个 pendingQueue 队列数组 ,插入传入的cb回调即传入的job函数,执行queueFlush方法:
function queueFlush() {
if (!isFlushing && !isFlushPending) {
isFlushPending = true
currentFlushPromise = resolvedPromise.then(flushJobs)
}
}可以看出watch的job执行都是一个微任务,当前同步任务执行完毕后,执行微任务 ,之后执行flushJobs方法:
function flushJobs(seen?: CountMap) {
isFlushPending = false
isFlushing = true
if (__DEV__) {
seen = seen || new Map()
}
flushPreFlushCbs(seen)
// Sort queue before flush.
// This ensures that:
// 1. Components are updated from parent to child. (because parent is always
// created before the child so its render effect will have smaller
// priority number)
// 2. If a component is unmounted during a parent component's update,
// its update can be skipped.
queue.sort((a, b) => getId(a) - getId(b))
// conditional usage of checkRecursiveUpdate must be determined out of
// try ... catch block since Rollup by default de-optimizes treeshaking
// inside try-catch. This can leave all warning code unshaked. Although
// they would get eventually shaken by a minifier like terser, some minifiers
// would fail to do that (e.g. https://github.com/evanw/esbuild/issues/1610)
const check = __DEV__
? (job: SchedulerJob) => checkRecursiveUpdates(seen!, job)
: NOOP
try {
for (flushIndex = 0; flushIndex < queue.length; flushIndex++) {
const job = queue[flushIndex]
if (job && job.active !== false) {
if (__DEV__ && check(job)) {
continue
}
// console.log(`running:`, job.id)
callWithErrorHandling(job, null, ErrorCodes.SCHEDULER)
}
}
} finally {
flushIndex = 0
queue.length = 0
flushPostFlushCbs(seen)
isFlushing = false
currentFlushPromise = null
// some postFlushCb queued jobs!
// keep flushing until it drains.
if (
queue.length ||
pendingPreFlushCbs.length ||
pendingPostFlushCbs.length
) {
flushJobs(seen)
}
}
}然后执行flushPreFlushCbs(seen)方法:
export function flushPreFlushCbs(
seen?: CountMap,
parentJob: SchedulerJob | null = null
) {
if (pendingPreFlushCbs.length) {
currentPreFlushParentJob = parentJob // job 函数
activePreFlushCbs = [...new Set(pendingPreFlushCbs)] // 取代 pendingPreFlushCbs
pendingPreFlushCbs.length = 0 // 置空 下次不会再触发
if (__DEV__) {
seen = seen || new Map()
}
for (
preFlushIndex = 0;
preFlushIndex < activePreFlushCbs.length;
preFlushIndex++
) {
if (
__DEV__ &&
checkRecursiveUpdates(seen!, activePreFlushCbs[preFlushIndex])
) {
continue
}
activePreFlushCbs[preFlushIndex]() // 当前 job 函数执行
}
activePreFlushCbs = null
preFlushIndex = 0
currentPreFlushParentJob = null
// recursively flush until it drains
flushPreFlushCbs(seen, parentJob)
}
}当前pendingPreFlushCbs为传入的job方法,之后将去重后的pendingPreFlushCbs赋值给activePreFlushCbs,遍历执行activePreFlushCbspreFlushIndex,实际是执行每个job函数:
const job: SchedulerJob = () => {
if (!effect.active) {
return
}
if (cb) {
// watch(source, cb)
const newValue = effect.run()
if (
deep ||
forceTrigger ||
(isMultiSource
? (newValue as any[]).some((v, i) =>
hasChanged(v, (oldValue as any[])[i])
)
: hasChanged(newValue, oldValue)) ||
(__COMPAT__ &&
isArray(newValue) &&
isCompatEnabled(DeprecationTypes.WATCH_ARRAY, instance))
) {
// cleanup before running cb again
if (cleanup) {
cleanup()
}
callWithAsyncErrorHandling(cb, instance, ErrorCodes.WATCH_CALLBACK, [
newValue,
// pass undefined as the old value when it's changed for the first time
oldValue === INITIAL_WATCHER_VALUE ? undefined : oldValue,
onCleanup
])
oldValue = newValue
}
} else {
// watchEffect
effect.run()
}
}run方法执行实际执行getter即() => traverse(baseGetter()),此时newValue为cc
再看下traverse方法,它用于深度遍历对象的所有属性,确保对象的所有依赖都被追踪
export function traverse(value: unknown, seen?: Set<unknown>) {
if (!isObject(value) || (value as any)[ReactiveFlags.SKIP]) {
return value
}
seen = seen || new Set()
if (seen.has(value)) {
return value
}
seen.add(value)
if (isRef(value)) {
traverse(value.value, seen)
} else if (isArray(value)) {
for (let i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {
traverse(value[i], seen)
}
} else if (isSet(value) || isMap(value)) {
value.forEach((v: any) => {
traverse(v, seen)
})
} else if (isPlainObject(value)) {
for (const key in value) {
traverse((value as any)[key], seen)
}
}
return value
}该方法由于值类型不同,会递归处理返回最终的值 ,接着执行callWithAsyncErrorHandling方法:
export function callWithAsyncErrorHandling(
fn: Function | Function[],
instance: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
type: ErrorTypes,
args?: unknown[]
): any[] {
if (isFunction(fn)) {
const res = callWithErrorHandling(fn, instance, type, args)
if (res && isPromise(res)) {
res.catch(err => {
handleError(err, instance, type)
})
}
return res
}
const values = []
for (let i = 0; i < fn.length; i++) {
values.push(callWithAsyncErrorHandling(fn[i], instance, type, args))
}
return values
}
export function callWithErrorHandling(
fn: Function,
instance: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
type: ErrorTypes,
args?: unknown[]
) {
let res
// 统一处理监听 错误
try {
res = args ? fn(...args) : fn()
} catch (err) {
handleError(err, instance, type)
}
return res
}执行了cb回调函数即watch传入的匿名函数,callWithAsyncErrorHandling主要是对错误统一监听处理,最后将 newValue 赋值给 oldValue ,watch至此执行完毕
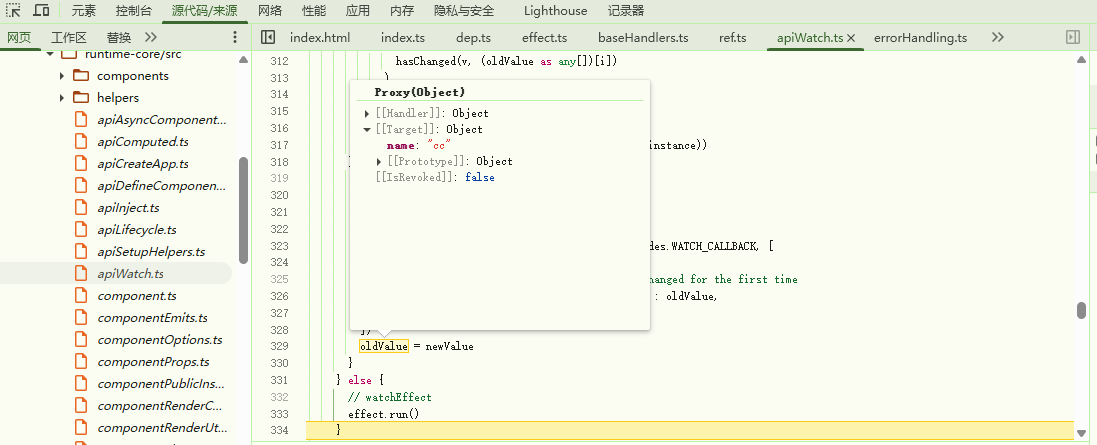
总结
1)watch函数实际执行的是doWatch方法,调度器scheduler在watch中很关键
2)scheduler、ReactiveEffect两者之间存在互相作用的关系,一旦effect触发了scheduler,那么会导致queuePreFlushCb(job)执行,job 方法就被塞入微任务的队列中
3)只要job()触发,那么就表示watch触发了一次