Mybatis解析
0.引入
Mybatis源码也是对Jbdc的再一次封装,不管怎么进行包装,还是会有获取链接、preparedStatement、封装参数、执行这些步骤的。本文来探索一下其运行原理。下面从最简单的mybatis使用案例,来看看mybatis的步骤。
java
public class Test01 {
// 测试方法!============
public static void main(String[] args) {
String configFile = "mybatis-config.xml";
try (
// 1. 加载配置文件
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(configFile)) {
// 2. 创建 SqlSessionFactory 对象
SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
// 3. 获取 SqlSession 对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sessionFactory.openSession();
// 获取mapper
InventoryMapper inventoryMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(InventoryMapper.class);
// 调用mapper的方法
List<Inventory> allInventory = inventoryMapper.getAllInventory();
for (Inventory inventory : allInventory) {
System.out.println(inventory);
}
// System.out.println(inventoryMapper.getInventoryById(1));
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
// 实体类对象
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Data
public class Inventory implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Integer goodsId;
private String goodsName;
private Date createTime;
private Date modifyTime;
private Integer inventory;
}数据库配置文件
properties
db.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
db.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/trans_inventory?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
db.username=root
db.password=123456配置文件如下:
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<properties resource="db.properties" />
<settings>
<!--开启驼峰命名-->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
<!-- 配置mybatis的环境信息 -->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<!-- 配置JDBC事务控制,由mybatis进行管理 -->
<transactionManager type="jdbc" />
<!-- 配置数据源,采用dbcp连接池 -->
<dataSource type="pooled">
<property name="driver" value="${db.driver}" />
<property name="url" value="${db.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${db.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${db.password}" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers> <!--mapper映射文件-->
<mapper resource="mapper/InventoryMapper.xml" />
</mappers>
</configuration>mapper接口和xml文件
java
public interface InventoryMapper {
List<Inventory> getAllInventory();
Inventory getInventoryById(@Param("id") Integer id);
}
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.feng.mapper.InventoryMapper">
<select id="getAllInventory" resultType="com.feng.entity.Inventory">
select *
from inventory
</select>
<select id="getInventoryById" resultType="com.feng.entity.Inventory">
select *
from inventory
where goods_id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>1.加载配置文件
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(configFile)
可以看到是这一行代码。其中Resources是Mybatis的工具类。从这个开始一层一层往下看
java
public class Resources {
// new 了一个ClassLoaderWrapper对象
private static final ClassLoaderWrapper classLoaderWrapper = new ClassLoaderWrapper();
public static InputStream getResourceAsStream(String resource) throws IOException {
return getResourceAsStream(null, resource);
}
// loader = null, resource = "xxxx.xml"
public static InputStream getResourceAsStream(ClassLoader loader, String resource) throws IOException {
// ====================== 这一行
InputStream in = classLoaderWrapper.getResourceAsStream(resource, loader);
if (in == null) {
throw new IOException("Could not find resource " + resource);
}
return in;
}
}
public class ClassLoaderWrapper {
ClassLoader defaultClassLoader;
ClassLoader systemClassLoader;
// --------- 构造函数
ClassLoaderWrapper() {
try {
// jdk的方法,得到系统类加载器
systemClassLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
} catch (SecurityException ignored) {
// AccessControlException on Google App Engine
}
}
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String resource, ClassLoader classLoader) {
// getResourceAsStream()方法里面用到了 getClassLoaders(null)
return getResourceAsStream(resource, getClassLoaders(classLoader));
}
// 得到所有的类加载器:::classLoader = null
ClassLoader[] getClassLoaders(ClassLoader classLoader) {
return new ClassLoader[] { classLoader, defaultClassLoader, Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(),
getClass().getClassLoader(), systemClassLoader };
}
// 遍历所有的类加载器,谁加载到了就返回谁的inputStream
InputStream getResourceAsStream(String resource, ClassLoader[] classLoader) {
for (ClassLoader cl : classLoader) {
if (null != cl) {
// try to find the resource as passed
InputStream returnValue = cl.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// now, some class loaders want this leading "/", so we'll add it and try again if we didn't find the resource
if (null == returnValue) {
returnValue = cl.getResourceAsStream("/" + resource);
}
if (null != returnValue) {
return returnValue;
}
}
}
return null;
}
}主要是通过ClassLoader.getResourceAsStream()方法获取指定的classpath路径下的Resource
2.创建SqlSessionFactory
java
// 2. 创建 SqlSessionFactory 对象
SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);第一步,无参构造函数创建了一个SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象,然后调用其build方法。这很明显是"建造者设计模式"。
主要来看后面的build(inputStream)方法
java
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) {
return build(inputStream, null, null);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
//1.创建一个xml解析的builder,是建造者模式
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
// 2.上面创建的parser.parse()【可以理解为创建Configuration对象,并设置其属性】
return build(parser.parse()); // 3.build出SqlSessionFactory
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
if (inputStream != null) {
inputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
// 3.我们发现SqlSessionFactory默认是DefaultSqlSessionFactory类型的
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
}
// XMLConfigBuilder.java里面
public XMLConfigBuilder(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties props) {
this(Configuration.class, inputStream, environment, props);
}
public XMLConfigBuilder(Class<? extends Configuration> configClass, InputStream inputStream, String environment,
Properties props) {
this(configClass, new XPathParser(inputStream, true, props, new XMLMapperEntityResolver()), environment, props);
}
private XMLConfigBuilder(Class<? extends Configuration> configClass, XPathParser parser, String environment,
Properties props) {
super(newConfig(configClass));
ErrorContext.instance().resource("SQL Mapper Configuration");
this.configuration.setVariables(props);
this.parsed = false;
this.environment = environment;
this.parser = parser;
}【XMLConfigBuilder类】parser.parse()
java
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
// 一级结点configuration【可以想一想mybatis的配置文件的样子】
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
// ===========解析各个结点!!!!!
// ----里面的各个方法都会把解析好的属性设置到configuration成员变量里面
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
// issue #117 read properties first
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfsImpl(settings);
loadCustomLogImpl(settings);
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
pluginsElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
/*
<!-- 配置mybatis的环境信息 -->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<!-- 配置JDBC事务控制,由mybatis进行管理 -->
<transactionManager type="jdbc" />
<!-- 配置数据源,采用dbcp连接池 -->
<dataSource type="pooled">
<property name="driver" value="${db.driver}" />
<property name="url" value="${db.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${db.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${db.password}" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
*/
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlersElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
//===重点关注一下这个。。。====
mappersElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}看到这里,我们可以大致梳理一下mybatis初始化的时序图;
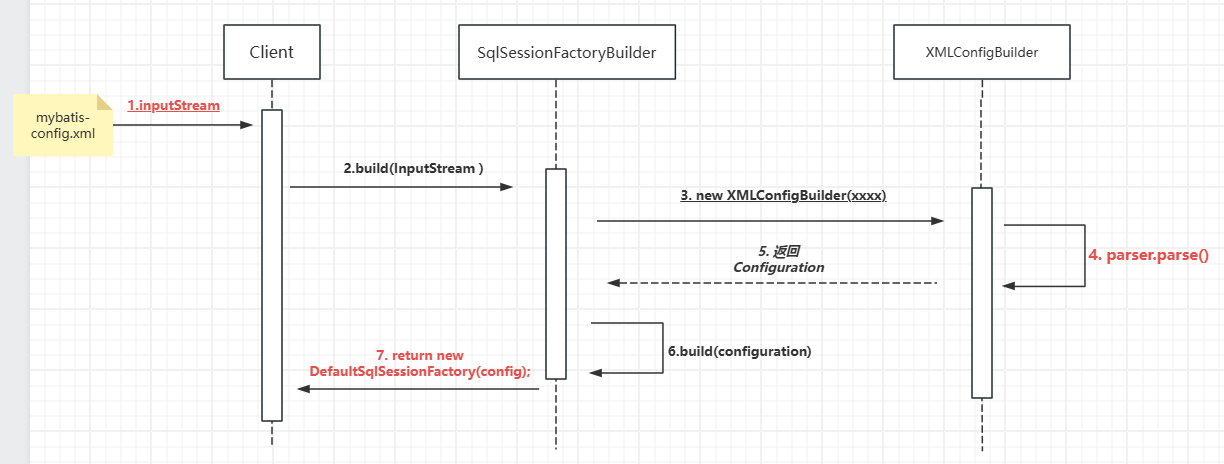
调用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象的build(inputStream)方法;
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder会根据输入流inputStream等信息创建XMLConfigBuilder对象;
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder调用XMLConfigBuilder对象的parse()方法;
XMLConfigBuilder对象返回Configuration对象;
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder根据Configuration对象创建一个DefaultSessionFactory对象;
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder返回 DefaultSessionFactory对象给Client,供Client使用。
mappersElement(root.evalNode("mappers")) 解析mappers标签
java
/*
<mappers> <!--mapper映射文件-->
<mapper resource="mapper/InventoryMapper.xml" />
<mapper ...........>
</mappers>
*/
private void mappersElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
//若没有 <mappers> 配置节点,直接返回,无需处理
if (context == null) {
return;
}
//遍历子节点 context是<mappers>
for (XNode child : context.getChildren()) { // <mapper>
//1.如果是包扫描方式
//扫描指定包路径下的所有 Mapper 接口
//通过 configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage) 调用,
//利用反射扫描包中的接口,并自动注册这些 Mapper
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
//若非 <package> 节点,则处理 <mapper> 配置
/*
<mapper resource="..."/> <!-- 类路径下的 XML -->
<mapper url="..."/> <!-- 网络或磁盘的 XML -->
<mapper class="..."/> <!-- Mapper 接口类 -->
*/
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
// resource方式----
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
try (InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource)) {
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource,
configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
}
//url方式-----
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
try (InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url)) {
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url,
configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
}
// class方式----
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException(
"A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}mapperParser.parse();
java
public void parse() {
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 1.
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
//2.把namespace(接口类型)和工厂类绑定起来
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
// 3.
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
// 4.
parsePendingStatements();
}- 第一个:
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
java
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.isEmpty()) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
// 看这里
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}解析标签,可以很清楚的看到有resultMap,很熟悉吧。除此之外,context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete")是不是更熟悉了?
解析增删改查:
java
//buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list) {
if (configuration.getDatabaseId() != null) {
buildStatementFromContext(list, configuration.getDatabaseId());
}
buildStatementFromContext(list, null);
}
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
//循环增删改查标签
for (XNode context : list) {
final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser = new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration, builderAssistant, context,
requiredDatabaseId);
try {
statementParser.parseStatementNode(); // 看下面的====
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteStatement(statementParser);
}
}
}
// 解析增删改查标签的具体方法
public void parseStatementNode() {
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {
return;
}
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
//1.SQL 类型判断
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
//查询操作(SELECT)默认使用缓存
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);
// 将 <include refid="..."> 替换为对应的 SQL 片段(如公共的列名列表),实现代码复用
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
// Parse selectKey after includes and remove them.
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// Parse the SQL (pre: <selectKey> and <include> were parsed and removed)
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);
if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) {
keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId);
} else {
keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys",
configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType))
? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
/*
动态 SQL 解析:将包含 ${}、#{}、<if>、<foreach> 的 SQL 转换为可执行的 SqlSource 对象。
最终 SQL:根据参数生成实际执行的 SQL 及参数映射(如预编译的 PreparedStatement)
*/
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
StatementType statementType = StatementType
.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");
if (resultTypeClass == null && resultMap == null) {
resultTypeClass = MapperAnnotationBuilder.getMethodReturnType(builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace(), id);
}
String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType");
ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType);
if (resultSetTypeEnum == null) {
resultSetTypeEnum = configuration.getDefaultResultSetType();
}
String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets");
boolean dirtySelect = context.getBooleanAttribute("affectData", Boolean.FALSE);
// 将所有配置封装为 MappedStatement 并注册到 Configuration,供后续执行使用
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType, fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap,
parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass, resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets, dirtySelect);
}
parseStatementNode()该方法负责将 XML 中的 SQL 节点解析为 MyBatis 内部可执行的 MappedStatement,处理包括动态 SQL、参数映射、主键生成、缓存配置等核心逻辑。
- 第二个
bindMapperForNamespace()
java
// 2.bindMapperForNamespace();往下走会发现是这个
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}上述源码表明,每一个mapper接口,和一个Mapper代理工厂对应起来的,存到map里面的。 【 放在knownMappers 】
回到这一节最开始
java
// 3.我们发现SqlSessionFactory默认是DefaultSqlSessionFactory类型的
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}这样SqlSessionFactory创建完成了。!!上面中间一大坨都是mybatis的初始化工作
3.SqlSession会话
java
//3. 获取 SqlSession 对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sessionFactory.openSession();从上面看出,sessionFactory的类型是DefaultSqlSessionFactory的,所以上面的opensession()是它的方法。
java
public class DefaultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory {
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
// Configuration类中有默认的protected ExecutorType defaultExecutorType = ExecutorType.SIMPLE;
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
// autoCommit: 是否自动提交事务!-- 这里传过来是false
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level,
boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
// 获取环境配置
/*
从全局 Configuration 对象中获取环境配置(<environments> 标签的配置),
包含 数据源(DataSource) 和 事务工厂(TransactionFactory) 信息
*/
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
// 获取事务工厂 我们配置的是jdbc
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
//基于数据源生成事务对象 Transaction
//level:事务隔离级别(如 READ_COMMITTED),若未指定则使用数据库默认。
//autoCommit:是否自动提交事务。这里是false,如果是修改数据库的话
//需手动调用 sqlSession.commit()。
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
// MyBatis 默认的 SqlSession 实现,持有 Executor 和 Configuration 对象。
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
}上述方法用于从数据源(DataSource)中创建一个新的 SqlSession 实例,核心流程包含 事务初始化 、执行器创建 和 会话构建 三个阶段。
其中,执行器Executor有三类:
- SIMPLE:普通执行器(默认)。
- REUSE:重用预处理语句(PreparedStatement)。
- BATCH:批量执行更新操作。
java
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) { // BATCH -- 批处理
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else { // ===== 普通执行器
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
//若二级缓存开启(cacheEnabled=true),会用 CachingExecutor 包装基础执行器。
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
return (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
}4.获取Mapper
java
InventoryMapper inventoryMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(InventoryMapper.class);从上面可以知道,sqlSession的类型是DefaultSqlSession。
java
// 它持有Configuration、Executor
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return configuration.getMapper(type, this);
}
}
// Configuration.java
public class Configuration {
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
// 从knownMappers的Map里根据接口类型(interface mapper.UserMapper)取出对应的工厂类。
// 在第二节里面【 每一个mapper接口,和一个Mapper代理工厂对应起来的,存到map里面的。】
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
// mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);======
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
....
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
// jdk动态代理--一看mapperProxy就是实现了jdk的InvocationHandler
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}MapperProxy<T>
java
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
}
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
}5.执行sql
java
List<Inventory> allInventory = inventoryMapper.getAllInventory();既然是生成的代理对象,那么肯定是执行的代理方法涩。invoke() 上一节的末尾
java
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
//判断是否需要去执行SQL还是直接执行方法
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
}
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
//为 Mapper 接口方法 创建并缓存调用器(MapperMethodInvoker)
private MapperMethodInvoker cachedInvoker(Method method) throws Throwable {
try {
// 1.缓存检查与创建
//利用 methodCache 缓存已处理的 Method 对象,避免重复创建 Invoker。
//类似 Java 8 Map 的 computeIfAbsent:若缓存中不存在该 Method,
// 则通过 Lambda 表达式创建 Invoker 并存入缓存。
return MapUtil.computeIfAbsent(methodCache, method, m -> {
//2.1处理普通接口方法(非 default)
if (!m.isDefault()) {
return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
}
//2.2 default
try {
if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava8(method));
}
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava9(method));
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InstantiationException | InvocationTargetException
| NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
});
} catch (RuntimeException re) {
Throwable cause = re.getCause();
throw cause == null ? re : cause;
}
}
}new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()))
PlainMethodInvoker是MapperProxy的静态内部类
java
private static class PlainMethodInvoker implements MapperMethodInvoker {
....
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {
// 调用的是MapperMethod::execute()方法
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
}MapperMethod:核心类,将方法调用转换为 SQL 操作:
- 解析方法参数。
- 匹配对应的 SQL 语句(通过
SqlCommand)。 - 处理返回结果(通过
MethodSignature)。
java
// ==MapperMethod.java
public class MapperMethod {
// 下面的源码一目了然了吧
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional() && (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ "' attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
}对于我们的例子,执行的是查询方法【List allInventory = inventoryMapper.getAllInventory();】
java
// ==MapperMethod.java
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args); // 肯定就是走到这里来了
private <E> Object executeForMany(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
List<E> result;
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
if (method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);
// 这俩
result = sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param, rowBounds);
} else {
result = sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param); // 这俩
}
// issue #510 Collections & arrays support
if (!method.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(result.getClass())) {
if (method.getReturnType().isArray()) {
return convertToArray(result);
}
return convertToDeclaredCollection(sqlSession.getConfiguration(), result);
}
return result;
}
// result = sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param);
// 一层层往下会来到
// DefaultSqlsession.java===
private <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler handler) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
dirty |= ms.isDirtySelect();
// 会发现---是执行器运行的sql
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, handler);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
// CachingExecutor.java
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler)
throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler,
CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
// delegate就是一个Executor类型的
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
//继续往下到了BaseExecutor.java
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds,
ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
// 执行查询
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
// 一直往下PreparedStatementHandler.java
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// PreparedStatement---它是java.sql包下面的了,所以说底层还是jdbc嚯
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
ps.execute();
return resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps);
}