集合体系概述


Collection常用方法

补充:addAll()
Collection的遍历方式
迭代器


增强for(空集合可以,null不可以)


lambda

集合对象存储对象原理

遍历方式的区别

List集合
特点、特有方法

遍历方式
(同上)
ArrayList底层原理



LinkedList底层原理



手写链表
java
/**
* 手写链表
*/
public class MyLinkedList<E> {
private int size = 0;
Node<E> first;
public static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
public Node(E item, Node<E> next){
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
}
public boolean add(E e) {
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(e, null);
if(first == null) {
first = newNode;
} else {
Node<E> temp = first;
while(temp.next != null) {
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = newNode;
}
size++;
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringJoiner s = new StringJoiner(",", "[", "]");
Node<E> temp = first;
while(temp != null) {
s.add(temp.item + "");
temp = temp.next;
}
return s.toString();
}
public int size(){
return size;
}
}
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList<String> list = new MyLinkedList<>();
list.add("1号客人");
list.add("2号客人");
list.add("3号客人");
list.add("4号客人");
System.out.println(list);
}
}Set集合
特点

HashSet底层原理




了接下数据结构(树)

查询性能提高:排序



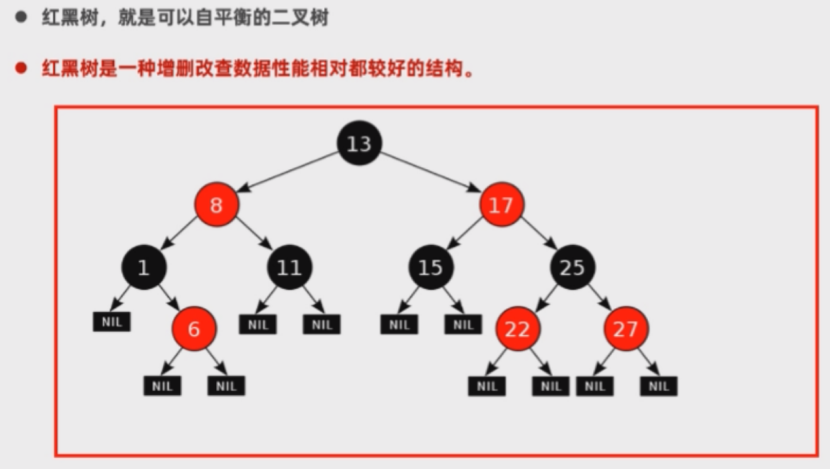
去重机制


LinkedHashSet底层原理-有序

TreeSet底层原理-排序


*优先选择

Map集合
概述

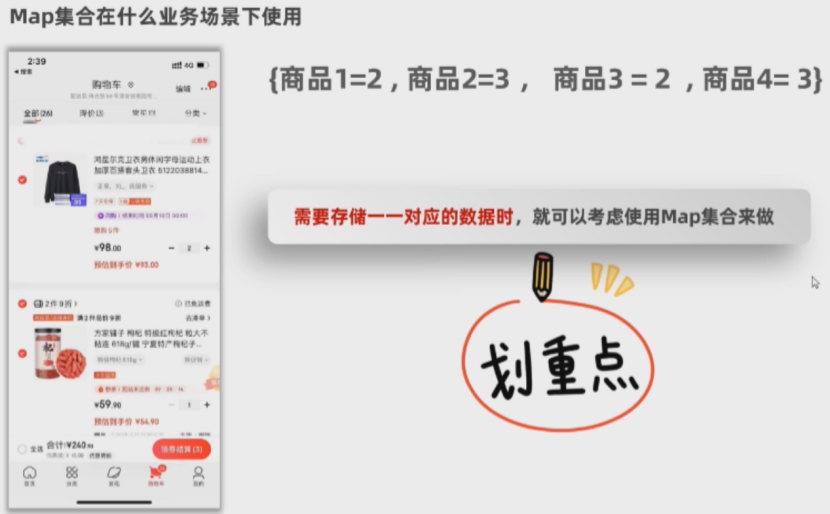

常用方法

遍历方法



HashMap-原理



LinkedHashMap-原理

TreeMap-原理
