OCC模块概览

参数几何(曲线与曲面类型)

参数

直线

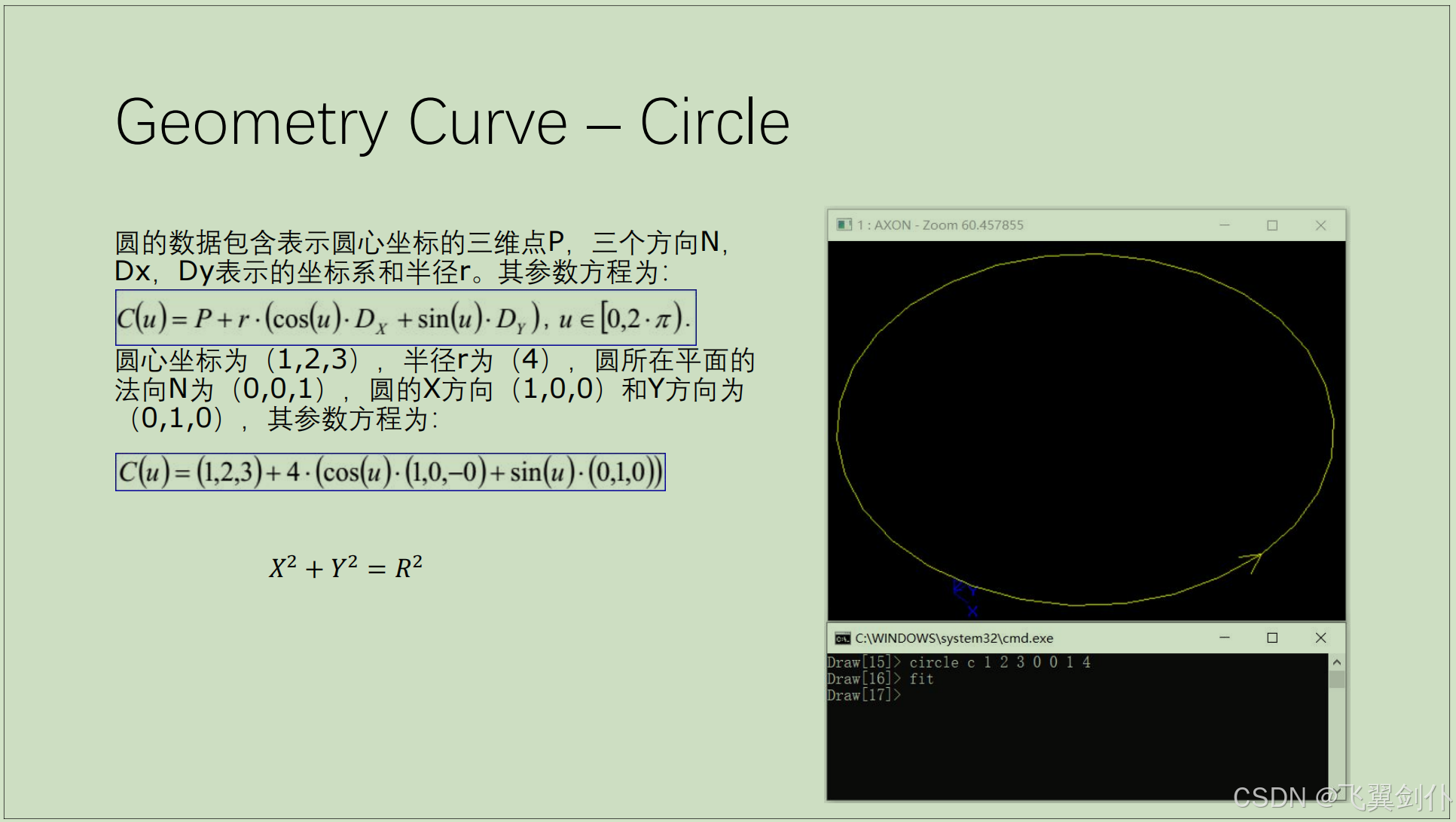
圆
球

Bezier曲线
在Draw Test Harness中绘制Bezier曲线命令:
beziercurve bc 3 0 1 0 4 1 -2 0 5 2 3 0 6
fit
圆的参数方程与隐式方程式的转换
在解析几何中,圆的参数方程和隐式方程之间的转换可以通过代数操作实现。以下我们将详细讲解如何将圆的参数方程转换为隐式方程,以及如何将隐式方程转换回参数方程。
1. 圆的参数方程
圆的参数方程通常表示为:
{ x = h + r cos θ y = k + r sin θ \begin{cases} x = h + r \cos \theta \\ y = k + r \sin \theta \end{cases} {x=h+rcosθy=k+rsinθ
其中:
- ( h , k ) (h, k) (h,k) 是圆心坐标,
- r r r 是圆的半径,
- θ \theta θ 是参数,取值范围通常是 0 ≤ θ < 2 π 0 \leq \theta < 2\pi 0≤θ<2π。
在原点处的圆,即:
h = 0 k = 0 h = 0 \\ k = 0 h=0k=0
则:
{ x = r cos θ y = r sin θ \begin{cases} x = r \cos \theta \\ y = r \sin \theta \end{cases} {x=rcosθy=rsinθ

理解:
参数方程使用一个变量(如 θ \theta θ)来描述x和y的变化。当 θ \theta θ 从0变化到 2 π 2\pi 2π 时,点 ( x , y ) (x, y) (x,y) 沿着圆移动一周。
2. 将参数方程转换为隐式方程
要将参数方程转换为隐式方程(即标准形式的圆的方程),我们可以利用三角恒等式 cos 2 θ + sin 2 θ = 1 \cos^2 \theta + \sin^2 \theta = 1 cos2θ+sin2θ=1。具体步骤如下:
步骤 1:分离参数
从参数方程中解出 cos θ \cos \theta cosθ 和 sin θ \sin \theta sinθ:
cos θ = x − h r sin θ = y − k r \cos \theta = \frac{x - h}{r} \\ \sin \theta = \frac{y - k}{r} cosθ=rx−hsinθ=ry−k
步骤 2:代入三角恒等式
将 cos θ \cos \theta cosθ 和 sin θ \sin \theta sinθ 代入 cos 2 θ + sin 2 θ = 1 \cos^2 \theta + \sin^2 \theta = 1 cos2θ+sin2θ=1:
( x − h r ) 2 + ( y − k r ) 2 = 1 \left( \frac{x - h}{r} \right)^2 + \left( \frac{y - k}{r} \right)^2 = 1 (rx−h)2+(ry−k)2=1
步骤 3:化简为标准形式
两边同时乘以 r 2 r^2 r2,得到:
( x − h ) 2 + ( y − k ) 2 = r 2 (x - h)^2 + (y - k)^2 = r^2 (x−h)2+(y−k)2=r2
这就是圆的隐式方程。
3. 将隐式方程转换为参数方程
将隐式方程 ( x − h ) 2 + ( y − k ) 2 = r 2 (x - h)^2 + (y - k)^2 = r^2 (x−h)2+(y−k)2=r2 转换为参数方程,可以通过引入参数 θ \theta θ 来表示圆上的点。具体步骤如下:
步骤 1:引入参数
假设 x x x 和 y y y 可以用角度 θ \theta θ 表示:
{ x = h + r cos θ y = k + r sin θ \begin{cases} x = h + r \cos \theta \\ y = k + r \sin \theta \end{cases} {x=h+rcosθy=k+rsinθ
其中, θ \theta θ 是从圆心到圆上某点的连线与 x 轴正方向之间的夹角。
步骤 2:验证参数方程满足隐式方程
将 x = h + r cos θ x = h + r \cos \theta x=h+rcosθ 和 y = k + r sin θ y = k + r \sin \theta y=k+rsinθ 代入隐式方程:
( x − h ) 2 + ( y − k ) 2 = ( r cos θ ) 2 + ( r sin θ ) 2 = r 2 ( cos 2 θ + sin 2 θ ) = r 2 (x - h)^2 + (y - k)^2 = (r \cos \theta)^2 + (r \sin \theta)^2 = r^2 (\cos^2 \theta + \sin^2 \theta) = r^2 (x−h)2+(y−k)2=(rcosθ)2+(rsinθ)2=r2(cos2θ+sin2θ)=r2
满足隐式方程。
4. 总结
- 参数方程 :通过角度 θ \theta θ 描述圆上点的位置,形式为:
{ x = h + r cos θ y = k + r sin θ \begin{cases} x = h + r \cos \theta \\ y = k + r \sin \theta \end{cases} {x=h+rcosθy=k+rsinθ - 隐式方程 :不涉及参数,直接描述圆上点的坐标关系,形式为:
( x − h ) 2 + ( y − k ) 2 = r 2 (x - h)^2 + (y - k)^2 = r^2 (x−h)2+(y−k)2=r2
通过上述方法,可以实现圆的参数方程和隐式方程之间的相互转换。
球面的参数方程与隐式方程式的转换
在解析几何中,球面的参数方程和隐式方程之间可以通过坐标变换进行相互转换。以下是一步步的解释:
1. 球面的隐式方程
球面在三维空间中的隐式方程通常表示为:
( x − h ) 2 + ( y − k ) 2 + ( z − l ) 2 = r 2 (x - h)^2 + (y - k)^2 + (z - l)^2 = r^2 (x−h)2+(y−k)2+(z−l)2=r2
其中:
- ( h , k , l ) (h, k, l) (h,k,l) 是球心坐标,
- r r r 是球的半径。
这个方程描述了三维空间中所有到中心点 ( h , k , l ) (h, k, l) (h,k,l) 的距离为 r r r 的点。
2. 球面的参数方程
球面可以用两个角度参数 θ \theta θ 和 ϕ \phi ϕ 来表示,通常称为极角(polar angle)和方位角(azimuthal angle)。参数方程的形式如下:
{ x = h + r sin θ cos ϕ y = k + r sin θ sin ϕ z = l + r cos θ \begin{cases} x = h + r \sin\theta \cos\phi \\ y = k + r \sin\theta \sin\phi \\ z = l + r \cos\theta \end{cases} ⎩ ⎨ ⎧x=h+rsinθcosϕy=k+rsinθsinϕz=l+rcosθ
其中:
- 0 ≤ θ ≤ π 0 \leq \theta \leq \pi 0≤θ≤π 是极角,表示点与球心的连线与 z z z-轴之间的夹角,
- 0 ≤ ϕ < 2 π 0 \leq \phi < 2\pi 0≤ϕ<2π 是方位角,表示在水平面( x x x- y y y 平面)上的旋转角度。
在原点处的球面,即:
h = 0 k = 0 l = 0 h = 0 \\ k = 0 \\ l = 0 h=0k=0l=0
则:
{ x = r sin θ cos ϕ y = r sin θ sin ϕ z = r cos θ \begin{cases} x = r \sin\theta \cos\phi \\ y = r \sin\theta \sin\phi \\ z = r \cos\theta \end{cases} ⎩ ⎨ ⎧x=rsinθcosϕy=rsinθsinϕz=rcosθ

3. 隐式方程到参数方程的转换
假设我们有球面的隐式方程:
( x − h ) 2 + ( y − k ) 2 + ( z − l ) 2 = r 2 (x - h)^2 + (y - k)^2 + (z - l)^2 = r^2 (x−h)2+(y−k)2+(z−l)2=r2
我们可以引入球坐标系来将其转化为参数方程。
步骤 1:定义参数化
在三维空间中,球面对称性非常适合使用球坐标系来表示。我们可以用两个角度 θ \theta θ 和 ϕ \phi ϕ 来描述球面上的每一点:
- θ \theta θ 是从 z z z-轴向下测量的角度,
- ϕ \phi ϕ 是绕 z z z-轴旋转的角度。
步骤 2:引入球坐标变换
将隐式方程中的 x , y , z x, y, z x,y,z 用球坐标参数化表示:
{ x = h + r sin θ cos ϕ y = k + r sin θ sin ϕ z = l + r cos θ \begin{cases} x = h + r \sin\theta \cos\phi \\ y = k + r \sin\theta \sin\phi \\ z = l + r \cos\theta \end{cases} ⎩ ⎨ ⎧x=h+rsinθcosϕy=k+rsinθsinϕz=l+rcosθ
其中 r r r 是半径,固定不变。
步骤 3:验证参数方程满足隐式方程
将参数方程代入隐式方程:
( x − h ) 2 + ( y − k ) 2 + ( z − l ) 2 = r 2 (x - h)^2 + (y - k)^2 + (z - l)^2 = r^2 (x−h)2+(y−k)2+(z−l)2=r2
代入 x , y , z x, y, z x,y,z 的表达式:
r sin θ cos ϕ \] 2 + \[ r sin θ sin ϕ \] 2 + \[ r cos θ \] 2 = r 2 ( sin 2 θ cos 2 ϕ ) + r 2 ( sin 2 θ sin 2 ϕ ) + r 2 cos 2 θ = r 2 sin 2 θ ( cos 2 ϕ + sin 2 ϕ ) + r 2 cos 2 θ = r 2 sin 2 θ ( 1 ) + r 2 cos 2 θ = r 2 ( sin 2 θ + cos 2 θ ) = r 2 \\begin{aligned} \&\[r \\sin\\theta \\cos\\phi\]\^2 + \[r \\sin\\theta \\sin\\phi\]\^2 + \[r \\cos\\theta\]\^2 \\\\ \&= r\^2 (\\sin\^2\\theta \\cos\^2\\phi) + r\^2 (\\sin\^2\\theta \\sin\^2\\phi) + r\^2 \\cos\^2\\theta \\\\ \&= r\^2 \\sin\^2\\theta (\\cos\^2\\phi + \\sin\^2\\phi) + r\^2 \\cos\^2\\theta \\\\ \&= r\^2 \\sin\^2\\theta (1) + r\^2 \\cos\^2\\theta \\\\ \&= r\^2 (\\sin\^2\\theta + \\cos\^2\\theta) \\\\ \&= r\^2 \\end{aligned} \[rsinθcosϕ\]2+\[rsinθsinϕ\]2+\[rcosθ\]2=r2(sin2θcos2ϕ)+r2(sin2θsin2ϕ)+r2cos2θ=r2sin2θ(cos2ϕ+sin2ϕ)+r2cos2θ=r2sin2θ(1)+r2cos2θ=r2(sin2θ+cos2θ)=r2 这验证了参数方程确实满足隐式方程。 *** ** * ** *** #### **4. 参数方程到隐式方程的转换** 假设我们有球面的参数方程: { x = h + r sin θ cos ϕ y = k + r sin θ sin ϕ z = l + r cos θ \\begin{cases} x = h + r \\sin\\theta \\cos\\phi \\\\ y = k + r \\sin\\theta \\sin\\phi \\\\ z = l + r \\cos\\theta \\end{cases} ⎩ ⎨ ⎧x=h+rsinθcosϕy=k+rsinθsinϕz=l+rcosθ 我们需要将其转换为隐式方程。 ##### **步骤 1:消去参数 θ \\theta θ 和 ϕ \\phi ϕ** 从参数方程中解出 sin θ cos ϕ \\sin\\theta \\cos\\phi sinθcosϕ、 sin θ sin ϕ \\sin\\theta \\sin\\phi sinθsinϕ 和 cos θ \\cos\\theta cosθ: { x − h = r sin θ cos ϕ y − k = r sin θ sin ϕ z − l = r cos θ \\begin{cases} x - h = r \\sin\\theta \\cos\\phi \\\\ y - k = r \\sin\\theta \\sin\\phi \\\\ z - l = r \\cos\\theta \\end{cases} ⎩ ⎨ ⎧x−h=rsinθcosϕy−k=rsinθsinϕz−l=rcosθ ##### **步骤 2:平方并相加** 将前两个方程分别平方: ( x − h ) 2 = r 2 sin 2 θ cos 2 ϕ , ( y − k ) 2 = r 2 sin 2 θ sin 2 ϕ (x - h)\^2 = r\^2 \\sin\^2\\theta \\cos\^2\\phi, \\quad (y - k)\^2 = r\^2 \\sin\^2\\theta \\sin\^2\\phi (x−h)2=r2sin2θcos2ϕ,(y−k)2=r2sin2θsin2ϕ 将它们相加: ( x − h ) 2 + ( y − k ) 2 = r 2 sin 2 θ ( cos 2 ϕ + sin 2 ϕ ) = r 2 sin 2 θ (x - h)\^2 + (y - k)\^2 = r\^2 \\sin\^2\\theta (\\cos\^2\\phi + \\sin\^2\\phi) = r\^2 \\sin\^2\\theta (x−h)2+(y−k)2=r2sin2θ(cos2ϕ+sin2ϕ)=r2sin2θ 同时,对第三个方程平方: ( z − l ) 2 = r 2 cos 2 θ (z - l)\^2 = r\^2 \\cos\^2\\theta (z−l)2=r2cos2θ ##### **步骤 3:相加得到隐式方程** 将上述两个结果相加: ( x − h ) 2 + ( y − k ) 2 + ( z − l ) 2 = r 2 sin 2 θ + r 2 cos 2 θ = r 2 ( sin 2 θ + cos 2 θ ) = r 2 (x - h)\^2 + (y - k)\^2 + (z - l)\^2 = r\^2 \\sin\^2\\theta + r\^2 \\cos\^2\\theta = r\^2 (\\sin\^2\\theta + \\cos\^2\\theta) = r\^2 (x−h)2+(y−k)2+(z−l)2=r2sin2θ+r2cos2θ=r2(sin2θ+cos2θ)=r2 这就得到了球面的隐式方程: ( x − h ) 2 + ( y − k ) 2 + ( z − l ) 2 = r 2 (x - h)\^2 + (y - k)\^2 + (z - l)\^2 = r\^2 (x−h)2+(y−k)2+(z−l)2=r2 *** ** * ** *** #### **总结** 1. 球面的隐式方程是关于 x , y , z x, y, z x,y,z 的二次方程,描述了所有到球心距离为 r r r 的点。 2. 球面的参数方程使用两个角度 θ \\theta θ 和 ϕ \\phi ϕ 来表示球面上的任意一点。 3. 通过将参数方程代入隐式方程并利用三角恒等式,可以验证两者的一致性。 4. 反过来,通过消去参数 θ \\theta θ 和 ϕ \\phi ϕ 并平方相加,可以从参数方程推导出隐式方程。 ### 参数曲线与离散函数表 源码文件:`OCCT-7_9_0\src\ElCLib\ElCLib.cxx` | 曲线类型 | 离散函数 | |:-----|:-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| | 直线 | gp_Pnt2d ElCLib::LineValue(const Standard_Real U, const gp_Ax2d\& Pos) | | 圆 | gp_Pnt2d ElCLib::CircleValue(const Standard_Real U, const gp_Ax22d\& Pos, const Standard_Real Radius) | | 椭圆 | gp_Pnt2d ElCLib::EllipseValue(const Standard_Real U, const gp_Ax22d\& Pos, const Standard_Real MajorRadius, const Standard_Real MinorRadius) | | 抛物线 | gp_Pnt2d ElCLib::ParabolaValue(const Standard_Real U, const gp_Ax22d\& Pos, const Standard_Real Focal) | | 双曲线 | gp_Pnt2d ElCLib::HyperbolaValue(const Standard_Real U, const gp_Ax22d\& Pos, const Standard_Real MajorRadius, const Standard_Real MinorRadius) | | 样条曲线 | BSplCLib | ### 参数曲面与离散函数表 源码文件:`OCCT-7_9_0\src\ElSLib\ElSLib.cxx` | 曲面类型 | 离散函数 | |:-----|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| | 平面 | void ElSLib::PlaneD0(const Standard_Real U, const Standard_Real V, const gp_Ax3\& Pos, gp_Pnt\& P) | | 圆柱面 | void ElSLib::CylinderD0(const Standard_Real U, const Standard_Real V, const gp_Ax3\& Pos, const Standard_Real Radius, gp_Pnt\& P) | | 圆柱面 | void ElSLib::ConeD0(const Standard_Real U, const Standard_Real V, const gp_Ax3\& Pos, const Standard_Real Radius, const Standard_Real SAngle, gp_Pnt\& P) | | 球面 | void ElSLib::SphereD0(const Standard_Real U, const Standard_Real V, const gp_Ax3\& Pos, const Standard_Real Radius, gp_Pnt\& P) | | 圆环面 | void ElSLib::TorusD0(const Standard_Real U, const Standard_Real V, const gp_Ax3\& Pos, const Standard_Real MajorRadius, const Standard_Real MinorRadius, gp_Pnt\& P) | | 样条曲面 | BSplSLib | **参考文档**: * 刘星《基于Open Cascade的开发培训》(bilibili.com) * OCC官网(https://dev.opencascade.org/release) * [A Primer on Bézier Curves](https://pomax.github.io/bezierinfo/index.html) * https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/421129261 * https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/55878540