文章目录
首先回顾项目架构
-MAIN.C 主程序
-GLOBALS.H 全局类型及变量(如Token类属及语法树结点的组成)
-UTIL.H、UTIL.C 各步骤的实用函数。如输出Token,生成语法树结点等
-SCAN.C、SCAN.H 词法分析程序及其头文件
-PARSE.C、PARSE.H 语法分析程序及其头文件
-ANALYZE.C、ANALYZE.H 语义检查程序及其头文件
-SYMTAB.C、SYMTAB.H 符号表生成程序及其头文件
-CGEN.H、CGEN.C、CODE.C、CODE.H 目标代码生成程序及其头文件
-TM 编译sample.tny源程序后得到目标代码,在该虚拟机上运行得到结果明确任务
- 本次实现完成的是
语法分析

parse.c文件
c
typedef enum {StmtK,ExpK} NodeKind;
typedef enum {IfK,RepeatK,AssignK,ReadK,WriteK} StmtKind;
typedef enum {OpK,ConstK,IdK} ExpKind;
typedef enum {Void,Integer,Boolean} ExpType;
#define MAXCHILDREN 3
typedef struct treeNode
{ struct treeNode * child[MAXCHILDREN];
struct treeNode * sibling;
int lineno;
NodeKind nodekind;
union { StmtKind stmt; ExpKind exp;} kind;
union { TokenType op;
int val;
char * name; } attr;
ExpType type;
} TreeNode;
/****************************************************/
/* File: parse.c */
/* The parser implementation for the TINY compiler */
/****************************************************/
#include "globals.h"
#include "util.h"
#include "scan.h"
#include "parse.h"
static TokenType token; /* holds current token */
/* function prototypes for recursive calls */
static TreeNode * stmt_sequence(void);
static TreeNode * statement(void);
static TreeNode * if_stmt(void);
static TreeNode * repeat_stmt(void);
static TreeNode * assign_stmt(void);
static TreeNode * read_stmt(void);
static TreeNode * write_stmt(void);
static TreeNode * exp(void);
static TreeNode * simple_exp(void);
static TreeNode * term(void);
static TreeNode * factor(void);
static void syntaxError(char * message)
{ fprintf(listing,"\n>>> ");
fprintf(listing,"Syntax error at line %d: %s",lineno,message);
Error = TRUE;
}
static void match(TokenType expected)
{ if (token == expected) token = getToken();
else {
syntaxError("unexpected token -> ");
printToken(token,tokenString);
fprintf(listing," ");
}
}
TreeNode * stmt_sequence(void)
{ TreeNode * t = statement();
TreeNode * p = t;
while ((token!=ENDFILE) && (token!=END) &&
(token!=ELSE) && (token!=UNTIL))
{ TreeNode * q;
match(SEMI);
q = statement();
if (q!=NULL) {
if (t==NULL) t = p = q;
else /* now p cannot be NULL either */
{ p->sibling = q;
p = q;
}
}
}
return t;
}
TreeNode * statement(void)
{ TreeNode * t = NULL;
switch (token) {
case IF : t = if_stmt(); break;
case REPEAT : t = repeat_stmt(); break;
case ID : t = assign_stmt(); break;
case READ : t = read_stmt(); break;
case WRITE : t = write_stmt(); break;
default : syntaxError("unexpected token -> ");
printToken(token,tokenString);
token = getToken();
break;
} /* end case */
return t;
}
TreeNode * if_stmt(void)
{
...... //此处请自己填写
}
TreeNode * repeat_stmt(void)
{
...... //此处请自己填写
}
TreeNode * assign_stmt(void)
{
...... //此处请自己填写
}
TreeNode * read_stmt(void)
{
...... //此处请自己填写
}
TreeNode * write_stmt(void)
{
...... //此处请自己填写
}
TreeNode * exp(void)
{ TreeNode * t = simple_exp();
if ((token==LT)||(token==EQ)) {
TreeNode * p = newExpNode(OpK);
if (p!=NULL) {
p->child[0] = t;
p->attr.op = token;
t = p;
}
match(token);
if (t!=NULL)
t->child[1] = simple_exp();
}
return t;
}
TreeNode * simple_exp(void)
{
...... //此处请自己填写
}
TreeNode * term(void)
{
...... //此处请自己填写
}
TreeNode * factor(void)
{
...... //此处请自己填写
}
/****************************************/
/* the primary function of the parser */
/****************************************/
/* Function parse returns the newly
* constructed syntax tree
*/
TreeNode * parse(void)
{ TreeNode * t;
token = getToken();
t = stmt_sequence();
if (token!=ENDFILE)
syntaxError("Code ends before file\n");
return t;
}具体的实现
-
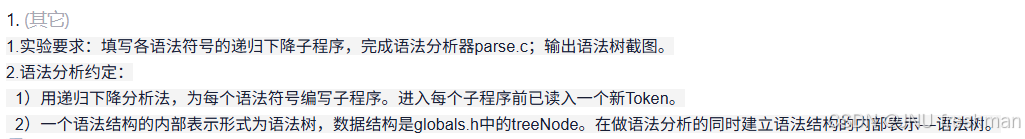
完善这个
parse.c文件:直接把parse.c和要求丢给ai即可要求:填写各语法符号的递归下降子程序,完成语法分析器parse.c。
约定:
-用递归下降分析法,为每个语法符号编写子程序。进入每个子程序前已读入一个新Token。
-一个语法结构的内部表示形式为语法树,数据结构是globals.h中的treeNode。在做语法分析的同时建立语法结构的内部表示------语法树。 -
生成完成之后,修改
main.c中的参数设置
c
/* set NO_PARSE to TRUE to get a scanner-only compiler */
#define NO_PARSE FALSE
/* set NO_ANALYZE to TRUE to get a parser-only compiler */
#define NO_ANALYZE TRUE
/* set NO_CODE to TRUE to get a compiler that does not
* generate code
*/
#define NO_CODE TRUE- 还有下面的参数
c
/* allocate and set tracing flags */
int EchoSource = FALSE;
int TraceScan = FALSE;
int TraceParse = TRUE;
int TraceAnalyze = FALSE;
int TraceCode = FALSE;
int Error = FALSE;- 接着就可以测试
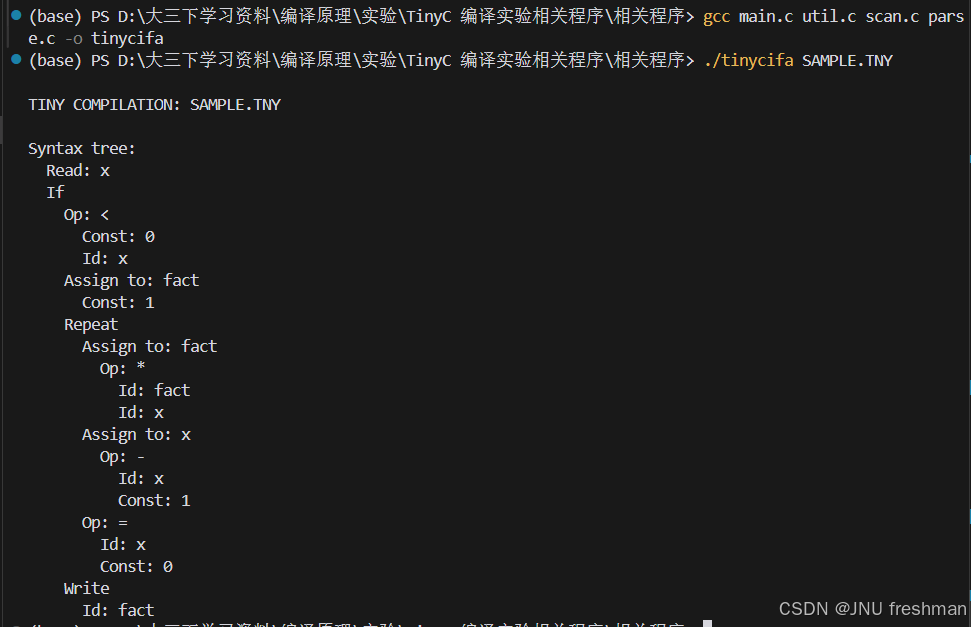
语法分析,xxxxx替换为编译之后的文件名,自己取
bash
gcc main.c util.c scan.c parse.c -o xxxxx- 测试,
xxxxx是上面编译之后的程序,SAMPLE.TNY是文件夹里面本身就有的测试文件
bash
./xxxxx SAMPLE.TNY 结果图