文章目录
- 前言
- 一、整体实现思路
- [二、SSE 协议实现的 AI 对话](#二、SSE 协议实现的 AI 对话)
-
- [什么是 SSE?](#什么是 SSE?)
- 实现流程概述
-
- [1. 后端 Golang 服务](#1. 后端 Golang 服务)
- [2. 前端页面](#2. 前端页面)
- [三、WebSocket 协议实现的 AI 对话](#三、WebSocket 协议实现的 AI 对话)
-
- [什么是 WebSocket?](#什么是 WebSocket?)
- 实现流程概述
-
- [1. 后端 Golang 服务](#1. 后端 Golang 服务)
- [2. 前端页面](#2. 前端页面)
- 四、演示效果
-
- [SSE 实现效果:](#SSE 实现效果:)
- [WebSocket 实现效果:](#WebSocket 实现效果:)
- 五、总结
- 参考文献
前言
在上一篇文章中,我们学习了如何通过 Ollama 在本地部署大模型,并使用 Golang 实现了流式与非流式的 API 调用。
本篇将继续实战,目标是打造一个完整的 网页端 AI 对话系统。该系统基于前后端协作,通过 WebSocket 和 SSE(Server-Sent Events)两种流式传输协议,实现模型回复的实时展示效果。
最终实现效果为:
用户在网页输入问题,模型实时生成回答,前端页面逐字展示,交互体验类似 ChatGPT。
一、整体实现思路
本次项目的基本流程如下:
- 用户在前端页面输入问题并提交;
- Golang 后端接收请求,调用本地 Ollama 模型 API;
- 模型输出以流式方式返回;
- 后端通过 SSE 或 WebSocket 协议,将模型输出逐步推送到前端;
- 前端接收并实时渲染,实现流畅的"打字机式"回答效果。
二、SSE 协议实现的 AI 对话
什么是 SSE?
SSE(Server-Sent Events)是一种基于 HTTP 的单向推送协议,允许服务器持续向浏览器发送数据。
- 特点:
- 建立在 HTTP 协议之上;
- 天然支持流式传输,顺序性好;
- 实现简单、浏览器原生支持;
- 仅支持服务器向客户端单向推送(不支持客户端主动通信);
- 适用于生成式模型这类持续输出的场景。
结论:SSE 是构建大模型"逐字输出"效果的理想协议。
实现流程概述
1. 后端 Golang 服务
main.go文件下:
go
package main
import (
"bufio"
"bytes"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"net/http"
)
type ChatRequest struct {
Model string `json:"model"`
Stream bool `json:"stream"`
Messages []struct {
Role string `json:"role"`
Content string `json:"content"`
} `json:"messages"`
}
func streamChatHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// 设置SSE响应头
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "text/event-stream")
w.Header().Set("Cache-Control", "no-cache")
w.Header().Set("Connection", "keep-alive")
// 读取用户提交的问题
userInput := r.URL.Query().Get("question")
if userInput == "" {
http.Error(w, "missing question param", http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
// 准备请求体
reqData := ChatRequest{
Model: "deepseek-r1:8b",
Stream: true,
}
reqData.Messages = append(reqData.Messages, struct {
Role string `json:"role"`
Content string `json:"content"`
}{
Role: "user",
Content: userInput,
})
jsonData, err := json.Marshal(reqData)
if err != nil {
http.Error(w, "json marshal error", http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
// 调用本地Ollama服务
resp, err := http.Post("http://localhost:11434/api/chat", "application/json", bytes.NewBuffer(jsonData))
if err != nil {
http.Error(w, "call ollama error", http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
// 流式读取模型输出
scanner := bufio.NewScanner(resp.Body)
flusher, _ := w.(http.Flusher)
for scanner.Scan() {
line := scanner.Text()
if line == "" {
continue
}
var chunk struct {
Message struct {
Content string `json:"content"`
} `json:"message"`
Done bool `json:"done"`
}
if err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(line), &chunk); err != nil {
continue
}
// 通过SSE格式发送到前端
fmt.Fprintf(w, "data: %s\n\n", chunk.Message.Content)
flusher.Flush()
if chunk.Done {
break
}
}
}
func main() {
http.Handle("/", http.FileServer(http.Dir("./static"))) // 静态文件
http.HandleFunc("/chat", streamChatHandler) // SSE接口
fmt.Println("Server running at http://localhost:8080")
http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil)
}这段代码的主要功能是:
-
提供静态文件服务(网页)
- 使用
http.FileServer让浏览器访问./static目录下的 HTML 页面。
- 使用
-
实现
/chat接口- 接收前端输入的问题(通过 URL 参数
?question=xxx); - 构造请求体,调用本地 Ollama API(模型推理);
- 使用
Scanner流式读取模型输出; - 将每段输出通过 SSE 协议 推送给前端浏览器,实现打字机式显示效果。
- 接收前端输入的问题(通过 URL 参数
2. 前端页面
在 static 目录下,新建一个简单页面:
static/index.html:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>🧠 AI 对话演示 (SSE版)</title>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
height: 100vh;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
font-family: "Helvetica Neue", Arial, sans-serif;
background: #f0f2f5;
}
header {
background: #2196F3;
color: white;
padding: 15px 20px;
font-size: 22px;
font-weight: bold;
box-shadow: 0 2px 4px rgba(0,0,0,0.1);
}
#chat-area {
flex: 1;
overflow-y: auto;
padding: 20px;
background: #e5e5e5;
}
.message {
margin-bottom: 15px;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
.user, .ai {
font-weight: bold;
margin-bottom: 5px;
}
.user {
color: #4CAF50;
}
.ai {
color: #2196F3;
}
.text {
background: #ffffff;
padding: 12px;
border-radius: 8px;
max-width: 80%;
white-space: pre-wrap;
font-size: 16px;
line-height: 1.6;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
}
#input-area {
display: flex;
padding: 15px;
background: #fff;
border-top: 1px solid #ccc;
}
#question {
flex: 1;
padding: 10px;
font-size: 16px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 6px;
}
button {
margin-left: 10px;
padding: 10px 20px;
font-size: 16px;
background: #4CAF50;
color: white;
border: none;
border-radius: 6px;
cursor: pointer;
}
button:hover {
background: #45a049;
}
</style>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/marked/marked.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<header>🧠 AI 对话演示 (SSE版)</header>
<div id="chat-area">
<!-- 聊天记录显示区 -->
</div>
<div id="input-area">
<input type="text" id="question" placeholder="请输入你的问题..." autocomplete="off">
<button id="send-button" onclick="sendQuestion()">发送</button>
</div>
<script>
const chatArea = document.getElementById('chat-area');
const questionInput = document.getElementById('question');
const sendButton = document.getElementById('send-button');
let isReceiving = false; // 是否正在接收回复
function sendQuestion() {
const question = questionInput.value.trim();
if (!question || isReceiving) {
return;
}
isReceiving = true;
questionInput.disabled = true;
sendButton.disabled = true;
// 创建用户消息
const userMessage = document.createElement('div');
userMessage.className = 'message';
userMessage.innerHTML = `
<div class="user">👤 你</div>
<div class="text">${question}</div>
`;
chatArea.appendChild(userMessage);
// 创建AI回复占位
const aiMessage = document.createElement('div');
aiMessage.className = 'message';
aiMessage.innerHTML = `
<div class="ai">🤖 AI</div>
<div class="text" id="ai-response-${Date.now()}"></div>
`;
chatArea.appendChild(aiMessage);
chatArea.scrollTop = chatArea.scrollHeight; // 滚动到底部
const aiResponseDiv = aiMessage.querySelector('.text');
let bufferText = "";
const eventSource = new EventSource(`/chat?question=${encodeURIComponent(question)}`);
eventSource.onmessage = function(event) {
// 有数据就更新
bufferText += event.data;
aiResponseDiv.innerHTML = marked.parse(bufferText);
chatArea.scrollTop = chatArea.scrollHeight;
};
eventSource.onerror = function() {
// 只要出错或者连接结束,就解锁输入
eventSource.close();
finishReceiving();
};
questionInput.value = '';
}
function finishReceiving() {
isReceiving = false;
questionInput.disabled = false;
sendButton.disabled = false;
questionInput.focus();
}
// 按下 Enter 键发送
questionInput.addEventListener('keydown', function(event) {
if (event.key === 'Enter') {
event.preventDefault();
sendQuestion();
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>这段前端 HTML+JS 代码的作用是:
使用 SSE 实时接收 AI 回复:
- 用
EventSource发起/chat?question=xxx请求; - 后端返回的每一段
data:内容都会实时追加到bufferText; - 通过
marked.js将 Markdown 格式转为 HTML; - 最终流式更新显示在 AI 回复区,实现"打字机式"体验。
三、WebSocket 协议实现的 AI 对话
什么是 WebSocket?
WebSocket 是一种支持 双向通信 的长连接协议,适合需要持续交互的前后端应用。
- 特点:
- 建立后是持久连接,效率更高;
- 支持客户端主动发消息,服务端主动推送;
- 可用于实现多人对话、在线协作编辑等复杂互动场景;
- 相比 SSE,WebSocket 更灵活、功能更全面。
总结:WebSocket 更适合复杂、多用户、双向互动的 AI 对话系统。
实现流程概述
1. 后端 Golang 服务
同样是在main.go中实现我们的核心代码,这里我们需要引用websocket的包,所以需要先执行创建go mod导入websocket的开源库
bash
# 初始化仓库名
# xxx 为你想要的仓库名
go init xxx
# 导入websocket
go get github.com/gorilla/websocketmain.go 核心代码如下:
go
package main
import (
"bufio"
"bytes"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
"time"
"github.com/gorilla/websocket"
)
type ChatRequest struct {
Model string `json:"model"`
Stream bool `json:"stream"`
Messages []struct {
Role string `json:"role"`
Content string `json:"content"`
} `json:"messages"`
}
var upgrader = websocket.Upgrader{
CheckOrigin: func(r *http.Request) bool {
return true
},
}
func chatHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
conn, err := upgrader.Upgrade(w, r, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Println("Upgrade error:", err)
return
}
defer conn.Close()
fmt.Println("New connection")
for {
_, msg, err := conn.ReadMessage()
if err != nil {
log.Println("Read error:", err)
break
}
fmt.Println("收到消息:", string(msg))
userInput := string(msg)
// 准备请求体
reqData := ChatRequest{
Model: "deepseek-r1:8b",
Stream: true,
}
reqData.Messages = append(reqData.Messages, struct {
Role string `json:"role"`
Content string `json:"content"`
}{
Role: "user",
Content: userInput,
})
jsonData, err := json.Marshal(reqData)
if err != nil {
http.Error(w, "json marshal error", http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
// 调用本地Ollama服务
resp, err := http.Post("http://localhost:11434/api/chat", "application/json", bytes.NewBuffer(jsonData))
if err != nil {
http.Error(w, "call ollama error", http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
// 流式读取模型输出
scanner := bufio.NewScanner(resp.Body)
for scanner.Scan() {
line := scanner.Text()
if line == "" {
continue
}
var chunk struct {
Message struct {
Content string `json:"content"`
} `json:"message"`
Done bool `json:"done"`
}
if err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(line), &chunk); err != nil {
continue
}
err = conn.WriteMessage(websocket.TextMessage, []byte(chunk.Message.Content))
if err != nil {
log.Println("Write error:", err)
break
}
time.Sleep(50 * time.Millisecond)
if chunk.Done {
break
}
}
}
}
// 提供静态HTML页面
func homePage(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
http.ServeFile(w, r, "./static/index.html") // 当前目录的index.html
}
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/", homePage) // 网页入口
http.HandleFunc("/ws", chatHandler) // WebSocket接口
log.Println("服务器启动,访问:http://localhost:8080")
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil))
}这个代码主要实现了如下的流程,通过websocket 实现前端和后端的互相通信。
- 接收前端 WebSocket 消息(用户提问)
- 前端连接
/ws,建立 WebSocket。 - 每当收到一个用户问题(纯文本),后端将它封装为一个符合 Ollama API 要求的请求体(
ChatRequest)。
- 调用本地 Ollama 模型 API
- 使用
http.Post调用http://localhost:11434/api/chat,请求使用deepseek-r1:8b模型,开启stream=true。 - 用户输入作为 message content,角色为
"user"。
- 流式读取 Ollama 回复,并通过 WebSocket 实时发回前端
- 使用
bufio.Scanner按行读取流式响应(Ollama SSE 格式的响应); - 每条非空响应行解析为 JSON,取出
chunk.Message.Content; - 用
conn.WriteMessage(websocket.TextMessage, ...)发送内容回前端; - 加
50ms延迟模拟人类打字节奏; - 若响应中的
done == true,说明模型输出完成,跳出循环。
2. 前端页面
在 static 目录下,新建一个简单页面:
static/index.html:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>🧠 AI 对话演示 (WebSocket版)</title>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
height: 100vh;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
font-family: "Helvetica Neue", Arial, sans-serif;
background: #f0f2f5;
}
header {
background: #4CAF50;
color: white;
padding: 15px 20px;
font-size: 22px;
font-weight: bold;
box-shadow: 0 2px 4px rgba(0,0,0,0.1);
}
#chat-box {
flex: 1;
padding: 20px;
overflow-y: auto;
background: #e5e5e5;
}
.message {
margin-bottom: 15px;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
.user, .ai {
font-weight: bold;
margin-bottom: 5px;
}
.user {
color: #4CAF50;
}
.ai {
color: #2196F3;
}
.text {
background: #ffffff;
padding: 12px;
border-radius: 8px;
max-width: 80%;
white-space: pre-wrap;
font-size: 16px;
line-height: 1.6;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
}
#input-area {
display: flex;
padding: 15px;
background: #fff;
border-top: 1px solid #ccc;
}
#question {
flex: 1;
padding: 10px;
font-size: 16px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 6px;
}
button {
margin-left: 10px;
padding: 10px 20px;
font-size: 16px;
background: #4CAF50;
color: white;
border: none;
border-radius: 6px;
cursor: pointer;
}
button:hover {
background: #45a049;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<header>🧠 AI 对话演示 (WebSocket版)</header>
<div id="chat-box"></div>
<div id="input-area">
<input type="text" id="question" placeholder="请输入你的问题..." autocomplete="off">
<button onclick="sendQuestion()">发送</button>
</div>
<script>
let socket = null;
const chatBox = document.getElementById('chat-box');
const inputField = document.getElementById('question');
const sendButton = document.querySelector('button');
let currentAIMessage = null;
let isReceiving = false;
let messageBufferTimer = null; // 消息缓冲检测器
function connectWebSocket() {
socket = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8080/ws");
socket.onopen = function() {
console.log("WebSocket连接成功");
};
socket.onmessage = function(event) {
if (!currentAIMessage) {
currentAIMessage = document.createElement('div');
currentAIMessage.className = 'message';
currentAIMessage.innerHTML = `
<div class="ai">🤖 AI</div>
<div class="text"></div>
`;
chatBox.appendChild(currentAIMessage);
}
const aiTextDiv = currentAIMessage.querySelector('.text');
aiTextDiv.innerText += event.data;
chatBox.scrollTop = chatBox.scrollHeight;
// 每次收到消息就重置计时器
if (messageBufferTimer) {
clearTimeout(messageBufferTimer);
}
messageBufferTimer = setTimeout(() => {
finishReceiving();
}, 500); // 如果500ms内没有新消息,认为这次回答结束
};
socket.onclose = function() {
console.log("WebSocket连接关闭");
finishReceiving();
};
socket.onerror = function(error) {
console.error("WebSocket错误:", error);
finishReceiving();
};
}
function sendQuestion() {
const question = inputField.value.trim();
if (!question || isReceiving) {
return;
}
if (!socket || socket.readyState !== WebSocket.OPEN) {
connectWebSocket();
setTimeout(() => {
sendMessage(question);
}, 500); // 等待连接
} else {
sendMessage(question);
}
inputField.value = '';
}
function sendMessage(question) {
// 禁用输入,防止再次发送
isReceiving = true;
inputField.disabled = true;
sendButton.disabled = true;
// 显示用户消息
const userMessage = document.createElement('div');
userMessage.className = 'message';
userMessage.innerHTML = `
<div class="user">👤 你</div>
<div class="text">${question}</div>
`;
chatBox.appendChild(userMessage);
chatBox.scrollTop = chatBox.scrollHeight;
// 发送消息
socket.send(question);
// 创建新的AI消息占位
currentAIMessage = document.createElement('div');
currentAIMessage.className = 'message';
currentAIMessage.innerHTML = `
<div class="ai">🤖 AI</div>
<div class="text"></div>
`;
chatBox.appendChild(currentAIMessage);
chatBox.scrollTop = chatBox.scrollHeight;
}
function finishReceiving() {
isReceiving = false;
inputField.disabled = false;
sendButton.disabled = false;
currentAIMessage = null;
inputField.focus();
}
inputField.addEventListener('keydown', function(event) {
if (event.key === 'Enter') {
event.preventDefault();
sendQuestion();
}
});
connectWebSocket();
</script>
</body>
</html>该部分代码的主要功能如下:
-
建立 WebSocket 连接
javascriptsocket = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8080/ws");自动连接后端 WebSocket 服务端点
/ws。 -
发送用户问题
- 用户输入内容后点击"发送"或按回车键。
- 调用
sendQuestion()->sendMessage()将问题通过socket.send(question)发送到后端。
-
实时接收 AI 回答(流式)
socket.onmessage每次收到一段模型回复内容。- 累加到 AI 消息框中,实现"逐字推送"的流式显示效果。
- 若 500ms 内未再收到新消息,则自动认为回答结束,解锁输入。
四、演示效果
SSE 实现效果:
页面流畅展示模型逐字生成过程,无卡顿,体验接近 ChatGPT
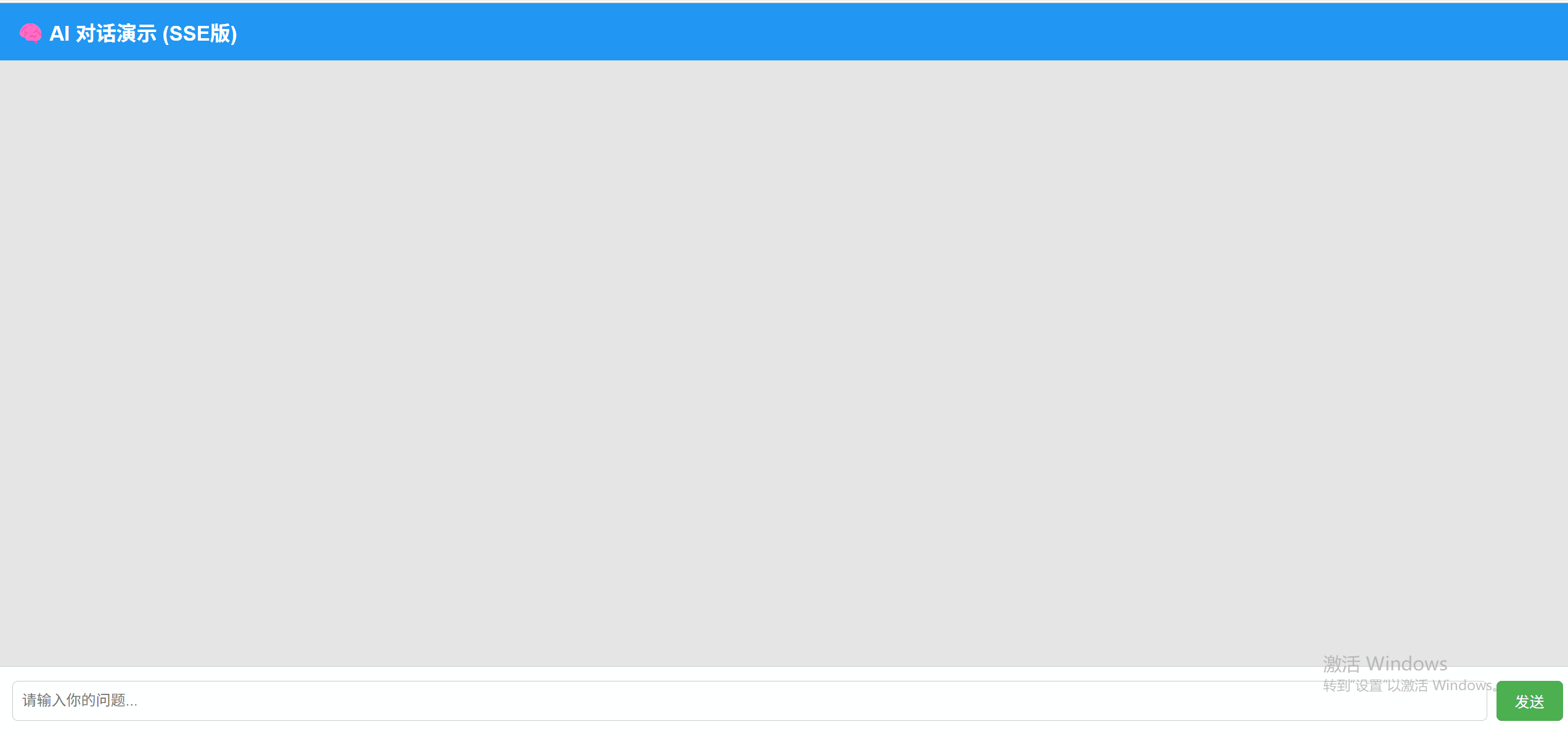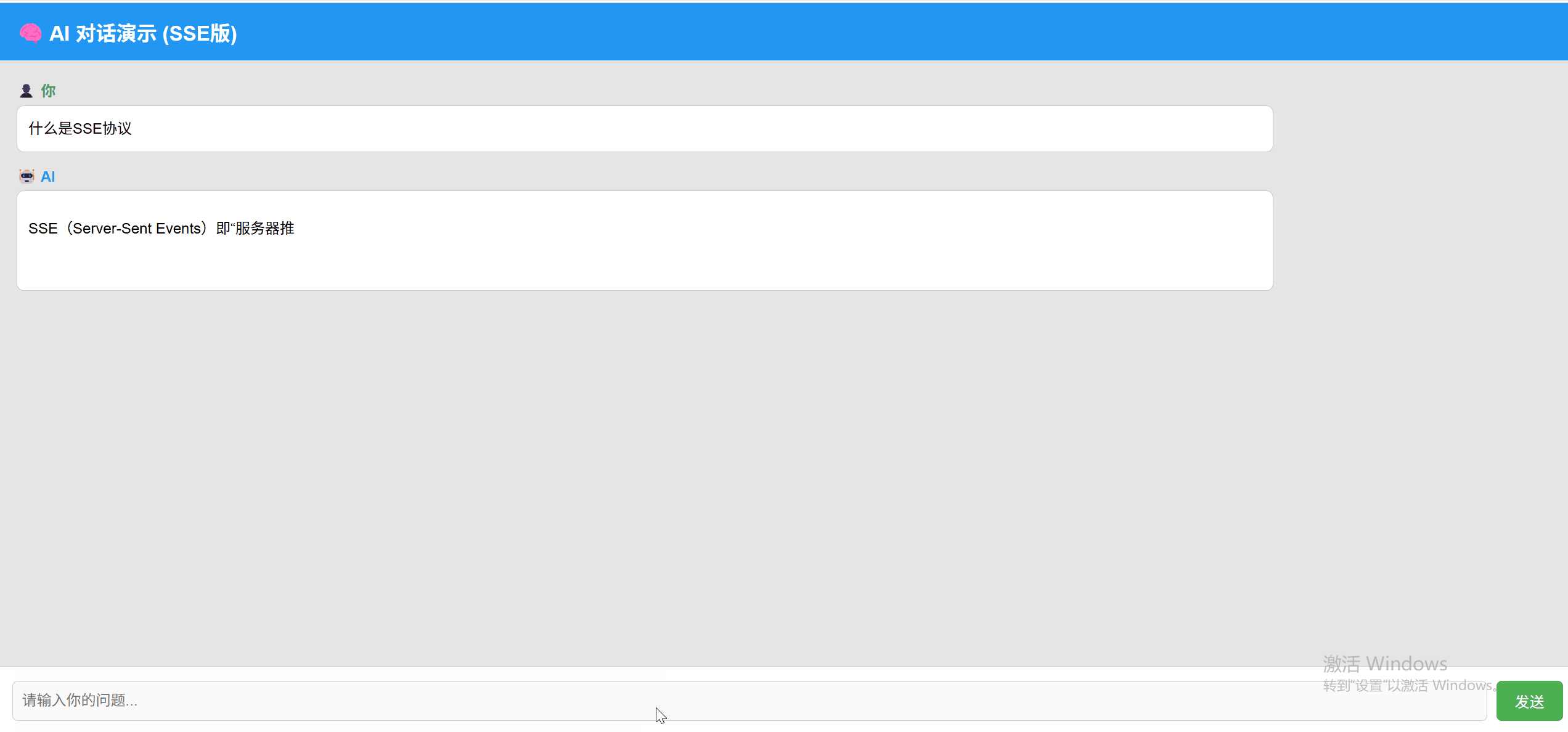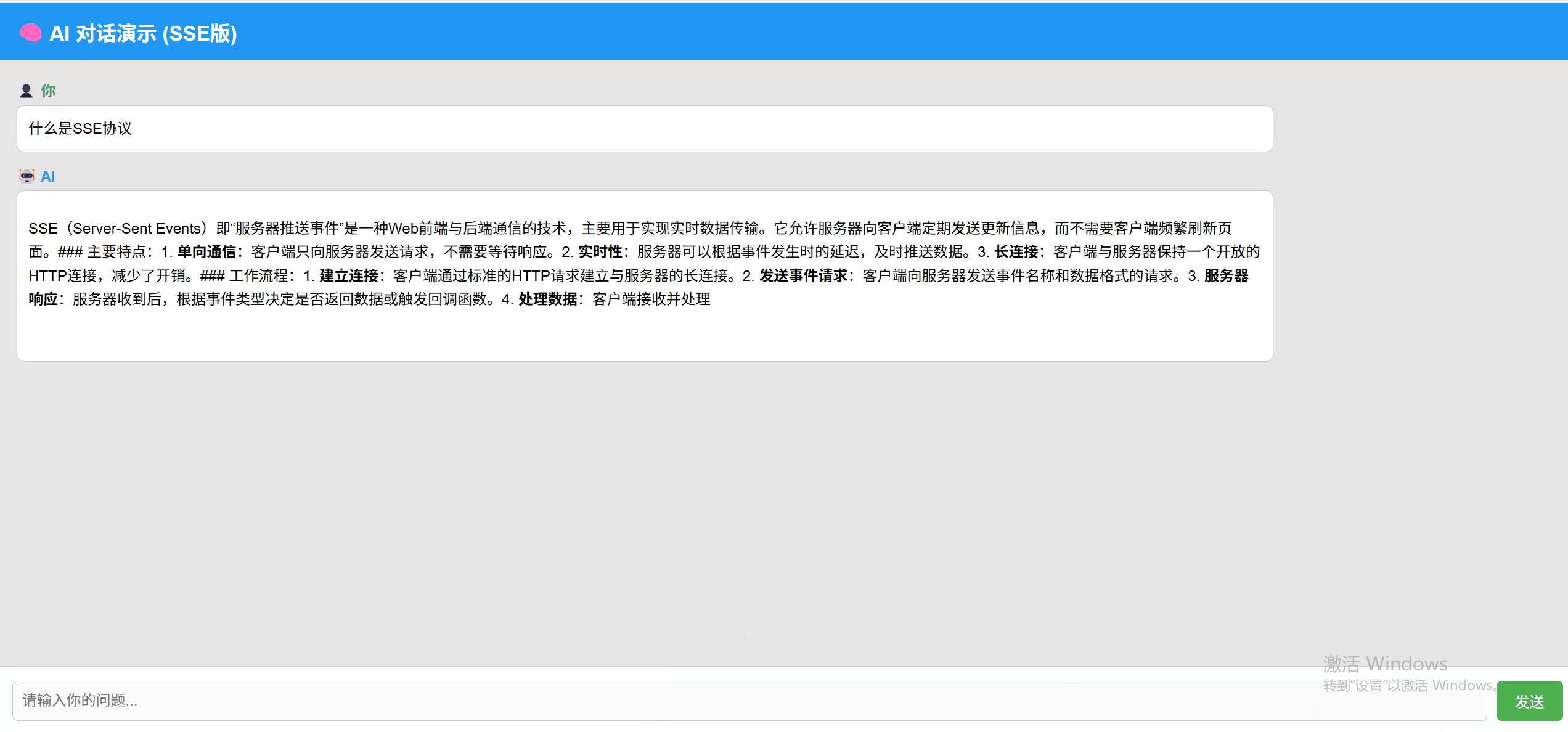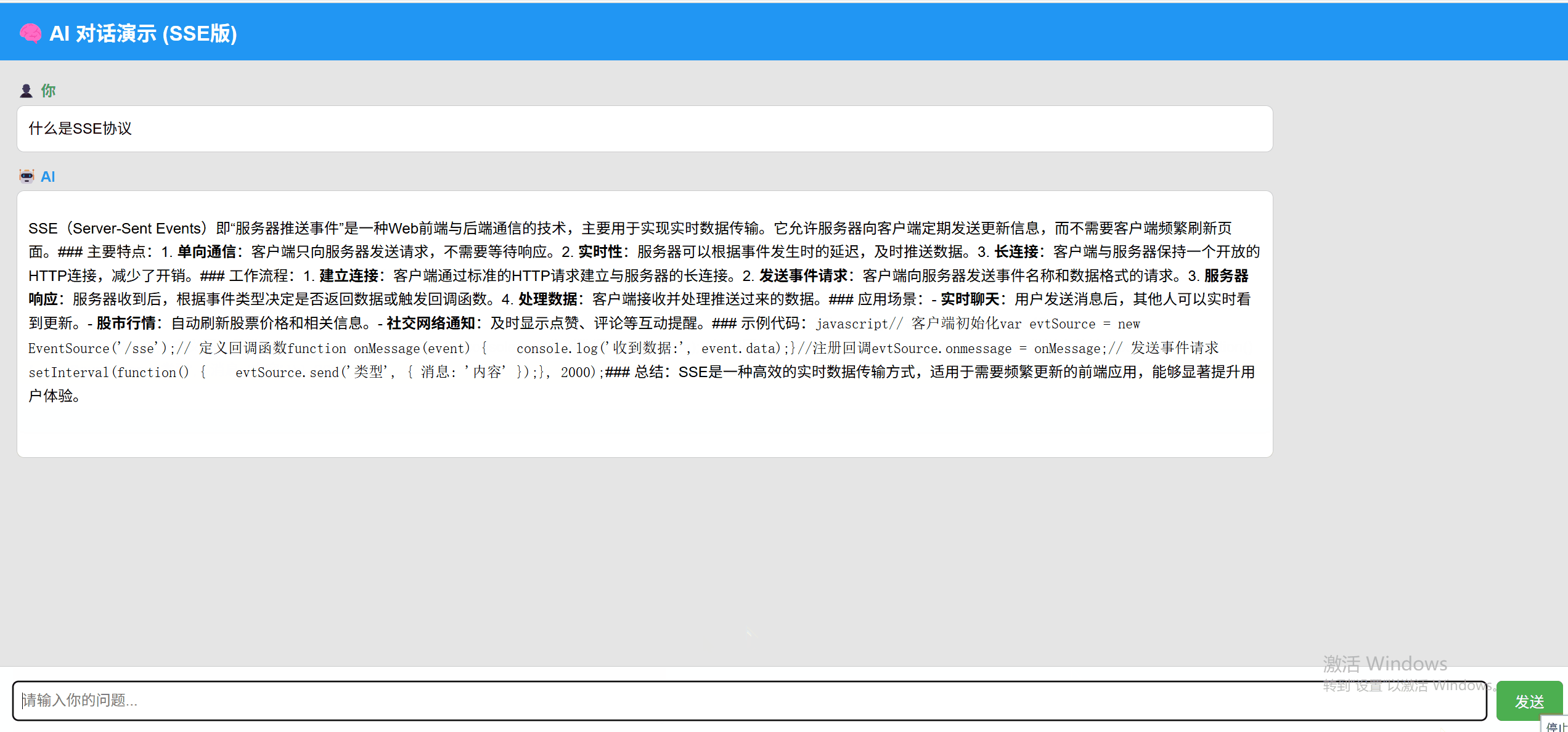
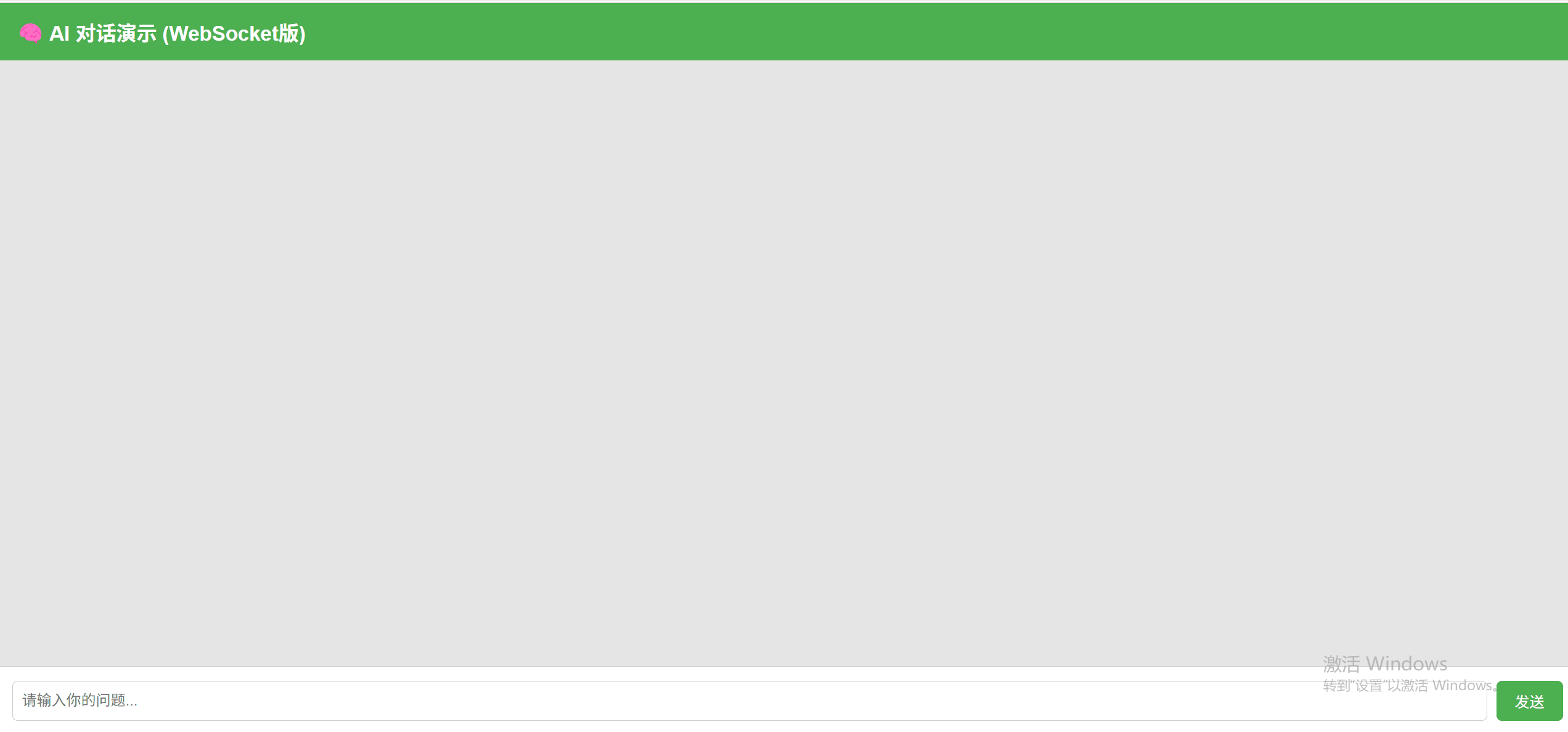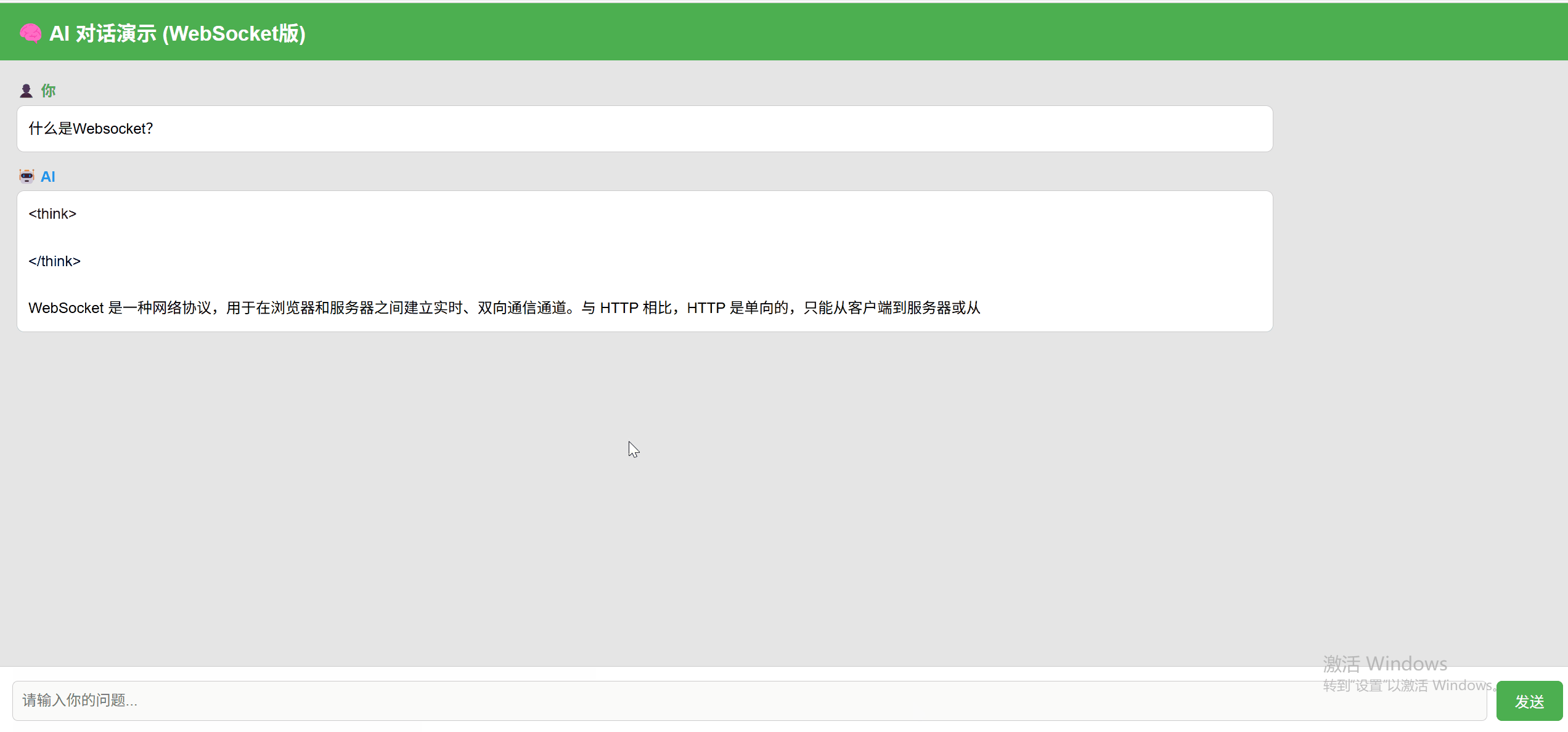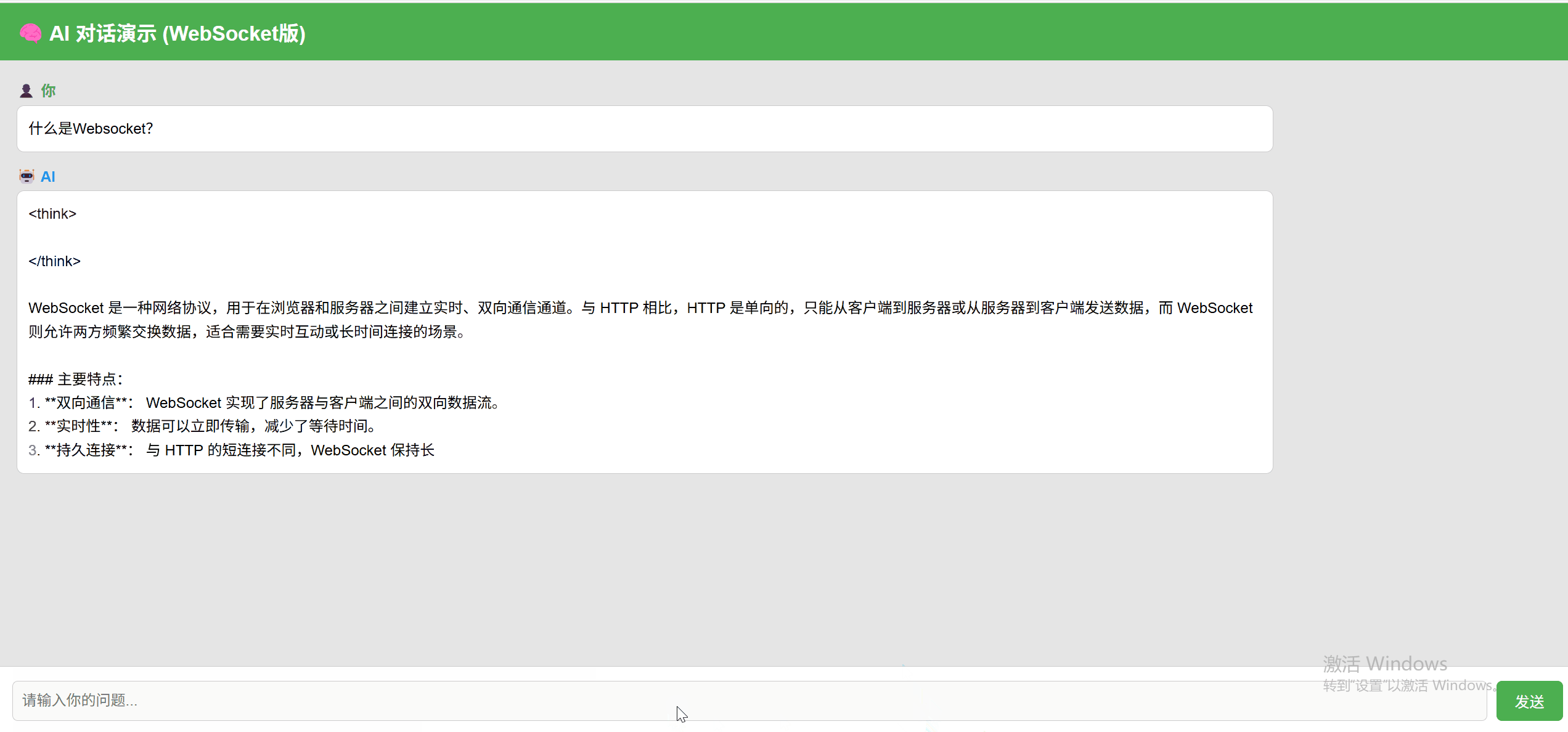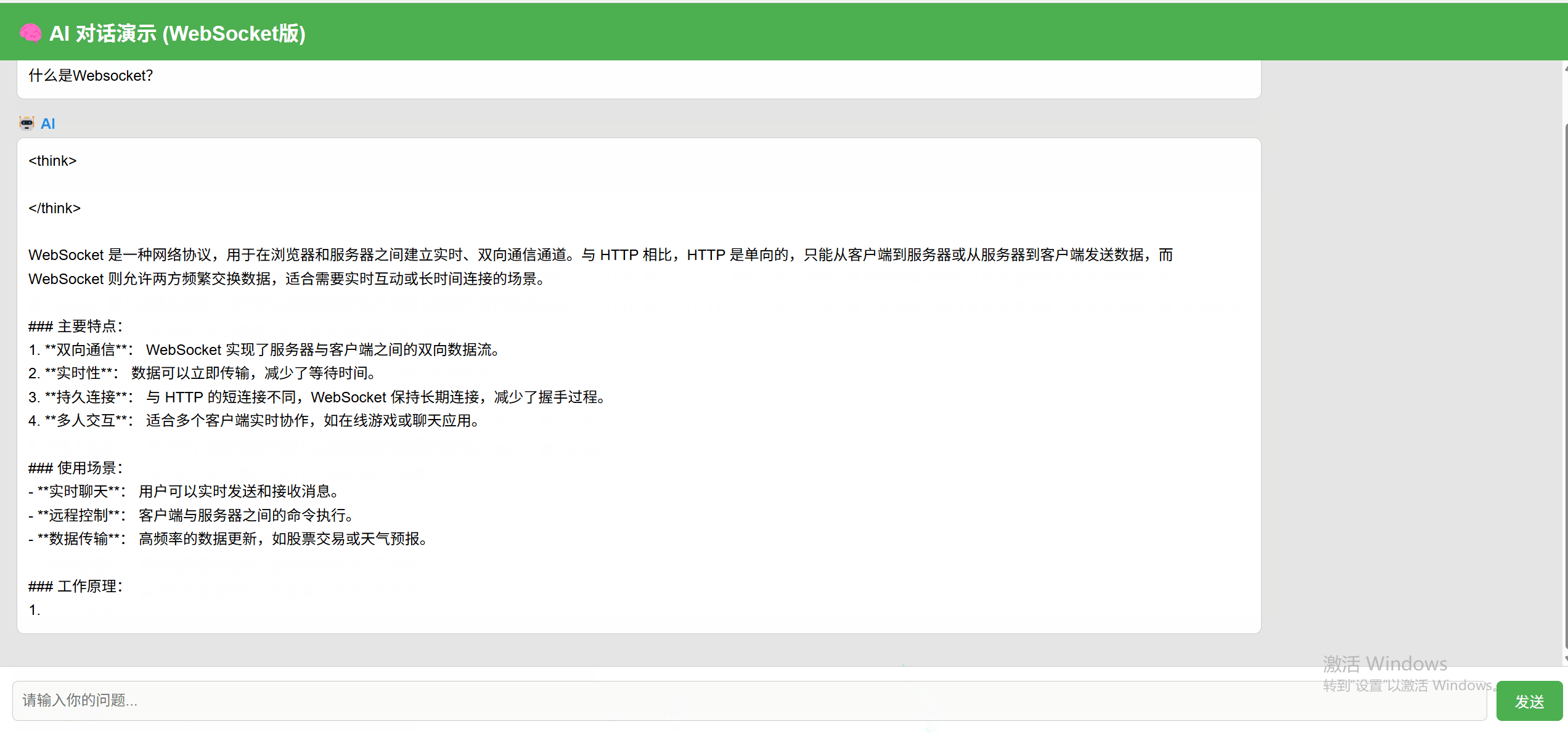
WebSocket 实现效果:
支持完整的输入-回复闭环,并实时回显模型结果
相比之下,虽然视觉效果相似,但 WebSocket 的底层机制更强大。
下图展示了两种方式的信息流对比:

五、总结
通过本文实战,我们完成了以下技术点:
- 使用 Golang 后端对接本地部署的大模型 Ollama;
- 掌握两种主流流式推送协议 ------ SSE 和 WebSocket;
- 实现网页端 AI 对话演示系统,体验与 ChatGPT 相似的效果;
- 理解了两种协议的优劣与适用场景,为后续拓展(如上下文记忆、多用户对话等)打下基础。
在下一篇中,我们将继续探索:如何让聊天具备上下文记忆能力,让对话真正实现连续性与智能化。
参考文献
【万字详解,带你彻底掌握 WebSocket 用法(至尊典藏版)写的不错】
【Server-Sent Events 的协议细节和实现】
【Spring AI 与前端技术融合:打造网页聊天 AI 的实战指南】
【基于 Golang Fiber 实现 AI 领域的 SSE 流式通信实践】