一:进程程序替换
-
一旦程序替换成功,就去执行新代码了,原始代码的后半部分已经不存在了
-
exec*系列的函数,没有成功返回值,只有失败返回值-1
在程序替换的过程中,并没有创建新的进程,只是把当前进程的代码和数据用新的程序的代码和数据覆盖式的进行替换
1-1 execl
在Linux系统里,execl的一个系统调用函数,其作用是进程的程序替换
函数原型
#include<unistd.h>
int execl(const char* path,const char* arg,...)
- path:此参数为一个字符串指针,指向要执行的程序(命令)的完整路径。例如usr/bin/ls就代表ls命令的可执行文件完整路径
- arg:这是传给新程序的第一个参数,一般是程序(命令)自身的名称
- ...:这是可变参数列表,用来传递参数给新程序。参数列表的最后必须以NULL结尾,从而表明参数传递结束。
objectivec
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main()
{
printf("我的程序要运行了\n");
execl("/usr/bin/ls","ls","-l","-a",NULL);
printf("我的程序运行完毕了\n");
return 0;
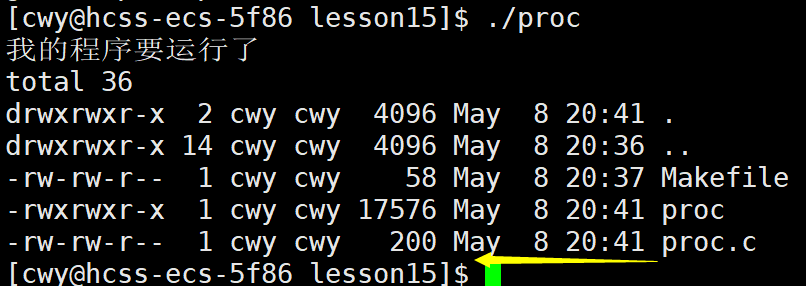
}如上面代码所示, execl函数尝试执行/usr/bin/ls程序,并且传递了三个参数ls(程序本身),-l(用于显示详细信息),-a(显示全部信息),参数列表以NULL为结尾。若execl调用成功,当前进程就会被ls -l -a命令替换,从而显示当前目录下所有文件的详细信息。execl("/usr/bin/ls","ls","-l","-a",NULL);这条命令相当于先找到ls命令的路径,然后我们在终端输入的ls -l -a命令以逗号传递给每一个参数。我们可以看到下图中执行完ls -l -a将所有文件的详细信息打印后,后面没有打印 "我的程序运行完毕了" 这条语句,这是因为程序一旦替换成功就不再执行后序代码了,所以就没有打印
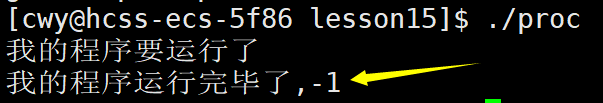
如下面代码所示,当我们将ls命令的路径和参数都传错时,execl进程的程序替换就会失败,我们用变量n来接收返回值,然后打印n的值,如下图所示,n的值为-1
objectivec
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main()
{
printf("我的程序要运行了\n");
int n = execl("/usr/bn/ls","aa","-l","-a",NULL);
printf("我的程序运行完毕了,%d\n",n);
return 0;
}
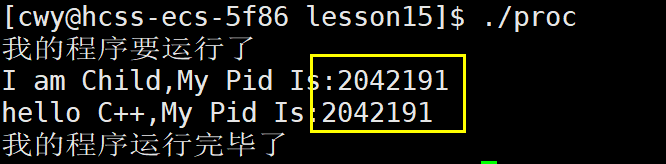
在上面我们讲到在程序替换过程中没有创建新进程,如何验证呢?如下面代码所示,在proc.c代码中,我们创建一个子进程并在其中打印子进程的进程ID并用execl将当前目录下的可执行文件other,传递other给新程序实现进程替换。而在other.cc代码中打印其进程ID
proc.c代码:
objectivec
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<unistd.h>
3 #include<sys/types.h>
4 #include<sys/wait.h>
5 #include<stdlib.h>
6
7 int main()
8 {
9 printf("我的程序要运行了\n");
10 if(fork() == 0)
11 {
12 printf("I am Child,My Pid Is:%d\n",getpid());
13 sleep(1);
14 //execl("/usr/bin/ls","ls","-l","-a",NULL);
15 execl("./other","other",NULL);
16 exit(1);
17 }
18 waitpid(-1,NULL,0);
19 printf("我的程序运行完毕了\n");
20 return 0;
21 }
other.cc代码:
cpp
1 #include<iostream>
2 #include<unistd.h>
3
4 int main()
5 {
6 std::cout << "hello C++,My Pid Is:" << getpid() << std::endl;
7
8 return 0;
9 }由下图可见,两个代码的PID一样说明execl实现进程替换过程中没有创建新程序
1-2 execlp
函数原型:
#include<unistd.h>
int execlp(const char* file,const char* arg,...);
execlp中的p相当于PATH,因此execlp会自动在环境变量PATH中查找指定的命令,这意味着我们在使用这个函数时不需要将程序的路径传递给函数,只需要写需要执行的文件名即可
objectivec
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<unistd.h>
3 #include<sys/types.h>
4 #include<sys/wait.h>
5 #include<stdlib.h>
6
7 int main()
8 {
9 printf("我的程序要运行了\n");
10 if(fork() == 0)
11 {
12 printf("I am Child,My Pid Is:%d\n",getpid());
13 sleep(1);
14 execlp("ls","ls","-l","-a",NULL);
15
16 exit(1);
17 }
18 waitpid(-1,NULL,0);
19 printf("我的程序运行完毕了\n");
20 return 0;
21 }如上代码所示,在子进程中执行execlp函数,执行ls -l -a命令,第一个参数为ls,因此系统会在PATH环境变量中搜索ls命令,后面的ls -l -a代表将当前目录下的所有文件的详细信息打印打印出来
1-3 execv
函数原型:
#include<unistd.h>
int execv(const char* path,char* const argv[]);
execv中的v可以理解为vector,相当于一个数组,参数path代表要执行的程序(命令)的完整路径,argv即提供一个命令行参数表(指针数组)
objectivec
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<unistd.h>
3 #include<sys/types.h>
4 #include<sys/wait.h>
5 #include<stdlib.h>
6
7 int main()
8 {
9 printf("我的程序要运行了\n");
10 if(fork() == 0)
11 {
12 printf("I am Child,My Pid Is:%d\n",getpid());
13 sleep(1);
14 char* const argv[] = {
15 (char* const)"ls",
16 (char* const)"-l",
17 (char* const)"-a",
18 NULL,
19 };
20
21 execv("/usr/bin/ls",argv);
22
23 }
24 waitpid(-1,NULL,0);
25 printf("我的程序运行完毕了\n");
26 return 0;
27 }如上代码所示,在子进程中,我们定义了一个指向char*的常量数组,数组变量分别为ls -l -a和NULL(表明结束),然后调用execv函数,在/usr/bin/ls目录下查找ls命令并执行ls命令,将argv数组传递给该命令
1-4 execvp
函数原型:
#include<unistd.h>
int execvp(const char* file,char* const argv[]);
execvp中的v代表传递一个指针数组给程序而不用传递参数列表,p代表PATH,因此不用写完整的路径。参数file要执行的程序名,argv传递给程序的参数数组
objectivec
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<unistd.h>
3 #include<sys/types.h>
4 #include<sys/wait.h>
5 #include<stdlib.h>
6
7 int main()
8 {
9 printf("我的程序要运行了\n");
10 if(fork() == 0)
11 {
12 printf("I am Child,My Pid Is:%d\n",getpid());
13 sleep(1);
14 char* const argv[] = {
15 (char* const)"ls",
16 (char* const)"-l",
17 (char* const)"-a",
18 NULL,
19 };
20 execvp(argv[0],argv);
21
22 }
23 waitpid(-1,NULL,0);
24 printf("我的程序运行完毕了\n");
25 return 0;
26 }如上代码所示:在子进程中,定义了一个参数数组argv,包含命令名ls和选项-l、-a,以NULL结尾,execvp函数根据argv[0](即ls)在环境变量PATH中查找ls可执行文件并执行该文件,同时将argv作为参数传递给它
二:自定义XShell代码
cpp
1 #include<iostream>
2 #include<cstdio>
3 #include<cstring>
4 #include<cstdlib>
5 #include<unistd.h>
6 #include<sys/types.h>
7 #include<sys/wait.h>
8
9 #define COMMAND_SIZE 1024
10 #define FORMAT "[%s@%s %s]# "
11 #define MAXARGC 128
12
13 char* g_argv[MAXARGC];
14 int g_argc = 0;
15
16 char cwd[1024];
17 char cwdenv[1024];
18
19 //最新退出码
20 int lastcode = 0;
21
22 const char* GetUserName()
23 {
24 const char* name = getenv("USER");
25 return name == NULL ? "None" : name;
26 }
27
28 const char* GetHostName()
29 {
30 const char* hostname = getenv("HOSTNAME");
31 return hostname == NULL ? "None" : hostname;
32 }
33
34 const char* GetPwd()
35 {
36 //const char* pwd = getenv("PWD");
37 const char* pwd = getcwd(cwd,sizeof(cwd));
38 if(pwd != NULL)
39 {
40 snprintf(cwdenv,sizeof(cwdenv),"PWD=%s",cwd);
41 putenv(cwdenv);
42 }
43 return pwd == NULL ? "None" : pwd;
44 }
45
46 const char* GetHome()
47 {
48 const char* home = getenv("HOME");
49 return home == NULL ? "" : home;
50 }
51
52 // / /a/b/c路径获取切分
53 std::string DirName(const char* pwd)
54 {
55 #define SLASH "/"
56 std::string dir = pwd;
57 if(dir == SLASH)
58 {
59 return "/";
60 }
61 auto pos = dir.rfind(SLASH);
62 if(pos == std::string::npos)
63 return "BUG?";
64 return dir.substr(pos + 1);
65 }
66
67
68 void MakeCommandline(char cmd_prompt[],int size)
69 {
70
71 //snprintf(cmd_prompt,size,FORMAT,GetUserName(),GetHostName(),GetPwd());
72 snprintf(cmd_prompt,size,FORMAT,GetUserName(),GetHostName(),DirName(GetPwd()).c_str());
73 }
74
75 //1.输出命令行提示符
76 void PrintCommandline()
77 {
78 char prompt[COMMAND_SIZE];
79 MakeCommandline(prompt,sizeof(prompt));
80 printf("%s",prompt);
81 fflush(stdout);
82 }
83
84 //2、获取命令行
85 bool GetCommandline(char* out,int size)
86 {
87 //ls -a -l => "ls -a -l"
88 char* c = fgets(out,size,stdin);
89 if(c == NULL)
90 return false;
91 out[strlen(out) - 1] = 0;//清楚\n
92 if(strlen(out) == 0)
93 return false;
94 return true;
95 }
96
97 //3.命令行分析
98 bool ParseCommandline(char* commandline)
99 {
100 #define SEP " "
101 g_argc = 0;
102 g_argv[g_argc++] = strtok(commandline,SEP);
103 while((bool)(g_argv[g_argc++] = strtok(nullptr,SEP)));
104 g_argc--;
105 return g_argc > 0 ? true : false;
106 }
107
108 //4、检查并执行内建命令
109 bool CheckAndExecBuiltin()
110 {
111 std::string cmd = g_argv[0];
112 if(cmd == "cd")
113 {
114 //cd
115 if(g_argc == 1)
116 {
117 std::string home = GetHome();
118 if(home.empty())
119 {
120 return true;
121 }
122 chdir(home.c_str());
123 }
124 else
125 {
126 //cd ~
127 std::string where = g_argv[1];
128 if(where == "~")
129 {
130 std::string home = GetHome();
131 if(home.empty())
132 return true;
133 chdir(home.c_str());
134 }
135 else
136 {
137 //cd /home/
138 std::string where = g_argv[1];
139 chdir(where.c_str());
140 }
141 }
142 return true;
143 }
144 else if(cmd == "echo")
145 {
146 if(g_argc == 2)
147 {
148 //echo "hello world"
149 //echo $?
150 //echo $PATH
151 std::string opt = g_argv[1];
152 if(opt == "$?")
153 {
154 std::cout << lastcode << std::endl;
155 lastcode = 0;
156 return true;
157 }
158 }
159 }
160 return false;
161 }
162 //5、执行命令
163 int Execute()
164 {
165 pid_t id = fork();
166
167 if(id == 0)
168 {
169 //child
170 execvp(g_argv[0],g_argv);
171 exit(1);
172 }
173
174 //father
175 int status = 0;
176 pid_t rid = waitpid(id,&status,0);
177 if(rid > 0)
178 {
179 lastcode = WEXITSTATUS(status);
180 }
181 return 0;
182 }
183
184 void PrintArgv()
185 {
186 for(int i = 0;g_argv[i];i++)
187 {
188 printf("argv[%d]->%s\n",i,g_argv[i]);
189 }
190 printf("argc:%d\n",g_argc);
191 }
192
193 int main()
194 {
195 while(1)
196 {
197 //1.输出命令行提示符
198 PrintCommandline();
199 char commandline[COMMAND_SIZE];
200 //2.获取命令行
201 if(!GetCommandline(commandline,sizeof(commandline)))
202 continue;
203 //printf("echo %s\n",commandline);
204
205 //3.命令行分析 "ls -a l" => "ls" "-a" "-l"
206 if(!ParseCommandline(commandline))
207 continue;
208 //PrintArgv();
209
210 //4、检查并处理内建命令
211 if(CheckAndExecBuiltin())
212 continue;
213
214 //5、执行命令
215 Execute();
216 }
217 return 0;
218 }