文章目录
- 前言
- 一、代码分析及流程讲解
-
- (一)初始化模块
-
- [正确答案映射字典(题目序号: 正确选项索引)](#正确答案映射字典(题目序号: 正确选项索引))
- 图像显示工具函数
- (二)轮廓处理工具模块
- (三)几何变换核心模块
- 二、主处理流程
-
- 图像读取
- [>>> 阶段1:图像预处理 <<<](#>>> 阶段1:图像预处理 <<<)
- [>>> 阶段2:答题卡定位 <<<](#>>> 阶段2:答题卡定位 <<<)
- [>>> 阶段3:选项识别 <<<](#>>> 阶段3:选项识别 <<<)
- [>>> 阶段4:评分系统 <<<](#>>> 阶段4:评分系统 <<<)
- 总结
前言
一、代码分析及流程讲解
(一)初始化模块
python
import numpy as np
import cv2
import os正确答案映射字典(题目序号: 正确选项索引)
python
ANSWER_KEY = {0:1, 1:4, 2:0, 3:3, 4:1} 图像显示工具函数
python
def cv_show(name, value):
"""可视化显示图像,按任意键继续"""
cv2.imshow(name, value)
cv2.waitKey(0)(二)轮廓处理工具模块
轮廓定向排序函数
参数:
cnts: 轮廓列表
method: 排序方向(left-to-right/right-to-left/top-to-bottom/bottom-to-top)
返回值:
排序后的轮廓及边界框
python
def sort_contours(cnts, method='left-to-right'):
reverse = False
i = 0
if method == 'right-to-left' or method == 'bottom-to-top':
reverse = True
if method == 'top-to-bottom' or method == 'bottom-to-top':
i = 1
# 获取轮廓边界框并排序
boundingBoxes = [cv2.boundingRect(c) for c in cnts]
(cnts, boundingBoxes) = zip(*sorted(
zip(cnts, boundingBoxes),
key=lambda b: b[1][i],
reverse=reverse))
return cnts, boundingBoxes保持宽高比的图像缩放函数
参数:
width: 目标宽度
height: 目标高度
inter: 插值方法
python
def resize(image, width=None, height=None, inter=cv2.INTER_AREA):
dim = None
(h, w) = image.shape[:2]
if width is None and height is None:
return image
if width is None:
r = height / float(h)
dim = (int(w * r), height)
else:
r = width / float(w)
dim = (width, int(h * r))
return cv2.resize(image, dim, interpolation=inter)(三)几何变换核心模块
坐标点规范化排序(左上、右上、右下、左下)
实现方法:
-
计算各点坐标和,最小值为左上,最大值为右下
-
计算坐标差值,最小值为右上,最大值为左下
python
def order_points(pts):
rect = np.zeros((4, 2), dtype='float32')
s = pts.sum(axis=1)
rect[0] = pts[np.argmin(s)] # 左上点
rect[2] = pts[np.argmax(s)] # 右下点
diff = np.diff(pts, axis=1)
rect[1] = pts[np.argmin(diff)] # 右上点
rect[3] = pts[np.argmax(diff)] # 左下点
return rect透视变换函数
参数:
image: 原始图像
pts: 源图像四个坐标点
处理流程: 1. 坐标点规范化排序。2. 计算变换后图像尺寸。 3. 生成透视变换矩阵。 4. 执行透视变换
python
def four_point_transform(image, pts):
rect = order_points(pts)
(tl, tr, br, bl) = rect
# 计算目标图像尺寸(取最大宽高)
widthA = np.sqrt(((br[0]-bl[0])**2) + (br[1]-bl[1])**2)
widthB = np.sqrt(((tr[0]-tl[0])**2) + (tr[1]-tl[1])**2)
maxWidth = max(int(widthA), int(widthB))
heightA = np.sqrt(((tr[0]-br[0])**2) + (tr[1]-br[1])**2)
heightB = np.sqrt(((tl[0]-bl[0])**2) + (tl[1]-bl[1])**2)
maxHeight = max(int(heightA), int(heightB))
# 构建目标坐标矩阵
dst = np.array([
[0, 0],
[maxWidth-1, 0],
[maxWidth-1, maxHeight-1],
[0, maxHeight-1]], dtype="float32")
# 执行透视变换
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(rect, dst)
warped = cv2.warpPerspective(image, M, (maxWidth, maxHeight))
return warped二、主处理流程
图像读取
python
image = cv2.imread('../data/images/test_01.png')
contours_img = image.copy()>>> 阶段1:图像预处理 <<<
1、灰度转换(注意:COLOR_BGRA2GRAY适用于含alpha通道图像,通常使用COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
python
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGRA2GRAY) 2、高斯滤波(5x5卷积核去噪)
python
blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (5,5), 0)
cv_show('blurred', blurred)
3、Canny边缘检测(双阈值设置)
python
edged = cv2.Canny(blurred, 75, 200)
cv_show('edged', edged)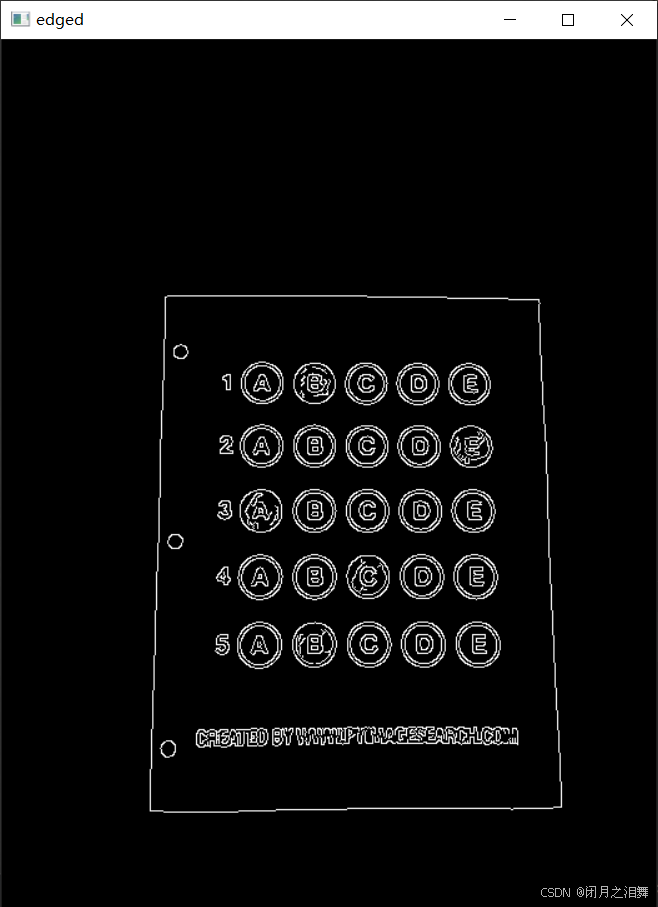
>>> 阶段2:答题卡定位 <<<
1、轮廓检测(仅检测最外层轮廓)
python
cnts = cv2.findContours(edged.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)[-2]2、绘制所有轮廓(红色,3px线宽)
python
cv2.drawContours(contours_img, cnts, -1, (0,0,255), 3)
cv_show('contours_img', contours_img)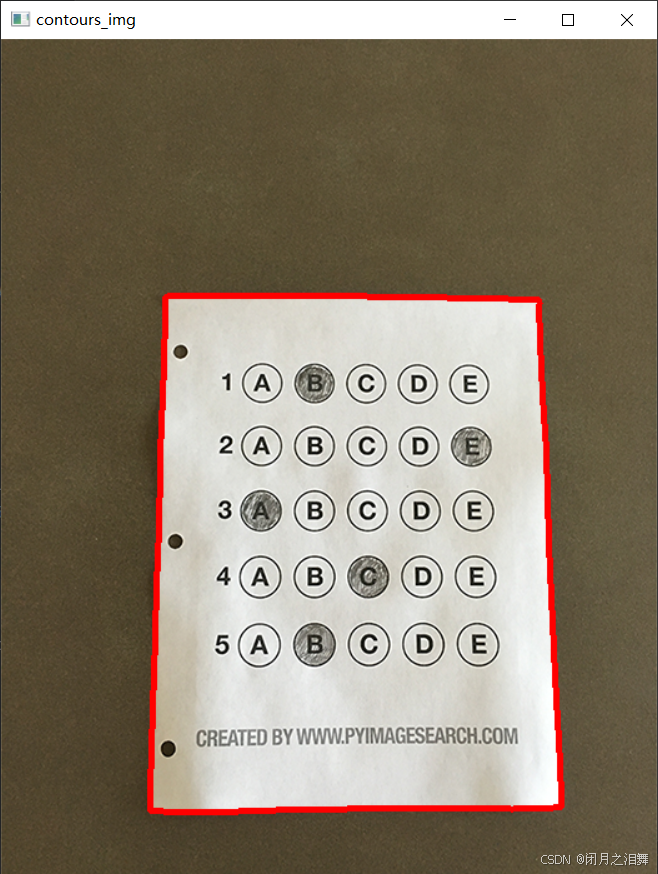
3、轮廓筛选(按面积降序排列)
python
cnts = sorted(cnts, key=cv2.contourArea, reverse=True)
for c in cnts:
# 多边形近似(精度=2%周长)
peri = cv2.arcLength(c, True)
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(c, 0.02*peri, True)
if len(approx) == 4: # 识别四边形轮廓
doCnt = approx
break4、执行透视变换
python
warped_t = four_point_transform(image, doCnt.reshape(4, 2))
warped_new = warped_t.copy()
cv_show('warped', warped_t)
>>> 阶段3:选项识别 <<<
1、灰度转换与二值化
python
warped_gray = cv2.cvtColor(warped_t, cv2.COLOR_BGRA2GRAY)2、自适应阈值处理(反色二值化+OTSU算法)
python
thresh = cv2.threshold(warped_gray, 0, 255,
cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
cv_show('thresh', thresh)
3、选项轮廓检测
python
cnts = cv2.findContours(thresh.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)[-2]4、绘制绿色轮廓(1px线宽)
python
warped_contours = cv2.drawContours(warped_t.copy(), cnts, -1, (0,255,0), 1)
cv_show('warped_contours', warped_contours)
5、选项筛选条件(宽高>20px,宽高比0.9-1.1)
python
questionCnts = []
for c in cnts:
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
ar = w / float(h)
if w >= 20 and h >= 20 and 0.9 <= ar <= 1.1:
questionCnts.append(c)6、轮廓排序(从上到下)
python
questionCnts = sort_contours(questionCnts, method="top-to-bottom")[0]>>> 阶段4:评分系统 <<<
python
correct = 01、遍历每道题(每5个选项为一题)
python
for (q, i) in enumerate(np.arange(0, len(questionCnts), 5)):
# 当前题目选项排序(左到右)
cnts = sort_contours(questionCnts[i:i+5])[0]
bubbled = None
# 遍历每个选项
for (j, c) in enumerate(cnts):
# 创建选项掩膜
mask = np.zeros(thresh.shape, dtype="uint8")
cv_show('mask',mask)
cv2.drawContours(mask, [c], -1, 255, -1) # 填充式绘制
# 应用掩膜统计像素
thresh_mask_and = cv2.bitwise_and(thresh, thresh, mask=mask)
cv_show('thresh_mask_and',thresh_mask_and)
total = cv2.countNonZero(thresh_mask)
# 记录最大填涂区域
if bubbled is None or total > bubbled[0]:
bubbled = (total, j)
# 答案比对
color = (0, 0, 255) # 默认红色(错误)
k = ANSWER_KEY[q]
if k == bubbled[1]:
color = (0, 255, 0) # 绿色(正确)
correct += 1
# 绘制结果轮廓
cv2.drawContours(warped_new, [cnts[k]], -1, color, 3)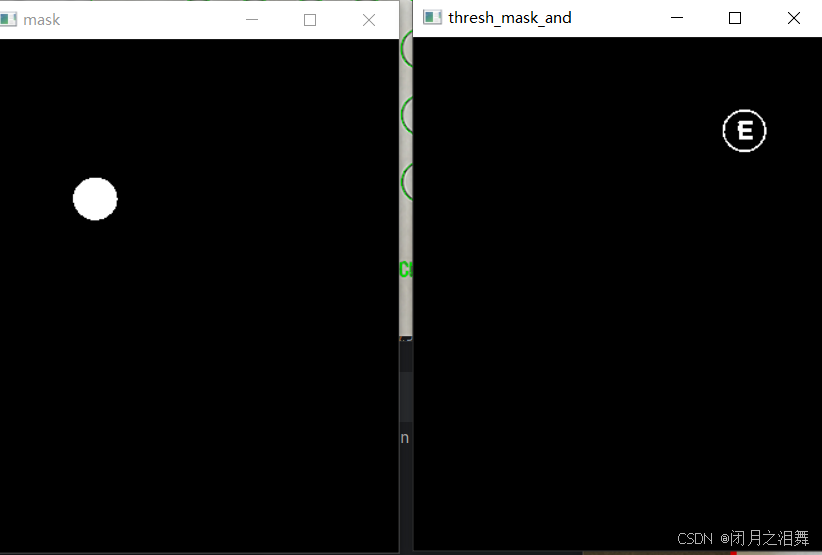
通过掩膜的方法依次遍历每个选项。
2、分数计算与显示
python
score = (correct / 5.0) * 100
print("[INFO] score: {:.2f}%".format(score))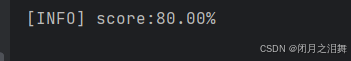
3、在图像左上角添加红色分数文本
python
cv2.putText(warped_new, "{:.2f}%".format(score), (10, 20),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.9, (0, 0, 255), 2)4、结果展示
python
cv_show('Original', image) # 显示原始图像
cv_show("Exas", warped_new) # 显示评分结果
cv2.waitKey(0) # 等待退出
总结
完整代码展示
python
import numpy as np
import cv2
import os
ANSWER_KEY={0:1,1:4,2:0,3:3,4:1}
def cv_show(name,value):
cv2.imshow(name,value)
cv2.waitKey(0)
def sort_contours(cnts,method='left-to-right'):
reverse=False
i=0
if method=='right-to-left' or method=='bottom-to-top':
reverse=True
if method=='top-to-bottom' or method=='bottom-to-top':
i=1
boundingBoxes=[cv2.boundingRect(c) for c in cnts]
(cnts,boundingBoxes)=zip(*sorted(zip(cnts,boundingBoxes),key=lambda b:b[1][i],reverse=reverse))
return cnts,boundingBoxes
def resize(image,width=None,height=None,inter=cv2.INTER_AREA):
dim=None
(h,w)=image.shape[:2]
if width is None and height is None:
return image
if width is None:
r=height/float(h)
dim=(int(w*r),height)
else:
r=width/float(w)
dim=(width,int(h*r))
resized=cv2.resize(image,dim,interpolation=inter)
return resized
def order_points(pts):
#一共四个坐标点
rect=np.zeros((4,2),dtype='float32')
#按顺序找到对应的坐标0123,分别是左上右上右下、左下
s=pts.sum(axis=1) #对矩阵的每一行进行求和操作
rect[0]=pts[np.argmin(s)]
rect[2]=pts[np.argmax(s)]
diff=np.diff(pts,axis=1)
rect[1]=pts[np.argmin(diff)]
rect[3]=pts[np.argmax(diff)]
return rect
def four_point_transform(image,pts):
#获取输入的坐标点
rect=order_points(pts)
(tl,tr,br,bl)=rect
#计算输入的w和h值
widthA=np.sqrt(((br[0]-bl[0])**2) +( br[1] - bl[1])**2)
widthB = np.sqrt(((tr[0] - tl[0]) ** 2) + (tr[1] - tl[1]) ** 2)
maxwidth=max(int(widthA),int(widthB))
heightA=np.sqrt(((tr[0]-br[0])**2) +( tr[1] - br[1])**2)
heightB=np.sqrt(((tl[0]-bl[0])**2) +( tl[1] - bl[1])**2)
maxheight=max(int(heightA),int(heightB))
dst=np.array([[0,0],[maxwidth,0],[maxwidth,maxheight],[0,maxheight]],dtype='float32')
M=cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(rect,dst)
warped=cv2.warpPerspective(image,M,(maxwidth,maxheight))
return warped
#预处理
image=cv2.imread('../data/images/test_01.png')
contours_img=image.copy()
"灰度处理、做高斯滤波、边缘检测"
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGRA2GRAY)
blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray,(5,5),0)
cv_show('blurred',blurred)
edged = cv2.Canny(blurred, 75, 200)
cv_show('edged',edged)
#轮廓检测
cnts=cv2.findContours(edged,cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)[-2]
cv2.drawContours(contours_img,cnts,-1,(0,0,255),3)
cv_show('contours_img',contours_img)
doCnt=None
#根据轮廓大小进行排序,准备透视变换
cnts=sorted(cnts,key=cv2.contourArea,reverse=True)
for c in cnts:
peri=cv2.arcLength(c,True)
approx=cv2.approxPolyDP(c,0.02*peri,True)
if len(approx)==4:
doCnt=approx
break
#执行透视变换
warped_t=four_point_transform(image,doCnt.reshape(4,2))
warped_new=warped_t.copy()
cv_show('warped',warped_t)
warped=cv2.cvtColor(warped_t,cv2.COLOR_BGRA2GRAY)
#阈值处理
thresh=cv2.threshold(warped,0,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
cv_show('thresh',thresh)
thresh_contours=thresh.copy()
cnts=cv2.findContours(thresh,cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)[-2]
warped_contours=cv2.drawContours(warped_t,cnts,-1,(0,255,0),1)
cv_show('warped_contours',warped_contours)
questionCnts=[]
for c in cnts:
(x,y,w,h)=cv2.boundingRect(c)
ar=w/float(h)
#根据实际情况指定标准
if w>20 and h >20 and 0.9<ar<=1.1:
questionCnts.append(c)
#按照从上到下的顺序排序
questionCnts=sort_contours(questionCnts,method="top-to-bottom")[0]
correct=0 #计算正确率
#依次取出每行的数据
for (q,i) in enumerate(np.arange(0,len(questionCnts),5)):
cnts=sort_contours(questionCnts[i:i+5])[0]
bubbled=None
#遍历每一个结果
for (j,c) in enumerate(cnts):
mask=np.zeros(thresh.shape,dtype='uint8')
cv2.drawContours(mask,[c],-1,255,-1)#-1代表填充
cv_show('mask',mask)
thresh_mask_and=cv2.bitwise_and(thresh,thresh,mask=mask)
cv_show('thresh_mask_and',thresh_mask_and)
total=cv2.countNonZero(thresh_mask_and)
if bubbled is None or total>bubbled[0]:
bubbled=(total,j)
color=(0,0,255)
k=ANSWER_KEY[q]
if k==bubbled[1]:
color=(0,255,0)
correct+=1
cv2.drawContours(warped_new,[cnts[k]],-1,color,3)
cv_show('warped',warped_new)
score=(correct/5.0)*100
print("[INFO] score:{:.2f}%".format(score))
cv2.putText(warped_new,"{:.2f}%".format(score),(10,20),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,0.9,(0,0,255),2)
cv_show('Oringinal',image)
cv_show("Exas",warped_new)
cv2.waitKey(0)该代码通过经典的OpenCV图像处理技术,构建了一个完整的答题卡自动评分系统,展现了计算机视觉在自动化领域的典型应用。其模块化设计、清晰的代码结构和可调参数,为二次开发提供了良好的基础,具备较高的实用价值和扩展潜力。