高并发写入场景下,MySQL 常成为系统瓶颈。本文深入分析其局限性,提供全面的解决方案和实施建议。
1. MySQL 面临的高并发写入挑战
1.1 锁机制制约
InnoDB 虽然支持行级锁,但高并发写入同一数据时,锁竞争仍然严重:
sql
-- 多个并发事务同时执行类似操作时
BEGIN;
UPDATE orders SET status = 'PAID' WHERE id = 10001;
COMMIT;上述简单操作在秒杀场景下会导致大量事务相互等待,响应时间从毫秒级飙升至秒级。
1.2 事务处理开销
每个事务都需要维护 ACID 特性,具体包括:
- 记录 undo 日志:记录修改前数据,支持事务回滚
- 写入 redo 日志:保证持久性,即使系统崩溃也能恢复
- 写入 binlog:用于主从复制和时间点恢复
- 校验约束:确保数据一致性
- 实现并发控制:管理多事务间的隔离性
1.3 索引维护成本
每次数据写入可能触发多个索引更新:
sql
CREATE TABLE user_logs (
id BIGINT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
user_id BIGINT NOT NULL,
action VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
create_time TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
details TEXT,
INDEX idx_user_id (user_id),
INDEX idx_action (action),
INDEX idx_create_time (create_time)
);当有大量并发写入时,每个索引都需要维护 B+树结构,成本倍增。
2. 案例分析:电商秒杀场景
模拟 10 万用户同时抢购 1000 件商品的性能测试:
sql
-- 传统实现
BEGIN;
-- 1. 检查库存
SELECT stock FROM products WHERE id = 123 FOR UPDATE;
-- 2. 更新库存
UPDATE products SET stock = stock - 1 WHERE id = 123;
-- 3. 创建订单
INSERT INTO orders (user_id, product_id, price) VALUES (456, 123, 99.00);
COMMIT;测试结果(4 核 8G,MySQL 8.0,InnoDB 默认配置):
| 并发量 | 平均响应时间 | 数据库 CPU | 成功率 | 事务/秒 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 QPS | 15ms | 25% | 100% | 100 |
| 500 QPS | 120ms | 70% | 99.5% | 497 |
| 1000 QPS | 520ms | 95% | 88% | 880 |
| 2000 QPS | 3500ms | 100% | 45% | 900 |
当并发达到 1000 QPS 时,响应时间迅速恶化,数据库成为明显瓶颈。
3. 数据一致性模型与性能权衡
在分布式系统中,需要根据业务需求在一致性和性能间做出权衡:
java
/**
* 根据业务场景选择一致性策略
*/
public enum ConsistencyStrategy {
STRONG_CONSISTENCY("强一致性", "所有节点同步更新,性能较低", CAP.CP),
EVENTUAL_CONSISTENCY("最终一致性", "异步复制,短暂不一致,性能高", CAP.AP),
SESSION_CONSISTENCY("会话一致性", "同一会话内保证读写一致", CAP.AP),
CAUSAL_CONSISTENCY("因果一致性", "保证有因果关系的操作顺序一致", CAP.AP);
private final String name;
private final String description;
private final CAP capModel;
ConsistencyStrategy(String name, String description, CAP capModel) {
this.name = name;
this.description = description;
this.capModel = capModel;
}
// Getters略
}
enum CAP {
CP("一致性+分区容忍性,牺牲可用性"),
AP("可用性+分区容忍性,牺牲强一致性"),
CA("一致性+可用性,不适用于分布式系统");
private final String description;
CAP(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
// Getter略
}事务隔离级别对性能的影响:
java
/**
* 事务隔离级别性能与一致性比较
*
* READ_UNCOMMITTED: 最高性能,但可能读取脏数据
* READ_COMMITTED: 避免脏读,但可能不可重复读和幻读
* REPEATABLE_READ: 避免脏读和不可重复读,但可能幻读
* SERIALIZABLE: 最高一致性,但性能最低
*/
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED) // 权衡性能与一致性
public void performBatchUpdate(List<Data> dataList) {
// 批量更新实现
for (Data data : dataList) {
repository.save(data);
}
}4. MySQL 性能优化实战
在寻找替代方案前,可先尝试这些 MySQL 优化策略:
4.1 InnoDB 参数调优
ini
# my.cnf 关键参数
# 增加缓冲池大小(系统内存的50%-70%)
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 4G
# 调整为0可提高写入性能,但牺牲部分持久性保证
innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit = 0
# 批量写入时调大以减少刷盘次数
innodb_flush_log_at_timeout = 10
# 控制检查点频率,避免密集IO
innodb_io_capacity = 2000
innodb_io_capacity_max = 4000
# 关闭双写缓冲区可提升性能(风险:系统崩溃可能导致数据页损坏)
# innodb_doublewrite = 0
# 增加日志文件大小减少切换频率
innodb_log_file_size = 1G实测结果:在 1000 QPS 场景下,优化后响应时间从 520ms 降至 180ms,吞吐量提升约 60%。
4.2 批量写入技术
传统逐行写入改为批量操作:
sql
-- 单行插入改为批量插入
INSERT INTO user_logs (user_id, action, details) VALUES
(101, 'login', '{"ip":"192.168.1.1"}'),
(102, 'search', '{"keyword":"mysql"}'),
(103, 'click', '{"item_id":12345}'),
...
(150, 'checkout', '{"order_id":9876}');
-- 高效更新多行
INSERT INTO user_stats (user_id, login_count, last_login)
VALUES (101, 1, NOW()), (102, 1, NOW()), ...
ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE
login_count = login_count + 1,
last_login = VALUES(last_login);
-- 大批量数据导入
LOAD DATA INFILE '/tmp/user_events.csv'
INTO TABLE user_events
FIELDS TERMINATED BY ','
ENCLOSED BY '"'
LINES TERMINATED BY '\n'
(user_id, event_type, timestamp, payload);批量写入性能对比(每批 100 条记录):
| 写入方式 | 每秒写入记录数 | 资源消耗率 |
|---|---|---|
| 单行 INSERT | 2,500 | CPU 95%, IO 80% |
| 批量 INSERT | 45,000 | CPU 70%, IO 60% |
| LOAD DATA | 120,000 | CPU 85%, IO 95% |
4.3 技术原因深度解析
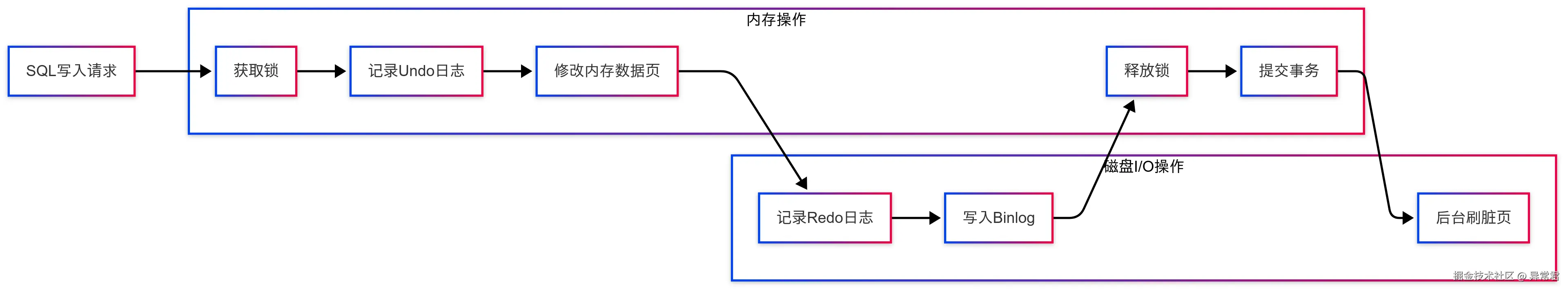
日志机制区别:
- Redo 日志:物理日志,记录对页的修改,用于崩溃恢复
- Undo 日志:逻辑日志,记录反向操作,用于回滚和 MVCC
- Binlog:逻辑日志,记录数据变更,用于复制和恢复
4.4 JVM 调优策略
对 Java 应用进行 JVM 调优可显著提升 MySQL 交互性能:
bash
# JDK 8的JVM参数
JAVA_OPTS="-Xms4g -Xmx4g -XX:MetaspaceSize=256m -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=512m \
-XX:+UseG1GC -XX:MaxGCPauseMillis=100 -XX:+ParallelRefProcEnabled \
-XX:+UseStringDeduplication -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError \
-XX:HeapDumpPath=/var/log/heapdump.hprof \
-XX:+PrintGCDetails -XX:+PrintGCDateStamps -Xloggc:/var/log/gc.log"
# JDK 11+的JVM参数
JAVA_OPTS="-Xms4g -Xmx4g -XX:MetaspaceSize=256m -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=512m \
-XX:+UseG1GC -XX:MaxGCPauseMillis=100 -XX:+ParallelRefProcEnabled \
-XX:+UseStringDeduplication -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError \
-XX:HeapDumpPath=/var/log/heapdump.hprof \
-Xlog:gc*=info:file=/var/log/gc.log:time,uptime,level,tags:filecount=5,filesize=100m"
# JDK 21的JVM参数(含虚拟线程支持)
JAVA_OPTS="-Xms4g -Xmx4g -XX:MetaspaceSize=256m -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=512m \
-XX:+UseG1GC -XX:MaxGCPauseMillis=100 -XX:+ParallelRefProcEnabled \
-XX:+UseStringDeduplication -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError \
-XX:HeapDumpPath=/var/log/heapdump.hprof \
-Xlog:gc*=info:file=/var/log/gc.log:time,uptime,level,tags:filecount=5,filesize=100m"关键 JVM 优化点:
- 使用 G1 垃圾收集器,控制最大暂停时间
- 合理设置堆内存,避免频繁 GC
- 开启字符串去重,减少内存占用
- 配置 GC 日志,便于问题排查
5. 高并发写入解决方案
5.1 限流保护策略
使用令牌桶算法保护数据库免受流量冲击:
java
/**
* 限流器配置
*/
@Configuration
public class RateLimiterConfig {
@Bean
public RateLimiter apiRateLimiter() {
// 每秒允许1000个请求
return RateLimiter.create(1000.0);
}
@Bean
public RateLimiter dbWriteRateLimiter() {
// 数据库写入限制为每秒500次
return RateLimiter.create(500.0);
}
}
/**
* 限流服务接口
*/
public interface RateLimitService {
<T> T executeWithRateLimit(Supplier<T> task, String operationType);
void executeWithRateLimit(Runnable task, String operationType);
boolean tryAcquirePermit(String operationType, long timeout, TimeUnit unit);
}
/**
* 限流服务实现
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class GuavaRateLimitService implements RateLimitService {
private final Map<String, RateLimiter> limiters;
private final MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
public GuavaRateLimitService(
@Qualifier("apiRateLimiter") RateLimiter apiRateLimiter,
@Qualifier("dbWriteRateLimiter") RateLimiter dbWriteRateLimiter,
MeterRegistry meterRegistry) {
this.meterRegistry = meterRegistry;
// 初始化不同操作类型的限流器
Map<String, RateLimiter> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("api", apiRateLimiter);
map.put("db_write", dbWriteRateLimiter);
this.limiters = Collections.unmodifiableMap(map);
}
@Override
public <T> T executeWithRateLimit(Supplier<T> task, String operationType) {
RateLimiter limiter = getLimiter(operationType);
Timer.Sample sample = Timer.start(meterRegistry);
boolean acquired = limiter.tryAcquire(100, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (!acquired) {
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("rate.limit.acquire.time",
"operation", operationType,
"result", "rejected"));
meterRegistry.counter("rate.limit.rejected", "operation", operationType).increment();
log.warn("Rate limit exceeded for operation: {}", operationType);
throw new RateLimitExceededException("Rate limit exceeded for: " + operationType);
}
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("rate.limit.acquire.time",
"operation", operationType,
"result", "acquired"));
try {
return task.get();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Error executing rate-limited task: {}", operationType, e);
throw e;
}
}
@Override
public void executeWithRateLimit(Runnable task, String operationType) {
executeWithRateLimit(() -> {
task.run();
return null;
}, operationType);
}
@Override
public boolean tryAcquirePermit(String operationType, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
RateLimiter limiter = getLimiter(operationType);
boolean acquired = limiter.tryAcquire(timeout, unit);
if (acquired) {
meterRegistry.counter("rate.limit.acquired", "operation", operationType).increment();
} else {
meterRegistry.counter("rate.limit.rejected", "operation", operationType).increment();
}
return acquired;
}
private RateLimiter getLimiter(String operationType) {
RateLimiter limiter = limiters.get(operationType);
if (limiter == null) {
log.warn("No rate limiter configured for operation: {}, using default", operationType);
limiter = limiters.get("api"); // 默认使用API限流器
}
return limiter;
}
}5.2 断路器模式实现
防止系统级联失败的断路器实现:
java
/**
* 断路器配置
*/
@Configuration
public class CircuitBreakerConfig {
@Bean
public CircuitBreaker databaseCircuitBreaker() {
io.github.resilience4j.circuitbreaker.CircuitBreakerConfig config =
io.github.resilience4j.circuitbreaker.CircuitBreakerConfig.custom()
.failureRateThreshold(50) // 50%的失败率将打开断路器
.waitDurationInOpenState(Duration.ofSeconds(60)) // 开路状态持续60秒
.permittedNumberOfCallsInHalfOpenState(10) // 半开状态允许10次调用测试
.slidingWindowSize(100) // 基于最近100次调用计算失败率
.recordExceptions(DataAccessException.class, TimeoutException.class) // 记录这些异常
.build();
return CircuitBreaker.of("database", config);
}
@Bean
public CircuitBreaker cacheCircuitBreaker() {
io.github.resilience4j.circuitbreaker.CircuitBreakerConfig config =
io.github.resilience4j.circuitbreaker.CircuitBreakerConfig.custom()
.failureRateThreshold(50)
.waitDurationInOpenState(Duration.ofSeconds(30)) // 缓存服务恢复更快
.permittedNumberOfCallsInHalfOpenState(5)
.slidingWindowSize(50)
.build();
return CircuitBreaker.of("cache", config);
}
@Bean
public CircuitBreakerRegistry circuitBreakerRegistry() {
return CircuitBreakerRegistry.ofDefaults();
}
}
/**
* 断路器服务接口
*/
public interface CircuitBreakerService {
<T> T executeWithCircuitBreaker(Supplier<T> task, String breakerName, Supplier<T> fallback);
void executeWithCircuitBreaker(Runnable task, String breakerName, Runnable fallback);
}
/**
* 断路器服务实现
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class Resilience4jCircuitBreakerService implements CircuitBreakerService {
private final Map<String, CircuitBreaker> breakers;
private final MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
public Resilience4jCircuitBreakerService(
@Qualifier("databaseCircuitBreaker") CircuitBreaker databaseCircuitBreaker,
@Qualifier("cacheCircuitBreaker") CircuitBreaker cacheCircuitBreaker,
MeterRegistry meterRegistry) {
this.meterRegistry = meterRegistry;
// 初始化断路器映射
Map<String, CircuitBreaker> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("database", databaseCircuitBreaker);
map.put("cache", cacheCircuitBreaker);
this.breakers = Collections.unmodifiableMap(map);
// 注册监听器记录状态变化
breakers.forEach((name, breaker) -> {
breaker.getEventPublisher()
.onStateTransition(event -> {
log.info("Circuit breaker '{}' state changed from {} to {}",
name, event.getStateTransition().getFromState(),
event.getStateTransition().getToState());
meterRegistry.counter("circuit.breaker.state.transition",
"name", name,
"from", event.getStateTransition().getFromState().name(),
"to", event.getStateTransition().getToState().name())
.increment();
});
breaker.getEventPublisher()
.onSuccess(event -> meterRegistry.counter("circuit.breaker.outcome",
"name", name,
"outcome", "success")
.increment());
breaker.getEventPublisher()
.onError(event -> meterRegistry.counter("circuit.breaker.outcome",
"name", name,
"outcome", "error",
"exception", event.getThrowable().getClass().getSimpleName())
.increment());
});
}
@Override
public <T> T executeWithCircuitBreaker(Supplier<T> task, String breakerName, Supplier<T> fallback) {
CircuitBreaker breaker = getBreaker(breakerName);
Timer.Sample sample = Timer.start(meterRegistry);
try {
T result = breaker.executeSupplier(task);
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("circuit.breaker.execution.time",
"name", breakerName,
"outcome", "success"));
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("circuit.breaker.execution.time",
"name", breakerName,
"outcome", "fallback"));
log.warn("Circuit breaker '{}' triggered fallback for exception: {}",
breakerName, e.getMessage());
if (fallback != null) {
return fallback.get();
} else {
throw e;
}
}
}
@Override
public void executeWithCircuitBreaker(Runnable task, String breakerName, Runnable fallback) {
executeWithCircuitBreaker(() -> {
task.run();
return null;
}, breakerName, fallback == null ? null : () -> {
fallback.run();
return null;
});
}
private CircuitBreaker getBreaker(String breakerName) {
CircuitBreaker breaker = breakers.get(breakerName);
if (breaker == null) {
log.warn("No circuit breaker configured for name: {}, using default", breakerName);
breaker = breakers.values().iterator().next(); // 使用第一个作为默认
}
return breaker;
}
}5.3 接口定义与设计模式
采用接口和实现分离模式,提高代码可测试性和可维护性:
java
/**
* 缓存服务接口
*/
public interface CacheService {
<T> T get(String key, Class<T> type);
void put(String key, Object value, long expireTime);
void remove(String key);
boolean exists(String key);
}
/**
* Redis缓存实现
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class RedisCacheService implements CacheService {
private final StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
private final ObjectMapper objectMapper;
private final CircuitBreakerService circuitBreakerService;
public RedisCacheService(StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate,
ObjectMapper objectMapper,
CircuitBreakerService circuitBreakerService) {
this.redisTemplate = redisTemplate;
this.objectMapper = objectMapper;
this.circuitBreakerService = circuitBreakerService;
}
@Override
public <T> T get(String key, Class<T> type) {
return circuitBreakerService.executeWithCircuitBreaker(
() -> {
try {
String value = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (value == null || value.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return objectMapper.readValue(value, type);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Error getting object from cache: {}", key, e);
throw new CacheException("Failed to get object from cache", e);
}
},
"cache",
() -> null // 缓存失败时返回null
);
}
@Override
public void put(String key, Object value, long expireTime) {
circuitBreakerService.executeWithCircuitBreaker(
() -> {
try {
String json = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(value);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, json, expireTime, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Error putting object to cache: {}", key, e);
throw new CacheException("Failed to put object to cache", e);
}
},
"cache",
() -> { /* 缓存写入失败不执行回退逻辑 */ }
);
}
@Override
public void remove(String key) {
circuitBreakerService.executeWithCircuitBreaker(
() -> {
try {
redisTemplate.delete(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Error removing key from cache: {}", key, e);
throw new CacheException("Failed to remove key from cache", e);
}
},
"cache",
() -> { /* 缓存删除失败不执行回退逻辑 */ }
);
}
@Override
public boolean exists(String key) {
return circuitBreakerService.executeWithCircuitBreaker(
() -> {
try {
return Boolean.TRUE.equals(redisTemplate.hasKey(key));
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Error checking key existence: {}", key, e);
throw new CacheException("Failed to check key existence", e);
}
},
"cache",
() -> false // 缓存检查失败时默认不存在
);
}
}5.4 读写分离架构

实现示例(基于 Spring 框架):
java
@Configuration
public class DataSourceConfig {
private final Environment env;
public DataSourceConfig(Environment env) {
this.env = env;
}
@Bean
@Primary
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.master")
public DataSource masterDataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.slave")
public DataSource slaveDataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean
public DataSource routingDataSource() {
ReplicaRoutingDataSource routingDataSource = new ReplicaRoutingDataSource();
Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources = new HashMap<>();
targetDataSources.put("master", masterDataSource());
targetDataSources.put("slave", slaveDataSource());
routingDataSource.setTargetDataSources(targetDataSources);
routingDataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(masterDataSource());
return routingDataSource;
}
}
// 自定义路由数据源
class ReplicaRoutingDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
// 根据事务是否只读决定路由
return TransactionSynchronizationManager.isCurrentTransactionReadOnly()
? "slave" : "master";
}
}
// 在Service中使用
@Service
public class UserService {
private final UserRepository userRepository;
public UserService(UserRepository userRepository) {
this.userRepository = userRepository;
}
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED, propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void createUser(User user) {
userRepository.save(user);
}
@Transactional(readOnly = true, isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED)
public List<User> findAllUsers() {
return userRepository.findAll();
}
}5.5 主从一致性保障
采用更轻量级的方式处理主从复制延迟问题:
java
/**
* 主从数据一致性服务接口
*/
public interface ReplicationConsistencyService {
<T> T readWithConsistency(String key, Function<JdbcTemplate, T> query);
<T> T readFromMaster(Function<JdbcTemplate, T> query);
boolean isReplicationHealthy();
}
/**
* 主从一致性服务实现
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class MySQLReplicationConsistencyService implements ReplicationConsistencyService {
private final JdbcTemplate masterTemplate;
private final JdbcTemplate slaveTemplate;
private final MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
private final CacheService cacheService;
public MySQLReplicationConsistencyService(
@Qualifier("masterJdbcTemplate") JdbcTemplate masterTemplate,
@Qualifier("slaveJdbcTemplate") JdbcTemplate slaveTemplate,
MeterRegistry meterRegistry,
CacheService cacheService) {
this.masterTemplate = masterTemplate;
this.slaveTemplate = slaveTemplate;
this.meterRegistry = meterRegistry;
this.cacheService = cacheService;
}
/**
* 检查从库复制状态,根据延迟程度选择数据源
*/
@Override
public <T> T readWithConsistency(String key, Function<JdbcTemplate, T> query) {
Timer.Sample sample = Timer.start(meterRegistry);
try {
if (isReplicationDelayed()) {
log.warn("Replication lag detected, falling back to master for key: {}", key);
// 如果延迟过大,回退到主库读取
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("db.read.time",
"source", "master",
"reason", "replication_delayed"));
return query.apply(masterTemplate);
}
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("db.read.time", "source", "slave"));
return query.apply(slaveTemplate);
} catch (Exception e) {
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("db.read.time",
"source", "error",
"error", e.getClass().getSimpleName()));
log.error("Error reading data with key: {}", key, e);
throw new DatabaseAccessException("Failed to read data", e);
}
}
/**
* 对关键数据保证强一致性,直接从主库读取
*/
@Override
public <T> T readFromMaster(Function<JdbcTemplate, T> query) {
Timer.Sample sample = Timer.start(meterRegistry);
try {
T result = query.apply(masterTemplate);
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("db.read.time", "source", "master_forced"));
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("db.read.time",
"source", "master_error",
"error", e.getClass().getSimpleName()));
log.error("Error reading data from master", e);
throw new DatabaseAccessException("Failed to read data from master", e);
}
}
/**
* 检查复制是否健康
*/
@Override
public boolean isReplicationHealthy() {
return !isReplicationDelayed();
}
/**
* 轻量级检测复制延迟
*/
private boolean isReplicationDelayed() {
try {
// 使用缓存减少检查频率
String cacheKey = "replication:status:check";
Boolean status = cacheService.get(cacheKey, Boolean.class);
if (status != null) {
return !status; // true表示健康,false表示延迟
}
// 每个库写入一个唯一标记并检查是否同步
String marker = "check_" + System.currentTimeMillis();
String key = "replication_check";
// 主库写入
masterTemplate.update("INSERT INTO replication_check(id, value) VALUES(?, ?) " +
"ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE value = ?", key, marker, marker);
// 等待短暂时间让复制发生
Thread.sleep(100);
// 从库读取
try {
String value = slaveTemplate.queryForObject(
"SELECT value FROM replication_check WHERE id = ?", String.class, key);
boolean isHealthy = marker.equals(value); // 相等表示复制正常
// 缓存结果5秒,减少频繁检查
cacheService.put(cacheKey, isHealthy, 5);
if (!isHealthy) {
log.warn("Replication lag detected: marker mismatch");
meterRegistry.counter("replication.status", "status", "delayed").increment();
}
return !isHealthy; // 返回是否有延迟
} catch (EmptyResultDataAccessException e) {
// 数据尚未复制到从库
log.warn("Replication lag detected: data not replicated yet");
meterRegistry.counter("replication.status", "status", "delayed").increment();
cacheService.put(cacheKey, false, 5); // 缓存结果
return true; // 有延迟
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Error checking replication status", e);
meterRegistry.counter("replication.status", "status", "error").increment();
return true; // 出错时默认认为有延迟,回主库
}
}
}5.6 分布式锁实现
高并发环境下,分布式锁是协调资源访问的关键机制:
java
/**
* 分布式锁服务接口
*/
public interface DistributedLockService {
boolean acquireLock(String lockKey, String requestId, long expireTime);
boolean releaseLock(String lockKey, String requestId);
<T> T executeWithLock(String lockKey, long expireTime, Supplier<T> task);
void executeWithLock(String lockKey, long expireTime, Runnable task);
}
/**
* Redis分布式锁实现
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class RedisDistributedLockService implements DistributedLockService {
private final StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
private final MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
private final CircuitBreakerService circuitBreakerService;
public RedisDistributedLockService(StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate,
MeterRegistry meterRegistry,
CircuitBreakerService circuitBreakerService) {
this.redisTemplate = redisTemplate;
this.meterRegistry = meterRegistry;
this.circuitBreakerService = circuitBreakerService;
}
/**
* 获取分布式锁
* @param lockKey 锁的键
* @param requestId 请求标识(用于释放锁时验证)
* @param expireTime 锁过期时间(毫秒)
* @return 是否获取成功
*/
@Override
public boolean acquireLock(String lockKey, String requestId, long expireTime) {
Timer.Sample sample = Timer.start(meterRegistry);
try {
return circuitBreakerService.executeWithCircuitBreaker(
() -> {
Boolean result = redisTemplate.opsForValue()
.setIfAbsent(lockKey, requestId, expireTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
boolean acquired = Boolean.TRUE.equals(result);
if (acquired) {
meterRegistry.counter("lock.acquire.count", "result", "success").increment();
log.debug("Acquired lock: {}", lockKey);
} else {
meterRegistry.counter("lock.acquire.count", "result", "failure").increment();
log.debug("Failed to acquire lock: {}", lockKey);
}
return acquired;
},
"cache",
() -> {
log.error("Circuit breaker triggered for lock acquisition: {}", lockKey);
return false; // 断路器触发时默认获取锁失败
}
);
} catch (Exception e) {
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("lock.acquire.time", "result", "error"));
meterRegistry.counter("lock.acquire.errors",
"error", e.getClass().getSimpleName()).increment();
log.error("Failed to acquire lock for key: {}", lockKey, e);
return false;
} finally {
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("lock.acquire.time"));
}
}
/**
* 释放分布式锁
* @param lockKey 锁的键
* @param requestId 请求标识(确保只有加锁者才能解锁)
* @return 是否释放成功
*/
@Override
public boolean releaseLock(String lockKey, String requestId) {
Timer.Sample sample = Timer.start(meterRegistry);
try {
return circuitBreakerService.executeWithCircuitBreaker(
() -> {
String script = "if redis.call('get', KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1] then " +
"return redis.call('del', KEYS[1]) else return 0 end";
Long result = redisTemplate.execute(new DefaultRedisScript<>(script, Long.class),
Collections.singletonList(lockKey), requestId);
boolean released = result != null && result == 1L;
if (released) {
meterRegistry.counter("lock.release.count", "result", "success").increment();
log.debug("Released lock: {}", lockKey);
} else {
meterRegistry.counter("lock.release.count", "result", "failure").increment();
log.debug("Failed to release lock: {}", lockKey);
}
return released;
},
"cache",
() -> {
log.error("Circuit breaker triggered for lock release: {}", lockKey);
return false; // 断路器触发时默认释放锁失败
}
);
} catch (Exception e) {
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("lock.release.time", "result", "error"));
meterRegistry.counter("lock.release.errors",
"error", e.getClass().getSimpleName()).increment();
log.error("Failed to release lock for key: {}", lockKey, e);
return false;
} finally {
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("lock.release.time"));
}
}
/**
* 使用锁执行任务
* @param lockKey 锁键
* @param expireTime 过期时间
* @param task 任务
* @return 执行结果
*/
@Override
public <T> T executeWithLock(String lockKey, long expireTime, Supplier<T> task) {
String requestId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
boolean locked = acquireLock(lockKey, requestId, expireTime);
if (!locked) {
throw new LockAcquisitionException("Failed to acquire lock: " + lockKey);
}
try {
return task.get();
} finally {
releaseLock(lockKey, requestId);
}
}
/**
* 使用锁执行无返回值任务
*/
@Override
public void executeWithLock(String lockKey, long expireTime, Runnable task) {
executeWithLock(lockKey, expireTime, () -> {
task.run();
return null;
});
}
}5.7 自适应线程池配置
高并发环境下的智能线程池配置,包括 Java 21 虚拟线程支持:
java
@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class ThreadPoolConfig {
@Bean
public ScheduledExecutorService metricsScheduler() {
return Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("metrics-scheduler-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build());
}
/**
* 常规线程池 - 适用于IO密集型任务
*/
@Bean(destroyMethod = "shutdown")
public ThreadPoolExecutor ioTaskExecutor() {
int cpuCores = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
// 创建自适应线程池
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(
// 核心线程数 = CPU核心数 * 2(IO密集型任务)
cpuCores * 2,
// 最大线程数 = CPU核心数 * 4
cpuCores * 4,
// 空闲线程存活时间
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
// 使用有界队列防止OOM
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1000),
// 自定义线程工厂
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("io-task-%d")
.setDaemon(false)
.setUncaughtExceptionHandler((t, e) ->
log.error("Uncaught exception in thread {}", t.getName(), e))
.build(),
// 拒绝策略:调用者运行,防止任务丢失,但可能导致调用线程阻塞
new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy()
);
}
/**
* CPU密集型任务线程池
*/
@Bean(destroyMethod = "shutdown")
public ThreadPoolExecutor cpuTaskExecutor() {
int cpuCores = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(
// CPU密集型任务核心线程数 = CPU核心数
cpuCores,
// 最大线程数 = CPU核心数 + 1
cpuCores + 1,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(500),
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("cpu-task-%d")
.setDaemon(false)
.setUncaughtExceptionHandler((t, e) ->
log.error("Uncaught exception in thread {}", t.getName(), e))
.build(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy()
);
}
/**
* Java 21虚拟线程执行器 - 适用于大量IO阻塞任务
*/
@Bean
public Executor virtualThreadExecutor() {
// 使用虚拟线程,可以处理大量并发任务而不消耗过多系统资源
return Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor();
}
/**
* 监控线程池状态
*/
@Bean
public ThreadPoolMetricsCollector threadPoolMetrics(MeterRegistry registry,
@Qualifier("ioTaskExecutor") ThreadPoolExecutor ioExecutor,
@Qualifier("cpuTaskExecutor") ThreadPoolExecutor cpuExecutor,
ScheduledExecutorService metricsScheduler) {
return new ThreadPoolMetricsCollector(registry,
Map.of("io", ioExecutor, "cpu", cpuExecutor),
metricsScheduler);
}
/**
* 线程池监控指标收集器
*/
@Slf4j
public static class ThreadPoolMetricsCollector {
private final MeterRegistry registry;
private final Map<String, ThreadPoolExecutor> executors;
private final ScheduledExecutorService scheduler;
public ThreadPoolMetricsCollector(MeterRegistry registry,
Map<String, ThreadPoolExecutor> executors,
ScheduledExecutorService scheduler) {
this.registry = registry;
this.executors = executors;
this.scheduler = scheduler;
// 注册线程池指标
registerMetrics();
}
private void registerMetrics() {
executors.forEach((name, executor) -> {
// 活跃线程数
Gauge.builder("threadpool.active.threads", executor, ThreadPoolExecutor::getActiveCount)
.description("Number of active threads")
.tag("pool", name)
.register(registry);
// 队列大小
Gauge.builder("threadpool.queue.size", executor, e -> e.getQueue().size())
.description("Current queue size")
.tag("pool", name)
.register(registry);
// 线程池大小
Gauge.builder("threadpool.pool.size", executor, ThreadPoolExecutor::getPoolSize)
.description("Current pool size")
.tag("pool", name)
.register(registry);
// 完成任务数
Gauge.builder("threadpool.completed.tasks", executor, ThreadPoolExecutor::getCompletedTaskCount)
.description("Completed task count")
.tag("pool", name)
.register(registry);
// 线程池利用率
Gauge.builder("threadpool.utilization", executor,
e -> (double) e.getActiveCount() / e.getMaximumPoolSize())
.description("Thread pool utilization (active/max)")
.tag("pool", name)
.register(registry);
});
// 定期记录线程池状态
scheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(this::logPoolStatus, 0, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
private void logPoolStatus() {
executors.forEach((name, executor) -> {
log.info("{} pool status - Active: {}, PoolSize: {}, QueueSize: {}, Completed: {}, Utilization: {}.2f%",
name,
executor.getActiveCount(),
executor.getPoolSize(),
executor.getQueue().size(),
executor.getCompletedTaskCount(),
(double) executor.getActiveCount() / executor.getMaximumPoolSize() * 100);
// 根据利用率动态调整核心线程数
adjustPoolSize(name, executor);
});
}
/**
* 根据负载动态调整线程池大小
*/
private void adjustPoolSize(String name, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
double utilization = (double) executor.getActiveCount() / executor.getMaximumPoolSize();
int currentCoreSize = executor.getCorePoolSize();
int maxSize = executor.getMaximumPoolSize();
// 如果利用率超过80%,且核心线程数小于最大线程数,增加核心线程数
if (utilization > 0.8 && currentCoreSize < maxSize) {
int newCoreSize = Math.min(currentCoreSize + 2, maxSize);
executor.setCorePoolSize(newCoreSize);
log.info("Increased {} pool core size from {} to {}", name, currentCoreSize, newCoreSize);
}
// 如果利用率低于30%,且核心线程数大于初始配置,减少核心线程数
else if (utilization < 0.3 && currentCoreSize > Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()) {
int newCoreSize = Math.max(currentCoreSize - 1, Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
executor.setCorePoolSize(newCoreSize);
log.info("Decreased {} pool core size from {} to {}", name, currentCoreSize, newCoreSize);
}
}
}
}5.8 重试机制实现
带退避策略且限制递归深度的智能重试机制:
java
/**
* 重试服务接口
*/
public interface RetryService {
<T> T executeWithRetry(Supplier<T> operation, Predicate<Exception> retryable, int maxAttempts);
boolean isTemporaryException(Exception e);
}
/**
* 重试服务实现
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class ExponentialBackoffRetryService implements RetryService {
private final MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
private final CircuitBreakerService circuitBreakerService;
public ExponentialBackoffRetryService(MeterRegistry meterRegistry,
CircuitBreakerService circuitBreakerService) {
this.meterRegistry = meterRegistry;
this.circuitBreakerService = circuitBreakerService;
}
/**
* 使用指数退避策略执行带重试的操作
* @param operation 要执行的操作
* @param retryable 判断异常是否需要重试的断言
* @param maxAttempts 最大尝试次数
* @return 操作结果
*/
@Override
public <T> T executeWithRetry(Supplier<T> operation,
Predicate<Exception> retryable,
int maxAttempts) {
int attempts = 0;
Exception lastException = null;
Timer.Sample sample = Timer.start(meterRegistry);
while (attempts < maxAttempts) {
try {
attempts++;
// 使用断路器包装操作
T result = circuitBreakerService.executeWithCircuitBreaker(
operation,
"retryable-operation",
() -> {
throw new CircuitBreakerOpenException("Circuit breaker is open");
}
);
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("retry.time",
"attempts", String.valueOf(attempts),
"result", "success"));
meterRegistry.counter("retry.success",
"attempts", String.valueOf(attempts)).increment();
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
lastException = e;
// 断路器打开时不再重试
if (e instanceof CircuitBreakerOpenException) {
log.warn("Circuit breaker open, aborting retry");
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("retry.time",
"result", "circuit_breaker_open"));
meterRegistry.counter("retry.failures",
"reason", "circuit_breaker_open").increment();
break;
}
if (!retryable.test(e)) {
log.warn("Non-retryable exception occurred, aborting: {}", e.getMessage());
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("retry.time",
"attempts", String.valueOf(attempts),
"result", "non_retryable"));
meterRegistry.counter("retry.failures",
"reason", "non_retryable",
"exception", e.getClass().getSimpleName()).increment();
break; // 不可重试的异常,立即退出
}
if (attempts >= maxAttempts) {
log.error("Max retry attempts reached ({})", maxAttempts);
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("retry.time",
"attempts", String.valueOf(attempts),
"result", "max_attempts"));
meterRegistry.counter("retry.failures",
"reason", "max_attempts",
"exception", e.getClass().getSimpleName()).increment();
break; // 达到最大重试次数,退出
}
// 计算指数退避等待时间
// waitTime = 100 * 2^attempt with jitter and cap at 5 seconds
long baseWaitTime = (long) Math.pow(2, attempts) * 100;
// 添加随机抖动,避免惊群效应
long jitter = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextLong(50);
long waitTime = Math.min(baseWaitTime + jitter, 5000); // 最大等待5秒
log.warn("Retry attempt {} after exception: {}, waiting {}ms",
attempts, e.getMessage(), waitTime);
try {
Thread.sleep(waitTime);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("retry.time",
"attempts", String.valueOf(attempts),
"result", "interrupted"));
meterRegistry.counter("retry.failures",
"reason", "interrupted").increment();
throw new RuntimeException("Retry interrupted", ie);
}
}
}
// 所有重试失败,抛出最后一个异常
if (lastException != null) {
throw new RetryExhaustedException("Operation failed after " + attempts + " attempts", lastException);
} else {
// 这种情况不应该发生,但为了代码完整性
throw new IllegalStateException("Retry failed without an exception");
}
}
/**
* 判断异常是否为临时性错误(适合重试),限制递归深度
*/
@Override
public boolean isTemporaryException(Exception e) {
return isTemporaryException(e, 0);
}
/**
* 带递归深度限制的临时性异常检查
*/
private boolean isTemporaryException(Exception e, int depth) {
// 限制递归深度,防止栈溢出
if (depth > 5) {
return false;
}
return e instanceof DataAccessException ||
e instanceof TimeoutException ||
e instanceof ConnectException ||
(e.getCause() != null && e.getCause() instanceof Exception &&
isTemporaryException((Exception) e.getCause(), depth + 1));
}
}5.9 分布式事务模式实现
5.9.1 TCC (Try-Confirm-Cancel) 模式
java
/**
* TCC事务参与者接口
*/
public interface TccParticipant<T> {
/**
* Try阶段 - 资源预留
*/
T tryPhase(T context);
/**
* Confirm阶段 - 确认执行
*/
void confirmPhase(T context);
/**
* Cancel阶段 - 取消操作
*/
void cancelPhase(T context);
}
/**
* TCC事务协调器
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class TccTransactionCoordinator {
private final MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
public TccTransactionCoordinator(MeterRegistry meterRegistry) {
this.meterRegistry = meterRegistry;
}
/**
* 执行TCC事务
*/
public <T> T executeTransaction(T initialContext, List<TccParticipant<T>> participants) {
Timer.Sample sample = Timer.start(meterRegistry);
List<TccParticipant<T>> succeededParticipants = new ArrayList<>();
T context = initialContext;
try {
// 执行所有参与者的Try阶段
for (TccParticipant<T> participant : participants) {
log.debug("Executing try phase for participant: {}", participant.getClass().getSimpleName());
context = participant.tryPhase(context);
succeededParticipants.add(participant);
}
// 所有Try成功,执行Confirm阶段
for (TccParticipant<T> participant : participants) {
log.debug("Executing confirm phase for participant: {}", participant.getClass().getSimpleName());
participant.confirmPhase(context);
}
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("tcc.transaction.time", "result", "success"));
meterRegistry.counter("tcc.transaction.result", "result", "success").increment();
log.info("TCC transaction completed successfully");
return context;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("TCC transaction failed, executing cancel phase", e);
// Try或Confirm失败,执行Cancel阶段
for (TccParticipant<T> participant : succeededParticipants) {
try {
log.debug("Executing cancel phase for participant: {}", participant.getClass().getSimpleName());
participant.cancelPhase(context);
} catch (Exception cancelEx) {
log.error("Failed to cancel participant: {}", participant.getClass().getSimpleName(), cancelEx);
// 记录补偿失败,可能需要人工干预
meterRegistry.counter("tcc.transaction.cancel.failures").increment();
}
}
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("tcc.transaction.time", "result", "failure"));
meterRegistry.counter("tcc.transaction.result", "result", "failure").increment();
throw new TransactionFailedException("TCC transaction failed", e);
}
}
}
/**
* 订单服务TCC实现示例
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class OrderTccParticipant implements TccParticipant<OrderContext> {
private final JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public OrderTccParticipant(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
@Override
public OrderContext tryPhase(OrderContext context) {
log.info("Reserving order for user: {}, product: {}",
context.getUserId(), context.getProductId());
// 创建订单,状态为PENDING
Long orderId = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(
"INSERT INTO orders (user_id, product_id, quantity, price, status, created_at) " +
"VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, 'PENDING', NOW()) RETURNING id",
Long.class,
context.getUserId(),
context.getProductId(),
context.getQuantity(),
context.getPrice()
);
context.setOrderId(orderId);
return context;
}
@Override
public void confirmPhase(OrderContext context) {
log.info("Confirming order: {}", context.getOrderId());
// 将订单状态更新为CONFIRMED
int updated = jdbcTemplate.update(
"UPDATE orders SET status = 'CONFIRMED', updated_at = NOW() " +
"WHERE id = ? AND status = 'PENDING'",
context.getOrderId()
);
if (updated != 1) {
throw new ConcurrencyException("Order has been modified: " + context.getOrderId());
}
}
@Override
public void cancelPhase(OrderContext context) {
log.info("Cancelling order: {}", context.getOrderId());
if (context.getOrderId() != null) {
// 将订单状态更新为CANCELLED
jdbcTemplate.update(
"UPDATE orders SET status = 'CANCELLED', updated_at = NOW() " +
"WHERE id = ? AND status = 'PENDING'",
context.getOrderId()
);
}
}
}
/**
* 库存服务TCC实现示例
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class InventoryTccParticipant implements TccParticipant<OrderContext> {
private final JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public InventoryTccParticipant(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
@Override
public OrderContext tryPhase(OrderContext context) {
log.info("Reserving inventory for product: {}, quantity: {}",
context.getProductId(), context.getQuantity());
// 锁定库存行
Integer currentStock = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(
"SELECT stock FROM products WHERE id = ? FOR UPDATE",
Integer.class,
context.getProductId()
);
if (currentStock < context.getQuantity()) {
throw new InsufficientStockException("Not enough stock for product: " + context.getProductId());
}
// 创建库存预留记录
jdbcTemplate.update(
"INSERT INTO inventory_reservations (product_id, quantity, order_id, status, created_at) " +
"VALUES (?, ?, ?, 'RESERVED', NOW())",
context.getProductId(),
context.getQuantity(),
context.getOrderId()
);
return context;
}
@Override
public void confirmPhase(OrderContext context) {
log.info("Confirming inventory reservation for order: {}", context.getOrderId());
// 减少实际库存
int updated = jdbcTemplate.update(
"UPDATE products SET stock = stock - ? WHERE id = ? AND stock >= ?",
context.getQuantity(),
context.getProductId(),
context.getQuantity()
);
if (updated != 1) {
throw new ConcurrencyException("Product stock has been modified: " + context.getProductId());
}
// 更新预留状态
jdbcTemplate.update(
"UPDATE inventory_reservations SET status = 'CONFIRMED', updated_at = NOW() " +
"WHERE order_id = ? AND status = 'RESERVED'",
context.getOrderId()
);
}
@Override
public void cancelPhase(OrderContext context) {
log.info("Cancelling inventory reservation for order: {}", context.getOrderId());
// 更新预留状态
jdbcTemplate.update(
"UPDATE inventory_reservations SET status = 'CANCELLED', updated_at = NOW() " +
"WHERE order_id = ? AND status = 'RESERVED'",
context.getOrderId()
);
}
}
/**
* 使用TCC模式创建订单
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class OrderService {
private final TccTransactionCoordinator tccCoordinator;
private final OrderTccParticipant orderParticipant;
private final InventoryTccParticipant inventoryParticipant;
private final PaymentTccParticipant paymentParticipant;
public OrderService(TccTransactionCoordinator tccCoordinator,
OrderTccParticipant orderParticipant,
InventoryTccParticipant inventoryParticipant,
PaymentTccParticipant paymentParticipant) {
this.tccCoordinator = tccCoordinator;
this.orderParticipant = orderParticipant;
this.inventoryParticipant = inventoryParticipant;
this.paymentParticipant = paymentParticipant;
}
public OrderResponse createOrder(OrderRequest request) {
// 创建上下文对象
OrderContext context = new OrderContext();
context.setUserId(request.getUserId());
context.setProductId(request.getProductId());
context.setQuantity(request.getQuantity());
context.setPrice(request.getPrice());
// 组装参与者列表 - 按执行顺序
List<TccParticipant<OrderContext>> participants = Arrays.asList(
orderParticipant, // 首先创建订单
inventoryParticipant, // 然后预留库存
paymentParticipant // 最后处理支付
);
// 执行TCC事务
try {
OrderContext result = tccCoordinator.executeTransaction(context, participants);
return OrderResponse.builder()
.orderId(result.getOrderId())
.status("CONFIRMED")
.message("Order created successfully")
.build();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Failed to create order", e);
return OrderResponse.builder()
.status("FAILED")
.message("Failed to create order: " + e.getMessage())
.build();
}
}
}5.9.2 SAGA 模式
java
/**
* SAGA事务参与者接口
*/
public interface SagaParticipant<T> {
/**
* 执行正向操作
*/
T execute(T context);
/**
* 执行补偿操作
*/
void compensate(T context);
}
/**
* SAGA事务协调器
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class SagaTransactionCoordinator {
private final MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
public SagaTransactionCoordinator(MeterRegistry meterRegistry) {
this.meterRegistry = meterRegistry;
}
/**
* 执行SAGA事务
*/
public <T> T executeTransaction(T initialContext, List<SagaParticipant<T>> participants) {
Timer.Sample sample = Timer.start(meterRegistry);
List<SagaParticipant<T>> executedParticipants = new ArrayList<>();
T context = initialContext;
try {
// 按顺序执行所有参与者的操作
for (SagaParticipant<T> participant : participants) {
log.debug("Executing saga step: {}", participant.getClass().getSimpleName());
context = participant.execute(context);
executedParticipants.add(participant);
}
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("saga.transaction.time", "result", "success"));
meterRegistry.counter("saga.transaction.result", "result", "success").increment();
log.info("SAGA transaction completed successfully");
return context;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("SAGA transaction failed, executing compensations", e);
// 反向执行补偿操作
Collections.reverse(executedParticipants);
for (SagaParticipant<T> participant : executedParticipants) {
try {
log.debug("Executing compensation for: {}", participant.getClass().getSimpleName());
participant.compensate(context);
} catch (Exception compensateEx) {
log.error("Failed to compensate: {}", participant.getClass().getSimpleName(), compensateEx);
// 记录补偿失败,可能需要人工干预
meterRegistry.counter("saga.compensation.failures").increment();
}
}
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("saga.transaction.time", "result", "failure"));
meterRegistry.counter("saga.transaction.result", "result", "failure").increment();
throw new TransactionFailedException("SAGA transaction failed", e);
}
}
}
/**
* 订单创建SAGA参与者
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class CreateOrderSagaParticipant implements SagaParticipant<OrderContext> {
private final JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public CreateOrderSagaParticipant(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
@Override
public OrderContext execute(OrderContext context) {
log.info("Creating order for user: {}, product: {}",
context.getUserId(), context.getProductId());
// 创建订单
Long orderId = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(
"INSERT INTO orders (user_id, product_id, quantity, price, status, created_at) " +
"VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, 'CREATED', NOW()) RETURNING id",
Long.class,
context.getUserId(),
context.getProductId(),
context.getQuantity(),
context.getPrice()
);
context.setOrderId(orderId);
return context;
}
@Override
public void compensate(OrderContext context) {
log.info("Compensating order creation: {}", context.getOrderId());
if (context.getOrderId() != null) {
// 标记订单为CANCELLED
jdbcTemplate.update(
"UPDATE orders SET status = 'CANCELLED', updated_at = NOW() WHERE id = ?",
context.getOrderId()
);
}
}
}
/**
* 库存扣减SAGA参与者
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class ReduceInventorySagaParticipant implements SagaParticipant<OrderContext> {
private final JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public ReduceInventorySagaParticipant(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
@Override
public OrderContext execute(OrderContext context) {
log.info("Reducing inventory for product: {}, quantity: {}",
context.getProductId(), context.getQuantity());
int updated = jdbcTemplate.update(
"UPDATE products SET stock = stock - ? WHERE id = ? AND stock >= ?",
context.getQuantity(),
context.getProductId(),
context.getQuantity()
);
if (updated != 1) {
throw new InsufficientStockException("Not enough stock for product: " + context.getProductId());
}
// 记录库存变更
jdbcTemplate.update(
"INSERT INTO inventory_changes (product_id, order_id, quantity, type, created_at) " +
"VALUES (?, ?, ?, 'DECREASE', NOW())",
context.getProductId(),
context.getOrderId(),
context.getQuantity()
);
return context;
}
@Override
public void compensate(OrderContext context) {
log.info("Compensating inventory reduction: product={}, quantity={}",
context.getProductId(), context.getQuantity());
// 恢复库存
jdbcTemplate.update(
"UPDATE products SET stock = stock + ? WHERE id = ?",
context.getQuantity(),
context.getProductId()
);
// 记录库存变更
jdbcTemplate.update(
"INSERT INTO inventory_changes (product_id, order_id, quantity, type, created_at) " +
"VALUES (?, ?, ?, 'INCREASE', NOW())",
context.getProductId(),
context.getOrderId(),
context.getQuantity()
);
}
}
/**
* 订单服务SAGA实现
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class SagaOrderService {
private final SagaTransactionCoordinator sagaCoordinator;
private final CreateOrderSagaParticipant createOrderParticipant;
private final ReduceInventorySagaParticipant reduceInventoryParticipant;
private final ProcessPaymentSagaParticipant processPaymentParticipant;
public SagaOrderService(SagaTransactionCoordinator sagaCoordinator,
CreateOrderSagaParticipant createOrderParticipant,
ReduceInventorySagaParticipant reduceInventoryParticipant,
ProcessPaymentSagaParticipant processPaymentParticipant) {
this.sagaCoordinator = sagaCoordinator;
this.createOrderParticipant = createOrderParticipant;
this.reduceInventoryParticipant = reduceInventoryParticipant;
this.processPaymentParticipant = processPaymentParticipant;
}
public OrderResponse createOrder(OrderRequest request) {
// 创建上下文对象
OrderContext context = new OrderContext();
context.setUserId(request.getUserId());
context.setProductId(request.getProductId());
context.setQuantity(request.getQuantity());
context.setPrice(request.getPrice());
// 组装参与者列表 - 按执行顺序
List<SagaParticipant<OrderContext>> participants = Arrays.asList(
createOrderParticipant, // 创建订单
reduceInventoryParticipant, // 减少库存
processPaymentParticipant // 处理支付
);
// 执行SAGA事务
try {
OrderContext result = sagaCoordinator.executeTransaction(context, participants);
return OrderResponse.builder()
.orderId(result.getOrderId())
.status("COMPLETED")
.message("Order created successfully")
.build();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Failed to create order", e);
return OrderResponse.builder()
.status("FAILED")
.message("Failed to create order: " + e.getMessage())
.build();
}
}
}5.10 缓存分层设计
将大型缓存服务拆分为更小的职责单一的组件:
java
/**
* 缓存读取服务接口
*/
public interface ProductCacheReader {
Product getProduct(String productId);
boolean exists(String productId);
}
/**
* 缓存写入服务接口
*/
public interface ProductCacheWriter {
void putProduct(String productId, Product product, long expireTime);
void invalidateProduct(String productId);
void batchInvalidate(List<String> productIds);
}
/**
* 缓存回源服务接口
*/
public interface ProductFallbackStrategy {
Product getFromDatabase(String productId);
}
/**
* 多级缓存读取实现
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class MultiLevelProductCacheReader implements ProductCacheReader {
private final LoadingCache<String, Optional<Product>> localCache;
private final CacheService remoteCacheService;
private final BloomFilterInitializer bloomFilter;
private final ProductFallbackStrategy fallbackStrategy;
private final DistributedLockService lockService;
private final ProductCacheWriter cacheWriter;
private final MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
public MultiLevelProductCacheReader(CacheService remoteCacheService,
BloomFilterInitializer bloomFilter,
ProductFallbackStrategy fallbackStrategy,
DistributedLockService lockService,
ProductCacheWriter cacheWriter,
MeterRegistry meterRegistry) {
this.remoteCacheService = remoteCacheService;
this.bloomFilter = bloomFilter;
this.fallbackStrategy = fallbackStrategy;
this.lockService = lockService;
this.cacheWriter = cacheWriter;
this.meterRegistry = meterRegistry;
// 创建本地缓存
this.localCache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(10000)
.expireAfterWrite(5, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.recordStats()
.build(new CacheLoader<String, Optional<Product>>() {
@Override
public Optional<Product> load(String key) throws Exception {
// 只在本地缓存未命中时执行
Product product = getFromRemoteCache(key);
return Optional.ofNullable(product);
}
});
// 注册缓存统计信息
registerCacheMetrics();
}
private void registerCacheMetrics() {
Gauge.builder("cache.local.size", localCache, cache -> cache.size())
.description("Local cache size")
.register(meterRegistry);
Gauge.builder("cache.local.hitRate", localCache, cache -> cache.stats().hitRate())
.description("Local cache hit rate")
.register(meterRegistry);
}
@Override
public Product getProduct(String productId) {
Timer.Sample sample = Timer.start(meterRegistry);
try {
// 1. 布隆过滤器快速判断ID是否可能存在(防止缓存穿透)
if (!bloomFilter.mightExist(productId)) {
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("cache.get.time", "result", "bloom_filter_rejected"));
meterRegistry.counter("cache.reject", "reason", "bloom_filter").increment();
log.debug("Product ID rejected by bloom filter: {}", productId);
return null;
}
// 2. 检查本地缓存(防止缓存雪崩和减轻Redis压力)
try {
Optional<Product> cachedProduct = localCache.get(productId);
if (cachedProduct.isPresent()) {
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("cache.get.time", "result", "local_hit"));
meterRegistry.counter("cache.hit", "level", "local").increment();
log.debug("Product found in local cache: {}", productId);
return cachedProduct.get();
}
// 空值缓存,防止穿透
if (cachedProduct.isEmpty()) {
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("cache.get.time", "result", "negative_cached"));
meterRegistry.counter("cache.hit", "level", "negative").increment();
log.debug("Product not found (cached negative): {}", productId);
return null;
}
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
// 本地缓存异常,回退到直接查询远程缓存
log.warn("Local cache error: {}", e.getMessage());
meterRegistry.counter("cache.errors",
"level", "local",
"error", e.getClass().getSimpleName()).increment();
}
// 3. 检查远程缓存(Redis)
Product product = getFromRemoteCacheWithLock(productId);
// 4. 更新本地缓存
if (product != null || localCache.getIfPresent(productId) == null) {
localCache.put(productId, Optional.ofNullable(product));
}
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("cache.get.time",
"result", product != null ? "found" : "not_found"));
return product;
} catch (Exception e) {
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("cache.get.time", "result", "error"));
meterRegistry.counter("cache.errors",
"operation", "get",
"error", e.getClass().getSimpleName()).increment();
log.error("Error retrieving product: {}", productId, e);
throw new CacheException("Failed to retrieve product", e);
}
}
@Override
public boolean exists(String productId) {
try {
return getProduct(productId) != null;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Error checking product existence: {}", productId, e);
return false;
}
}
/**
* 从远程缓存获取产品
*/
private Product getFromRemoteCache(String productId) {
String redisKey = "product:" + productId;
try {
// 从Redis获取
Product product = remoteCacheService.get(redisKey, Product.class);
if (product != null) {
meterRegistry.counter("cache.hit", "level", "redis").increment();
log.debug("Product found in Redis: {}", productId);
return product;
}
meterRegistry.counter("cache.miss", "level", "redis").increment();
log.debug("Product not found in Redis: {}", productId);
return null;
} catch (Exception e) {
meterRegistry.counter("cache.errors",
"operation", "redis_get",
"error", e.getClass().getSimpleName()).increment();
log.error("Error getting product from Redis: {}", productId, e);
return null; // 发生错误时返回null,将在后续处理
}
}
/**
* 使用分布式锁从远程缓存或数据库获取产品
*/
private Product getFromRemoteCacheWithLock(String productId) {
Product product = getFromRemoteCache(productId);
if (product != null) {
return product;
}
// Redis未命中,使用分布式锁防止缓存击穿
String lockKey = "lock:product:" + productId;
String redisKey = "product:" + productId;
try {
// 尝试获取锁,但不阻塞太久
return lockService.executeWithLock(lockKey, 5000, () -> {
// 双重检查,可能已被其他线程加载
Product cachedProduct = getFromRemoteCache(productId);
if (cachedProduct != null) {
return cachedProduct;
}
// 从数据库查询
Product dbProduct = fallbackStrategy.getFromDatabase(productId);
// 更新缓存
if (dbProduct != null) {
// 使用随机过期时间防止缓存雪崩
long expireTime = 3600 + ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(600);
cacheWriter.putProduct(productId, dbProduct, expireTime);
} else {
// 缓存空值防止缓存穿透
cacheWriter.putProduct(productId, null, 300); // 空值缓存时间较短
}
return dbProduct;
});
} catch (LockAcquisitionException e) {
// 未获取到锁,等待短暂时间后重试一次Redis
log.debug("Failed to acquire lock for product: {}, retrying Redis", productId);
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
product = getFromRemoteCache(productId);
if (product != null) {
return product;
}
// 仍未命中,直接查询数据库但不更新缓存
meterRegistry.counter("cache.db.direct_access").increment();
log.debug("Accessing database directly for product: {}", productId);
return fallbackStrategy.getFromDatabase(productId);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
throw new CacheException("Interrupted while waiting to retry", ie);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 缓存写入服务实现
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class ProductCacheWriterImpl implements ProductCacheWriter {
private final CacheService remoteCacheService;
private final MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
public ProductCacheWriterImpl(CacheService remoteCacheService, MeterRegistry meterRegistry) {
this.remoteCacheService = remoteCacheService;
this.meterRegistry = meterRegistry;
}
@Override
public void putProduct(String productId, Product product, long expireTime) {
Timer.Sample sample = Timer.start(meterRegistry);
String redisKey = "product:" + productId;
try {
remoteCacheService.put(redisKey, product, expireTime);
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("cache.write.time", "operation", "put"));
log.debug("Cached product: {}, expireTime: {}s", productId, expireTime);
} catch (Exception e) {
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("cache.write.time", "operation", "put_error"));
log.error("Error caching product: {}", productId, e);
meterRegistry.counter("cache.errors",
"operation", "put",
"error", e.getClass().getSimpleName()).increment();
}
}
@Override
public void invalidateProduct(String productId) {
Timer.Sample sample = Timer.start(meterRegistry);
String redisKey = "product:" + productId;
try {
remoteCacheService.remove(redisKey);
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("cache.write.time", "operation", "invalidate"));
log.debug("Invalidated cache for product: {}", productId);
} catch (Exception e) {
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("cache.write.time", "operation", "invalidate_error"));
log.error("Error invalidating product cache: {}", productId, e);
meterRegistry.counter("cache.errors",
"operation", "invalidate",
"error", e.getClass().getSimpleName()).increment();
}
}
@Override
public void batchInvalidate(List<String> productIds) {
Timer.Sample sample = Timer.start(meterRegistry);
try {
for (String productId : productIds) {
try {
invalidateProduct(productId);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Error invalidating product: {}", productId, e);
// 继续处理其他产品
}
}
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("cache.write.time", "operation", "batch_invalidate"));
log.info("Batch invalidated {} products", productIds.size());
} catch (Exception e) {
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("cache.write.time", "operation", "batch_invalidate_error"));
log.error("Error during batch invalidation", e);
meterRegistry.counter("cache.errors",
"operation", "batch_invalidate",
"error", e.getClass().getSimpleName()).increment();
}
}
}
/**
* 缓存回源策略实现
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class DatabaseProductFallbackStrategy implements ProductFallbackStrategy {
private final ProductRepository productRepository;
private final MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
public DatabaseProductFallbackStrategy(ProductRepository productRepository, MeterRegistry meterRegistry) {
this.productRepository = productRepository;
this.meterRegistry = meterRegistry;
}
@Override
public Product getFromDatabase(String productId) {
Timer.Sample sample = Timer.start(meterRegistry);
try {
Product product = productRepository.findById(productId).orElse(null);
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("db.query.time",
"entity", "product",
"result", product != null ? "found" : "not_found"));
if (product != null) {
meterRegistry.counter("db.query.result", "entity", "product", "result", "found").increment();
log.debug("Product found in database: {}", productId);
} else {
meterRegistry.counter("db.query.result", "entity", "product", "result", "not_found").increment();
log.debug("Product not found in database: {}", productId);
}
return product;
} catch (Exception e) {
sample.stop(meterRegistry.timer("db.query.time",
"entity", "product",
"result", "error"));
meterRegistry.counter("db.query.errors",
"entity", "product",
"error", e.getClass().getSimpleName()).increment();
log.error("Error querying product from database: {}", productId, e);
throw new DatabaseAccessException("Failed to query product from database", e);
}
}
}6. 单元测试示例
关键业务逻辑测试示例:
java
@ExtendWith(MockitoExtension.class)
class StockServiceTest {
@Mock
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Mock
private DistributedLockService lockService;
@Mock
private MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
@Mock
private Timer timer;
@Mock
private Counter counter;
@InjectMocks
private StockService stockService;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
when(meterRegistry.timer(anyString(), any(String[].class))).thenReturn(timer);
when(meterRegistry.counter(anyString(), any(String[].class))).thenReturn(counter);
}
@Test
void decreaseStock_SufficientStock_ReturnsTrue() {
// Arrange
Long productId = 123L;
int quantity = 2;
when(lockService.executeWithLock(anyString(), anyLong(), any()))
.thenAnswer(invocation -> {
Supplier<?> task = invocation.getArgument(2);
return task.get();
});
when(jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(
eq("SELECT stock FROM products WHERE id = ? FOR UPDATE"),
eq(Integer.class),
eq(productId)
)).thenReturn(10);
when(jdbcTemplate.update(
eq("UPDATE products SET stock = stock - ? WHERE id = ? AND stock >= ?"),
eq(quantity),
eq(productId),
eq(quantity)
)).thenReturn(1);
// Act
boolean result = stockService.decreaseStock(productId, quantity);
// Assert
assertTrue(result);
verify(jdbcTemplate).queryForObject(anyString(), eq(Integer.class), eq(productId));
verify(jdbcTemplate).update(anyString(), eq(quantity), eq(productId), eq(quantity));
verify(counter).increment();
}
@Test
void decreaseStock_InsufficientStock_ReturnsFalse() {
// Arrange
Long productId = 123L;
int quantity = 5;
when(lockService.executeWithLock(anyString(), anyLong(), any()))
.thenAnswer(invocation -> {
Supplier<?> task = invocation.getArgument(2);
return task.get();
});
when(jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(
eq("SELECT stock FROM products WHERE id = ? FOR UPDATE"),
eq(Integer.class),
eq(productId)
)).thenReturn(3); // Less than requested quantity
// Act
boolean result = stockService.decreaseStock(productId, quantity);
// Assert
assertFalse(result);
verify(jdbcTemplate).queryForObject(anyString(), eq(Integer.class), eq(productId));
verify(jdbcTemplate, never()).update(anyString(), anyInt(), anyLong(), anyInt());
verify(counter).increment();
}
@Test
void decreaseStock_LockAcquisitionFailure_ThrowsException() {
// Arrange
Long productId = 123L;
int quantity = 2;
when(lockService.executeWithLock(anyString(), anyLong(), any()))
.thenThrow(new LockAcquisitionException("Failed to acquire lock"));
// Act & Assert
Exception exception = assertThrows(LockAcquisitionException.class,
() -> stockService.decreaseStock(productId, quantity));
assertEquals("Failed to acquire lock", exception.getMessage());
verify(jdbcTemplate, never()).queryForObject(anyString(), any(), any());
verify(jdbcTemplate, never()).update(anyString(), any(), any(), any());
verify(counter).increment();
}
}
@ExtendWith(MockitoExtension.class)
class MultiLevelProductCacheReaderTest {
@Mock
private CacheService remoteCacheService;
@Mock
private BloomFilterInitializer bloomFilter;
@Mock
private ProductFallbackStrategy fallbackStrategy;
@Mock
private DistributedLockService lockService;
@Mock
private ProductCacheWriter cacheWriter;
@Mock
private MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
@Mock
private Timer timer;
@Mock
private Timer.Sample sample;
@Mock
private Counter counter;
private MultiLevelProductCacheReader cacheReader;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
when(meterRegistry.timer(anyString(), any(String[].class))).thenReturn(timer);
when(meterRegistry.counter(anyString(), any(String[].class))).thenReturn(counter);
when(Timer.start(meterRegistry)).thenReturn(sample);
cacheReader = new MultiLevelProductCacheReader(
remoteCacheService, bloomFilter, fallbackStrategy,
lockService, cacheWriter, meterRegistry);
}
@Test
void getProduct_BloomFilterRejects_ReturnsNull() {
// Arrange
String productId = "test123";
when(bloomFilter.mightExist(productId)).thenReturn(false);
// Act
Product result = cacheReader.getProduct(productId);
// Assert
assertNull(result);
verify(bloomFilter).mightExist(productId);
verify(remoteCacheService, never()).get(anyString(), any());
verify(fallbackStrategy, never()).getFromDatabase(anyString());
verify(counter).increment();
}
@Test
void getProduct_RemoteCacheHit_ReturnsProduct() {
// Arrange
String productId = "test123";
Product product = new Product(productId, "Test Product", 100.0);
when(bloomFilter.mightExist(productId)).thenReturn(true);
when(remoteCacheService.get("product:" + productId, Product.class)).thenReturn(product);
// Act
Product result = cacheReader.getProduct(productId);
// Assert
assertNotNull(result);
assertEquals(productId, result.getId());
verify(bloomFilter).mightExist(productId);
verify(remoteCacheService).get("product:" + productId, Product.class);
verify(fallbackStrategy, never()).getFromDatabase(anyString());
verify(counter).increment();
}
@Test
void getProduct_DatabaseFallback_ReturnsAndCachesProduct() {
// Arrange
String productId = "test123";
Product product = new Product(productId, "Test Product", 100.0);
when(bloomFilter.mightExist(productId)).thenReturn(true);
when(remoteCacheService.get("product:" + productId, Product.class)).thenReturn(null);
when(fallbackStrategy.getFromDatabase(productId)).thenReturn(product);
when(lockService.executeWithLock(anyString(), anyLong(), any())).thenAnswer(inv -> {
Supplier<?> task = inv.getArgument(2);
return task.get();
});
// Act
Product result = cacheReader.getProduct(productId);
// Assert
assertNotNull(result);
assertEquals(productId, result.getId());
verify(bloomFilter).mightExist(productId);
verify(remoteCacheService).get("product:" + productId, Product.class);
verify(fallbackStrategy).getFromDatabase(productId);
verify(cacheWriter).putProduct(eq(productId), eq(product), anyLong());
verify(counter, atLeastOnce()).increment();
}
@Test
void getProduct_LockFailure_DirectDatabaseAccess() {
// Arrange
String productId = "test123";
Product product = new Product(productId, "Test Product", 100.0);
when(bloomFilter.mightExist(productId)).thenReturn(true);
when(remoteCacheService.get("product:" + productId, Product.class)).thenReturn(null);
when(fallbackStrategy.getFromDatabase(productId)).thenReturn(product);
when(lockService.executeWithLock(anyString(), anyLong(), any()))
.thenThrow(new LockAcquisitionException("Failed to acquire lock"));
// Act
Product result = cacheReader.getProduct(productId);
// Assert
assertNotNull(result);
assertEquals(productId, result.getId());
verify(bloomFilter).mightExist(productId);
verify(remoteCacheService, times(2)).get("product:" + productId, Product.class);
verify(fallbackStrategy).getFromDatabase(productId);
verify(cacheWriter, never()).putProduct(anyString(), any(), anyLong());
verify(counter, atLeastOnce()).increment();
}
}7. 方案决策
| 需求特征 | 写入量级 | 一致性要求 | 查询复杂度 | 成本敏感度 | 推荐方案 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 事务性业务数据 | 中等(<1000 QPS) | 强一致 | 复杂 | 中等 | MySQL 参数优化+批量写入 |
| 事务性业务数据 | 高(1000-5000 QPS) | 强一致 | 复杂 | 低 | MySQL 分库分表+读写分离 |
| 用户行为数据 | 非常高(5000+ QPS) | 最终一致 | 中等 | 中等 | 消息队列+批量写入 |
| 埋点/日志数据 | 极高(10000+ QPS) | 弱一致 | 简单 | 高 | Redis 缓冲+定期同步 |
| 时序/监控数据 | 极高(10000+ QPS) | 弱一致 | 聚合分析 | 中等 | 专用时序数据库 |
| 文档/配置数据 | 中等 | 最终一致 | 文档查询 | 中等 | MongoDB |
8. 渐进式迁移策略
从传统 MySQL 架构向高并发架构迁移的步骤:
-
评估和基准测试:
- 识别性能瓶颈和容量需求
- 建立性能基准和目标
- 制定监控指标
-
MySQL 优化:
- 实施参数调优
- 优化索引和查询
- 引入批量操作和连接池优化
-
读写分离:
- 配置主从复制
- 实现读写分离路由
- 处理主从延迟和一致性
-
缓存引入:
- 增加应用级缓存
- 实施 Redis 缓存
- 建立缓存更新策略
-
消息队列集成:
- 部署消息队列系统
- 实现异步写入
- 建立错误处理和重试机制
-
分库分表:
- 设计分片策略
- 实施数据迁移
- 引入分库分表中间件
-
完整监控:
- 监控各层性能指标
- 建立告警系统
- 实施健康检查
每个阶段都应包含以下步骤:
- 阶段前评估和规划
- 开发和测试
- 灰度发布
- 全量发布
- 效果评估
9. 总结
| 方案 | 适用场景 | 优势 | 劣势 | 实施复杂度 | 成本 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MySQL 参数优化 | 中等写入量 | 无需架构变更,实施简单 | 优化空间有限 | 低 | 低 |
| 批量写入 | 可批处理场景 | 显著提升写入效率 | 实时性降低 | 低 | 低 |
| 读写分离 | 读多写少场景 | 减轻主库压力 | 主库仍可能成为瓶颈 | 中 | 中 |
| 消息队列+异步写入 | 高峰写入场景 | 削峰填谷,提高系统稳定性 | 增加系统复杂度 | 中 | 中 |
| Redis 缓冲区 | 高频写入且需快速读取 | 极高写入性能,支持丰富数据结构 | 增加同步复杂度,内存成本高 | 中 | 中高 |
| MySQL 分库分表 | 大数据量强事务场景 | 保留 MySQL 特性,支持水平扩展 | 跨分片操作复杂,运维成本高 | 高 | 高 |
| NoSQL 存储 | 特定数据模型场景 | 为特定数据模型优化的性能 | SQL 能力弱,生态不如 MySQL 成熟 | 中高 | 中高 |
高并发写入场景下,MySQL 并非不可用,而是需要根据具体业务场景选择合适的优化策略或替代方案。通过合理的系统设计、技术选型和监控保障,可以构建出高性能、高可靠的数据处理系统。