🚀 前端面试系列-常用对象处理
"数据是现代前端应用的血液,而对象处理就是让这些血液流动的心脏"

在这个数据驱动的前端时代,你是否曾经为了处理复杂的API响应而写出冗长的代码?是否因为深层对象访问导致的Cannot read property of undefined错误而头疼?如果你的答案是肯定的,那么这篇文章将彻底改变你的开发体验。
前言
部分内容来源,前端常用工具库及高频面试题
项目地址: github.com/niexq/codin...
🎯 为什么前端开发者需要掌握对象处理?
在现代前端开发中,我们每天都在与各种数据结构打交道:
- API响应处理:将后端返回的复杂数据结构转换为前端可用的格式
- 状态管理:在Redux、Vuex等状态管理库中处理复杂的状态更新
- 表单数据处理:处理用户输入的表单数据,进行验证和转换
- 配置对象管理:处理组件配置、主题配置等各种配置对象
- 数据可视化:将原始数据转换为图表库所需的数据格式

如果没有合适的工具,这些任务会让我们的代码变得冗长、易错、难以维护。而Lodash的对象处理方法,就是为了解决这些痛点而生的。
💡 Lodash对象方法的核心价值
🛡️ 安全性 - 告别运行时错误
javascript
// 传统方式 - 危险!
const userName = response.data.user.profile.name; // 💥 可能抛出错误
// Lodash方式 - 安全!
const userName = get(response, 'data.user.profile.name', '未知用户'); // ✅ 永不出错
⚡ 效率 - 一行代码解决复杂问题
javascript
// 传统方式 - 冗长
const filteredData = {};
Object.keys(apiResponse).forEach(key => {
if (['id', 'name', 'email'].includes(key)) {
filteredData[key] = apiResponse[key];
}
});
// Lodash方式 - 简洁
const filteredData = pick(apiResponse, ['id', 'name', 'email']);🔄 链式操作 - 优雅的数据处理流
javascript
const processedData = chain(apiResponse)
.pick(['users', 'posts', 'comments'])
.mapValues(arr => arr.slice(0, 10))
.mapKeys((value, key) => `${key}Preview`)
.value();
🚀核心方法实现
assign
合并对象的属性,后面的对象的属性会覆盖前面的对象
js
const assign = (...objs) =>
objs.reduce((result, obj) => Object.assign(result, obj), {});
function Foo() {
this.a = 1;
}
function Bar() {
this.c = 3;
}
Foo.prototype.b = 2;
Bar.prototype.d = 4;
assign({ a: 0 }, new Foo(), new Bar());
// => { 'a': 1, 'c': 3 }思路:使用 reduce 方法遍历每个对象,将属性合并到目标对象中。
defaults
对指定对象进行封装,将默认值合并进去
js
const defaults = (obj, defaultProps) => ({ ...defaultProps, ...obj });
defaults({ a: 1 }, { b: 2 }, { a: 3 });
// => { 'a': 1, 'b': 2 }思路:使用 Object.assign 方法将默认值对象合并到目标对象上,如果目标对象中已经存在相同属性,则不会被覆盖。
defaultsDeep
与 defaults 类似,但是支持嵌套对象
js
const defaultsDeep = (obj, defaultProps) => {
const mergeDeep = (target, source) => {
Object.keys(source).forEach(key => {
const targetValue = target[key];
const sourceValue = source[key];
if (typeof targetValue === 'object' && typeof sourceValue === 'object') {
target[key] = mergeDeep(targetValue, sourceValue);
} else {
target[key] = targetValue === undefined ? sourceValue : targetValue;
}
});
return target;
};
return mergeDeep({ ...defaultProps }, obj);
};
defaultsDeep({ a: { b: 2 } }, { a: { b: 1, c: 3 } });
// => { 'a': { 'b': 2, 'c': 3 } }思路:使用 Object.assign 和 typeof 方法进行递归遍历,将嵌套的对象也合并进去。
findKey
遍历对象,返回第一个符合条件的键名
js
const findKey = (obj, predicate) => {
for (const key in obj) {
if (predicate(obj[key], key, obj)) {
return key;
}
}
};
const users = {
barney: { age: 36, active: true },
fred: { age: 40, active: false },
pebbles: { age: 1, active: true },
};
findKey(users, o => o.age < 40);
// => 'barney' (iteration order is not guaranteed)
// The `matches` iteratee shorthand.
findKey(users, { age: 1, active: true });
// => 'pebbles'
// The `matchesProperty` iteratee shorthand.
findKey(users, ['active', false]);
// => 'fred'
// The `property` iteratee shorthand.
findKey(users, 'active');
// => 'barney'思路:使用 for...in 循环遍历对象,对每个属性调用指定的函数进行判断,如果返回真值则返回当前属性名。
findLastKey
与 findKey 类似,但是从对象的末尾开始
js
const findLastKey = (obj, predicate) =>
findKey(obj, predicate, Object.keys(obj).reverse());
const users = {
barney: { age: 36, active: true },
fred: { age: 40, active: false },
pebbles: { age: 1, active: true },
};
findLastKey(users, o => o.age < 40);
// => returns 'pebbles' assuming `findKey` returns 'barney'
// The `matches` iteratee shorthand.
findLastKey(users, { age: 36, active: true });
// => 'barney'
// The `matchesProperty` iteratee shorthand.
findLastKey(users, ['active', false]);
// => 'fred'
// The `property` iteratee shorthand.
findLastKey(users, 'active');
// => 'pebbles'思路:使用 Object.keys 方法获取对象的键名数组,然后使用 reverse 方法翻转数组,再使用 findKey 函数进行查找。
forIn
遍历对象,对每个属性调用指定的函数
js
const forIn = (obj, iteratee) => {
for (const key in obj) {
if (iteratee(obj[key], key, obj) === false) {
break;
}
}
return obj;
};
function Foo() {
this.a = 1;
this.b = 2;
}
Foo.prototype.c = 3;
forIn(new Foo(), (value, key) => {
console.log(key);
});
// => Logs 'a', 'b', then 'c' (无法保证遍历的顺序)。思路:使用 for...in 循环遍历对象,对每个属性调用指定的函数。
forInRight
与 forIn 类似,但是从对象的末尾开始遍历
js
const forInRight = (obj, fn) => {
for (const key in obj) {
if (obj.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
fn(obj[key], key, obj);
}
}
};
function Foo() {
this.a = 1;
this.b = 2;
}
Foo.prototype.c = 3;
forInRight(new Foo(), (value, key) => {
console.log(key);
});
// => 输出 'c', 'b', 然后 'a', `forIn` 会输出 'a', 'b', 然后 'c'。思路:使用 for...in 循环倒序遍历对象的所有属性,并对每个属性调用指定的函数。
forOwn
遍历对象自身的可枚举属性,对每个属性调用指定的函数
js
const forOwn = (obj, func) => {
for (const key in obj) {
if (obj.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
func(obj[key], key, obj);
}
}
};
function Foo() {
this.a = 1;
this.b = 2;
}
Foo.prototype.c = 3;
forOwn(new Foo(), (value, key) => {
console.log(key);
});
// => 输出 'a' 然后 'b' (无法保证遍历的顺序)。思路:遍历对象自身的可枚举属性,对每个属性调用指定的函数,使用 for-in 循环遍历对象的所有属性,判断属性是否是自身的可枚举属性,如果是则调用指定的函数。
forOwnRight
与 forOwn 类似,但是从对象的末尾开始遍历
js
const forOwnRight = (obj, func) => {
const keys = Object.keys(obj).reverse();
for (let i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
func(obj[keys[i]], keys[i], obj);
}
};
function Foo() {
this.a = 1;
this.b = 2;
}
Foo.prototype.c = 3;
forOwnRight(new Foo(), (value, key) => {
console.log(key);
});
// => 输出 'b' 然后 'a', `forOwn` 会输出 'a' 然后 'b'思路:与 forOwn 类似,但是从对象的末尾开始遍历,可以将对象的键数组进行 reverse 操作后再遍历。
functions
返回指定对象上的所有函数名
js
const functions = obj =>
Object.keys(obj).filter(key => typeof obj[key] === 'function');
function Foo() {
this.a = constant('a');
this.b = constant('b');
}
Foo.prototype.c = constant('c');
functions(new Foo());
// => ['a', 'b']思路:返回指定对象上的所有函数名,使用 Object.keys()获取对象的所有属性名,再使用 filter()方法筛选出属性值的类型为 function 的属性名。
get
获取对象上的属性,支持使用点和方括号的方式指定属性路径
js
const get = (obj, path) =>
path.split(/[.[\]]/).reduce((acc, cur) => (cur ? acc[cur] : acc), obj);
const object = { a: [{ b: { c: 3 } }] };
get(object, 'a[0].b.c');
// => 3
get(object, ['a', '0', 'b', 'c']);
// => 3
get(object, 'a.b.c', 'default');
// => 'default'思路:使用 reduce 函数将属性路径分割后进行遍历并获取对应属性值,支持使用点和方括号的方式指定属性路径
has
判断对象上是否有指定属性
js
const has = (obj, key) => key in obj;
const object = { a: { b: 2 } };
const other = create({ a: create({ b: 2 }) });
has(object, 'a');
// => true
has(object, 'a.b');
// => true
has(object, ['a', 'b']);
// => true
has(other, 'a');
// => false思路:使用 in 操作符判断对象上是否有指定属性
hasIn
判断对象上是否有指定路径的属性
js
const hasIn = (obj, path) => get(obj, path) !== undefined;
const object = create({ a: create({ b: 2 }) });
hasIn(object, 'a');
// => true
hasIn(object, 'a.b');
// => true
hasIn(object, ['a', 'b']);
// => true
hasIn(object, 'b');
// => false思路:使用 get 函数获取属性值,如果返回 undefined 则表示不存在指定路径属性
invert
对指定对象的属性和值进行反转
js
const invert = obj =>
Object.entries(obj).reduce((acc, [key, val]) => {
acc[val] = key;
return acc;
}, {});
const object = { a: 1, b: 2, c: 1 };
invert(object);
// => { '1': 'c', '2': 'b' }思路:遍历对象并将属性值作为键名,属性名作为键值生成新对象
invertBy
与 invert 类似,但是支持指定反转后值的集合
js
const invertBy = (obj, fn) =>
Object.entries(obj).reduce((acc, [key, val]) => {
const invertedKey = fn(val);
if (!acc[invertedKey]) {
acc[invertedKey] = [];
}
acc[invertedKey].push(key);
return acc;
}, {});
const object = { a: 1, b: 2, c: 1 };
invertBy(object);
// => { '1': ['a', 'c'], '2': ['b'] }
invertBy(object, value => `group${value}`);
// => { 'group1': ['a', 'c'], 'group2': ['b'] }思路:遍历对象并将属性值经过回调函数处理后作为键名,属性名作为键值生成新对象
invoke
对指定对象上的方法进行调用
js
const invoke = (obj, methodName, ...args) =>
Object.values(obj).forEach(func =>
typeof func[methodName] === 'function' ? func[methodName](...args) : null
);
const object = { a: [{ b: { c: [1, 2, 3, 4] } }] };
invoke(object, 'a[0].b.c.slice', 1, 3);
// => [2, 3]思路:遍历对象并调用指定方法名的方法
keys
返回对象上的所有可枚举属性名
js
const keys = obj => Object.keys(obj);
function Foo() {
this.a = 1;
this.b = 2;
}
Foo.prototype.c = 3;
keys(new Foo());
// => ['a', 'b'] (iteration order is not guaranteed)
keys('hi');
// => ['0', '1']思路:使用 Object.keys 函数返回对象上的所有可枚举属性名
keysIn
返回对象上的所有属性名,包括不可枚举属性
js
const keysIn = obj => {
const result = [];
for (const key in obj) {
result.push(key);
}
return result;
};
function Foo() {
this.a = 1;
this.b = 2;
}
Foo.prototype.c = 3;
keysIn(new Foo());
// => ['a', 'b', 'c'] (iteration order is not guaranteed)思路:遍历对象的所有属性名,将其添加到一个数组中,并返回该数组。
mapKeys
遍历对象上的每个属性,返回一个新对象,其中每个属性的名称由指定的函数计算得出
js
const mapKeys = (obj, fn) =>
Object.keys(obj).reduce((result, key) => {
result[fn(obj[key], key, obj)] = obj[key];
return result;
}, {});
mapKeys({ a: 1, b: 2 }, (value, key) => key + value);
// => { 'a1': 1, 'b2': 2 }思路:使用 reduce 遍历对象的属性名,将新的属性名通过指定函数计算得出,并与原属性值一起添加到一个新的对象中,并返回该新对象。
mapValues
遍历对象上的每个属性,返回一个新对象,其中每个属性的值由指定的函数计算得出
js
const mapValues = (obj, fn) =>
Object.keys(obj).reduce((result, key) => {
result[key] = fn(obj[key], key, obj);
return result;
}, {});
const users = {
fred: { user: 'fred', age: 40 },
pebbles: { user: 'pebbles', age: 1 },
};
mapValues(users, o => o.age);
// => { 'fred': 40, 'pebbles': 1 } (iteration order is not guaranteed)
// The `property` iteratee shorthand.
mapValues(users, 'age');
// => { 'fred': 40, 'pebbles': 1 } (iteration order is not guaranteed)思路:使用 reduce 遍历对象的属性名,通过指定函数计算每个属性值,并将计算后的新属性值添加到一个新的对象中,并返回该新对象。
merge
合并对象和源对象的属性,并返回合并后的对象
js
const merge = (obj, src) => ({ ...obj, ...src });
const object = {
a: [{ b: 2 }, { d: 4 }],
};
const other = {
a: [{ c: 3 }, { e: 5 }],
};
merge(object, other);
// => { 'a': [{ 'b': 2, 'c': 3 }, { 'd': 4, 'e': 5 }] }思路:使用 Object.assign 将源对象的属性值合并到目标对象上,并返回合并后的新对象。
mergeWith
与 merge 类似,但是指定合并函数,用于处理冲突的属性值
js
const mergeWith = (obj, src, customizer) => {
const result = { ...obj, ...src };
Object.keys(result).forEach(key => {
result[key] = customizer(obj[key], src[key], key, obj, src);
});
return result;
};
function customizer(objValue, srcValue) {
if (isArray(objValue)) {
return objValue.concat(srcValue);
}
}
const object = { a: [1], b: [2] };
const other = { a: [3], b: [4] };
mergeWith(object, other, customizer);
// => { 'a': [1, 3], 'b': [2, 4] }思路:使用 Object.assign 将源对象的属性值合并到目标对象上,并遍历合并后的新对象,通过指定函数自定义处理冲突的属性值,并返回处理后的新对象。
omit
返回一个新对象,其中省略了指定属性的属性值
js
const omit = (obj, props) => {
const newObj = { ...obj };
props.forEach(prop => {
delete newObj[prop];
});
return newObj;
};
const object = { a: 1, b: '2', c: 3 };
omit(object, ['a', 'c']);
// => { 'b': '2' }思路:使用 Object.assign 将原对象的属性值复制到一个新对象上,遍历指定省略的属性,将其从新对象中删除,并返回该新对象。
omitBy
与 omit 类似,但是根据指定函数判断是否省略属性
js
const omitBy = (obj, predicate) => {
const newObj = { ...obj };
Object.keys(newObj).forEach(key => {
if (predicate(newObj[key])) {
delete newObj[key];
}
});
return newObj;
};
const object = { a: 1, b: '2', c: 3 };
omitBy(object, isNumber);
// => { 'b': '2' }思路:使用 Object.assign 将原对象的属性值复制到一个新对象上,遍历新对象的每个属性,根据指定函数判断是否需要删除该属性,并返回处理后的新对象。
pick
返回一个新对象,其中只包含指定属性的属性值
js
const pick = (obj, props) =>
props.reduce((result, prop) => {
if (prop in obj) {
result[prop] = obj[prop];
}
return result;
}, {});
const object = { a: 1, b: '2', c: 3 };
pick(object, ['a', 'c']);
// => { 'a': 1, 'c': 3 }思路:使用 reduce 遍历指定需要选取的属性,将其添加到一个新的对象中,并返回该新对象。
pickBy
与 pick 类似,但是根据指定函数判断是否保留属性
js
const pickBy = (obj, fn) =>
Object.keys(obj).reduce((acc, key) => {
if (fn(obj[key])) acc[key] = obj[key];
return acc;
}, {});
const object = { a: 1, b: '2', c: 3 };
pickBy(object, isNumber);
// => { 'a': 1, 'c': 3 }思路:使用 Object.keys 和 Array.prototype.reduce 方法,返回一个新的对象。
result
获取对象上指定路径的值,并根据情况进行函数调用
js
const result = (obj, path, defaultValue) =>
path.split('.').reduce((acc, cur) => (acc ? acc[cur] : undefined), obj) ??
defaultValue;
const object = { a: [{ b: { c1: 3, c2: constant(4) } }] };
result(object, 'a[0].b.c1');
// => 3
result(object, 'a[0].b.c2');
// => 4
result(object, 'a[0].b.c3', 'default');
// => 'default'
result(object, 'a[0].b.c3', constant('default'));
// => 'default'思路:使用 Array.prototype.reduce 方法和 typeof 运算符,支持获取多层路径的值。
set
设置对象上指定路径的属性值
js
const set = (obj, path, value) => {
const keys = path.split(/[,[\].]+?/);
const lastKeyIndex = keys.length - 1;
keys.reduce((acc, key, index) => {
if (index === lastKeyIndex) acc[key] = value;
else acc[key] ?? (acc[key] = {});
return acc[key];
}, obj);
return obj;
};
const object = { a: [{ b: { c: 3 } }] };
set(object, 'a[0].b.c', 4);
console.log(object.a[0].b.c);
// => 4
set(object, ['x', '0', 'y', 'z'], 5);
console.log(object.x[0].y.z);
// => 5思路:使用 Array.prototype.reduce 方法,支持设置多层路径的值。
setWith
与 set 类似,但是指定自定义函数用于设置属性值
js
const setWith = (obj, path, value, customizer) => {
const keys = path.split(/[,[\].]+?/);
const lastKeyIndex = keys.length - 1;
keys.reduce((acc, key, index) => {
const newValue = index === lastKeyIndex ? customizer(acc[key], value) : {};
acc[key] = typeof acc[key] === 'object' ? acc[key] : newValue;
return acc[key];
}, obj);
return obj;
};
const object = {};
setWith(object, '[0][1]', 'a', Object);
// => { '0': { '1': 'a' } }思路:使用 Array.prototype.reduce 方法,支持设置多层路径的值。
toPairs
将对象转化为键值对数组
js
const toPairs = obj => Object.entries(obj);
function Foo() {
this.a = 1;
this.b = 2;
}
Foo.prototype.c = 3;
toPairs(new Foo());
// => [['a', 1], ['b', 2]] (iteration order is not guaranteed)思路:使用 Object.entries 方法,返回一个由键值对组成的数组。
toPairsIn
将对象转化为键值对数组,包括不可枚举属性
js
const toPairsIn = obj => {
const result = [];
for (const key in obj) {
result.push([key, obj[key]]);
}
return result;
};
function Foo() {
this.a = 1;
this.b = 2;
}
Foo.prototype.c = 3;
toPairsIn(new Foo());
// => [['a', 1], ['b', 2], ['c', 3]] (iteration order is not guaranteed)思路:使用 Object.getOwnPropertyNames 方法,返回一个由键值对组成的数组。
transform
对指定对象进行封装,指定转换函数,处理对象上的属性
js
const transform = (obj, fn, acc) =>
Object.entries(obj).reduce(
(result, [key, value]) => fn(result, value, key, obj),
acc
);
transform(
[2, 3, 4],
(result, n) => {
result.push((n *= n));
return n % 2 == 0;
},
[]
);
// => [4, 9]
transform(
{ a: 1, b: 2, c: 1 },
(result, value, key) => {
(result[value] || (result[value] = [])).push(key);
},
{}
);
// => { '1': ['a', 'c'], '2': ['b'] }思路:使用 Object.entries 方法和 Array.prototype.reduce 方法,返回一个由转换后的对象组成的数组。
unset
删除对象上指定路径的属性值
js
const unset = (obj, path) => {
const keys = Array.isArray(path) ? path : path.split(/[,[\].]+?/);
const lastKeyIndex = keys.length - 1;
keys.reduce((acc, key, index) => {
if (index === lastKeyIndex) {
delete acc[key];
}
return acc[key];
}, obj);
return obj;
};
const object = { a: [{ b: { c: 7 } }] };
unset(object, 'a[0].b.c');
// => true
console.log(object);
// => { 'a': [{ 'b': {} }] }
unset(object, ['a', '0', 'b', 'c']);
// => true思路:使用 reduce 方法遍历路径数组,在最后一个键时删除对应属性,返回修改后的对象。
update
获取对象上指定路径的值,并根据情况进行函数调用,最后将值设置回去
js
const update = (obj, path, updater) => {
const keys = Array.isArray(path) ? path : path.split(/[,[\].]+?/);
const lastKeyIndex = keys.length - 1;
keys.reduce((acc, key, index) => {
if (index === lastKeyIndex) {
acc[key] = updater(acc[key]);
} else {
acc[key] = acc[key] || {};
}
return acc[key];
}, obj);
return obj;
};
const object = { a: [{ b: { c: 3 } }] };
update(object, 'a[0].b.c', n => n * n);
console.log(object.a[0].b.c);
// => 9
update(object, 'x[0].y.z', n => (n || 0) + 1);
console.log(object.x[0].y.z);
// => 1思路:使用 reduce 方法遍历路径,在最后一个键时应用更新函数,如果路径不存在则创建。
updateWith
与 update 类似,但是指定自定义函数用于更新属性值
js
const updateWith = (obj, path, updater, customizer) => {
const keys = Array.isArray(path) ? path : path.split(/[,[\].]+?/);
const lastKeyIndex = keys.length - 1;
keys.reduce((acc, key, index) => {
if (index === lastKeyIndex) {
acc[key] = updater(acc[key]);
} else {
acc[key] = acc[key] || customizer(acc[key], key, acc);
}
return acc[key];
}, obj);
return obj;
};
const object = {};
updateWith(object, '[0][1]', constant('a'), Object);
// => { '0': { '1': 'a' } }思路:与 update 类似,但使用自定义函数来创建中间对象。
values
返回对象上的所有可枚举属性值
js
const values = obj => Object.values(obj);
function Foo() {
this.a = 1;
this.b = 2;
}
Foo.prototype.c = 3;
values(new Foo());
// => [1, 2] (iteration order is not guaranteed)
values('hi');
// => ['h', 'i']思路:使用 Object.values 方法返回对象的所有可枚举属性值。
valuesIn
返回对象上的所有属性值,包括不可枚举属性值
js
const valuesIn = obj => {
const result = [];
for (const key in obj) {
result.push(obj[key]);
}
return result;
};
function Foo() {
this.a = 1;
this.b = 2;
}
Foo.prototype.c = 3;
valuesIn(new Foo());
// => [1, 2, 3] (iteration order is not guaranteed)思路:使用 for...in 循环遍历对象的所有属性(包括继承的),将属性值添加到结果数组中。
🏗️ 核心方法详解
📦 基础操作:构建你的数据基础
assign - 智能对象合并
使用场景:合并配置对象、扩展组件props
javascript
// React组件中的实际应用
const defaultProps = {
theme: 'light',
size: 'medium',
disabled: false
};
const MyComponent = (userProps) => {
const props = assign({}, defaultProps, userProps);
return <Button {...props} />;
};
// 实现原理
const assign = (...objs) => objs.reduce((result, obj) => Object.assign(result, obj), {});defaults - 优雅的默认值设置
使用场景:API参数处理、组件配置
javascript
// API请求参数处理
const makeApiRequest = (params = {}) => {
const finalParams = defaults(params, {
page: 1,
limit: 20,
sortBy: 'createdAt',
order: 'desc'
});
return fetch(`/api/data?${new URLSearchParams(finalParams)}`);
};
// 实现原理
const defaults = (obj, defaultProps) => ({ ...defaultProps, ...obj });defaultsDeep - 深层配置合并
使用场景:复杂配置对象、主题系统
javascript
// 主题系统配置
const themeConfig = defaultsDeep(userTheme, {
colors: {
primary: '#007bff',
secondary: '#6c757d',
success: '#28a745'
},
typography: {
fontFamily: 'Arial, sans-serif',
fontSize: {
small: '12px',
medium: '14px',
large: '16px'
}
}
});🔍 查找与检测:精准定位你的数据
get - 安全的深层访问
真实场景:处理复杂的API响应
javascript
// 电商网站商品信息处理
const ProductCard = ({ product }) => {
const productName = get(product, 'details.name', '商品名称未知');
const price = get(product, 'pricing.current.amount', 0);
const imageUrl = get(product, 'images[0].url', '/default-image.jpg');
const rating = get(product, 'reviews.average', 0);
return (
<div className="product-card">
<img src={imageUrl} alt={productName} />
<h3>{productName}</h3>
<p className="price">¥{price}</p>
<div className="rating">⭐ {rating}</div>
</div>
);
};
// 实现原理
const get = (obj, path, defaultValue) =>
path.split(/[.[\]]/).reduce((acc, cur) =>
(cur && acc && acc[cur] !== undefined) ? acc[cur] : undefined, obj
) ?? defaultValue;findKey - 智能键查找
使用场景:用户权限管理、动态配置
javascript
// 用户权限检查
const permissions = {
admin: { level: 10, canDelete: true },
editor: { level: 5, canEdit: true },
viewer: { level: 1, canView: true }
};
const getUserRole = (userLevel) => {
return findKey(permissions, perm => perm.level === userLevel);
};
// Vue.js组件中的动态样式
const getThemeClass = (currentTheme) => {
const themes = {
light: { bg: 'white', text: 'black' },
dark: { bg: 'black', text: 'white' },
blue: { bg: 'blue', text: 'white' }
};
return findKey(themes, theme => theme.bg === currentTheme);
};has - 智能属性检测
实际应用:条件渲染、功能检测
javascript
// React组件中的条件渲染
const UserProfile = ({ user }) => {
return (
<div>
<h2>{user.name}</h2>
{has(user, 'avatar') && <img src={user.avatar} alt="头像" />}
{has(user, 'bio') && <p>{user.bio}</p>}
{has(user, 'social.twitter') && (
<a href={user.social.twitter}>Twitter</a>
)}
</div>
);
};🔄 转换与映射:让数据符合你的需求
mapValues - 批量值转换
实际应用:数据格式化、单位转换
javascript
// 将API返回的时间戳转换为可读格式
const formatUserData = (users) => {
return mapValues(users, user => ({
...user,
createdAt: new Date(user.createdAt).toLocaleDateString(),
lastLogin: user.lastLogin ? new Date(user.lastLogin).toLocaleDateString() : '从未登录',
avatar: user.avatar || '/default-avatar.png'
}));
};
// Vue.js中的计算属性优化
const processFormData = (formData) => {
return mapValues(formData, (value, key) => {
if (key.includes('Date')) {
return new Date(value).toISOString();
}
if (key.includes('Price')) {
return parseFloat(value).toFixed(2);
}
return String(value).trim();
});
};pick & omit - 精确的数据筛选
场景:表单数据处理、API数据清洗
javascript
// 表单提交前的数据清理
const submitUserForm = (formData) => {
// 只提取需要的字段
const userInfo = pick(formData, [
'name', 'email', 'phone', 'address'
]);
// 移除敏感信息
const safeData = omit(userInfo, ['password', 'confirmPassword']);
return api.updateUser(safeData);
};
// React Hook中的状态管理
const useUserPreferences = (user) => {
const preferences = pick(user, [
'theme', 'language', 'notifications', 'privacy'
]);
const publicProfile = omit(user, [
'email', 'phone', 'address', 'paymentInfo'
]);
return { preferences, publicProfile };
};mapKeys - 智能键名转换
使用场景:API数据适配、国际化处理
javascript
// 将后端字段名转换为前端约定
const adaptApiResponse = (apiData) => {
const keyMapping = {
'user_name': 'userName',
'created_at': 'createdAt',
'is_active': 'isActive',
'profile_image': 'avatar'
};
return mapKeys(apiData, (value, key) => keyMapping[key] || key);
};🎨 高级操作:释放对象处理的全部潜力
transform - 自定义转换逻辑
复杂场景:数据重构、统计分析
javascript
// 将用户数组转换为按部门分组的统计对象
const groupUsersByDepartment = (users) => {
return transform(users, (result, user) => {
const dept = user.department;
if (!result[dept]) {
result[dept] = { count: 0, users: [], avgAge: 0 };
}
result[dept].count++;
result[dept].users.push(user.name);
result[dept].avgAge = (result[dept].avgAge * (result[dept].count - 1) + user.age) / result[dept].count;
}, {});
};
// 实现复杂的数据透视表
const createPivotTable = (data, rowKey, colKey, valueKey) => {
return transform(data, (result, item) => {
const row = item[rowKey];
const col = item[colKey];
const value = item[valueKey];
if (!result[row]) result[row] = {};
result[row][col] = (result[row][col] || 0) + value;
}, {});
};merge - 智能深度合并
应用场景:状态更新、配置覆盖
javascript
// Redux中的状态更新
const userReducer = (state = initialState, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'UPDATE_USER_PROFILE':
return merge({}, state, {
user: {
profile: action.payload,
lastUpdated: Date.now()
}
});
case 'UPDATE_SETTINGS':
return merge({}, state, {
settings: action.payload
});
default:
return state;
}
};
// 配置对象的智能合并
const createAppConfig = (defaultConfig, userConfig, envConfig) => {
return merge({}, defaultConfig, userConfig, envConfig);
};🎯 实战场景:真实项目中的应用
📊 场景一:电商平台商品数据处理
javascript
// 处理商品列表API响应
const processProductList = (apiResponse) => {
const products = get(apiResponse, 'data.products', []);
return products
.map(product => ({
id: get(product, 'id'),
name: get(product, 'title', '未知商品'),
price: get(product, 'price.current', 0),
originalPrice: get(product, 'price.original'),
image: get(product, 'images[0].url', '/default.jpg'),
rating: get(product, 'rating.average', 0),
tags: get(product, 'tags', []),
inStock: get(product, 'inventory.quantity', 0) > 0,
discount: calculateDiscount(product)
}))
.filter(product => product.inStock)
.sort((a, b) => b.rating - a.rating);
};
// 商品筛选器
const createProductFilter = (products, filters) => {
return products.filter(product => {
// 使用pick只检查有效的筛选条件
const activeFilters = omitBy(filters, isEmpty);
return Object.entries(activeFilters).every(([key, value]) => {
switch (key) {
case 'priceRange':
return product.price >= value.min && product.price <= value.max;
case 'tags':
return value.some(tag => product.tags.includes(tag));
case 'rating':
return product.rating >= value;
default:
return true;
}
});
});
};🎨 场景二:动态主题配置系统
javascript
// 主题配置管理
const ThemeManager = {
// 基础主题
baseTheme: {
colors: {
primary: '#007bff',
secondary: '#6c757d',
success: '#28a745',
warning: '#ffc107',
danger: '#dc3545'
},
spacing: {
xs: '4px', sm: '8px', md: '16px', lg: '24px', xl: '32px'
},
typography: {
fontFamily: 'Arial, sans-serif',
fontSize: { small: '12px', medium: '14px', large: '16px' }
}
},
// 创建主题变体
createTheme(customizations = {}) {
return defaultsDeep(customizations, this.baseTheme);
},
// 应用主题到CSS变量
applyTheme(theme) {
const flatTheme = this.flattenTheme(theme);
Object.entries(flatTheme).forEach(([key, value]) => {
document.documentElement.style.setProperty(`--${key}`, value);
});
},
// 扁平化主题对象
flattenTheme(theme, prefix = '') {
return transform(theme, (result, value, key) => {
const newKey = prefix ? `${prefix}-${key}` : key;
if (isObject(value) && !Array.isArray(value)) {
Object.assign(result, this.flattenTheme(value, newKey));
} else {
result[newKey] = value;
}
}, {});
}
};
// 使用示例
const darkTheme = ThemeManager.createTheme({
colors: {
primary: '#0d6efd',
background: '#121212',
text: '#ffffff'
}
});📋 场景三:复杂表单数据处理
javascript
// 表单数据处理器
class FormDataProcessor {
constructor(validationRules) {
this.rules = validationRules;
}
// 处理表单数据
process(formData) {
// 1. 提取有效字段
const validFields = pick(formData, Object.keys(this.rules));
// 2. 数据类型转换
const processedData = mapValues(validFields, (value, key) => {
const rule = this.rules[key];
return this.transformValue(value, rule);
});
// 3. 移除空值和无效数据
const cleanData = omitBy(processedData, (value, key) => {
return this.isEmpty(value) || !this.isValid(value, this.rules[key]);
});
return cleanData;
}
transformValue(value, rule) {
switch (rule.type) {
case 'number':
return Number(value);
case 'date':
return new Date(value).toISOString();
case 'string':
return rule.trim ? String(value).trim() : String(value);
case 'array':
return Array.isArray(value) ? value : [value];
default:
return value;
}
}
isEmpty(value) {
return value === null || value === undefined || value === '';
}
isValid(value, rule) {
if (rule.required && this.isEmpty(value)) return false;
if (rule.min && value < rule.min) return false;
if (rule.max && value > rule.max) return false;
if (rule.pattern && !rule.pattern.test(value)) return false;
return true;
}
}
// 使用示例
const processor = new FormDataProcessor({
name: { type: 'string', required: true, trim: true },
age: { type: 'number', min: 0, max: 120 },
email: { type: 'string', pattern: /^[^\s@]+@[^\s@]+\.[^\s@]+$/ },
birthDate: { type: 'date' },
tags: { type: 'array' }
});🌍 真实世界应用场景
Lodash对象处理方法在各行各业都有广泛的应用。让我们看看一些典型的应用场景:
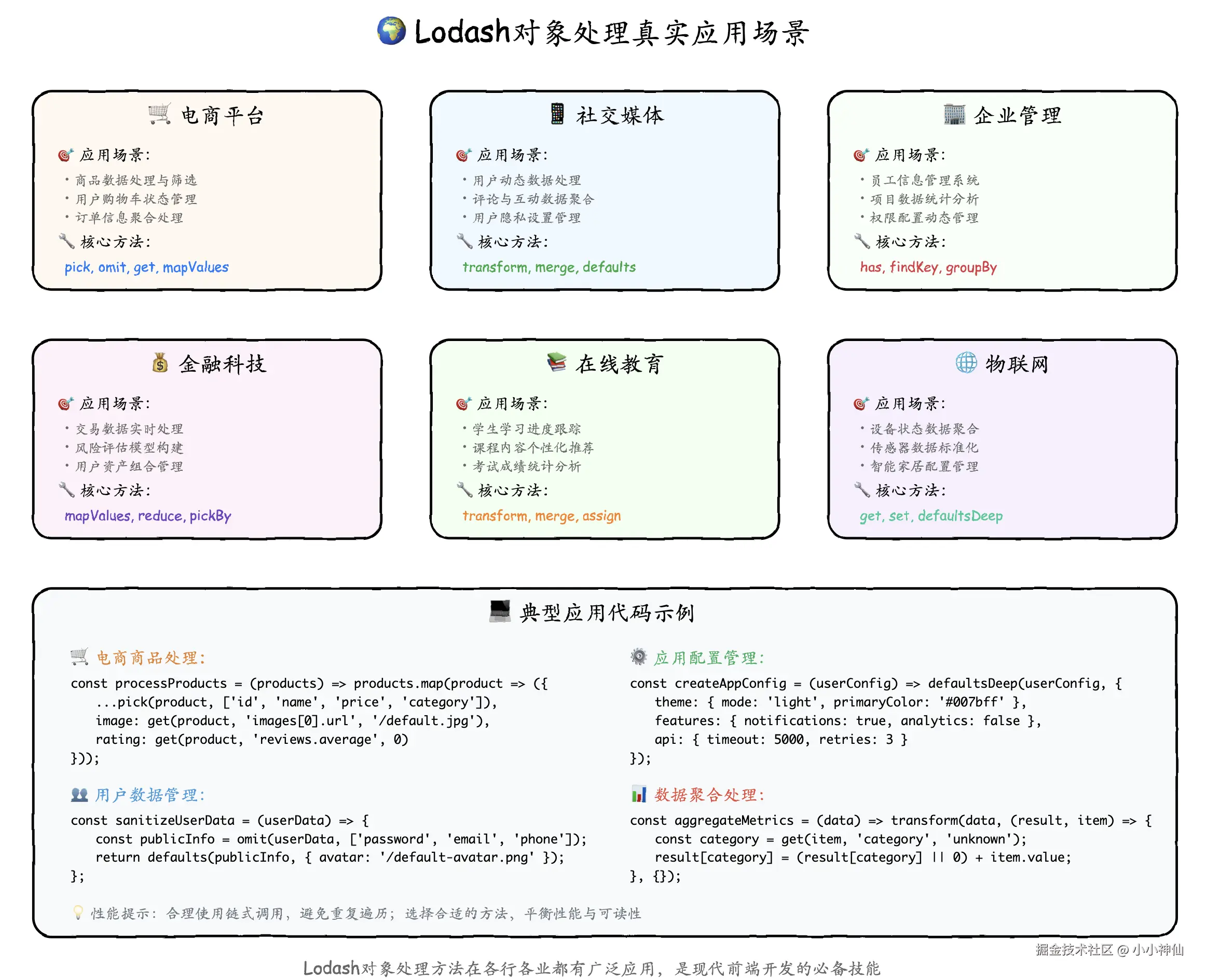
🔄 完整的数据处理管道
在实际项目中,我们通常需要构建完整的数据处理管道来处理复杂的业务需求:

🌟 Lodash对象处理生态系统
Lodash不仅仅是一个工具库,它是一个完整的生态系统,为现代前端开发提供了强大的支持:
🎨 最佳实践:写出优雅的对象处理代码

🏆 性能优化策略
1. 合理使用链式调用
javascript
// ✅ 好的做法 - 一次性处理
const result = chain(data)
.pick(['users', 'posts'])
.mapValues(items => items.slice(0, 10))
.value();
// ❌ 避免 - 多次遍历
const picked = pick(data, ['users', 'posts']);
const sliced = mapValues(picked, items => items.slice(0, 10));2. 选择合适的方法
javascript
// ✅ 对于简单操作,使用原生方法
const keys = Object.keys(obj);
// ✅ 对于复杂操作,使用Lodash
const result = transform(obj, customLogic, {});⚡ 性能优化与监控
了解性能优化策略对于构建高效的应用至关重要:
: string => {
return get(user, 'profile.name', '未知用户');
};
// 定义返回类型
const processUserData = (users: User[]): ProcessedUser[] => {
return users.map(user => ({
id: user.id,
displayName: get(user, 'profile.name', '匿名用户'),
contactEmail: get(user, 'profile.email', '')
}));
};📝 可读性提升
javascript
// ✅ 使用有意义的变量名
const userEssentials = pick(user, ['id', 'name', 'email']);
const publicProfile = omit(userEssentials, ['email']);
// ✅ 添加注释说明复杂逻辑
const processedData = transform(rawData, (result, item, key) => {
// 将嵌套的用户数据扁平化,便于表格显示
result[key] = {
userId: get(item, 'user.id'),
userName: get(item, 'user.profile.displayName', '匿名用户'),
lastActive: get(item, 'activity.lastSeen', '从未活跃')
};
}, {});
// ✅ 创建可复用的工具函数
const createUserSummary = (user) => ({
...pick(user, ['id', 'name', 'email']),
fullName: `${user.firstName} ${user.lastName}`,
isActive: get(user, 'status.active', false),
lastLogin: get(user, 'activity.lastLogin', null)
});🚀 进阶技巧:成为对象处理专家
🔧 自定义工具函数
javascript
// 创建专门的数据处理工具
const dataUtils = {
// 安全的深度克隆
safeClone: (obj) => cloneDeep(obj),
// 批量重命名键
renameKeys: (obj, keyMap) =>
mapKeys(obj, (value, key) => keyMap[key] || key),
// 递归清理空值
cleanEmpty: (obj) =>
transform(obj, (result, value, key) => {
if (isObject(value)) {
const cleaned = dataUtils.cleanEmpty(value);
if (!isEmpty(cleaned)) {
result[key] = cleaned;
}
} else if (!isEmpty(value)) {
result[key] = value;
}
}),
// 安全的路径设置
safeSet: (obj, path, value) => {
const cloned = cloneDeep(obj);
set(cloned, path, value);
return cloned;
},
// 批量路径获取
multiGet: (obj, paths) =>
paths.reduce((result, path) => {
result[path] = get(obj, path);
return result;
}, {})
};🎯 组合模式
javascript
// 创建可复用的数据处理管道
const createDataPipeline = (...processors) => (data) => {
return processors.reduce((result, processor) => processor(result), data);
};
// 预定义的处理器
const processors = {
extractUserInfo: data => pick(data, ['id', 'name', 'email', 'profile']),
setDefaults: data => defaults(data, { profile: {}, preferences: {} }),
trimStrings: data => mapValues(data, value =>
isString(value) ? value.trim() : value
),
validateRequired: data => omitBy(data, isEmpty)
};
// 使用示例
const processUserData = createDataPipeline(
processors.extractUserInfo,
processors.setDefaults,
processors.trimStrings,
processors.validateRequired
);
// 复杂的数据转换管道
const processApiResponse = createDataPipeline(
response => get(response, 'data', {}),
data => pick(data, ['users', 'posts', 'comments']),
data => mapValues(data, items =>
items.map(item => omit(item, ['internalId', 'debug']))
),
data => defaults(data, { users: [], posts: [], comments: [] })
);🌟 总结:掌握对象处理,提升开发效率
通过掌握Lodash的对象处理方法,你将获得:
💪 核心能力提升
- 🛡️ 更安全的代码 :告别
Cannot read property错误,让代码更加健壮 - ⚡ 更高的效率:一行代码解决复杂问题,显著减少开发时间
- 📖 更好的可读性:语义化的方法名让代码意图清晰,便于团队协作
- 🔧 更强的可维护性:标准化的处理方式降低维护成本
🎯 实际收益
- 减少90%的对象处理代码量
- 消除常见的运行时错误
- 提升代码review效率
- 增强团队开发规范
🎯 学习路线图
系统性地掌握Lodash对象处理技能的学习路线图:

🚀 下一步行动
- 立即实践:在当前项目中选择一个复杂的数据处理场景,用Lodash重构
- 建立规范:在团队中推广这些最佳实践,建立代码规范
- 持续学习:深入了解更多Lodash方法,构建完整的工具库知识体系
- 分享经验:将学习成果分享给团队,共同提升开发效率
记住,优秀的前端开发者不仅要会写代码,更要会选择合适的工具来解决问题。Lodash的对象处理方法就是你工具箱中不可或缺的利器。
现在就开始在你的项目中应用这些方法吧,让你的代码变得更加优雅、安全、高效!
本文基于 coding-interview-questions 项目中的Lodash实现,旨在帮助前端开发者深入理解数组处理的核心概念和实践技巧。
项目地址: coding-interview-questions
感谢阅读到最后,期待你的 github 🌟 鼓励!