scheduler工作阶段在React内部被称为schedule阶段。
在《React源码3》,我们已经将update加入队列并返回到了根容器节点root。
javascript
function updateContainer(element, container, parentComponent, callback) {
//前面略过
var root = enqueueUpdate(current$1, update, lane);
if (root !== null) {
scheduleUpdateOnFiber(root, current$1, lane, eventTime);
entangleTransitions(root, current$1, lane);
}
return lane;
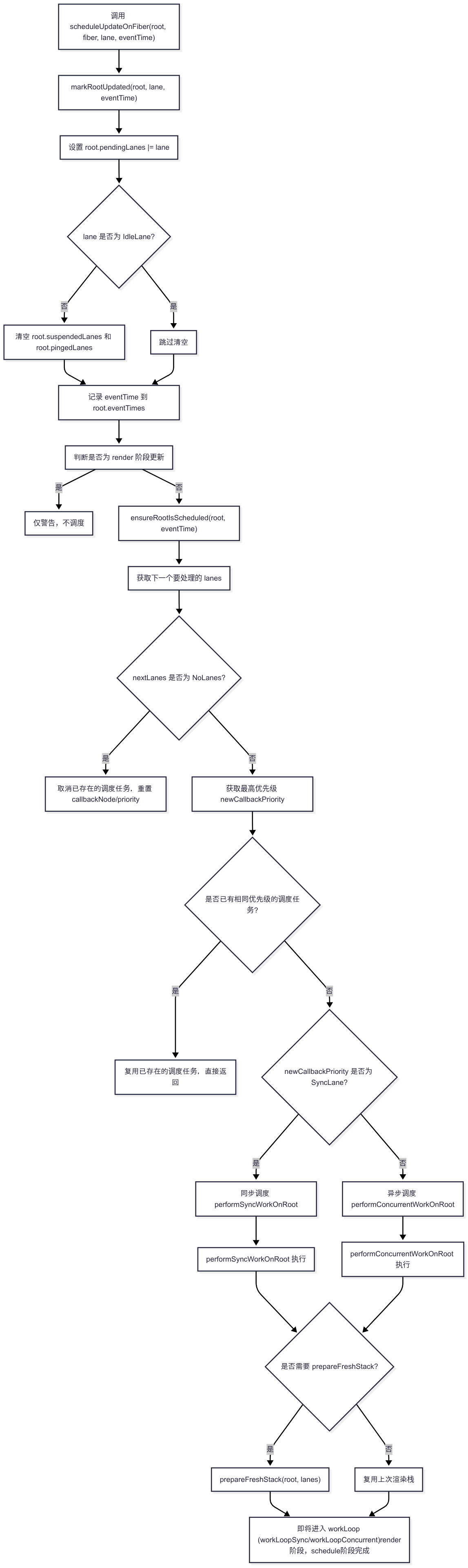
}scheduleUpdateOnFiber函数是React中Schedule模块主要函数,用于调度更新,下面几种情况都会调用scheduleUpdateOnFiber函数:
- 页面初次渲染
- 类组件setState/forceUpdate
- 函数组件setState
Schedule模块流程图
一、schdeuleUpdateOnFiber函数
javascript
function scheduleUpdateOnFiber(root, fiber, lane, eventTime) {
checkForNestedUpdates();
{
if (isRunningInsertionEffect) {
error('useInsertionEffect must not schedule updates.');
}
}
{
if (isFlushingPassiveEffects) {
didScheduleUpdateDuringPassiveEffects = true;
}
} // Mark that the root has a pending update.
markRootUpdated(root, lane, eventTime);
if ((executionContext & RenderContext) !== NoLanes && root === workInProgressRoot) {
// This update was dispatched during the render phase. This is a mistake
// if the update originates from user space (with the exception of local
// hook updates, which are handled differently and don't reach this
// function), but there are some internal React features that use this as
// an implementation detail, like selective hydration.
warnAboutRenderPhaseUpdatesInDEV(fiber); // Track lanes that were updated during the render phase
} else {
// This is a normal update, scheduled from outside the render phase. For
// example, during an input event.
{
if (isDevToolsPresent) {
addFiberToLanesMap(root, fiber, lane);
}
}
warnIfUpdatesNotWrappedWithActDEV(fiber);
if (root === workInProgressRoot) {
// Received an update to a tree that's in the middle of rendering. Mark
// that there was an interleaved update work on this root. Unless the
// `deferRenderPhaseUpdateToNextBatch` flag is off and this is a render
// phase update. In that case, we don't treat render phase updates as if
// they were interleaved, for backwards compat reasons.
if ( (executionContext & RenderContext) === NoContext) {
workInProgressRootInterleavedUpdatedLanes = mergeLanes(workInProgressRootInterleavedUpdatedLanes, lane);
}
if (workInProgressRootExitStatus === RootSuspendedWithDelay) {
// The root already suspended with a delay, which means this render
// definitely won't finish. Since we have a new update, let's mark it as
// suspended now, right before marking the incoming update. This has the
// effect of interrupting the current render and switching to the update.
// TODO: Make sure this doesn't override pings that happen while we've
// already started rendering.
markRootSuspended$1(root, workInProgressRootRenderLanes);
}
}
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, eventTime);
if (lane === SyncLane && executionContext === NoContext && (fiber.mode & ConcurrentMode) === NoMode && // Treat `act` as if it's inside `batchedUpdates`, even in legacy mode.
!( ReactCurrentActQueue$1.isBatchingLegacy)) {
// Flush the synchronous work now, unless we're already working or inside
// a batch. This is intentionally inside scheduleUpdateOnFiber instead of
// scheduleCallbackForFiber to preserve the ability to schedule a callback
// without immediately flushing it. We only do this for user-initiated
// updates, to preserve historical behavior of legacy mode.
resetRenderTimer();
flushSyncCallbacksOnlyInLegacyMode();
}
}
}二、markRootUpdated函数
负责标记根节点有新任务,并为调度系统提供最新的优先级和时间信息。
javascript
function markRootUpdated(root, updateLane, eventTime) {
root.pendingLanes |= updateLane; // If there are any suspended transitions, it's possible this new update
// could unblock them. Clear the suspended lanes so that we can try rendering
// them again.
//
// TODO: We really only need to unsuspend only lanes that are in the
// `subtreeLanes` of the updated fiber, or the update lanes of the return
// path. This would exclude suspended updates in an unrelated sibling tree,
// since there's no way for this update to unblock it.
//
// We don't do this if the incoming update is idle, because we never process
// idle updates until after all the regular updates have finished; there's no
// way it could unblock a transition.
if (updateLane !== IdleLane) {
root.suspendedLanes = NoLanes;
root.pingedLanes = NoLanes;
}
var eventTimes = root.eventTimes;
var index = laneToIndex(updateLane); // We can always overwrite an existing timestamp because we prefer the most
// recent event, and we assume time is monotonically increasing.
eventTimes[index] = eventTime;
}三、ensureRootIsScheduled函数
确保当前 FiberRoot 上有一个合适优先级的调度任务被安排,即根据最新的更新优先级,决定是否需要新建、复用或取消调度任务,并最终调度同步或异步的渲染入口。
- 获取下一个需要处理的 lanes(优先级),如果没有任务,取消已存在的调度任务。
- 判断当前任务优先级是否和已存在的调度任务一致,如果一致则复用,不一致则取消旧任务。
- 根据优先级安排调度:
- 如果是同步优先级(SyncLane),调度 performSyncWorkOnRoot。
- 否则,调度performConcurrentWorkOnRoot ,并传递合适的 scheduler 优先级。
- 将调度任务的引用和优先级记录到 root 上。
javascript
function ensureRootIsScheduled(root, currentTime) {
var existingCallbackNode = root.callbackNode; // Check if any lanes are being starved by other work. If so, mark them as
// expired so we know to work on those next.
markStarvedLanesAsExpired(root, currentTime); // Determine the next lanes to work on, and their priority.
var nextLanes = getNextLanes(root, root === workInProgressRoot ? workInProgressRootRenderLanes : NoLanes);
if (nextLanes === NoLanes) {
// Special case: There's nothing to work on.
if (existingCallbackNode !== null) {
cancelCallback$1(existingCallbackNode);
}
root.callbackNode = null;
root.callbackPriority = NoLane;
return;
} // We use the highest priority lane to represent the priority of the callback.
var newCallbackPriority = getHighestPriorityLane(nextLanes); // Check if there's an existing task. We may be able to reuse it.
var existingCallbackPriority = root.callbackPriority;
if (existingCallbackPriority === newCallbackPriority && // Special case related to `act`. If the currently scheduled task is a
// Scheduler task, rather than an `act` task, cancel it and re-scheduled
// on the `act` queue.
!( ReactCurrentActQueue$1.current !== null && existingCallbackNode !== fakeActCallbackNode)) {
{
// If we're going to re-use an existing task, it needs to exist.
// Assume that discrete update microtasks are non-cancellable and null.
// TODO: Temporary until we confirm this warning is not fired.
if (existingCallbackNode == null && existingCallbackPriority !== SyncLane) {
error('Expected scheduled callback to exist. This error is likely caused by a bug in React. Please file an issue.');
}
} // The priority hasn't changed. We can reuse the existing task. Exit.
return;
}
if (existingCallbackNode != null) {
// Cancel the existing callback. We'll schedule a new one below.
cancelCallback$1(existingCallbackNode);
} // Schedule a new callback.
var newCallbackNode;
if (newCallbackPriority === SyncLane) {
// Special case: Sync React callbacks are scheduled on a special
// internal queue
if (root.tag === LegacyRoot) {
if ( ReactCurrentActQueue$1.isBatchingLegacy !== null) {
ReactCurrentActQueue$1.didScheduleLegacyUpdate = true;
}
scheduleLegacySyncCallback(performSyncWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root));
} else {
scheduleSyncCallback(performSyncWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root));
}
{
// Flush the queue in a microtask.
if ( ReactCurrentActQueue$1.current !== null) {
// Inside `act`, use our internal `act` queue so that these get flushed
// at the end of the current scope even when using the sync version
// of `act`.
ReactCurrentActQueue$1.current.push(flushSyncCallbacks);
} else {
scheduleMicrotask(function () {
// In Safari, appending an iframe forces microtasks to run.
// https://github.com/facebook/react/issues/22459
// We don't support running callbacks in the middle of render
// or commit so we need to check against that.
if ((executionContext & (RenderContext | CommitContext)) === NoContext) {
// Note that this would still prematurely flush the callbacks
// if this happens outside render or commit phase (e.g. in an event).
flushSyncCallbacks();
}
});
}
}
newCallbackNode = null;
} else {
var schedulerPriorityLevel;
switch (lanesToEventPriority(nextLanes)) {
case DiscreteEventPriority:
schedulerPriorityLevel = ImmediatePriority;
break;
case ContinuousEventPriority:
schedulerPriorityLevel = UserBlockingPriority;
break;
case DefaultEventPriority:
schedulerPriorityLevel = NormalPriority;
break;
case IdleEventPriority:
schedulerPriorityLevel = IdlePriority;
break;
default:
schedulerPriorityLevel = NormalPriority;
break;
}
newCallbackNode = scheduleCallback$1(schedulerPriorityLevel, performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root));
}
root.callbackPriority = newCallbackPriority;
root.callbackNode = newCallbackNode;
} // This is the entry point for every concurrent task, i.e. anything that
// goes through Scheduler.四、performSyncWorkOnRoot函数
以同步方式执行根节点的渲染和提交流程,用于处理最高优先级(SyncLane)的更新。
javascript
function performSyncWorkOnRoot(root) {
{
syncNestedUpdateFlag();
}
if ((executionContext & (RenderContext | CommitContext)) !== NoContext) {
throw new Error('Should not already be working.');
}
flushPassiveEffects();
var lanes = getNextLanes(root, NoLanes);
if (!includesSomeLane(lanes, SyncLane)) {
// There's no remaining sync work left.
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, now());
return null;
}
var exitStatus = renderRootSync(root, lanes);
if (root.tag !== LegacyRoot && exitStatus === RootErrored) {
// If something threw an error, try rendering one more time. We'll render
// synchronously to block concurrent data mutations, and we'll includes
// all pending updates are included. If it still fails after the second
// attempt, we'll give up and commit the resulting tree.
var errorRetryLanes = getLanesToRetrySynchronouslyOnError(root);
if (errorRetryLanes !== NoLanes) {
lanes = errorRetryLanes;
exitStatus = recoverFromConcurrentError(root, errorRetryLanes);
}
}
if (exitStatus === RootFatalErrored) {
var fatalError = workInProgressRootFatalError;
prepareFreshStack(root, NoLanes);
markRootSuspended$1(root, lanes);
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, now());
throw fatalError;
}
if (exitStatus === RootDidNotComplete) {
throw new Error('Root did not complete. This is a bug in React.');
} // We now have a consistent tree. Because this is a sync render, we
// will commit it even if something suspended.
var finishedWork = root.current.alternate;
root.finishedWork = finishedWork;
root.finishedLanes = lanes;
commitRoot(root, workInProgressRootRecoverableErrors, workInProgressTransitions); // Before exiting, make sure there's a callback scheduled for the next
// pending level.
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, now());
return null;
}
function flushRoot(root, lanes) {
if (lanes !== NoLanes) {
markRootEntangled(root, mergeLanes(lanes, SyncLane));
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, now());
if ((executionContext & (RenderContext | CommitContext)) === NoContext) {
resetRenderTimer();
flushSyncCallbacks();
}
}
}五、performConcurrentWorkOnRoot函数
并发渲染的核心入口,负责调度和执行并发模式下的 Fiber 树渲染。
javascript
function performConcurrentWorkOnRoot(root, didTimeout) {
{
resetNestedUpdateFlag();
} // Since we know we're in a React event, we can clear the current
// event time. The next update will compute a new event time.
currentEventTime = NoTimestamp;
currentEventTransitionLane = NoLanes;
if ((executionContext & (RenderContext | CommitContext)) !== NoContext) {
throw new Error('Should not already be working.');
} // Flush any pending passive effects before deciding which lanes to work on,
// in case they schedule additional work.
var originalCallbackNode = root.callbackNode;
var didFlushPassiveEffects = flushPassiveEffects();
if (didFlushPassiveEffects) {
// Something in the passive effect phase may have canceled the current task.
// Check if the task node for this root was changed.
if (root.callbackNode !== originalCallbackNode) {
// The current task was canceled. Exit. We don't need to call
// `ensureRootIsScheduled` because the check above implies either that
// there's a new task, or that there's no remaining work on this root.
return null;
}
} // Determine the next lanes to work on, using the fields stored
// on the root.
var lanes = getNextLanes(root, root === workInProgressRoot ? workInProgressRootRenderLanes : NoLanes);
if (lanes === NoLanes) {
// Defensive coding. This is never expected to happen.
return null;
} // We disable time-slicing in some cases: if the work has been CPU-bound
// for too long ("expired" work, to prevent starvation), or we're in
// sync-updates-by-default mode.
// TODO: We only check `didTimeout` defensively, to account for a Scheduler
// bug we're still investigating. Once the bug in Scheduler is fixed,
// we can remove this, since we track expiration ourselves.
var shouldTimeSlice = !includesBlockingLane(root, lanes) && !includesExpiredLane(root, lanes) && ( !didTimeout);
var exitStatus = shouldTimeSlice ? renderRootConcurrent(root, lanes) : renderRootSync(root, lanes);
if (exitStatus !== RootInProgress) {
if (exitStatus === RootErrored) {
// If something threw an error, try rendering one more time. We'll
// render synchronously to block concurrent data mutations, and we'll
// includes all pending updates are included. If it still fails after
// the second attempt, we'll give up and commit the resulting tree.
var errorRetryLanes = getLanesToRetrySynchronouslyOnError(root);
if (errorRetryLanes !== NoLanes) {
lanes = errorRetryLanes;
exitStatus = recoverFromConcurrentError(root, errorRetryLanes);
}
}
if (exitStatus === RootFatalErrored) {
var fatalError = workInProgressRootFatalError;
prepareFreshStack(root, NoLanes);
markRootSuspended$1(root, lanes);
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, now());
throw fatalError;
}
if (exitStatus === RootDidNotComplete) {
// The render unwound without completing the tree. This happens in special
// cases where need to exit the current render without producing a
// consistent tree or committing.
//
// This should only happen during a concurrent render, not a discrete or
// synchronous update. We should have already checked for this when we
// unwound the stack.
markRootSuspended$1(root, lanes);
} else {
// The render completed.
// Check if this render may have yielded to a concurrent event, and if so,
// confirm that any newly rendered stores are consistent.
// TODO: It's possible that even a concurrent render may never have yielded
// to the main thread, if it was fast enough, or if it expired. We could
// skip the consistency check in that case, too.
var renderWasConcurrent = !includesBlockingLane(root, lanes);
var finishedWork = root.current.alternate;
if (renderWasConcurrent && !isRenderConsistentWithExternalStores(finishedWork)) {
// A store was mutated in an interleaved event. Render again,
// synchronously, to block further mutations.
exitStatus = renderRootSync(root, lanes); // We need to check again if something threw
if (exitStatus === RootErrored) {
var _errorRetryLanes = getLanesToRetrySynchronouslyOnError(root);
if (_errorRetryLanes !== NoLanes) {
lanes = _errorRetryLanes;
exitStatus = recoverFromConcurrentError(root, _errorRetryLanes); // We assume the tree is now consistent because we didn't yield to any
// concurrent events.
}
}
if (exitStatus === RootFatalErrored) {
var _fatalError = workInProgressRootFatalError;
prepareFreshStack(root, NoLanes);
markRootSuspended$1(root, lanes);
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, now());
throw _fatalError;
}
} // We now have a consistent tree. The next step is either to commit it,
// or, if something suspended, wait to commit it after a timeout.
root.finishedWork = finishedWork;
root.finishedLanes = lanes;
finishConcurrentRender(root, exitStatus, lanes);
}
}
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, now());
if (root.callbackNode === originalCallbackNode) {
// The task node scheduled for this root is the same one that's
// currently executed. Need to return a continuation.
return performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root);
}
return null;
}六、prepareFreshStack函数
prepareFreshStack的作用是为一次新的 Fiber 树渲染初始化全局状态,主要包括:
- 重置当前 root 的渲染相关状态(如 finishedWork、finishedLanes 等)。
- 取消上一次渲染遗留的超时(timeout)。
- 如果上一次渲染被中断,清理未完成的 workInProgress。
- 创建新的 workInProgress Fiber 树(即 root.current 的 alternate),并将全局变量 workInProgress指向它。
- 设置本次渲染的 lanes(优先级)。
- 重置本次渲染相关的全局变量(如 workInProgressRoot、workInProgressRootRenderLanes 等)。
- 清空上次渲染遗留的错误、跳过的 lanes、pinged lanes 等。
javascript
function prepareFreshStack(root, lanes) {
root.finishedWork = null;
root.finishedLanes = NoLanes;
var timeoutHandle = root.timeoutHandle;
if (timeoutHandle !== noTimeout) {
// The root previous suspended and scheduled a timeout to commit a fallback
// state. Now that we have additional work, cancel the timeout.
root.timeoutHandle = noTimeout; // $FlowFixMe Complains noTimeout is not a TimeoutID, despite the check above
cancelTimeout(timeoutHandle);
}
if (workInProgress !== null) {
var interruptedWork = workInProgress.return;
while (interruptedWork !== null) {
var current = interruptedWork.alternate;
unwindInterruptedWork(current, interruptedWork);
interruptedWork = interruptedWork.return;
}
}
workInProgressRoot = root;
var rootWorkInProgress = createWorkInProgress(root.current, null);
workInProgress = rootWorkInProgress;
workInProgressRootRenderLanes = subtreeRenderLanes = workInProgressRootIncludedLanes = lanes;
workInProgressRootExitStatus = RootInProgress;
workInProgressRootFatalError = null;
workInProgressRootSkippedLanes = NoLanes;
workInProgressRootInterleavedUpdatedLanes = NoLanes;
workInProgressRootPingedLanes = NoLanes;
workInProgressRootConcurrentErrors = null;
workInProgressRootRecoverableErrors = null;
finishQueueingConcurrentUpdates();
{
ReactStrictModeWarnings.discardPendingWarnings();
}
return rootWorkInProgress;
}